Design a data structure that supports adding new words and finding if a string matches any previously added string.
Implement the WordDictionary class:
WordDictionary()Initializes the object.void addWord(word)Addswordto the data structure, it can be matched later.bool search(word)Returnstrueif there is any string in the data structure that matcheswordorfalseotherwise.wordmay contain dots'.'where dots can be matched with any letter.
Example:
Input
["WordDictionary","addWord","addWord","addWord","search","search","search","search"]
[[],["bad"],["dad"],["mad"],["pad"],["bad"],[".ad"],["b.."]]
Output
[null,null,null,null,false,true,true,true]
Explanation
WordDictionary wordDictionary = new WordDictionary();
wordDictionary.addWord("bad");
wordDictionary.addWord("dad");
wordDictionary.addWord("mad");
wordDictionary.search("pad"); // return False
wordDictionary.search("bad"); // return True
wordDictionary.search(".ad"); // return True
wordDictionary.search("b.."); // return True
Constraints:
1 <= word.length <= 25wordinaddWordconsists of lowercase English letters.wordinsearchconsist of'.'or lowercase English letters.- There will be at most
2dots inwordforsearchqueries. - At most
104calls will be made toaddWordandsearch.
My Solution:
class WordDictionary: def __init__(self): self.words = set() def addWord(self, word: str) -> None: self.words.add(word) def search(self, word: str) -> bool: idx_1 = word.find('.') if idx_1 == -1: # word contains no '.' return word in self.words else: # word contains at least one '.' idx_2 = word[idx_1 + 1:].find('.') idx_2 = idx_1 + 1 + idx_2 for w in self.words: if len(w) != len(word): continue if word[:idx_1] == w[:idx_1] and word[idx_1 + 1:idx_2] == w[idx_1 + 1:idx_2] and word[idx_2 + 1:] == w[idx_2 + 1:]: return True return False # Your WordDictionary object will be instantiated and called as such: # obj = WordDictionary() # obj.addWord(word) # param_2 = obj.search(word)
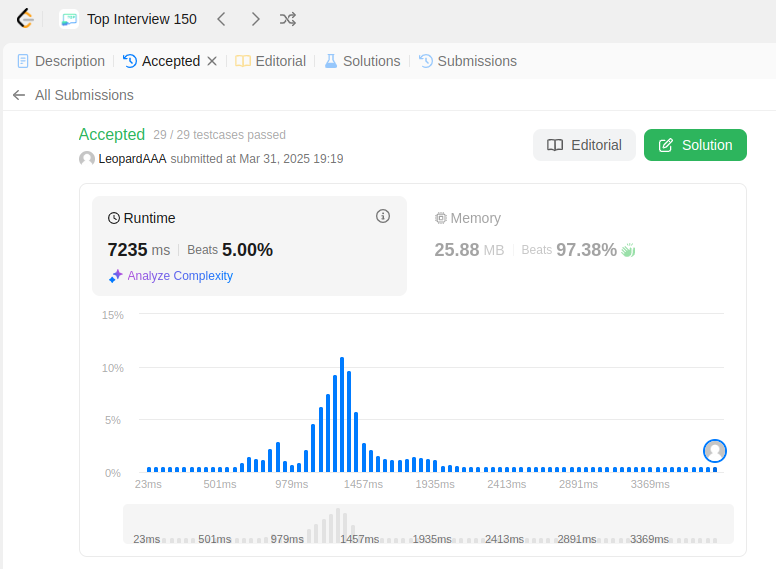
ChatGPT's Solution:
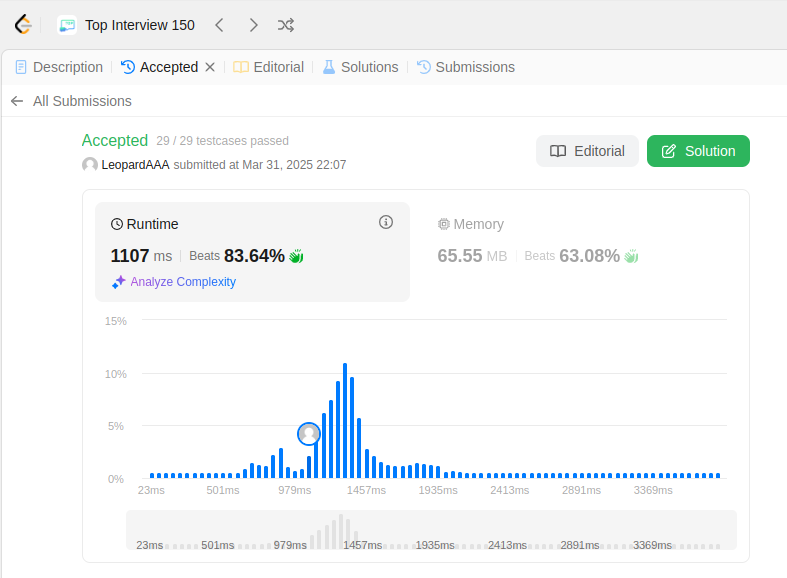
class TrieNode: def __init__(self): # Each node stores a dictionary of children and a boolean for end of word. self.children = {} self.is_end_of_word = False class WordDictionary: def __init__(self): self.root = TrieNode() def addWord(self, word: str) -> None: node = self.root for char in word: if char not in node.children: node.children[char] = TrieNode() node = node.children[char] node.is_end_of_word = True def search(self, word: str) -> bool: return self._search_in_node(word, 0, self.root) def _search_in_node(self, word: str, index: int, node: TrieNode) -> bool: if index == len(word): return node.is_end_of_word char = word[index] if char == '.': for child in node.children.values(): if self._search_in_node(word, index + 1, child): return True elif char in node.children: return self._search_in_node(word, index + 1, node.children[char]) return False # Your WordDictionary object will be instantiated and called as such: # obj = WordDictionary() # obj.addWord(word) # param_2 = obj.search(word)




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号