Great question — the difference between linear regression and generalized linear regression (GLM) is fundamental in statistical modeling.
Let’s break it down clearly 👇
🔹 1. Linear Regression (Ordinary Linear Model)
Purpose: Model a continuous response variable yyy as a linear function of predictors.
Model form:
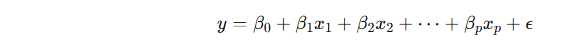
where:
-
y: continuous dependent variable
-
xi: independent variables
-
βi: coefficients
-
ϵ: normally distributed error term (ϵ∼N(0,σ2))
Assumptions:
-
y is normally distributed (for given predictors).
-
Variance of errors is constant (homoscedasticity).
-
Relationship between predictors and y is linear.
🔹 2. Generalized Linear Model (GLM)
Purpose: Extend linear regression to handle non-normal response variables
(e.g., binary, count, proportion, etc.)
Model structure:
GLMs have three components:
-
Random component: specifies the distribution of y
(from the exponential family, e.g., Normal, Binomial, Poisson). -
Systematic component: linear predictor
![1]()
-
Link function: connects the mean of yyy to the linear predictor
![1]()
Common Examples of GLMs
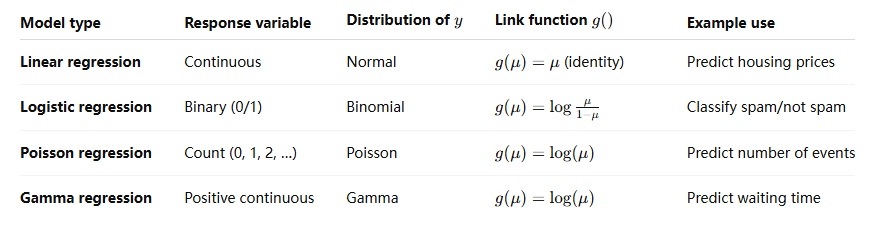
🔹 Key Difference Summary
| Aspect | Linear Regression | Generalized Linear Regression |
|---|---|---|
| Response variable | Continuous (real-valued) | Can be binary, count, or continuous (depending on family) |
| Error distribution | Normal | Exponential family (Normal, Binomial, Poisson, etc.) |
| Link function | Identity g(μ)=μ | Any appropriate link (logit, log, etc.) |
| Variance | Constant | Depends on mean (varies with distribution) |
| Examples | Predict temperature | Predict probability or counts |
🔹 Intuition
-
Linear regression assumes yyy behaves nicely (normal, continuous, linear).
-
GLM is a flexible generalization that says:
“Let’s keep the linear predictor part, but allow different response distributions and nonlinear transformations of the mean.”


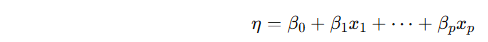


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号