R语言实现多组样本两两t检验的完整教程
t检验的核心思想是通过样本均值与方差的比较,评估两个总体均值是否存在显著差异。当有三个或更多组数据时,单次t检验已不再适用,因此通常的做法是先进行方差齐性检验与单因素方差分析(ANOVA),如果总体差异显著,再进行组间的两两t检验,用于具体比较每对样本组之间的差异。
多组样本执行两两t.test时,当有分组少于2个数据,t.test会报错,当要检测的数据为常量时,t.test会报错,
下面代码将解决以上问题
library(readr) library(dplyr) library(purrr) library(rstatix) # 构建函数进行两两t.test pf_ttest <- function(my_comparison, data) { group1 <- my_comparison[1] group2 <- my_comparison[2] data1 <- filter(data, group == group1) %>% pull(value) data2 <- filter(data, group == group2) %>% pull(value) cat(sprintf("比较 %s (n=%d) vs %s (n=%d)\n", group1, length(data1), group2, length(data2))) tryCatch( { test_result <- t.test(data1, data2) tibble( group1 = group1, group2 = group2, p = test_result$p.value, statistic = test_result$statistic, df = test_result$parameter ) }, error = function(e) { cat(sprintf("错误: %s\n", e$message)) } ) } # 创建比较组 create_comparisons <- function(groups) { comp <- combn(groups, 2) lapply(1:ncol(comp), function(i) as.character(comp[, i])) } # 准备数据:2列,第1列为分组,第2列为数值 data <- readxl::read_xlsx("OP.xlsx") col_names <- names(data) xlab=col_names[1] ylab=col_names[2] data=dplyr::rename(data, group = 1, value = 2) # 创建比较组 my_comparisons <- create_comparisons(unique(data$group)) stat_test <- map_dfr(my_comparisons, pf_ttest, data) %>% mutate(p.adj = p.adjust(p)) %>% add_significance( p.col = "p.adj", cutpoints = c(0, 0.001, 0.01, 0.05, 1), symbols = c("***", "**", "*", "ns") )
比较 Homo sapiens (n=22) vs M. assmensiss (n=4)
比较 Homo sapiens (n=22) vs M.mulatta (n=1)
错误: 'y'观察值数量不足
比较 Homo sapiens (n=22) vs M. arctoides (n=2)
比较 Homo sapiens (n=22) vs M. mulatta (n=15)
比较 Homo sapiens (n=22) vs M. fascicularis (n=1)
错误: 'y'观察值数量不足
比较 0mascus leucogenys (n=25) vs Pongo pygmaeus (n=7)
head(stat_test)
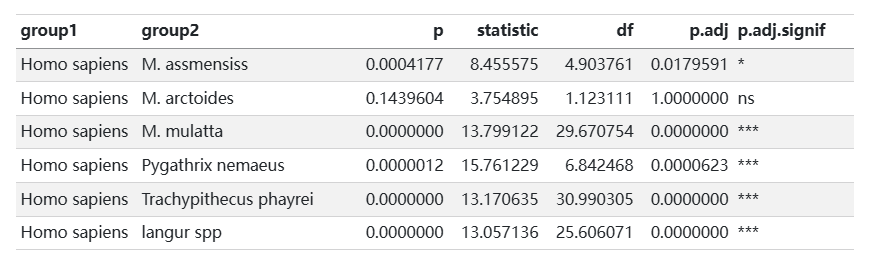
write_tsv(stat_test, "stat_test.tsv")
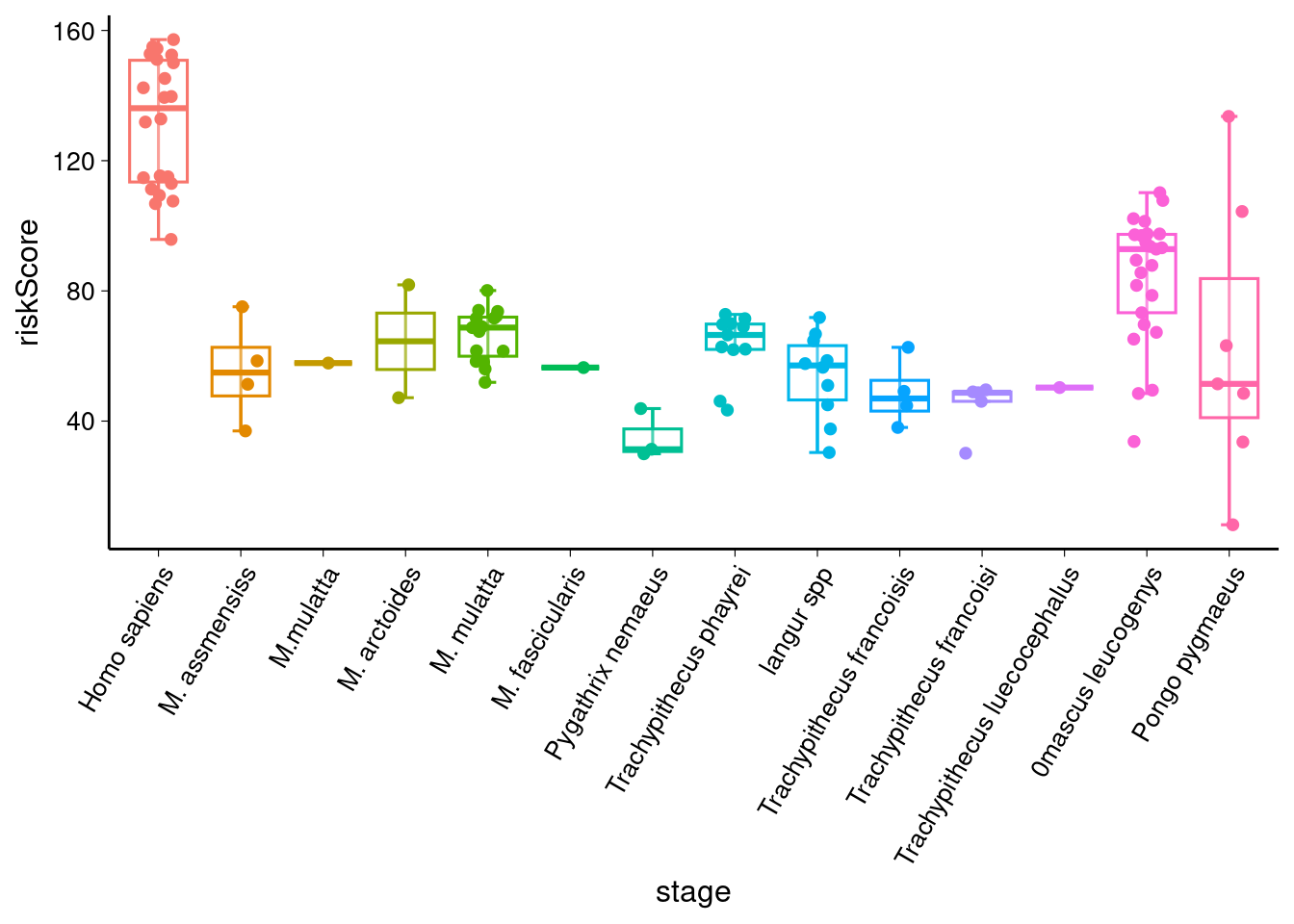
# 绘制箱形图 sig_comparisons <- stat_test %>% filter(p < 0.05) %>% select(group1, group2) %>% as.data.frame() %>% # 确保是 data.frame split(1:nrow(.)) %>% # 按行分割 lapply(function(x) as.character(x)) # 创建基础图形 library(ggpubr) p1 <- ggboxplot(data, x = "group", y = "value", color = "group", alpha = 0.3, xlab = xlab, ylab = ylab, bxp.errorbar = TRUE, bxp.errorbar.width = 0.2, add = "jitter", legend = "none" ) + theme( plot.title = element_text(size = 15, hjust = 0.5), axis.title = element_text(size = 12), axis.text.x = element_text(size = 10, angle = 60, hjust = 1), axis.text.y = element_text(size = 10), axis.ticks = element_line(linewidth = 0.2), ) p1
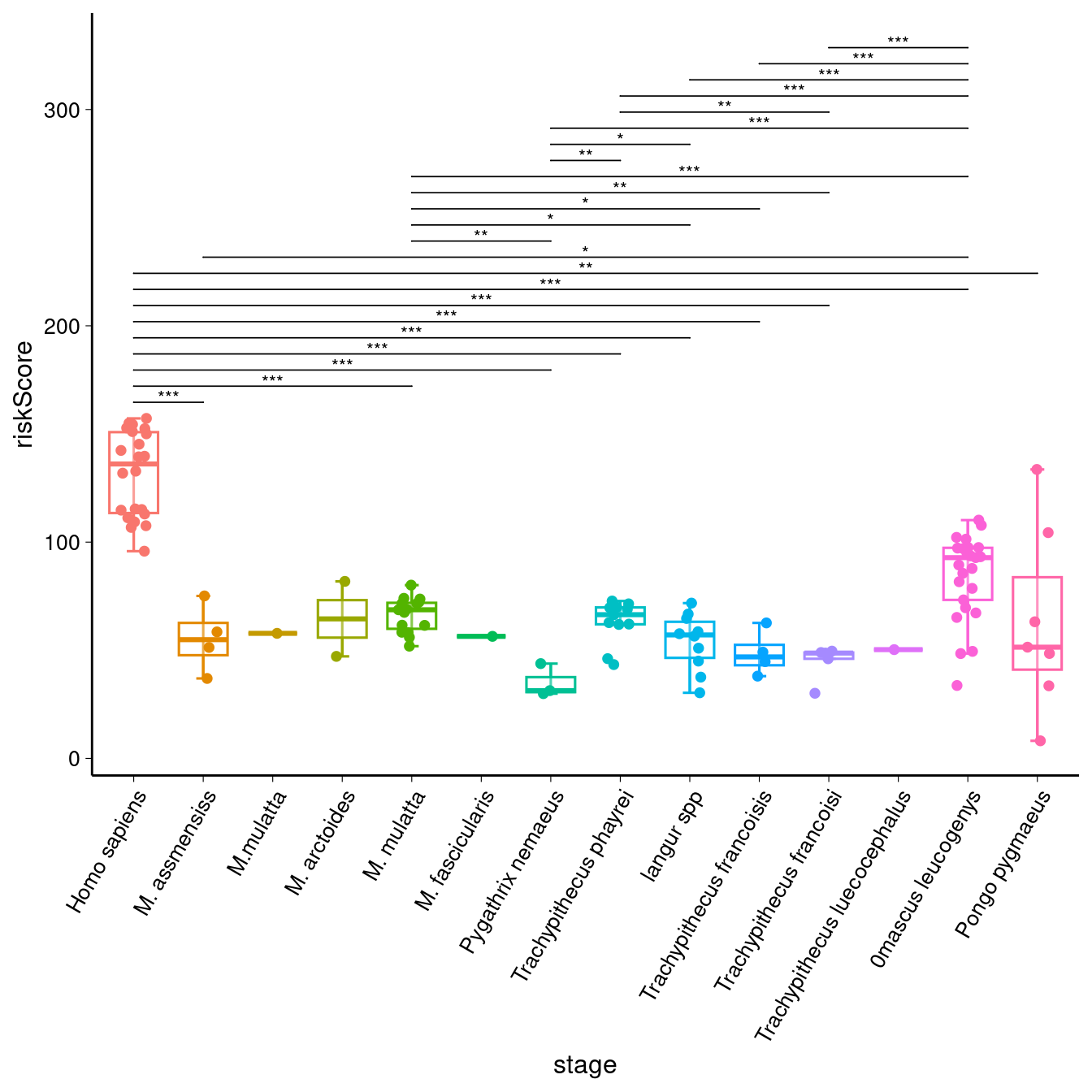
p1 + stat_compare_means( comparisons = sig_comparisons, method = "t.test", label = "p.signif", # 显示显著性符号(*, **, ***) symnum.args = list( cutpoints = c(0, 0.001, 0.01, 0.05, Inf), symbols = c("***", "**", "*", "ns") ), hide.ns = TRUE, # 隐藏不显著的标签 vjust = 0.75, tip.length = 0, step.increase = 0.05, size = 3 )



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号