Ubuntu22.04(ROS2 humble)小车仿真环境搭建
下载 mobile-3d-lidar-sim
mobile-3d-lidar-sim:ROS2 Humble 社区中最轻量、专门用于 3D 雷达 仿真的项目
这个项目结构非常简单,只有一个机器人模型,且原生配置了 Velodyne 3D 雷达 插件。
mkdir -p ~/ros2/mobile-3d-lidar-sim/src
cd ~/ros2/mobile-3d-lidar-sim/src
git clone https://github.com/louislelay/mobile-3d-lidar-sim.git
sudo apt install ros-humble-velodyne-simulator -y
cd ..
colcon build --symlink-install
发布全局静态地图
cd /home/zylyehuo/ros2/pcd2pgm_ws2/map/custom
ros2 run nav2_map_server map_server --ros-args -p yaml_filename:=drone_map_03.yaml -p use_sim_time:=true
ros2 run nav2_lifecycle_manager lifecycle_manager --ros-args -p node_names:="['map_server']" -p autostart:=true
ros2 run tf2_ros static_transform_publisher 0 0 0 0 0 0 map odom
发布局部代价地图
cd /home/zylyehuo/ros2/ros2_lexi/src/lexigraph/scripts
python3 ./my_costmap.py
my_costmap.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import rclpy
from rclpy.node import Node
import numpy as np
from sensor_msgs.msg import PointCloud2
from nav_msgs.msg import OccupancyGrid
import sensor_msgs_py.point_cloud2 as pc2
from scipy.ndimage import distance_transform_edt
from tf2_ros import TransformException
from tf2_ros.buffer import Buffer
from tf2_ros.transform_listener import TransformListener
class MapFixedCostmap(Node):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__('map_fixed_costmap_node')
# --- 参数配置 ---
self.declare_parameter('resolution', 0.05) # 分辨率
self.declare_parameter('width_m', 20.0) # 局部窗口在 map 中的大小
self.declare_parameter('inflation_r', 0.4)
self.declare_parameter('robot_r', 0.3)
self.res = self.get_parameter('resolution').value
self.width_m = self.get_parameter('width_m').value
self.inflation_r = self.get_parameter('inflation_r').value
self.robot_r = self.get_parameter('robot_r').value
self.grid_dim = int(self.width_m / self.res)
# --- TF 监听器 ---
self.tf_buffer = Buffer()
self.tf_listener = TransformListener(self.tf_buffer, self)
# --- 订阅与发布 ---
self.subscription = self.create_subscription(
PointCloud2, '/velodyne2/velodyne_points2', self.pc_callback, 10)
self.publisher = self.create_publisher(OccupancyGrid, '/my_costmap', 10)
self.get_logger().info("Costmap Node Started: Fixed to MAP frame.")
def pc_callback(self, msg):
try:
# 1. 获取机器人 (base_link) 在 map 系下的实时位置
try:
# 获取 map 到 base_link 的变换
t = self.tf_buffer.lookup_transform('map', 'base_link', rclpy.time.Time())
robot_x = t.transform.translation.x
robot_y = t.transform.translation.y
except TransformException as ex:
self.get_logger().warn(f'Could not transform base_link to map: {ex}')
return
# 2. 解析点云
gen = pc2.read_points(msg, field_names=("x", "y", "z"), skip_nans=True)
points_list = list(gen)
if not points_list:
self.publish_empty_map(robot_x, robot_y)
return
points = np.array([[p[0], p[1], p[2]] for p in points_list], dtype=np.float32)
# 3. 高度过滤
mask = (points[:, 2] > 0.1) & (points[:, 2] < 1.2)
obs_points = points[mask]
# 4. 初始化栅格
grid = np.zeros((self.grid_dim, self.grid_dim), dtype=np.int8)
# 这里的投影逻辑:
# 点云是在 body 系下的,要发布的地图在 map 系,
# 但栅格的内容依然是机器人观察到的局部障碍物。
# 将栅格的中心(cx, cy)对应机器人当前的 (robot_x, robot_y)
cx, cy = self.grid_dim // 2, self.grid_dim // 2
ix = (obs_points[:, 0] / self.res + cx).astype(int)
iy = (obs_points[:, 1] / self.res + cy).astype(int)
valid = (ix >= 0) & (ix < self.grid_dim) & (iy >= 0) & (iy < self.grid_dim)
grid[iy[valid], ix[valid]] = 100
# 5. 膨胀
final_data = self.inflate_map(grid)
# 6. 发布 (传入机器人当前 map 坐标作为原点参考)
self.publish_map(final_data, robot_x, robot_y)
except Exception as e:
self.get_logger().error(f"Error: {str(e)}")
def inflate_map(self, grid):
if not np.any(grid == 100):
return grid.flatten().astype(np.int8)
dist_map = distance_transform_edt(grid != 100) * self.res
costmap = np.zeros_like(grid, dtype=np.int8)
costmap[dist_map <= self.robot_r] = 100
inf_mask = (dist_map > self.robot_r) & (dist_map <= self.inflation_r)
norm_dist = (dist_map[inf_mask] - self.robot_r) / (self.inflation_r - self.robot_r)
costmap[inf_mask] = (99 * np.exp(-5.0 * norm_dist)).astype(np.int8)
return costmap.flatten()
def publish_empty_map(self, rx, ry):
self.publish_map(np.zeros(self.grid_dim**2, dtype=np.int8), rx, ry)
def publish_map(self, data, rx, ry):
grid_msg = OccupancyGrid()
grid_msg.header.stamp = self.get_clock().now().to_msg()
grid_msg.header.frame_id = 'map' # 固定在 map 系
grid_msg.info.resolution = self.res
grid_msg.info.width = self.grid_dim
grid_msg.info.height = self.grid_dim
# 将 OccupancyGrid 的原点动态设为机器人当前坐标减去地图一半
# 在 map 系下跟随机器人移动
grid_msg.info.origin.position.x = rx - (self.grid_dim * self.res) / 2.0
grid_msg.info.origin.position.y = ry - (self.grid_dim * self.res) / 2.0
grid_msg.info.origin.position.z = 0.0
grid_msg.info.origin.orientation.w = 1.0
grid_msg.data = data.tolist()
self.publisher.publish(grid_msg)
def main(args=None):
rclpy.init(args=args)
node = MapFixedCostmap()
try:
rclpy.spin(node)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
pass
finally:
node.destroy_node()
rclpy.shutdown()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
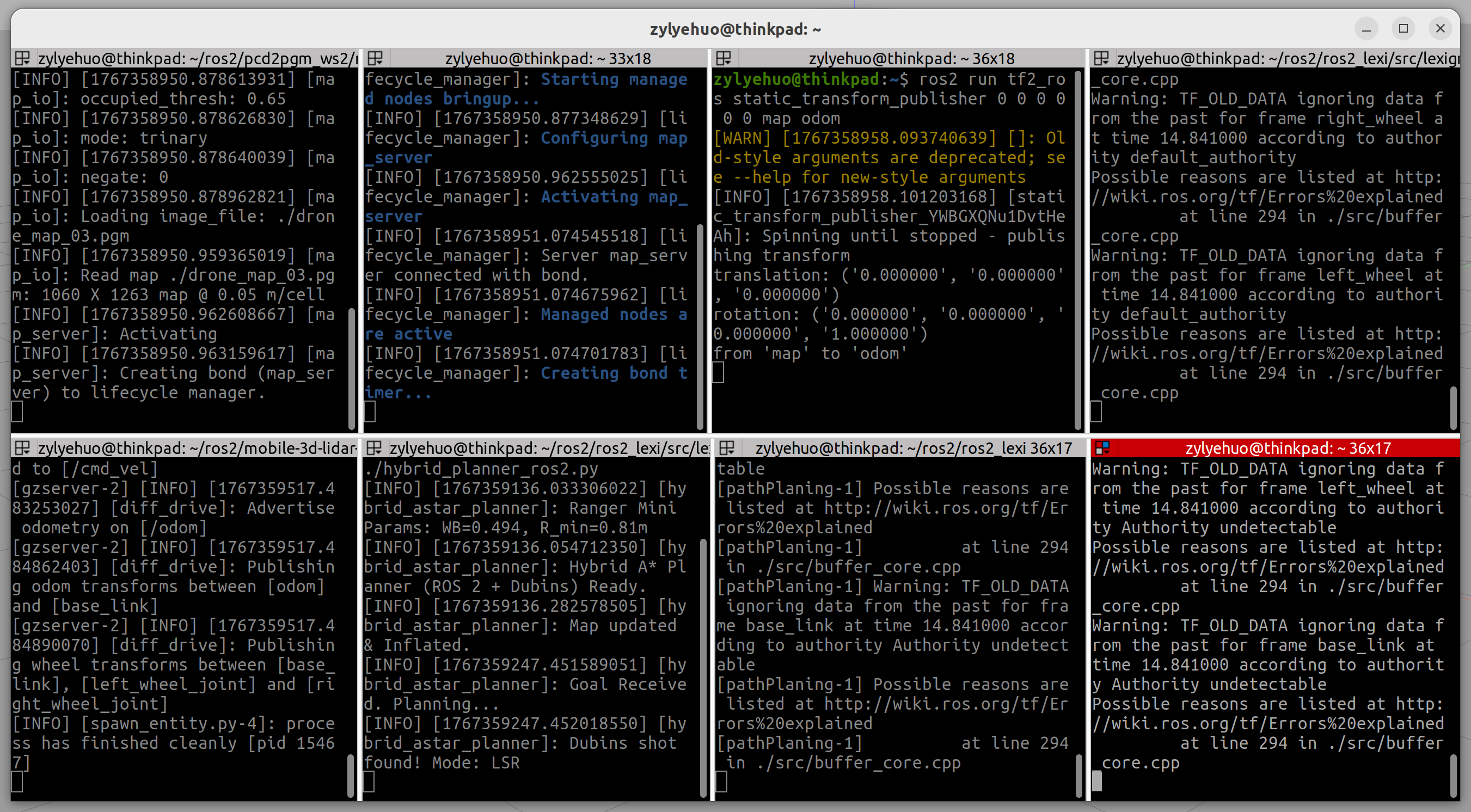
运行仿真环境
cd /home/zylyehuo/ros2/mobile-3d-lidar-sim
source ./install/setup.bash
ros2 launch my_bot launch_sim.launch.py
全局路径规划(hybrid-A*,Dubins)
cd /home/zylyehuo/ros2/ros2_lexi/src/lexigraph/scripts
python3 ./hybrid_planner_ros2.py
hybrid_planner_ros2.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import rclpy
from rclpy.node import Node
from rclpy.qos import QoSProfile, DurabilityPolicy, HistoryPolicy
import numpy as np
import heapq
import math
from nav_msgs.msg import OccupancyGrid, Path, Odometry
from geometry_msgs.msg import PoseStamped, Point
from scipy.ndimage import binary_dilation
# --- 辅助函数: 四元数转欧拉角 (避免依赖 tf_transformations) ---
def euler_from_quaternion(q):
"""
Convert a list/obj of [x, y, z, w] to [roll, pitch, yaw]
"""
x, y, z, w = q.x, q.y, q.z, q.w
t0 = +2.0 * (w * x + y * z)
t1 = +1.0 - 2.0 * (x * x + y * y)
roll_x = math.atan2(t0, t1)
t2 = +2.0 * (w * y - z * x)
t2 = +1.0 if t2 > +1.0 else t2
t2 = -1.0 if t2 < -1.0 else t2
pitch_y = math.asin(t2)
t3 = +2.0 * (w * z + x * y)
t4 = +1.0 - 2.0 * (y * y + z * z)
yaw_z = math.atan2(t3, t4)
return roll_x, pitch_y, yaw_z
# --- Dubins 曲线规划器 ---
class DubinsPath:
def __init__(self, start, end, curvature, step_size=0.1):
self.sx, self.sy, self.syaw = start
self.gx, self.gy, self.gyaw = end
self.c = curvature
self.r = 1.0 / curvature
self.step_size = step_size
self.path_x = []
self.path_y = []
self.path_yaw = []
self.cost = float('inf')
self.mode = ""
def mod2pi(theta):
return theta - 2.0 * math.pi * math.floor(theta / 2.0 / math.pi)
def pi_2_pi(angle):
return (angle + math.pi) % (2 * math.pi) - math.pi
def dubins_path_planning(sx, sy, syaw, gx, gy, gyaw, c, step_size=0.1):
"""
计算最短的 Dubins 路径
"""
gx -= sx
gy -= sy
l_rot = math.atan2(gy, gx)
l_dist = math.hypot(gx, gy)
# 将目标旋转到以(0,0,0)为起点的坐标系
theta = mod2pi(l_rot - syaw)
alpha = mod2pi(syaw - l_rot)
beta = mod2pi(gyaw - l_rot)
# 归一化距离
d = l_dist * c
best_cost = float('inf')
best_mode = None
best_lengths = None
# 定义6种Dubins模式
planners = [lsl, rsr, lsr, rsl, rlr, lrl]
modes = ["LSL", "RSR", "LSR", "RSL", "RLR", "LRL"]
for planner, mode in zip(planners, modes):
lengths = planner(alpha, beta, d)
if lengths is None:
continue
cost = sum(map(abs, lengths))
if cost < best_cost:
best_cost = cost
best_mode = mode
best_lengths = lengths
if best_mode is None:
return None
# 生成路径点
lengths = best_lengths
px, py, pyaw = [sx], [sy], [syaw]
# 辅助生成函数
def interpolate(length, mode_char, origin_x, origin_y, origin_yaw):
dist = 0.0
curr_x, curr_y, curr_yaw = origin_x, origin_y, origin_yaw
step = step_size
if mode_char == 'S':
d_step = step
else:
d_step = step * c # 弧度步长
while dist < length:
dist += step
if dist >= length: # 修正最后一步
d_step -= (dist - length) * (c if mode_char != 'S' else 1.0)
dist = length
if mode_char == 'L':
curr_yaw += d_step
elif mode_char == 'R':
curr_yaw -= d_step
# 移动
if mode_char == 'S':
curr_x += d_step * math.cos(curr_yaw)
curr_y += d_step * math.sin(curr_yaw)
else:
# 弧线运动 DX = 2*R*sin(d_theta/2)*cos(theta + d_theta/2) 近似
# 这里简单积分
curr_x += step * math.cos(curr_yaw)
curr_y += step * math.sin(curr_yaw)
px.append(curr_x)
py.append(curr_y)
pyaw.append(curr_yaw)
return curr_x, curr_y, curr_yaw
# 根据最佳模式生成
cx, cy, cyaw = sx, sy, syaw
for i, m in enumerate(best_mode):
l_segment = lengths[i] / c
cx, cy, cyaw = interpolate(l_segment, m, cx, cy, cyaw)
path = DubinsPath((sx, sy, syaw), (gx, gy, gyaw), c, step_size)
path.path_x = px
path.path_y = py
path.path_yaw = pyaw
path.cost = best_cost / c # 真实长度
path.mode = best_mode
return path
# --- Dubins 公式实现 (归一化坐标下) ---
def lsl(alpha, beta, d):
sa = math.sin(alpha)
sb = math.sin(beta)
ca = math.cos(alpha)
cb = math.cos(beta)
c_ab = math.cos(alpha - beta)
tmp0 = d + sa - sb
p_squared = 2 + (d * d) - (2 * c_ab) + (2 * d * (sa - sb))
if p_squared < 0: return None
tmp1 = math.atan2((cb - ca), tmp0)
t = mod2pi(-alpha + tmp1)
p = math.sqrt(p_squared)
q = mod2pi(beta - tmp1)
return t, p, q
def rsr(alpha, beta, d):
sa = math.sin(alpha)
sb = math.sin(beta)
ca = math.cos(alpha)
cb = math.cos(beta)
c_ab = math.cos(alpha - beta)
tmp0 = d - sa + sb
p_squared = 2 + (d * d) - (2 * c_ab) + (2 * d * (sb - sa))
if p_squared < 0: return None
tmp1 = math.atan2((ca - cb), tmp0)
t = mod2pi(alpha - tmp1)
p = math.sqrt(p_squared)
q = mod2pi(-beta + tmp1)
return t, p, q
def lsr(alpha, beta, d):
sa = math.sin(alpha)
sb = math.sin(beta)
ca = math.cos(alpha)
cb = math.cos(beta)
c_ab = math.cos(alpha - beta)
p_squared = -2 + (d * d) + (2 * c_ab) + (2 * d * (sa + sb))
if p_squared < 0: return None
p = math.sqrt(p_squared)
tmp2 = math.atan2((-ca - cb), (d + sa + sb)) - math.atan2(-2.0, p)
t = mod2pi(-alpha + tmp2)
q = mod2pi(-mod2pi(beta) + tmp2)
return t, p, q
def rsl(alpha, beta, d):
sa = math.sin(alpha)
sb = math.sin(beta)
ca = math.cos(alpha)
cb = math.cos(beta)
c_ab = math.cos(alpha - beta)
p_squared = (d * d) - 2 + (2 * c_ab) - (2 * d * (sa + sb))
if p_squared < 0: return None
p = math.sqrt(p_squared)
tmp2 = math.atan2((ca + cb), (d - sa - sb)) - math.atan2(2.0, p)
t = mod2pi(alpha - tmp2)
q = mod2pi(beta - tmp2)
return t, p, q
def rlr(alpha, beta, d):
sa = math.sin(alpha)
sb = math.sin(beta)
ca = math.cos(alpha)
cb = math.cos(beta)
c_ab = math.cos(alpha - beta)
tmp_rlr = (6.0 - d * d + 2.0 * c_ab + 2.0 * d * (sa - sb)) / 8.0
if abs(tmp_rlr) > 1.0: return None
p = mod2pi(2 * math.pi - math.acos(tmp_rlr))
t = mod2pi(alpha - math.atan2(ca - cb, d - sa + sb) + mod2pi(p / 2.0))
q = mod2pi(alpha - beta - t + mod2pi(p))
return t, p, q
def lrl(alpha, beta, d):
sa = math.sin(alpha)
sb = math.sin(beta)
ca = math.cos(alpha)
cb = math.cos(beta)
c_ab = math.cos(alpha - beta)
tmp_lrl = (6.0 - d * d + 2.0 * c_ab + 2.0 * d * (- sa + sb)) / 8.0
if abs(tmp_lrl) > 1.0: return None
p = mod2pi(2 * math.pi - math.acos(tmp_lrl))
t = mod2pi(-alpha - math.atan2(ca - cb, d + sa - sb) + p / 2.0)
q = mod2pi(mod2pi(beta) - alpha - t + mod2pi(p))
return t, p, q
# --- 节点类 ---
class NodeItem:
def __init__(self, x_ind, y_ind, theta_ind, x, y, yaw, x_list, y_list, p_ind, cost, steer):
self.x_ind = x_ind
self.y_ind = y_ind
self.theta_ind = theta_ind
self.x = x
self.y = y
self.yaw = yaw
self.x_list = x_list
self.y_list = y_list
self.p_ind = p_ind
self.cost = cost
self.steer = steer
class HybridAStarPlanner(Node):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__('hybrid_astar_planner')
# --- Ranger Mini 3.0 参数 ---
self.WB = 0.494
self.MAX_STEER = 0.55
self.ROBOT_RADIUS = 0.45
# --- 规划参数 ---
self.XY_RES = 0.1
self.YAW_RES = 0.15 # 稍微增大角度分辨率以减少搜索空间
self.MOTION_STEP = 0.1
# Dubins 最小转弯半径 R_min
# tan(max_steer) = WB / R
# R = WB / tan(max_steer)
self.MIN_TURN_RADIUS = self.WB / math.tan(self.MAX_STEER)
# 对应的曲率 (1/R)
self.MAX_CURVATURE = 1.0 / self.MIN_TURN_RADIUS * 0.95 # 留一点余量
self.get_logger().info(f"Ranger Mini Params: WB={self.WB}, R_min={self.MIN_TURN_RADIUS:.2f}m")
# --- 内部变量 ---
self.map_data = None
self.costmap = None
self.map_info = None
self.current_pose = None
# --- ROS 2 通信 ---
# Map QoS: 必须是 Transient Local 才能收到并在后续保留 map_server 发出的地图
map_qos = QoSProfile(
depth=1,
durability=DurabilityPolicy.TRANSIENT_LOCAL,
history=HistoryPolicy.KEEP_LAST,
)
self.path_pub = self.create_publisher(Path, '/bezai_path', 10)
self.create_subscription(OccupancyGrid, '/map', self.map_callback, map_qos)
self.create_subscription(Odometry, '/odom', self.odom_callback, 10)
self.create_subscription(PoseStamped, '/goal_pose', self.goal_callback, 10) # RViz2 默认话题通常是 /goal_pose
self.get_logger().info("Hybrid A* Planner (ROS 2 + Dubins) Ready.")
def map_callback(self, msg):
self.map_info = msg.info
self.XY_RES = msg.info.resolution
w, h = msg.info.width, msg.info.height
grid = np.array(msg.data).reshape((h, w))
obstacles = np.where((grid > 50) | (grid == -1), 1, 0)
# 膨胀
inflation_cells = int(np.ceil(self.ROBOT_RADIUS / self.XY_RES))
structure = np.ones((2*inflation_cells+1, 2*inflation_cells+1))
self.costmap = binary_dilation(obstacles, structure=structure).astype(int)
self.costmap = self.costmap.T # 转置以匹配 x,y 索引
self.get_logger().info("Map updated & Inflated.")
def odom_callback(self, msg):
p = msg.pose.pose.position
o = msg.pose.pose.orientation
_, _, yaw = euler_from_quaternion(o)
self.current_pose = (p.x, p.y, yaw)
def goal_callback(self, msg):
if self.costmap is None:
self.get_logger().warn("Map not received!")
return
if self.current_pose is None:
self.get_logger().warn("Odom not received!")
return
self.get_logger().info("Goal Received. Planning...")
g_x = msg.pose.position.x
g_y = msg.pose.position.y
_, _, g_yaw = euler_from_quaternion(msg.pose.orientation)
path_points = self.hybrid_a_star(self.current_pose, (g_x, g_y, g_yaw))
if path_points:
self.publish_path(path_points)
else:
self.get_logger().warn("No path found!")
def hybrid_a_star(self, start, goal):
sx, sy, syaw = start
gx, gy, gyaw = goal
sx_ind, sy_ind = self.coord2grid(sx, sy)
syaw_ind = int(pi_2_pi(syaw) / self.YAW_RES)
start_node = NodeItem(sx_ind, sy_ind, syaw_ind, sx, sy, syaw, [sx], [sy], -1, 0, 0)
open_list = {}
open_list[self.calc_index(start_node)] = start_node
pq = []
heapq.heappush(pq, (self.calc_cost(start_node, goal), self.calc_index(start_node)))
closed_set = {}
# 限制迭代次数
iter_count = 0
max_iter = 50000
while iter_count < max_iter:
iter_count += 1
if not pq:
return None
_, c_id = heapq.heappop(pq)
if c_id in open_list:
current = open_list[c_id]
del open_list[c_id]
else:
continue
closed_set[c_id] = current
# --- Analytic Expansion (Dubins Shot) ---
# 尝试直接用 Dubins 曲线连接当前点和终点
# 为节省算力,每隔N次尝试或当距离足够近时尝试
dist_to_goal = np.hypot(current.x - gx, current.y - gy)
# 策略:如果距离小于一定值,或者随机尝试(这里设置为始终尝试,追求最优解)
# 如果障碍物很密集,这一步会经常失败,耗费计算
if dist_to_goal < 10.0: # 仅在 10m 范围内尝试直接连接
dubins_path = dubins_path_planning(
current.x, current.y, current.yaw,
gx, gy, gyaw,
self.MAX_CURVATURE, self.MOTION_STEP
)
if dubins_path and self.check_dubins_collision(dubins_path):
self.get_logger().info(f"Dubins shot found! Mode: {dubins_path.mode}")
return self.reconstruct_path_with_dubins(current, closed_set, dubins_path)
# 正常 Hybrid A* 扩展
steer_inputs = [-self.MAX_STEER, 0, self.MAX_STEER]
for steer in steer_inputs:
node = self.kinematic_move(current, steer, self.MOTION_STEP)
if not self.check_collision(node):
continue
node_ind = self.calc_index(node)
if node_ind in closed_set:
continue
if node_ind not in open_list:
new_cost = self.calc_cost(node, goal)
open_list[node_ind] = node
heapq.heappush(pq, (new_cost, node_ind))
else:
if open_list[node_ind].cost > node.cost:
open_list[node_ind] = node
new_cost = self.calc_cost(node, goal)
heapq.heappush(pq, (new_cost, node_ind))
return None
def kinematic_move(self, node, steer, dt):
x, y, yaw = node.x, node.y, node.yaw
dist = 0.6 # 扩展弧长
step = 0.1 # 积分步长
traj_x, traj_y = [], []
d = 0
while d < dist:
x += step * math.cos(yaw)
y += step * math.sin(yaw)
yaw += step / self.WB * math.tan(steer)
d += step
traj_x.append(x)
traj_y.append(y)
yaw = pi_2_pi(yaw)
x_ind, y_ind = self.coord2grid(x, y)
yaw_ind = int(yaw / self.YAW_RES)
# cost 包含移动代价 + 转向惩罚
cost = node.cost + dist + abs(steer)*0.5
new_node = NodeItem(x_ind, y_ind, yaw_ind, x, y, yaw, traj_x, traj_y,
self.calc_index(node), cost, steer)
return new_node
def check_collision(self, node):
for x, y in zip(node.x_list, node.y_list):
ix, iy = self.coord2grid(x, y)
if self.is_collision(ix, iy):
return False
return True
def check_dubins_collision(self, dubins_path):
for x, y in zip(dubins_path.path_x, dubins_path.path_y):
ix, iy = self.coord2grid(x, y)
if self.is_collision(ix, iy):
return False
return True
def is_collision(self, ix, iy):
if ix < 0 or ix >= self.costmap.shape[0] or iy < 0 or iy >= self.costmap.shape[1]:
return True # 出界视为碰撞
if self.costmap[ix][iy] == 1:
return True
return False
def calc_cost(self, node, goal):
# 启发式函数
# Euclidean Dist
h = np.hypot(node.x - goal[0], node.y - goal[1])
return node.cost + h * 1.2
def reconstruct_path_with_dubins(self, current, closed_set, dubins_path):
# 1. 回溯之前的路径
path_x, path_y = [], []
curr = current
while curr.p_ind != -1:
path_x.extend(reversed(curr.x_list))
path_y.extend(reversed(curr.y_list))
curr = closed_set[curr.p_ind]
path_x.append(curr.x)
path_y.append(curr.y)
# 反转得到从起点到current的顺序
final_x = list(reversed(path_x))
final_y = list(reversed(path_y))
# 2. 加上 Dubins 部分
# Dubins路径本身就是顺序的,直接添加
final_x.extend(dubins_path.path_x)
final_y.extend(dubins_path.path_y)
return list(zip(final_x, final_y))
def publish_path(self, points):
path = Path()
path.header.frame_id = "map"
path.header.stamp = self.get_clock().now().to_msg()
for p in points:
pose = PoseStamped()
pose.header.frame_id = "map"
pose.pose.position.x = p[0]
pose.pose.position.y = p[1]
pose.pose.position.z = 0.0
pose.pose.orientation.w = 1.0
path.poses.append(pose)
self.path_pub.publish(path)
def coord2grid(self, x, y):
gx = int((x - self.map_info.origin.position.x) / self.XY_RES)
gy = int((y - self.map_info.origin.position.y) / self.XY_RES)
return gx, gy
def calc_index(self, node):
return (node.x_ind, node.y_ind, node.theta_ind)
def main(args=None):
rclpy.init(args=args)
planner = HybridAStarPlanner()
try:
rclpy.spin(planner)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
pass
finally:
planner.destroy_node()
rclpy.shutdown()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
局部路径规划(lexi避障)
cd /home/zylyehuo/ros2/ros2_lexi
source ./install/setup.bash
ros2 launch lexigraph run.launch.py
启动 rviz
rviz2
修改 rviz 配置
按照设置的话题对应添加组件



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号