浅谈高斯消元
线性代数相关定义
线型方程组
设有 \(n\) 个未知数 \(m\) 个方程的线性方程组
其中 \(a_{ij}\) 为第 \(i\) 个方程第 \(j\) 个未知数的系数,\(b_i\) 是第 \(i\) 个方程的常数项。
当常数项 \(b_1,b_2,b_3,\dots,b_m\) 不全为零时,该线性方程组叫做 \(n\) 元非齐次线性方程组。
当 \(b_1,b_2,b_3,\dots,b_m\) 全为零时,该线性方程组
称为 \(n\) 元齐次线性方程组。
\(n\) 元线性方程组往往简称为线性方程组或方程组。
对于 \(n\) 元齐次线性方程组,\(x_1 = x_2 = x_3 = x_n = 0\) 一定是它的解,这个解叫齐次线性方程组的零解。如果有一组不全为零的数是它的解,则叫做齐次线性方程组的非零解。
齐次线性方程组一定有零解,不一定有非零解。
矩阵
对于非齐次线性方程组
有如下几个矩阵:
其中 \(A\) 成为系数矩阵,\(x\) 称为未知数矩阵,\(b\) 称为常数项矩阵,\(B\) 称为增广矩阵。高斯消元就是在增广矩阵上进行的。
矩阵的初等变换
下面三种变换称为矩阵的初等行变换:
- 对换两行(对换 \(i,j\) 两行,记作 \(r_i \leftrightarrow r_j\))
- 以非零数 \(k\) 乘上某一行中所有元(第 \(i\) 行乘以 \(k\),记作 \(r_i \times k\))
- 把某一行数所有元的 \(k\) 倍加到另一行的所有元上去(第 \(j\) 行的 \(k\) 倍加到第 \(i\) 行上,记作 \(r_i+k\times r_j\))
把矩阵的初等行变换的“行”换成“列”,就得到了矩阵的初等列变换。
矩阵的初等行变换和矩阵的初等列变换,统称为初等变换。
高斯消元
主要思想
反复运用初等变换将原矩阵变换为形如
的上三角矩阵,然后从下至上回带求解。
而且可以观察到每一行对应主元之下,该主元的系数都为 \(0\)。
主要步骤
- 找到当前主元系数不为 \(0\) 的一行(这里通常也找系数绝对值较大的一行)。
- 将这一行与当前处理到的行交换。
- 运用初等变换将主元的系数变为 \(1\)。
- 运用初等变换将其余行(不包含当前行上面的行)的主元的系数变为 \(0\)(目的是变成上三角矩阵)。
最后通过上三角矩阵回带求解,得到答案。
无解 & 无穷解
通过初中知识可知,\(n\) 个未知数要有 \(n\) 个方程才能求解,如果在找主元不为 \(0\) 的一行是找不到了(即这个主元的所有系数都为 \(0\)),这是肯定是会出现两种情况。
- 无解,出现 \(0 = k \not= 0\) 时。
- 无穷解,出现 \(0 = 0\) 时。
故处理时如果出现找不到主元时先跳过这一行,最后在所有系数都为 \(0\) 的行中判断常数即可。
无解举例
此时无解。
无穷解举例
此时有无数解。
解释
下面通过几组样例,在程序中插入 printf 语句,追踪一下高斯消元的执行过程。
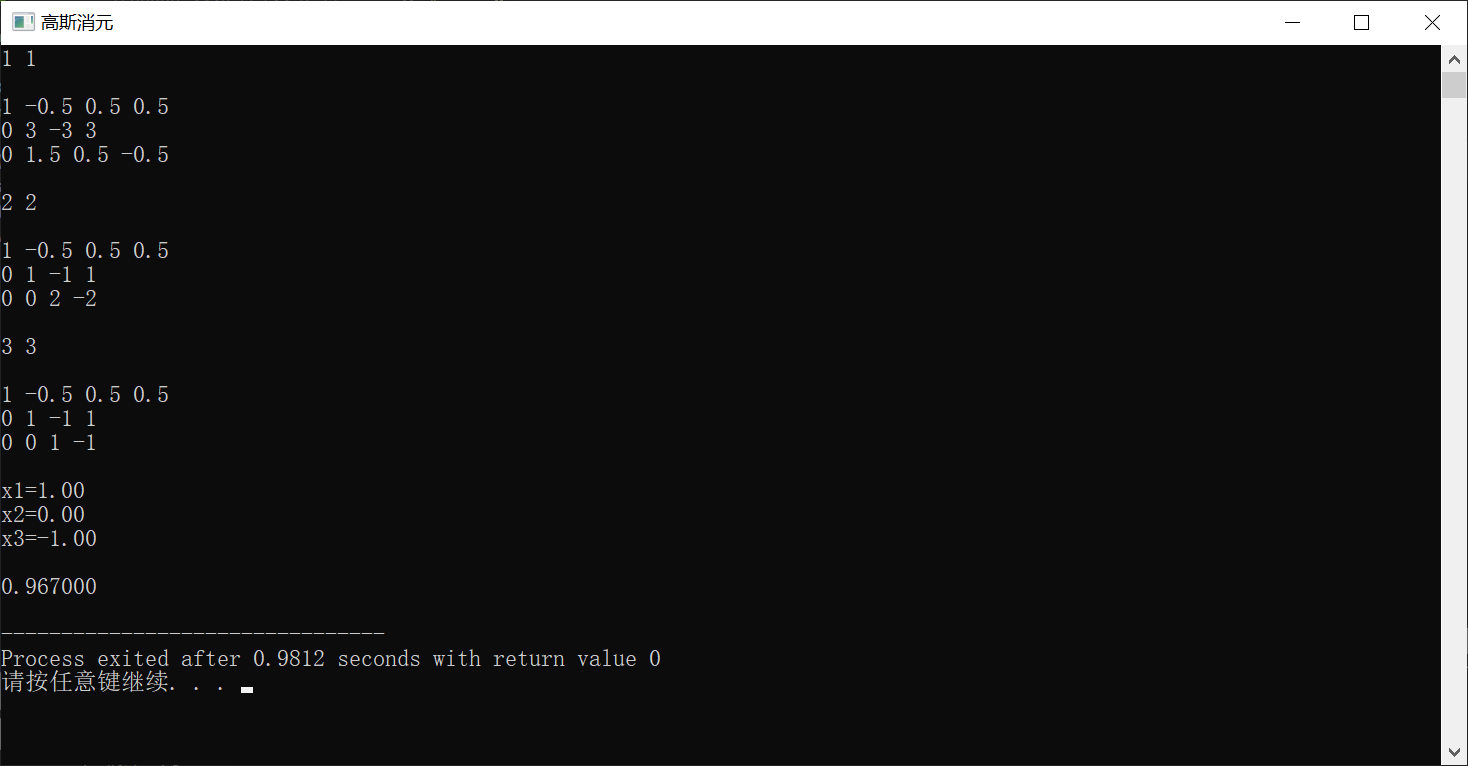
唯一解
输入:
3
2 -1 1 1
4 1 -1 5
1 1 1 0
输出:
x1=1.00
x2=0.00
x3=-1.00
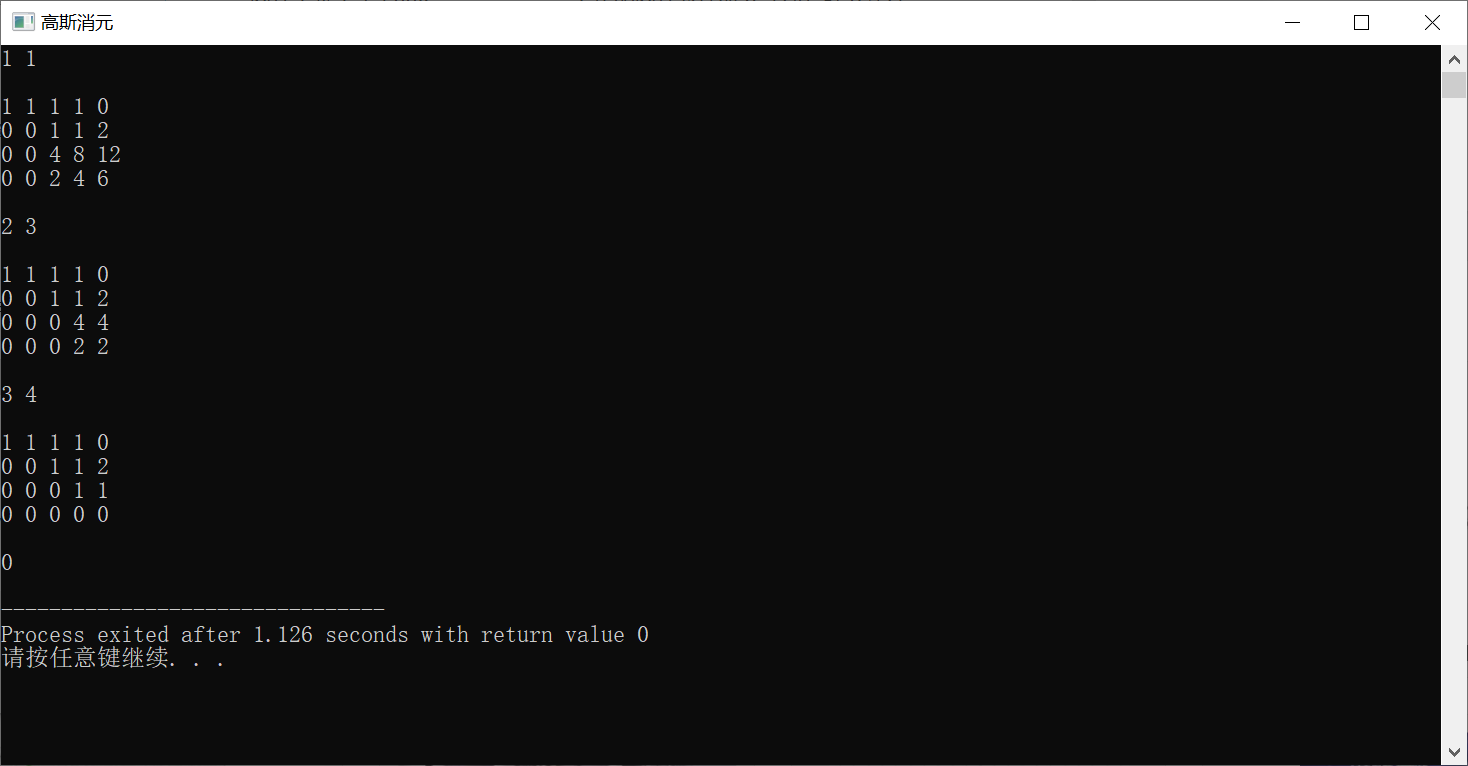
无穷解
输入:
4
0 0 2 4 6
0 0 1 1 2
0 0 4 8 12
1 1 1 1 0
输出:
0
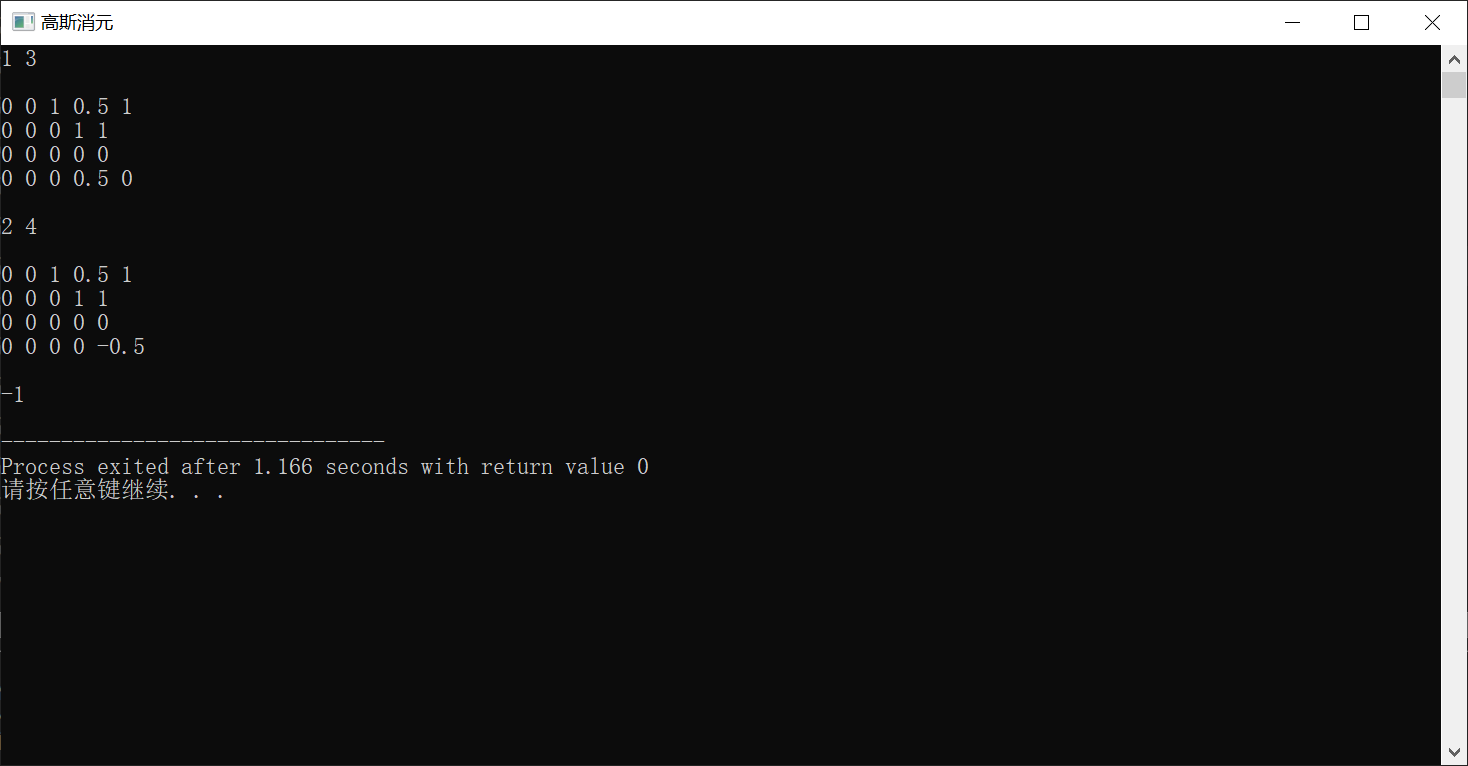
无解
输入:
4
0 0 2 1 2
0 0 1 1 1
0 0 0 1 1
0 0 0 0 0
输出:
-1
代码实现
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 105;
const double eps = 1e-7;//精度
double a[maxn][maxn];
double ans[maxn];
int n;
void print()
{
puts("");
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n + 1; j++) cout << a[i][j] << " ";
puts("");
}
puts("");
}//调试,输出矩阵
void gauss()
{
//row 行 col 列
int col = 1, row = 1;
for (col = 1; col <= n; col++)//枚举主元所在列(1~n)
{
//step1 找到主元非0的一行
int t = row;
for (int i = row; i <= n; i++)
{
if (fabs(a[i][col]) > eps)
{
t = i;
break;
}
}
// step2
if (fabs(a[t][col]) < eps) continue;//主元系数为0,即产生了自由元,先暂且不管
swap(a[row], a[t]);//否则替换两行
//step3 将主元系数置1,注意枚举顺序
for (int i = n + 1; i >= row; i--)
{
a[row][i] /= a[row][col];
}
//step4 将下面所有的主元系数消为0
for (int i = row + 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = n + 1; j >= col; j--)
{
a[i][j] -= a[i][col] * a[row][j];
}
}
//step5 处理下一个主元
row++;
}
//处理的主元个数小于n,产生了自由元,一定是无解/无穷解
if (row <= n)
{
for (int i = row; i <= n; i++)
{
if (fabs(a[i][n + 1]) > eps)
{
cout << "-1" << endl;
exit(0);
}
}
puts("0");
exit(0);
return;
}
else
{
//step6 回代求解答案
for (int i = n; i >= 1; i--)
{
ans[i] = a[i][n + 1];
for (int j = i + 1; j <= n; j++)
{
ans[i] -= ans[j] * a[i][j];
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) printf("x%d=%.2lf\n", i, ans[i]);
}
}
int main()
{
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
#define LOCAL
//freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
#endif
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n + 1; j++)
{
scanf("%lf", &a[i][j]);
}
}
gauss();
#ifdef LOCAL
fprintf(stderr, "%f\n", 1.0 * clock() / CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
#endif
return 0;
}
高斯-约当消元法
主要思想
与高斯消元思想相近,但略有不同。
反复运用初等变换将系数矩阵变换为形如
的单位矩阵。
主要步骤
- 找到当前主元系数不为 \(0\) 的一行(这里通常也找系数绝对值较大的一行)。
- 将这一行与当前处理到的行交换。
- 运用初等变换将主元的系数变为 \(1\)。
- 运用初等变换将其余行的主元的系数变为 \(0\)。
解释
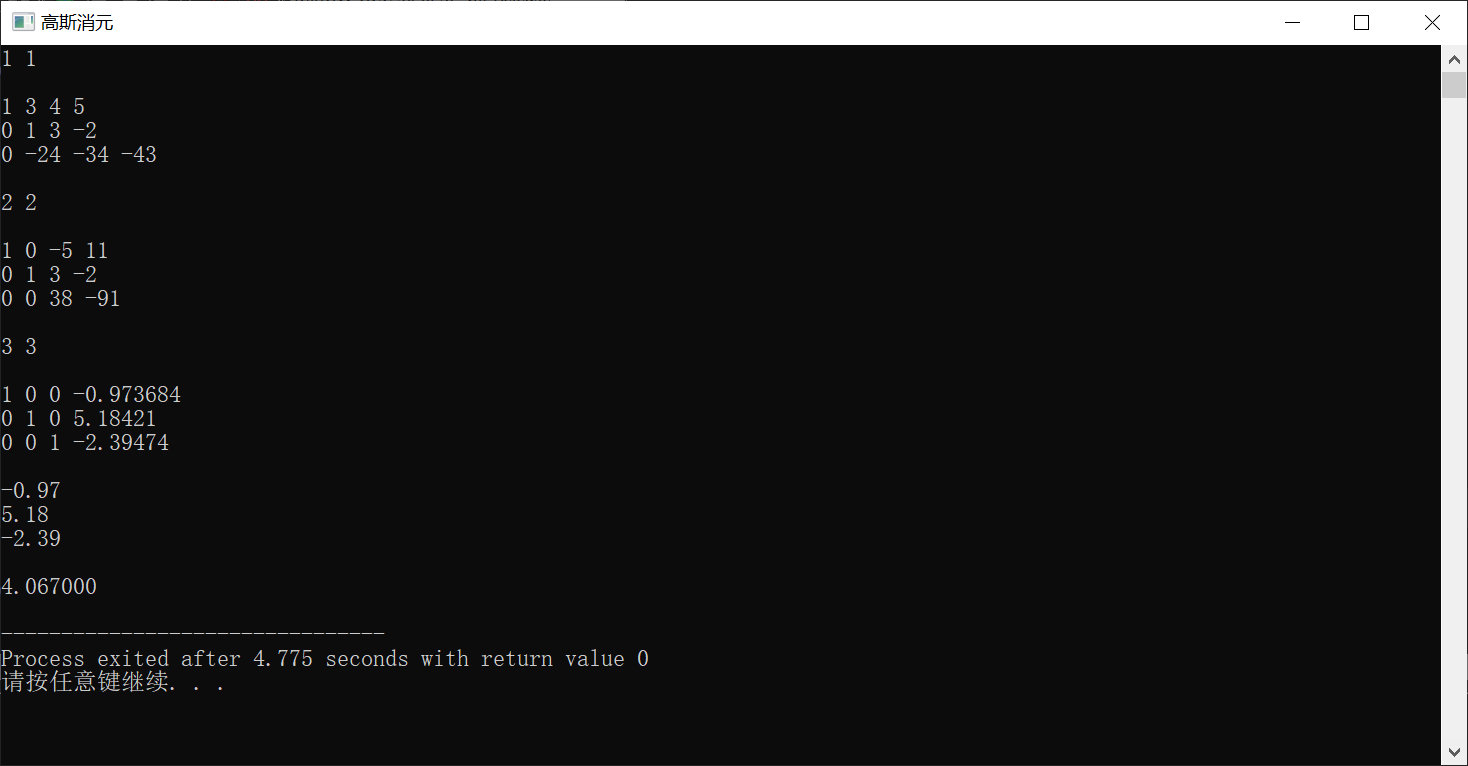
追踪高斯-约当消元的执行过程。
输入:
3
1 3 4 5
1 4 7 3
9 3 2 2
输出
-0.97
5.18
-2.39
代码实现
相比高斯消元只需改动一点,具体细节见代码。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 105;
const double eps = 1e-7;//精度
double a[maxn][maxn];
double ans[maxn];
int n;
void print()
{
puts("");
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n + 1; j++) cout << a[i][j] << " ";
puts("");
}
puts("");
}//调试,输出矩阵
void gauss()
{
//row 行 col 列
int col = 1, row = 1;
for (col = 1; col <= n; col++)//枚举主元所在列(1~n)
{
//step1 找到主元非0的一行
int t = row;
for (int i = row; i <= n; i++)
{
if (fabs(a[i][col]) > eps)
{
t = i;
break;
}
}
// step2
if (fabs(a[t][col]) < eps) continue;//主元系数为0,即产生了自由元,先暂且不管
swap(a[row], a[t]);//否则替换两行
//step3 将主元系数置1,注意枚举顺序
for (int i = n + 1; i >= row; i--)
{
a[row][i] /= a[row][col];
}
//step4 将所有的主元系数消为0
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (i == row) continue;
for (int j = n + 1; j >= col; j--)
{
a[i][j] -= a[i][col] * a[row][j];
}
}
//cout<<row<<" "<<col<<endl;
//print();
//step5 处理下一个主元
row++;
}
//处理的主元个数小于n,产生了自由元,一定是无解/无穷解
if (row <= n)
{
for (int i = row; i <= n; i++)
{
if (fabs(a[i][n + 1]) > eps)
{
cout << "No Solution" << endl;
exit(0);
}
}
puts("No Solution");
exit(0);
return;
}
else
{
//step6 输出答案
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) printf("%.2lf\n", a[i][n + 1]);
}
}
int main()
{
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
#define LOCAL
//freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
#endif
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n + 1; j++)
{
scanf("%lf", &a[i][j]);
}
}
gauss();
puts("");
#ifdef LOCAL
fprintf(stderr, "%f\n", 1.0 * clock() / CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
#endif
return 0;
}
例题
- AcWing 884. 高斯消元解异或线性方程组 & 题解:AcWing 884. 高斯消元解异或线性方程组 题解
- P2447 [SDOI2010] 外星千足虫 & 题解: P2447 [SDOI2010] 外星千足虫 题解
- 2962 [USACO09NOV] Lights G & 题解: \(\color{grey}\text{Pending}\dots\)
- P4035 [JSOI2008] 球形空间产生器 & 题解: \(\color{grey}\text{Pending}\dots\)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号