The SparkOperator in Apache Airflow is used to submit Spark applications (usually via spark-submit) from an Airflow DAG. Below is a clear, practical guide from setup to a working example.
1. When to use SparkOperator
Use SparkOperator if:
-
You want Airflow to orchestrate Spark jobs
-
You submit Spark jobs using
spark-submit -
Spark runs on:
-
Standalone cluster
-
YARN
-
Kubernetes
-
Mesos
-
If you use Databricks, EMR, or K8s-native Spark, there are specialized operators instead.
2. Prerequisites
A. Install provider package
B. Spark installed & accessible
spark-submit must be available on the Airflow worker machine.
Verify:
3. Airflow Connection (Optional but recommended)
Create a Spark connection in Airflow UI:
-
Conn Id:
spark_default -
Conn Type:
Spark -
Host: Spark master URL
Examples:-
spark://spark-master:7077 -
yarn -
k8s://https://kubernetes.default.svc
-
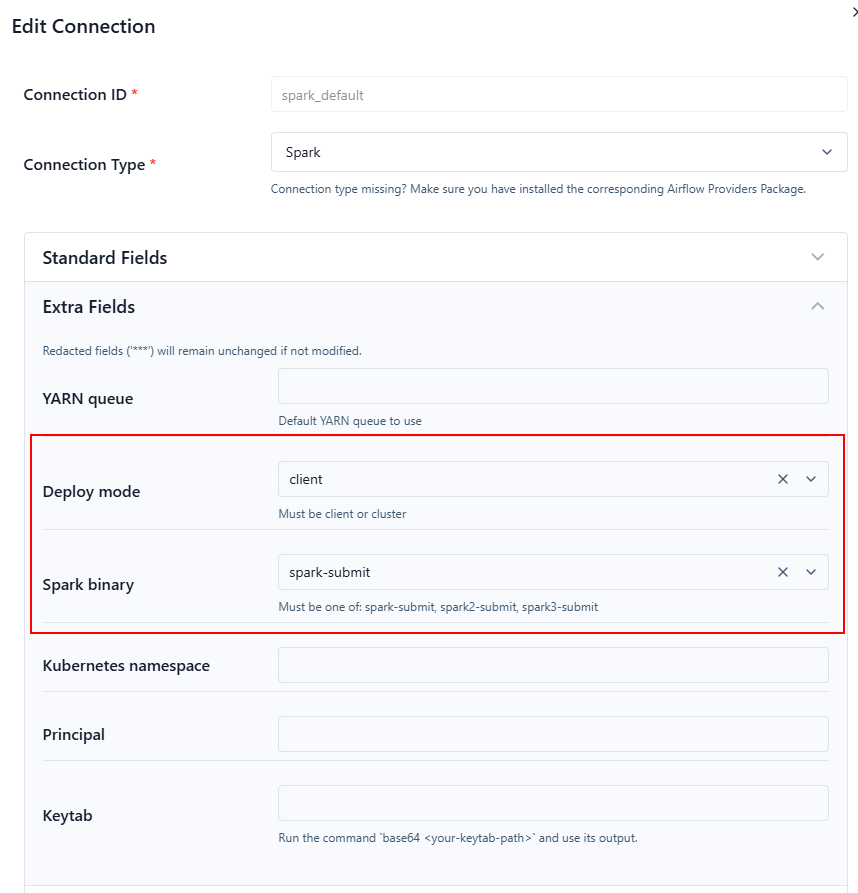
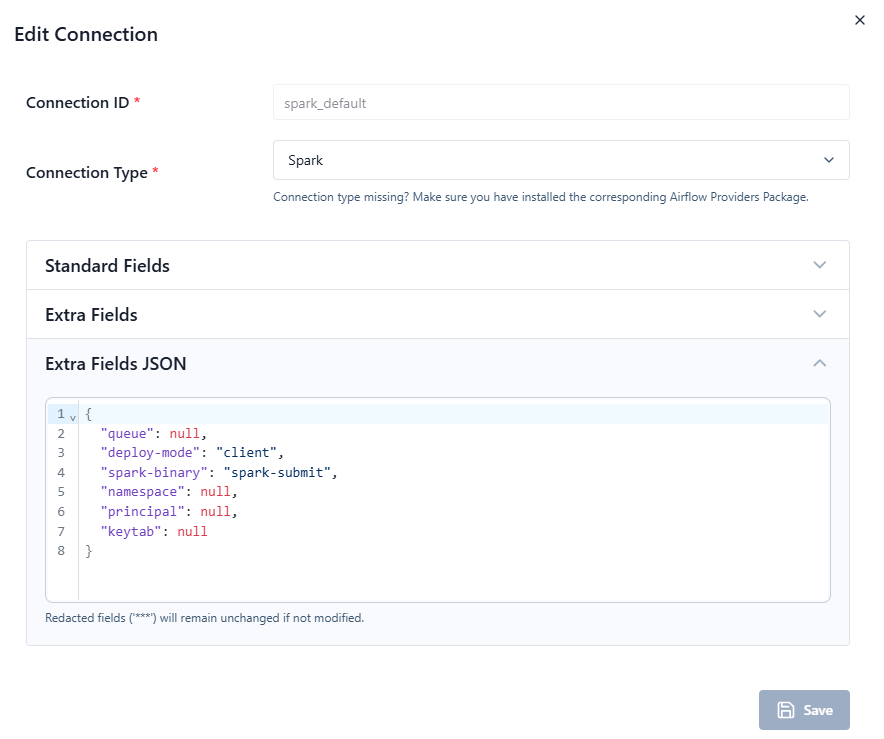
4. Minimal SparkOperator Example
from datetime import datetime from airflow.providers.apache.spark.operators.spark_submit import SparkSubmitOperator from airflow.sdk import DAG with DAG( dag_id="spark_submit_example", start_date=datetime(2024, 1, 1), catchup=False, schedule=None ) as dag: spark_task = SparkSubmitOperator( task_id="run_spark_app", application="/home/frank/zspark.py", conn_id="spark_default", verbose=True, )
Spark master and spark worker must be started under the (airflow-venv) prompt.
5. Example Spark Application (example.py)
6. Commonly Used Parameters
7. Passing Airflow Variables & Macros
In Spark:
8. Running on Different Environments
A. Spark Standalone
B. YARN
C. Kubernetes
9. Debugging Tips
-
Check Airflow task logs (spark-submit output is captured)
-
Use
verbose=True -
Confirm Spark paths are correct
-
Ensure Airflow worker has access to the application file
10. Common Errors
| Error | Cause |
|---|---|
spark-submit not found |
Spark not installed on worker |
Connection spark_default not found |
Missing Airflow connection |
| Job stuck in RUNNING | Cluster resource issue |
| File not found | App path not accessible to worker |
11. When NOT to use SparkOperator
Avoid SparkOperator if:
-
Using Databricks → use
DatabricksSubmitRunOperator -
Using EMR → use
EmrAddStepsOperator -
Using Kubernetes-native Spark → consider
KubernetesPodOperator
spark_task = SparkSubmitOperator( task_id="run_spark_app", application="/home/frank/zspark.py", conn_id="spark_default", verbose=True, )
For the above code, does the /home/frank/zspark.py must be on a Spark worker node?
Short answer: not necessarily — it depends on how your Spark cluster is set up and how spark-submit is executed.
How SparkSubmitOperator works
SparkSubmitOperator runs spark-submit from the machine where the Airflow task is executed (the Airflow worker).
So the path:
must be accessible on the Airflow worker, not automatically on Spark workers.
What happens after submission
Once spark-submit is launched:
-
Client mode (default in many setups):
-
The driver runs on the Airflow worker
-
Spark automatically ships the application file to executors
-
❌ The file does not need to exist on Spark worker nodes
-
-
Cluster mode:
-
The driver runs on a Spark worker / cluster node
-
The application must be:
-
On a shared filesystem, or
-
Distributed via Spark (e.g., HDFS, S3, or
--files)
-
-
❌ A local path like
/home/frank/zspark.pythat exists only on the Airflow worker will fail
-
Typical safe options
To avoid ambiguity:
-
Put the application on a shared filesystem
-
Or ensure identical paths on all nodes
-
Explicitly control deploy mode
Summary table
| Deploy mode | Where app must exist |
|---|---|
| client | Airflow worker only |
| cluster | Shared storage or Spark-accessible URI |
Recommendation
If you are running Airflow → Spark in production, use HDFS/S3/GS paths for the application. This avoids node-specific path issues entirely.




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号