The median is the middle value in an ordered integer list. If the size of the list is even, there is no middle value, and the median is the mean of the two middle values.
- For example, for
arr = [2,3,4], the median is3. - For example, for
arr = [2,3], the median is(2 + 3) / 2 = 2.5.
Implement the MedianFinder class:
MedianFinder()initializes theMedianFinderobject.void addNum(int num)adds the integernumfrom the data stream to the data structure.double findMedian()returns the median of all elements so far. Answers within10-5of the actual answer will be accepted.
Example 1:
Input ["MedianFinder", "addNum", "addNum", "findMedian", "addNum", "findMedian"] [[], [1], [2], [], [3], []] Output [null, null, null, 1.5, null, 2.0] Explanation MedianFinder medianFinder = new MedianFinder(); medianFinder.addNum(1); // arr = [1] medianFinder.addNum(2); // arr = [1, 2] medianFinder.findMedian(); // return 1.5 (i.e., (1 + 2) / 2) medianFinder.addNum(3); // arr[1, 2, 3] medianFinder.findMedian(); // return 2.0
Constraints:
-105 <= num <= 105- There will be at least one element in the data structure before calling
findMedian. - At most
5 * 104calls will be made toaddNumandfindMedian.
My Solution:
import numpy as np class MedianFinder: def __init__(self): self.nums = np.array([], dtype=int) def addNum(self, num: int) -> None: self.nums = np.append(self.nums, num) def findMedian(self) -> float: return np.median(self.nums) # Your MedianFinder object will be instantiated and called as such: # obj = MedianFinder() # obj.addNum(num) # param_2 = obj.findMedian()
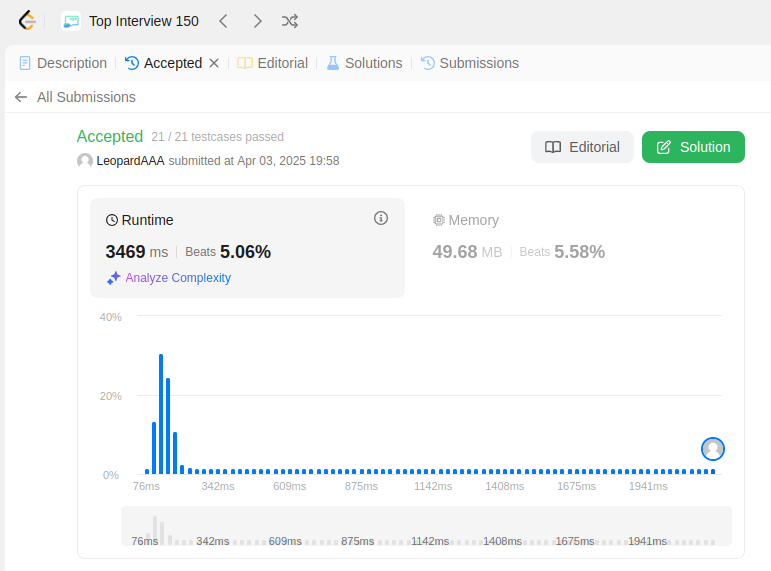
ChatGPT's Solution:
import heapq class MedianFinder: def __init__(self): # Max heap (store negative values for simulation) self.low = [] # Lower half # Min heap self.high = [] # Upper half def addNum(self, num: int) -> None: # Insert into max heap (store negative to simulate max heap) heapq.heappush(self.low, -num) # Ensure max heap root is not greater than min heap root if self.low and self.high and (-self.low[0] > self.high[0]): heapq.heappush(self.high, -heapq.heappop(self.low)) # Balance the heaps: Ensure low has equal or one more element than high if len(self.low) > len(self.high) + 1: heapq.heappush(self.high, -heapq.heappop(self.low)) elif len(self.high) > len(self.low): heapq.heappush(self.low, -heapq.heappop(self.high)) def findMedian(self) -> float: if len(self.low) > len(self.high): return -self.low[0] # Max heap root (stored as negative) return (-self.low[0] + self.high[0]) / 2 # Average of roots # Your MedianFinder object will be instantiated and called as such: # obj = MedianFinder() # obj.addNum(num) # param_2 = obj.findMedian()
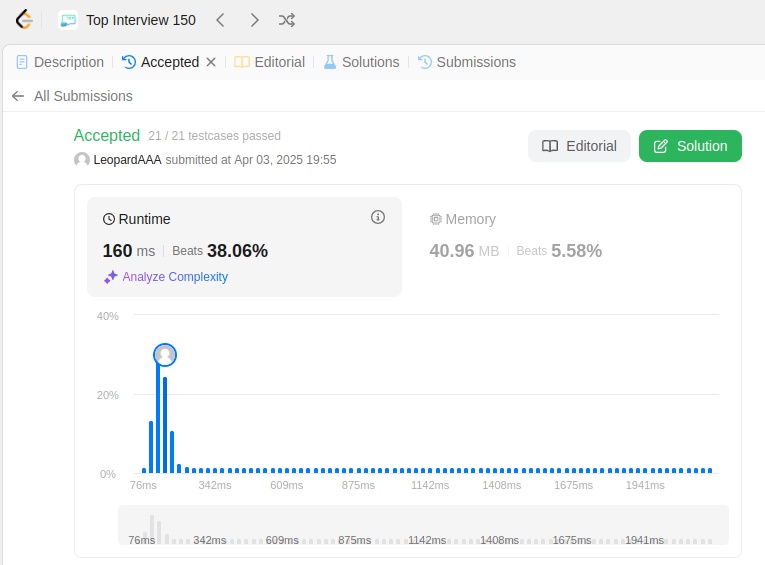




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号