折腾笔记[26]-基于深度学习的图像关键点提取及特征匹配
摘要
使用docker容器离线部署图像关键点检测模块, 体验基于深度学习的图像关键点提取及特征匹配.
关键词
docker;keypoint;feature extraction;matching;
关键信息
支持模型列表:
server:
name: "0.0.0.0"
port: 7860
defaults:
setting_threshold: 0.1
max_keypoints: 2000
keypoint_threshold: 0.05
enable_ransac: true
ransac_method: CV2_USAC_MAGSAC
ransac_reproj_threshold: 8
ransac_confidence: 0.9999
ransac_max_iter: 10000
ransac_num_samples: 4
match_threshold: 0.2
setting_geometry: Homography
matcher_zoo:
# example config
Example:
# show in `Matching Model` or not, default: true
enable: false
# matcher name
matcher: example
# skip ci or not, default: false
skip_ci: true
# dense matcher or not, default: true
dense: true
# info
info:
# dispaly name in `Matching Model`
name: example(example)
# conference/journal/workshop Year
source: "CVPR XXXX"
# github link
github: https://github.com/example/example
# paper link
paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/xxxx.xxxx
# project link
project: https://example.com
# show in `support algos` table
display: false
# low, medium, high
efficiency: low
dad(RoMa):
matcher: dad_roma
skip_ci: true
dense: true
info:
name: Dad(RoMa) #dispaly name
source: "ARXIV 2025"
paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.07347
github: https://github.com/Parskatt/dad
display: true
efficiency: low # low, medium, high
minima(loftr):
matcher: minima_loftr
dense: true
info:
name: MINIMA(LoFTR) #dispaly name
source: "ARXIV 2024"
paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.19412
github: https://github.com/LSXI7/MINIMA
display: true
minima(RoMa):
matcher: minima_roma
skip_ci: true
dense: true
info:
name: MINIMA(RoMa) #dispaly name
source: "ARXIV 2024"
paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.19412
github: https://github.com/LSXI7/MINIMA
display: false
efficiency: low # low, medium, high
omniglue:
enable: true
matcher: omniglue
dense: true
info:
name: OmniGlue
source: "CVPR 2024"
github: https://github.com/Vincentqyw/omniglue-onnx
paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2405.12979
project: https://hwjiang1510.github.io/OmniGlue
display: true
Mast3R:
enable: false
matcher: mast3r
dense: true
info:
name: Mast3R #dispaly name
source: "CVPR 2024"
github: https://github.com/naver/mast3r
paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2406.09756
project: https://dust3r.europe.naverlabs.com
display: true
efficiency: low # low, medium, high
DUSt3R:
# TODO: duster is under development
enable: true
# skip_ci: true
matcher: duster
dense: true
info:
name: DUSt3R #dispaly name
source: "CVPR 2024"
github: https://github.com/naver/dust3r
paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.14132
project: https://dust3r.europe.naverlabs.com
display: true
GIM(dkm):
enable: true
# skip_ci: true
matcher: gim(dkm)
dense: true
info:
name: GIM(DKM) #dispaly name
source: "ICLR 2024"
github: https://github.com/xuelunshen/gim
paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.11095
project: https://xuelunshen.com/gim
display: true
efficiency: low # low, medium, high
RoMa:
matcher: roma
skip_ci: true
dense: true
info:
name: RoMa #dispaly name
source: "CVPR 2024"
github: https://github.com/Parskatt/RoMa
paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.15404
project: https://parskatt.github.io/RoMa
display: true
efficiency: low # low, medium, high
dkm:
matcher: dkm
skip_ci: true
dense: true
info:
name: DKM #dispaly name
source: "CVPR 2023"
github: https://github.com/Parskatt/DKM
paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.00667
project: https://parskatt.github.io/DKM
display: true
efficiency: low # low, medium, high
loftr:
matcher: loftr
dense: true
info:
name: LoFTR #dispaly name
source: "CVPR 2021"
github: https://github.com/zju3dv/LoFTR
paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2104.00680
project: https://zju3dv.github.io/loftr
display: true
eloftr:
matcher: eloftr
dense: true
info:
name: Efficient LoFTR #dispaly name
source: "CVPR 2024"
github: https://github.com/zju3dv/efficientloftr
paper: https://zju3dv.github.io/efficientloftr/files/EfficientLoFTR.pdf
project: https://zju3dv.github.io/efficientloftr
display: true
xoftr:
matcher: xoftr
dense: true
info:
name: XoFTR #dispaly name
source: "CVPR 2024"
github: https://github.com/OnderT/XoFTR
paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2404.09692
project: null
display: true
cotr:
enable: false
skip_ci: true
matcher: cotr
dense: true
info:
name: CoTR #dispaly name
source: "ICCV 2021"
github: https://github.com/ubc-vision/COTR
paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.14167
project: null
display: true
efficiency: low # low, medium, high
topicfm:
matcher: topicfm
dense: true
info:
name: TopicFM #dispaly name
source: "AAAI 2023"
github: https://github.com/TruongKhang/TopicFM
paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.00485
project: null
display: true
aspanformer:
matcher: aspanformer
dense: true
info:
name: ASpanformer #dispaly name
source: "ECCV 2022"
github: https://github.com/Vincentqyw/ml-aspanformer
paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.14201
project: null
display: true
xfeat+lightglue:
enable: true
matcher: xfeat_lightglue
dense: true
info:
name: xfeat+lightglue
source: "CVPR 2024"
github: https://github.com/Vincentqyw/omniglue-onnx
paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2405.12979
project: https://hwjiang1510.github.io/OmniGlue
display: true
xfeat(sparse):
matcher: NN-mutual
feature: xfeat
dense: false
info:
name: XFeat #dispaly name
source: "CVPR 2024"
github: https://github.com/verlab/accelerated_features
paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.19174
project: null
display: true
xfeat(dense):
matcher: xfeat_dense
dense: true
info:
name: XFeat #dispaly name
source: "CVPR 2024"
github: https://github.com/verlab/accelerated_features
paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.19174
project: null
display: false
dedode:
matcher: Dual-Softmax
feature: dedode
dense: false
info:
name: DeDoDe #dispaly name
source: "3DV 2024"
github: https://github.com/Parskatt/DeDoDe
paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2308.08479
project: null
display: true
superpoint+superglue:
matcher: superglue
feature: superpoint_max
dense: false
info:
name: SuperGlue #dispaly name
source: "CVPR 2020"
github: https://github.com/magicleap/SuperGluePretrainedNetwork
paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.11763
project: null
display: true
superpoint+lightglue:
matcher: superpoint-lightglue
feature: superpoint_max
dense: false
info:
name: LightGlue #dispaly name
source: "ICCV 2023"
github: https://github.com/cvg/LightGlue
paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2306.13643
project: null
display: true
disk:
matcher: NN-mutual
feature: disk
dense: false
info:
name: DISK
source: "NeurIPS 2020"
github: https://github.com/cvlab-epfl/disk
paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.13566
project: null
display: true
disk+dualsoftmax:
matcher: Dual-Softmax
feature: disk
dense: false
info:
name: DISK
source: "NeurIPS 2020"
github: https://github.com/cvlab-epfl/disk
paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.13566
project: null
display: false
superpoint+dualsoftmax:
matcher: Dual-Softmax
feature: superpoint_max
dense: false
info:
name: SuperPoint
source: "CVPRW 2018"
github: https://github.com/magicleap/SuperPointPretrainedNetwork
paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/1712.07629
project: null
display: false
sift+lightglue:
matcher: sift-lightglue
feature: sift
dense: false
info:
name: LightGlue #dispaly name
source: "ICCV 2023"
github: https://github.com/cvg/LightGlue
paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2306.13643
project: null
display: true
disk+lightglue:
matcher: disk-lightglue
feature: disk
dense: false
info:
name: LightGlue
source: "ICCV 2023"
github: https://github.com/cvg/LightGlue
paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2306.13643
project: null
display: true
aliked+lightglue:
matcher: aliked-lightglue
feature: aliked-n16
dense: false
info:
name: ALIKED
source: "ICCV 2023"
github: https://github.com/Shiaoming/ALIKED
paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2304.03608.pdf
project: null
display: true
superpoint+mnn:
matcher: NN-mutual
feature: superpoint_max
dense: false
info:
name: SuperPoint #dispaly name
source: "CVPRW 2018"
github: https://github.com/magicleap/SuperPointPretrainedNetwork
paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/1712.07629
project: null
display: true
sift+sgmnet:
matcher: sgmnet
feature: sift
dense: false
info:
name: SGMNet #dispaly name
source: "ICCV 2021"
github: https://github.com/vdvchen/SGMNet
paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2108.08771
project: null
display: true
sosnet:
matcher: NN-mutual
feature: sosnet
dense: false
info:
name: SOSNet #dispaly name
source: "CVPR 2019"
github: https://github.com/scape-research/SOSNet
paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.05019
project: https://research.scape.io/sosnet
display: true
hardnet:
matcher: NN-mutual
feature: hardnet
dense: false
info:
name: HardNet #dispaly name
source: "NeurIPS 2017"
github: https://github.com/DagnyT/hardnet
paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/1705.10872
project: null
display: true
d2net:
matcher: NN-mutual
feature: d2net-ss
dense: false
info:
name: D2Net #dispaly name
source: "CVPR 2019"
github: https://github.com/Vincentqyw/d2-net
paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.03561
project: https://dusmanu.com/publications/d2-net.html
display: true
rord:
matcher: NN-mutual
feature: rord
dense: false
info:
name: RoRD #dispaly name
source: "IROS 2021"
github: https://github.com/UditSinghParihar/RoRD
paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.08573
project: https://uditsinghparihar.github.io/RoRD
display: true
alike:
matcher: NN-mutual
feature: alike
dense: false
info:
name: ALIKE #dispaly name
source: "TMM 2022"
github: https://github.com/Shiaoming/ALIKE
paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.02906
project: null
display: true
lanet:
matcher: NN-mutual
feature: lanet
dense: false
info:
name: LANet #dispaly name
source: "ACCV 2022"
github: https://github.com/wangch-g/lanet
paper: https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content/ACCV2022/papers/Wang_Rethinking_Low-level_Features_for_Interest_Point_Detection_and_Description_ACCV_2022_paper.pdf
project: null
display: true
r2d2:
matcher: NN-mutual
feature: r2d2
dense: false
info:
name: R2D2 #dispaly name
source: "NeurIPS 2019"
github: https://github.com/naver/r2d2
paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/1906.06195
project: null
display: true
darkfeat:
matcher: NN-mutual
feature: darkfeat
dense: false
info:
name: DarkFeat #dispaly name
source: "AAAI 2023"
github: https://github.com/THU-LYJ-Lab/DarkFeat
paper: null
project: null
display: true
sift:
matcher: NN-mutual
feature: sift
dense: false
info:
name: SIFT #dispaly name
source: "IJCV 2004"
github: null
paper: https://www.cs.ubc.ca/~lowe/papers/ijcv04.pdf
project: null
display: true
gluestick:
enable: true
matcher: gluestick
dense: true
info:
name: GlueStick #dispaly name
source: "ICCV 2023"
github: https://github.com/cvg/GlueStick
paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2304.02008
project: https://iago-suarez.com/gluestick
display: true
sold2:
enable: false
matcher: sold2
dense: true
info:
name: SOLD2 #dispaly name
source: "CVPR 2021"
github: https://github.com/cvg/SOLD2
paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.03362
project: null
display: true
sfd2+imp:
enable: true
matcher: imp
feature: sfd2
dense: false
info:
name: SFD2+IMP #dispaly name
source: "CVPR 2023"
github: https://github.com/feixue94/imp-release
paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2304.14837
project: https://feixue94.github.io/
display: true
sfd2+mnn:
enable: true
matcher: NN-mutual
feature: sfd2
dense: false
info:
name: SFD2+MNN #dispaly name
source: "CVPR 2023"
github: https://github.com/feixue94/sfd2
paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2304.14845
project: https://feixue94.github.io/
display: true
retrieval_zoo:
netvlad:
enable: true
openibl:
enable: true
cosplace:
enable: true
原理简介
基于深度学习的图像关键点提取及特征匹配综述
[https://hkxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/10.7527/S1000-6893.2023.28796]
- minima(loftr)
- omniglue
- DUST3R
- GIM(dkm)
- RoMa
- loftr
- eloftr
- xoftr
- topicfm
- aspanformer
- xfeat+lightglue
- xfeat(sparse)
- xfeat(dense)
- dedode
- superpoint+superglue
- superpoint+lightglue
- disk
- disk+dualsoftmax
- superpoint+dualsoftmax
- sift+lightglue
- disk+lightglue
- aliked+lightglue
- superpoint+mnn
- sift+sgmnet
- sosnet
- hardnet
- d2net
- nord
- alike
- lanet
- r2d2
- darkfeat
- sift
- gluestick
- sfd2+imp
- sfd2+mnn
图像匹配是飞行器视觉导航中的一项关键技术。
#图像匹配,#视觉导航,#深度学习,
#特征提取,#传统方法,#技术突破,
#单环节网络,#端到端网络,#模型对比,
#特征检测,#描述符学习,#相似度度量,#误差剔除,
#网络结构,#算法综述,#经典模型,
#飞行器技术,#AI应用,#计算机视觉,
1. 关键点检测方法
关键点检测是图像匹配的第一步,目的是在图像中找到具有区分性的点,这些点在不同视角或条件下应能被重复检测到。
1.1 基于学习的方法
-
SuperPoint: 使用卷积神经网络(CNN)直接从图像中检测关键点,同时生成关键点的描述子。SuperPoint通过在合成图像上训练,学习到的关键点检测器对仿射变换具有很好的重复性。
-
D2-Net: 通过VGG网络的特定层输出特征图进行关键点置信度计算,使用soft-nms技术在空间维度计算不同通道特征图的极值点,并针对每个通道特征计算其与通道最大值之比,作为特征点的似然分数。
-
ASLFeat: 使用L2Net不同层次的特征图进行特征点似然计算,并将它们映射至原始图像分辨率以提高获得的特征点空间位置精度。
-
R2D2: 直接通过神经网络预测特征点似然的方法,不需要对提取的特征图计算峰值性以获得对应位置处特征点的置信度。
1.2 传统方法与深度学习的结合
- Key.Net: 将手工设计的特征点检测方法中常用的滤波器组与CNN通过数据驱动学习得到的卷积特征图进行组合,提出在规整化网格中通过特征点响应分数加权平均进行特征点检测。
2. 特征描述方法
特征描述的目的是为每个检测到的关键点生成一个描述子,使得同一场景在不同图像中的对应点具有相似的描述子。
2.1 基于深度学习的描述子
-
L2Net: 采用7层全卷积网络结构,输入为32×32的局部图像,通过多个卷积层提取特征,并使用LocalResponseNormalization对输出层进行模长归一化。
-
HardNet: 在L2Net的基础上,采用基于最难负样本的三元组合页损失进行网络参数的学习,优化匹配样本和不匹配样本之间的相对距离。
-
HyNet: 分析了特征描述子欧式距离和余弦相似性在HardNet的三元组合页损失中对网络梯度计算的影响,提出对两者进行有机结合。
2.2 上下文信息增强的描述子
-
SuperGlue: 在SuperPoint特征点基础上构建关系图,利用图注意力机制对图像内部特征点的自注意力和图像间的特征点交叉注意力进行建模,学习得到具有全局感受野和跨图像上下文敏感的特征描述子。
-
ContextDesc: 利用ResNet-50以及特征点的位置分布将半全局图像信息和全局几何信息融入L2Net所刻画的局部信息。
3. 特征匹配方法
特征匹配是将两幅图像中的关键点根据其描述子进行匹配,建立点与点之间的对应关系。
3.1 基于学习的匹配方法
-
LoFTR: 一个端到端的深度学习框架,用于局部特征匹配。LoFTR利用Transformer结构对特征点进行匹配,显著提高了匹配的准确性。
-
SuperGlue: 使用图注意力机制进行特征点匹配,通过构建关系图和多头注意力机制,学习特征点之间的相互关系,实现精确匹配。
-
SGMNet: 通过种子匹配和加权注意力聚合进行特征匹配,旨在减少计算复杂度同时保持匹配准确性。
3.2 传统匹配方法
-
SIFT + LightGlue: 结合SIFT特征点检测和LightGlue匹配策略,利用SIFT算法检测关键点并生成描述子,然后使用LightGlue进行快速而准确的匹配。
-
ORB + SGMNet: 利用ORB算法检测关键点并生成二进制描述子,然后通过SGMNet进行特征匹配,适用于实时应用。
DaD简介
[https://github.com/Parskatt/dad]
[https://github.com/Parskatt/RoMa]
关键点是使运动恢复结构(SfM)系统能够扩展到数千张图像的核心要素。然而,设计关键点检测目标函数并非易事,因为SfM本身不可微分。传统方法通常通过优化涉及描述符的辅助目标来实现,但这会引入对描述符的依赖,存在明显弊端。本文提出一种基于强化学习的全自监督、无描述符的关键点检测目标函数。为防止训练退化,我们采用平衡式Top-K采样策略。虽然该方法已能生成具有竞争力的模型,但我们发现会涌现出两种仅能分别检测明暗关键点的异质检测器。为此,我们训练了第三种检测器DaD,通过优化明暗检测器逐点最大值的Kullback-Leibler散度来解决这一问题。本方法在多项基准测试中显著超越了当前最优技术。代码和模型权重已开源于此[https://github.com/parskatt/dad]。
Keypoints are what enable Structure-from-Motion (SfM) systems to scale to thousands of images. However, designing a keypoint detection objective is a non-trivial task, as SfM is non-differentiable. Typically, an auxiliary objective involving a descriptor is optimized. This however induces a dependency on the descriptor, which is undesirable. In this paper we propose a fully self-supervised and descriptor-free objective for keypoint detection, through reinforcement learning. To ensure training does not degenerate, we leverage a balanced top-K sampling strategy. While this already produces competitive models, we find that two qualitatively different types of detectors emerge, which are only able to detect light and dark keypoints respectively. To remedy this, we train a third detector, DaD, that optimizes the Kullback-Leibler divergence of the pointwise maximum of both light and dark detectors. Our approach significantly improve upon SotA across a range of benchmarks. Code and model weights are publicly available at this [https://github.com/parskatt/dad].
| DaD概览图 |
|---|
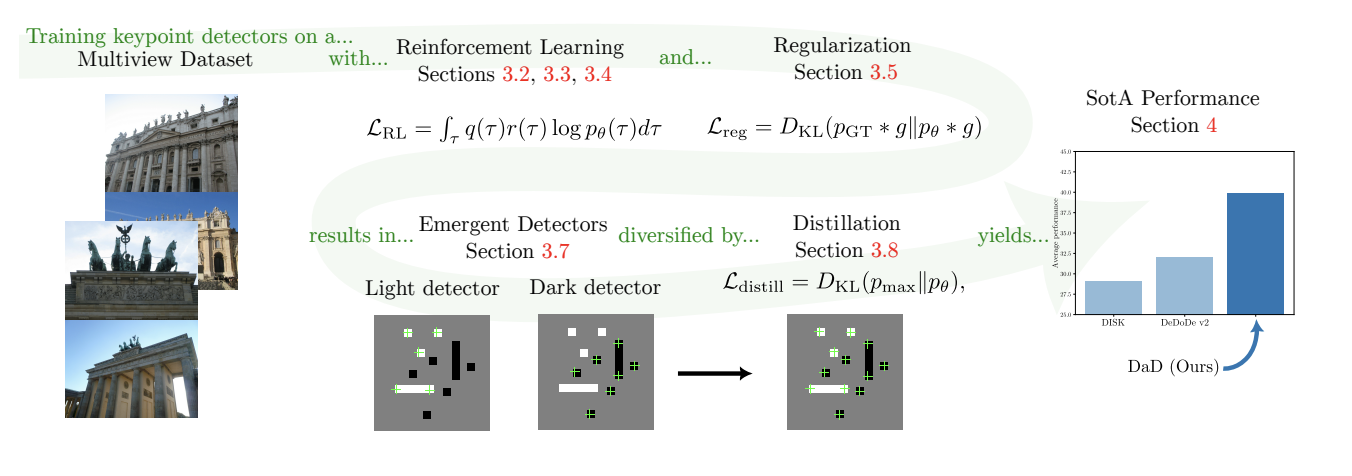 |
DaD(Distilled Reinforcement Learning for Diverse Keypoint Detection)是一种基于强化学习的自监督关键点检测方法,其核心数学原理可以分为以下几个部分:
1. 关键点检测的概率建模
关键点检测器 \(p_{\theta}\) 将图像 \(I\) 映射为一个概率分布,定义为:
其中 \(S \in \mathbb{R}^{H \times W}\) 是模型输出的分数图(scoremap),表示每个像素点作为关键点的概率。
2. 强化学习目标
通过最大化期望奖励来优化关键点检测器:
其梯度为:
具体到两视图匹配任务中,损失函数为:
其中 \(r\left(x_{m}^{A}, x_{m}^{B}\right)\) 是基于关键点重复性的奖励函数。
3. 奖励函数设计
奖励函数衡量关键点的重复性:
其中 \(\mathcal{P}^{A \rightarrow B}\) 是基于深度的点投影函数,\(f\) 是一个单调递减函数,定义为:
\(\tau\) 是距离阈值(如图像高度的0.25%)。
4. 关键点采样策略
为了避免关键点聚集,采用平衡的Top-K采样策略:
- 计算平滑后的概率分布:\[p_{\theta}^g(x) = (p_{\theta} * g)(x), \]其中 \(g\) 是高斯滤波器。
- 构建平衡分布:\[p_{\theta}^{KDE}(x) \propto p_{\theta}(x) \cdot p_{\theta}^g(x)^{-1/2}. \]
- 应用非极大值抑制(NMS)并采样Top-K关键点。
5. 正则化
通过KL散度约束分数图与深度估计的一致性:
其中 \(p_{depth}\) 是深度估计的指示分布。
6. 多样性蒸馏
为了解决模型倾向于仅检测“亮”或“暗”关键点的问题,提出基于点对最大值的知识蒸馏:
其中 \(p_{r}(x) \propto M_{\infty}\left(p_{\theta_{\text{dark}}}(x), p_{\theta_{\text{light}}}(x)\right)\),\(M_{\infty}\) 是广义均值函数(取最大值):
7. 总损失函数
最终训练目标为:
总结
DaD通过强化学习优化关键点检测器的重复性,结合平衡采样和多样性蒸馏,解决了自监督训练中关键点多样性不足的问题。其数学框架简洁高效,在多个基准测试中达到了最先进的性能。
DeDoDe_v2简介
[https://github.com/Parskatt/DeDoDe]
[https://github.com/Parskatt/DeDoDe/releases/tag/v2]
- dedode_detector_L_v2.pth
- dedode_detector_S_v2.pth
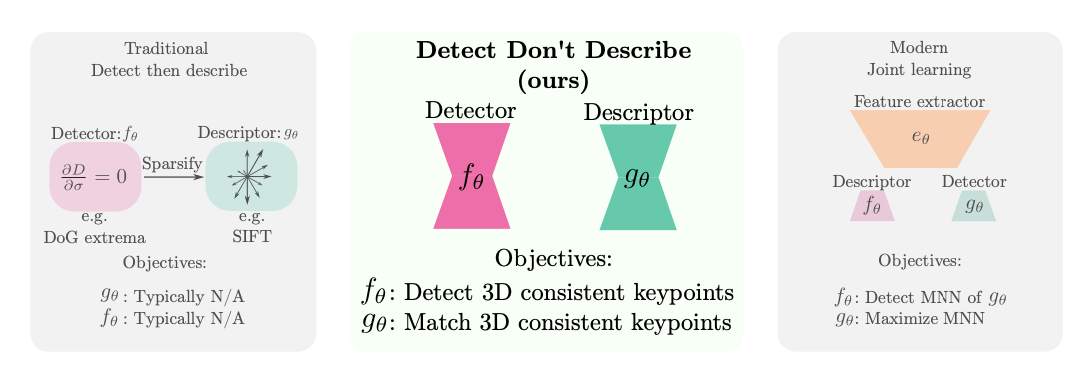
关键点检测是三维重建中的关键步骤,其目标是在场景的每个视角中检测出最多K个关键点。至关重要的是,这些检测到的关键点需要在不同视角间保持一致性,即对应于场景中的同一个三维点。关键点检测的主要挑战之一在于学习目标的构建。以往基于学习的方法通常联合学习描述符与关键点,并将关键点检测视为基于互最近邻的二分类任务。然而,这种基于描述符最近邻的关键点检测只是一种替代性任务,并不能保证产生三维一致的关键点。此外,这种做法将关键点与特定描述符绑定,增加了下游使用的复杂性。
本研究提出直接从三维一致性中学习关键点。为此,我们通过训练检测器来识别大规模运动恢复结构(SfM)生成的轨迹点。由于这些轨迹点往往过于稀疏,我们推导出一种半监督的双视角检测目标,以将关键点扩展至所需数量。对于描述符的训练,我们通过独立网络在关键点上最大化互最近邻目标。实验结果表明,我们的方法DeDoDe在多个几何基准测试中实现了显著提升。代码已发布于[https://github.com/Parskatt/DeDoDe]。
Keypoint detection is a pivotal step in 3D reconstruction, whereby sets of (up to) K points are detected in each view of a scene. Crucially, the detected points need to be consistent between views, i.e., correspond to the same 3D point in the scene. One of the main challenges with keypoint detection is the formulation of the learning objective. Previous learning-based methods typically jointly learn descriptors with keypoints, and treat the keypoint detection as a binary classification task on mutual nearest neighbours. However, basing keypoint detection on descriptor nearest neighbours is a proxy task, which is not guaranteed to produce 3D-consistent keypoints. Furthermore, this ties the keypoints to a specific descriptor, complicating downstream usage. In this work, we instead learn keypoints directly from 3D consistency. To this end, we train the detector to detect tracks from large-scale SfM. As these points are often overly sparse, we derive a semi-supervised two-view detection objective to expand this set to a desired number of detections. To train a descriptor, we maximize the mutual nearest neighbour objective over the keypoints with a separate network. Results show that our approach, DeDoDe, achieves significant gains on multiple geometry benchmarks. Code is provided at this [https://github.com/Parskatt/DeDoDe].
| DeDoDe发展脉络 | 训练DeDoDe关键点检测 |
|---|---|
 |
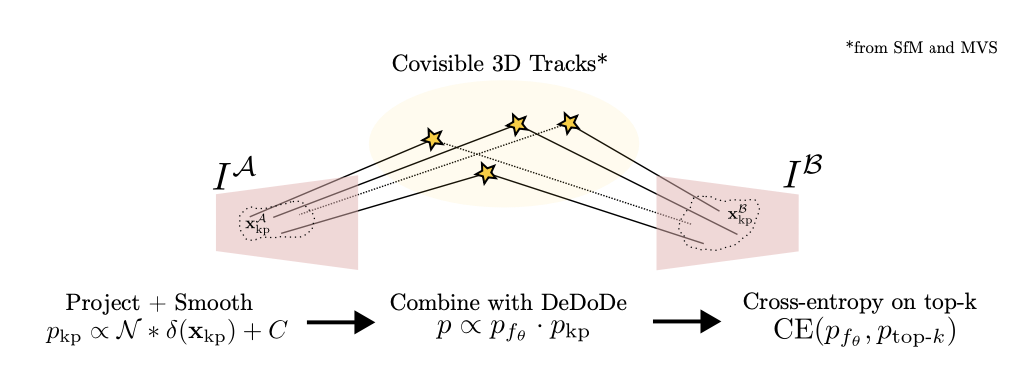 |
核心思想
DeDoDe提出了一种解耦的关键点检测与描述方法,通过直接优化3D一致性来学习关键点检测器,并独立优化描述符的匹配目标。其核心数学原理可分为两部分:
1. 关键点检测目标(Detect, Don't Describe)
给定图像\(I^j\),检测器\(f_\theta(x|I^j)\)输出关键点\(x\)的log密度。目标是最大化3D一致关键点的似然:
其中\(Z_\theta(I^j)\)是归一化因子:
定义概率分布:
2. 关键点先验分布
从SfM重建的3D轨迹生成平滑的关键点先验分布:
- 对检测到的关键点\(x_{kp}\)放置Dirac delta函数\(\delta(x_{kp})\)
- 与高斯核卷积并添加常数项:
- 通过深度图warping得到跨视图一致分布:
3. 后验检测分布
结合网络预测和先验分布,解决基础检测器召回率不足的问题:
4. 检测器训练目标
使用top-k阈值稳定训练:
添加覆盖正则项:
总损失:
描述符学习(Describe, Don't Detect)
1. 匹配概率定义
给定关键点\(x^A\)和\(x^B\),描述符网络\(g_\theta\)输出匹配概率:
2. 匹配似然目标
最大化相互最近邻的log似然:
创新点
- 解耦训练:关键点检测直接优化3D一致性,不依赖特定描述符
- 半监督目标:通过top-k策略和覆盖正则解决稀疏检测问题
- 模块化设计:检测器和描述符可独立改进和替换
数学优势
- 避免了传统方法中通过描述符最近邻作为代理目标的问题
- 直接优化3D一致性,理论保证更高
- 概率框架提供了稳定的训练目标
体验&本地离线部署
1. 下载及运行docker镜像
两种方式默认都是cpu推理.
方式1: 百度云下载(推荐)
- 模型已内置到镜像中
通过网盘分享的文件:image_keypoint_feature_matching
链接: [https://pan.baidu.com/s/1dz8ik6UzUYgL5_9mbHrjlg?pwd=5kmy] 提取码: 5kmy
- 导入:
docker load -i biu_image-matching-webui-v3-amd64.tar
docker run -it -p 7862:7860 biu_image-matching-webui:v3-amd64 python app_offline.py
方式2:huggingface(模型运行时才下载)
[https://github.com/Vincentqyw/image-matching-webui]
docker pull registry.hf.space/realcat-image-matching-webui:latest
docker run -it -p 7860:7860 --platform=linux/amd64 \
registry.hf.space/realcat-image-matching-webui:latest python app.py
# (可选)下载模型到本地
git lfs install
git clone https://huggingface.co/Realcat/imcui_checkpoints
2. 效果
| 运行界面 |
|---|
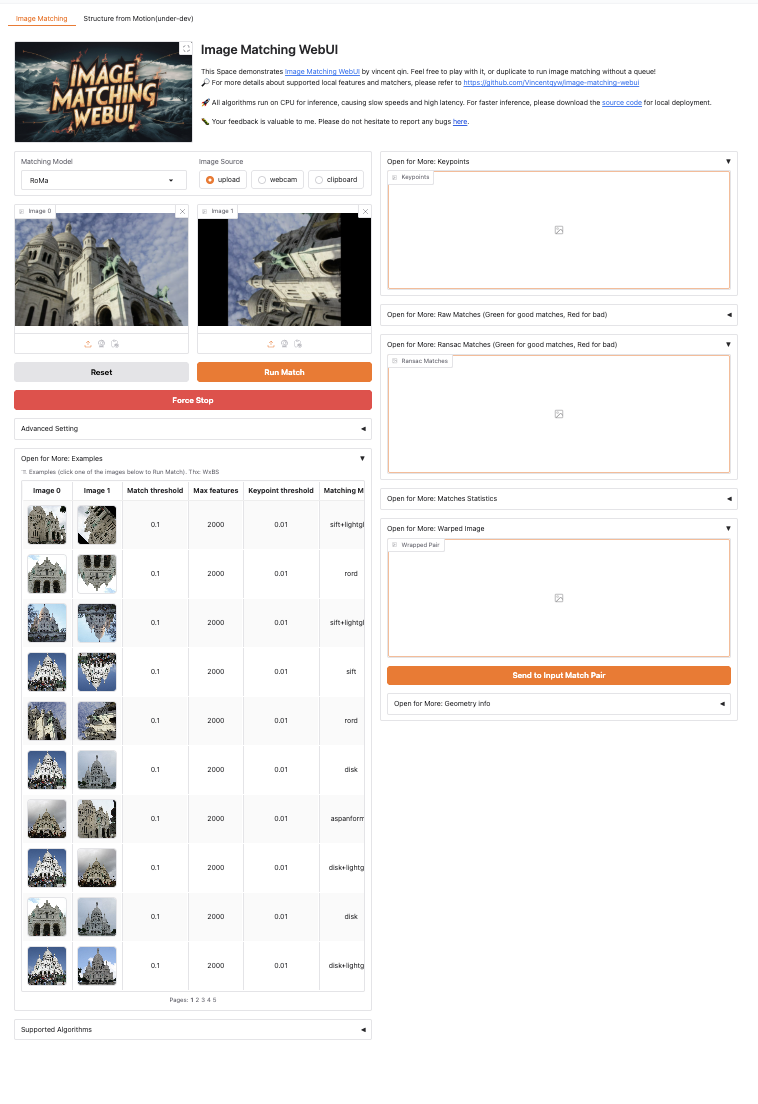 |
| 使用disk+lightglue方式提取特征点 | 使用disk+lightglue方式匹配特征点 |
|---|---|
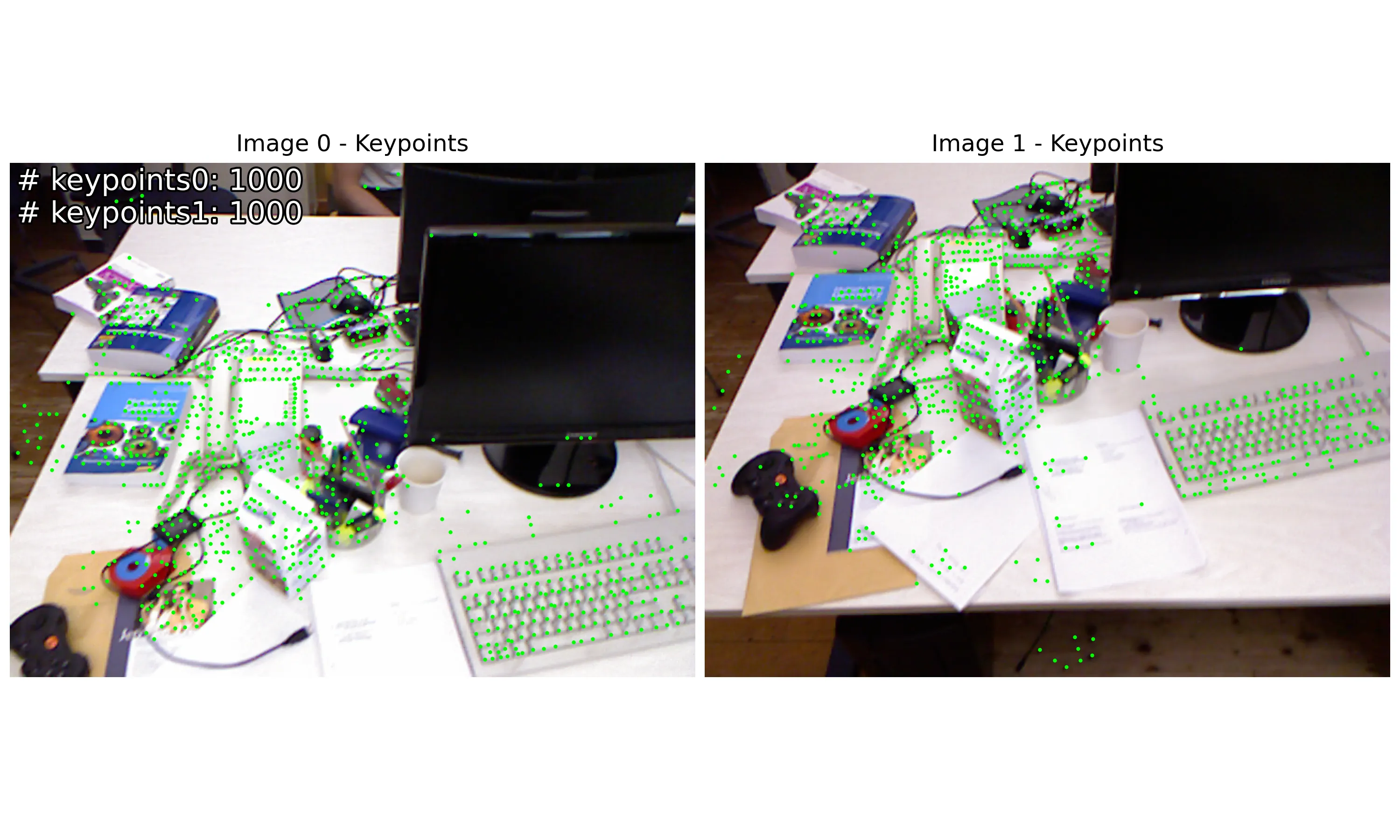 |
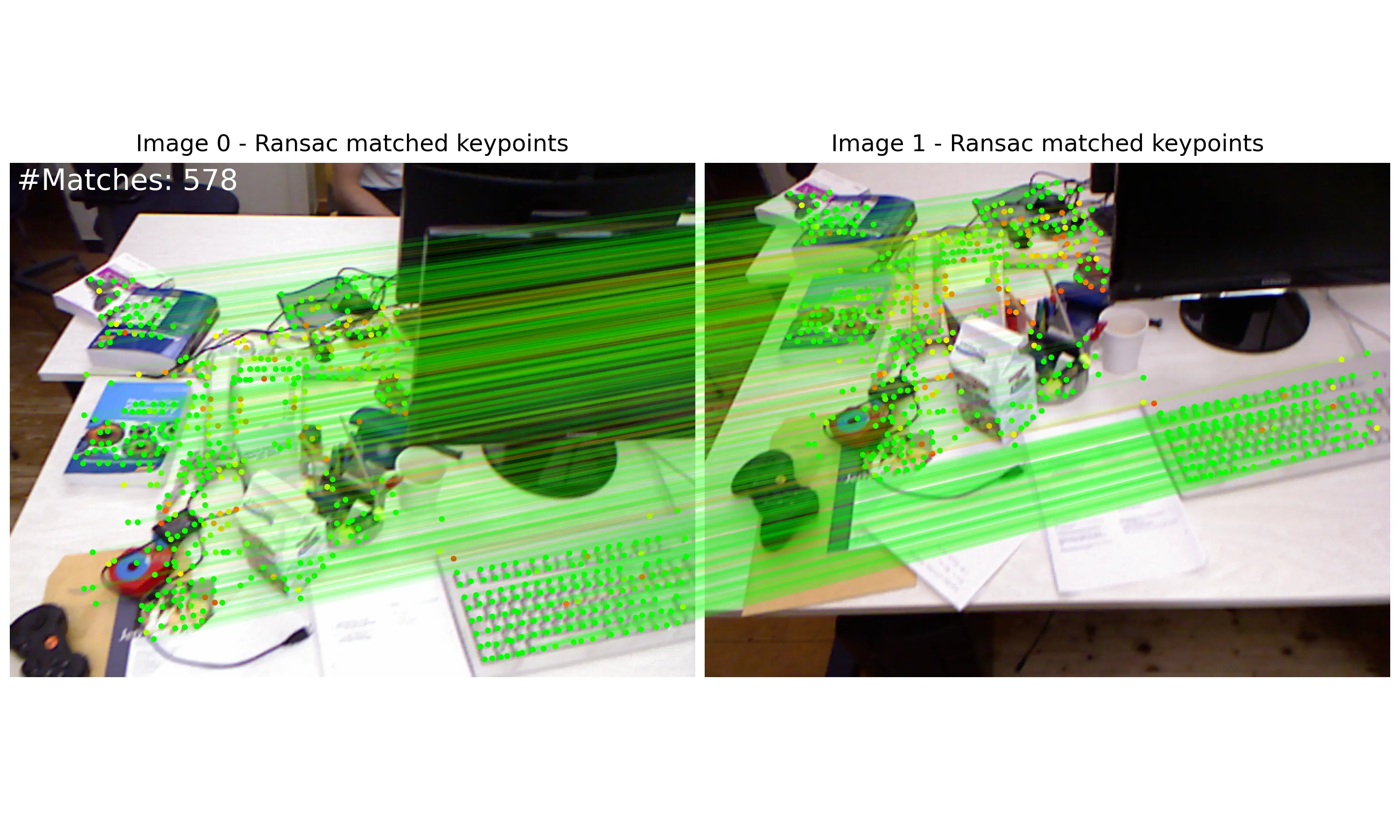 |
- Ransac匹配(绿色代表好的匹配,红色代表坏的匹配)
- 提示: Ransac Matches (Green for good matches, Red for bad)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号