A path in a binary tree is a sequence of nodes where each pair of adjacent nodes in the sequence has an edge connecting them. A node can only appear in the sequence at most once. Note that the path does not need to pass through the root.
The path sum of a path is the sum of the node's values in the path.
Given the root of a binary tree, return the maximum path sum of any non-empty path.
Example 1:
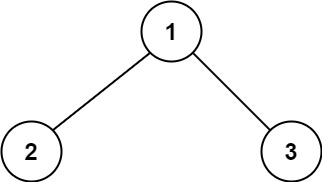
Input: root = [1,2,3] Output: 6 Explanation: The optimal path is 2 -> 1 -> 3 with a path sum of 2 + 1 + 3 = 6.
Example 2:
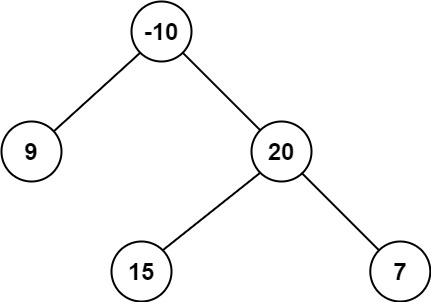
Input: root = [-10,9,20,null,null,15,7] Output: 42 Explanation: The optimal path is 15 -> 20 -> 7 with a path sum of 15 + 20 + 7 = 42.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 3 * 104]. -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
ChatGPT's Solution:
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def maxPathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int: # Initialize the result as the smallest possible integer self.max_sum = float('-inf') # Helper function that computes the maximum path sum through the current node def dfs(node): if not node: return 0 # Return 0 for a null node, as it does not contribute to the sum # Recursively calculate the max path sum for left and right subtrees left_gain = max(dfs(node.left), 0) # If negative, we discard it (take 0 instead) right_gain = max(dfs(node.right), 0) # If negative, we discard it (take 0 instead) # Calculate the price to start a new path at this node price_newpath = node.val + left_gain + right_gain # Update the global max_sum if the new path is better self.max_sum = max(self.max_sum, price_newpath) # Return the maximum sum path starting from the current node and extending to either left or right return node.val + max(left_gain, right_gain) # Start DFS traversal dfs(root) # Return the global max path sum return self.max_sum




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号