基础学习
3D高斯渲染 (1-2)ros下 接受c++节点发送的位姿,python节点渲染图像返回
https://www.cnblogs.com/gooutlook/p/18385485
ros 自定义消息(图像+标志位+位姿)python和c++发布和接受
https://www.cnblogs.com/gooutlook/p/18412553
注意
1 高斯渲染原版本代码送入的是世界到相机的位姿,自己改的是相机到世界(slam发送来)
2 高斯加载colmap数据时候R矩阵是转置后的R也就是相机到世界。

本工程代码
为什么要做这个,因为之前的版本 图像和位姿是分开两个话题发送的,然后接收端依靠时间戳同步,但是可能会导致数据对齐且写代码复杂问题,这里直接自定义一个复合数据,图像和位姿以及id全部封装一起一起发。
编译
执行脚本
#!/bin/bash #外部给与执行权限 #sudo chmod +x run_ros_nodes.sh # conda activate gaussian_splatting WORKSPACE_DIR="/home/r9000k/v2_project/gaosi_slam/ros/ros_cgg" # 修改1-1 自己创建的ros节点工程catkin_make根目录 python_DIR="/home/r9000k/v2_project/gaosi_slam/ros/ros_cgg/src/gaosi_img_pose_flag/src" # 修改1-2 自己创建的python脚本位置 data_dir="/home/r9000k/v2_project/data/NWPU" config_DIR="/home/dongdong/2project/0data/NWPU/FHY_config/GNSS_config.yaml" # 修改1-3 数据集 conda_envs="/home/r9000k/anaconda3" # 修改2-1 自己的conda 安装路径 # ROS_cv_briage_dir = "/home/r9000k/v1_software/opencv/catkin_ws_cv_bridge/devel/setup.bash" # 修改2-2 自己编译的cv_briage包节点,貌似不用也行 制定了依赖opencv3.4.9 而非自带4.2 # echo $ROS_cv_briage_dir conda_envs_int=$conda_envs"/etc/profile.d/conda.sh" # 不用改 conda自带初始化文件 echo $conda_envs_int conda_envs_bin=$conda_envs"/envs/gaussian_splatting/bin" # 不用改 conda自带python安装位置 脚本中需要指定是conda特定的环境python而不是系统默认的 echo $conda_envs_bin ROS_SETUP="/opt/ros/noetic/setup.bash" #不用改 安装时候添加到系统路径了 不需要每次都source 这里留着 #指定目录 # 启动 ROS Master 不用改 echo "Starting ROS 总结点..." gnome-terminal -- bash -c "\ cd $WORKSPACE_DIR; source devel/setup.bash; \ roscore; \ exec bash" # 等待 ROS Master 启动 sleep 3 echo "Running C++ 订阅节点..." gnome-terminal -- bash -c "\ cd $WORKSPACE_DIR; source devel/setup.bash; \ rosrun gaosi_img_pose_flag image_pose_flag_subscriber; \ exec bash" # source /home/r9000k/v2_project/gaosi_slam/ros/ros_cgg/devel/setup.bash # 运行 python 渲染图节点 # source conda_envs_int 和 source ROS_cv_briage_dir 非必要,但是考虑到脚本经常因为系统环境默认变量找不到导致的路径问题,这里还是强制给了也便于学习了解执行流程。 echo "Running python 订阅节点..." echo "1 激活conda本身(脚本执行需要) 2 激活conda环境 3运行python 节点 并跟上输入参数[训练模型保存根目录,指定要使用的模型训练次数,要测试的模型精度模式]" gnome-terminal -- bash -c "\ source $conda_envs_int; \ cd $WORKSPACE_DIR; source devel/setup.bash; \ conda activate gaussian_splatting ; \ cd $python_DIR; \ python3 v1_image_pose_subscriber.py \ -m $data_dir/gs_out/train1_out_sh0_num30000 \ --iteration 30000 \ --models baseline ;\ exec bash"
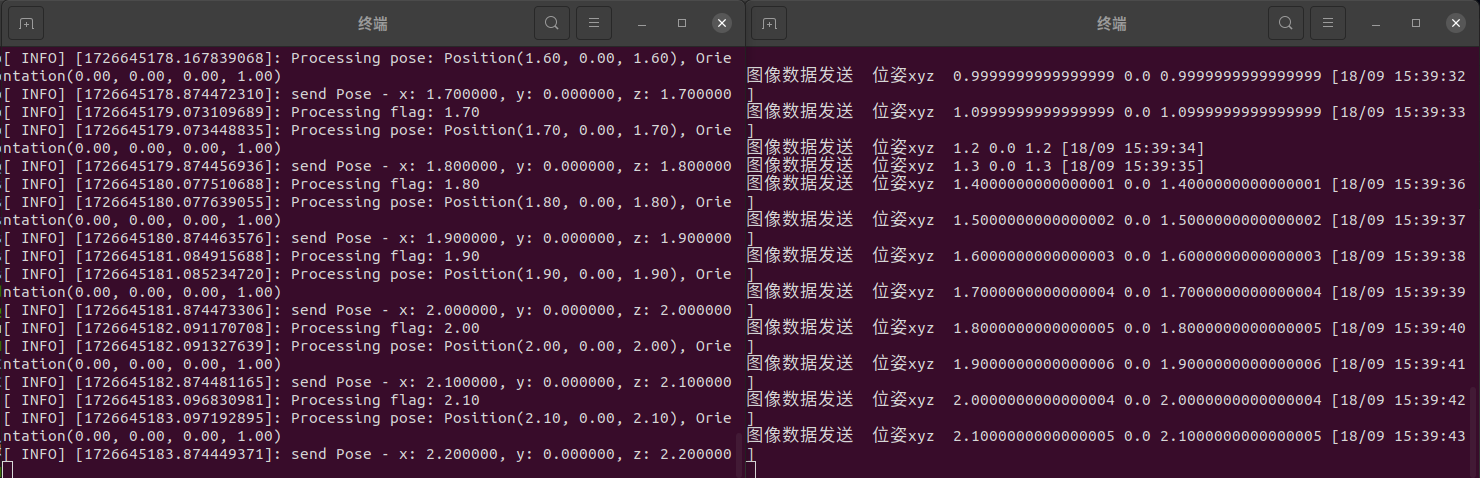
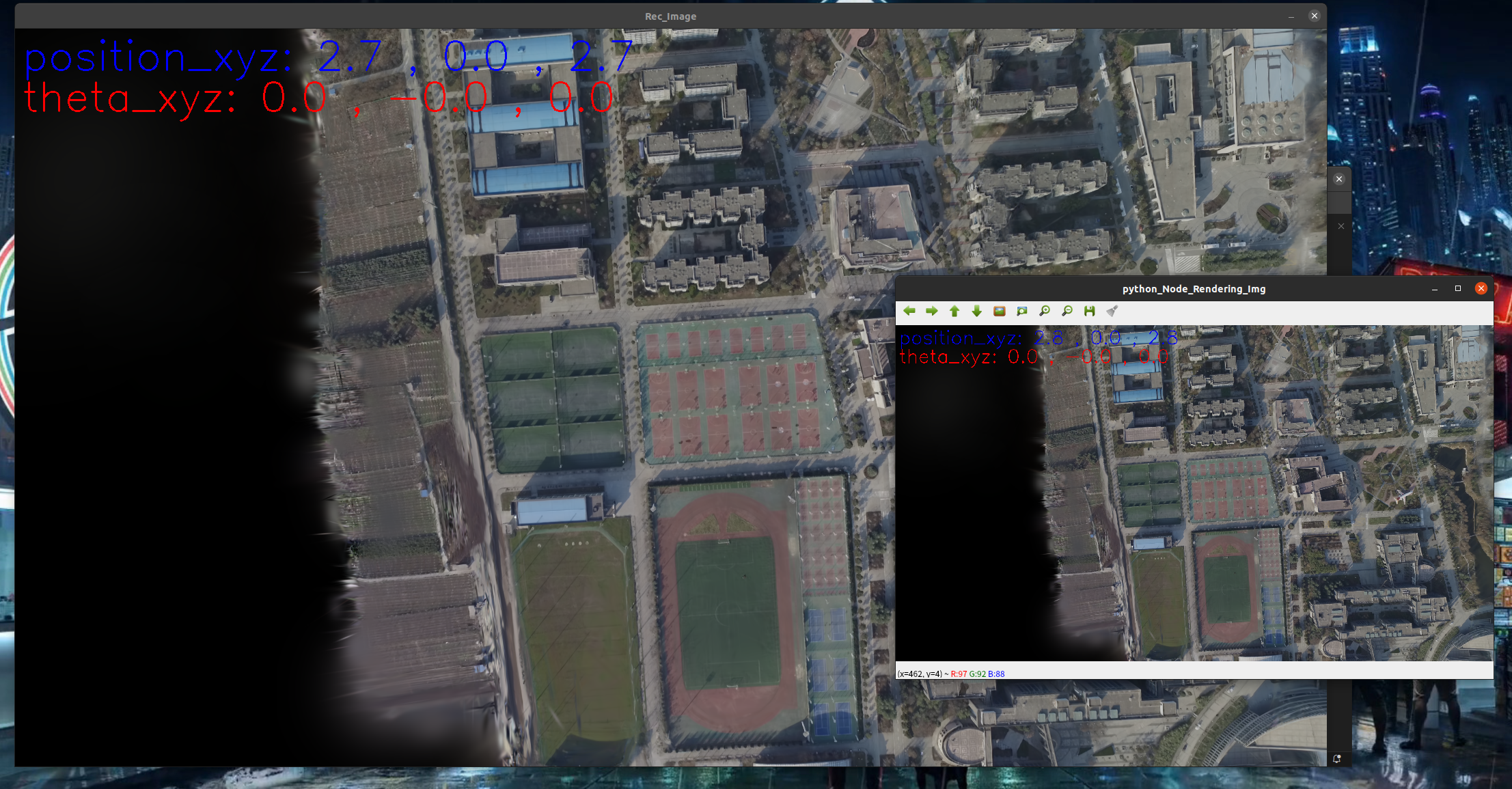
执行
创建消息

PoseImgFlagMsg.msg
# PoseImgFlagMsg.msg std_msgs/Time timestamp sensor_msgs/Image image std_msgs/Float64 flag geometry_msgs/Pose pose
std_msgs/Time timestamp 时间戳 sensor_msgs/Image image 图像 std_msgs/Float64 flag 请求的id, 某次请求渲染,可能要多张渲染图,同属于一个批次。 geometry_msgs/Pose pose 图像位姿
编译
CMakeLists.txt
1 工程名字 gaosi_img_pose_flag
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.0.2)
project(gaosi_img_pose_flag)
find_package(catkin REQUIRED COMPONENTS
roscpp
geometry_msgs
sensor_msgs
cv_bridge
message_filters # 消息同步
image_transport
std_msgs # 自定义消息
message_generation # 自定义消息
)
# 自定义消息
add_message_files(
FILES
PoseImgFlagMsg.msg
)
# 自定义消息
generate_messages(
DEPENDENCIES
std_msgs
sensor_msgs
geometry_msgs
)
find_package(OpenCV REQUIRED)
find_package(Boost REQUIRED COMPONENTS filesystem)
find_package(Eigen3 REQUIRED)
catkin_package(
CATKIN_DEPENDS roscpp geometry_msgs sensor_msgs cv_bridge std_msgs message_runtime
DEPENDS Boost
)
include_directories(
${catkin_INCLUDE_DIRS}
${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS}
${Boost_INCLUDE_DIRS}
"/usr/local/include/eigen3"
)
# # 编译发布节点
# add_executable(image_pose_flag_publisher src/image_pose_flag_publisher.cpp)
# # 自定义消息引用
# add_dependencies(image_pose_flag_publisher ${${PROJECT_NAME}_EXPORTED_TARGETS} ${catkin_EXPORTED_TARGETS})
# target_link_libraries(image_pose_flag_publisher
# ${catkin_LIBRARIES}
# ${OpenCV_LIBRARIES}
# ${Boost_LIBRARIES}
# )
add_executable(image_pose_flag_subscriber src/image_pose_flag_subscriber.cpp)
add_dependencies(image_pose_flag_subscriber ${${PROJECT_NAME}_EXPORTED_TARGETS} ${catkin_EXPORTED_TARGETS})
target_link_libraries(image_pose_flag_subscriber ${catkin_LIBRARIES} ${OpenCV_LIBRARIES})
ros包名字 未来调用需要用到
<name>gaosi_img_pose_flag</name>
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<package format="2">
<name>gaosi_img_pose_flag</name>
<version>0.0.1</version>
<description>
A package to publish and subscribe to images and GPS data using ROS.
</description>
<!-- Maintainer of the package -->
<maintainer email="your_email@example.com">Your Name</maintainer>
<!-- License of the package -->
<license>MIT</license>
<!-- Build tool required to build this package -->
<buildtool_depend>catkin</buildtool_depend>
<!-- Dependencies of the package during build and runtime -->
<build_depend>roscpp</build_depend>
<build_depend>sensor_msgs</build_depend>
<build_depend>cv_bridge</build_depend>
<build_depend>eigen</build_depend>
<build_depend>geometry_msgs</build_depend>
<build_depend>message_filters</build_depend>
<build_depend>image_transport</build_depend>
<!--自定义消息 -->
<build_depend>message_generation</build_depend>
<build_depend>message_runtime</build_depend>
<build_depend>std_msgs</build_depend>
<exec_depend>roscpp</exec_depend>
<exec_depend>sensor_msgs</exec_depend>
<exec_depend>cv_bridge</exec_depend>
<exec_depend>eigen</exec_depend>
<exec_depend>geometry_msgs</exec_depend>
<exec_depend>message_filters</exec_depend>
<exec_depend>image_transport</exec_depend>
<!--自定义消息 -->
<exec_depend>message_generation</exec_depend>
<exec_depend>message_runtime</exec_depend>
<exec_depend>std_msgs</exec_depend>
<!-- Declare additional dependencies required for building this package -->
<build_export_depend>roscpp</build_export_depend>
<build_export_depend>sensor_msgs</build_export_depend>
<build_export_depend>cv_bridge</build_export_depend>
<build_export_depend>eigen</build_export_depend>
<build_export_depend>geometry_msgs</build_export_depend>
<build_export_depend>message_filters</build_export_depend>
<build_export_depend>image_transport</build_export_depend>
<!--自定义消息 -->
<build_export_depend>message_generation</build_export_depend>
<build_export_depend>message_runtime</build_export_depend>
<build_export_depend>std_msgs</build_export_depend>
<!-- Export information, can be used by other packages -->
<export>
<!-- Export any specific information here -->
</export>
</package>

c++ 发送位姿,获取渲染图
image_pose_flag_subscriber.cpp
简单版本 发送端没有手动漫游
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include <ros/time.h>
#include <std_msgs/Time.h>
#include <queue>
#include <mutex>
#include <thread>
#include <iostream>
#include <sensor_msgs/Image.h>
#include <std_msgs/Float64.h>
#include <geometry_msgs/Pose.h>
#include <cv_bridge/cv_bridge.h>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <gaosi_img_pose_flag/PoseImgFlagMsg.h> // 更换为你包的名字
#include <Eigen/Dense>
#include <Eigen/Geometry> // For Quaterniond
// Global variables
std::queue<gaosi_img_pose_flag::PoseImgFlagMsg::ConstPtr> data_queue;
std::mutex queue_mutex;
// 用于过于早位姿的节点
Eigen::Quaterniond Q_c2w ;
Eigen::Vector3d t_c2w;
void publishPose(ros::Publisher& pose_pub, std_msgs::Float64 flag_,Eigen::Quaterniond &quat, Eigen::Vector3d &t)
{
cv::Mat image_;
//std_msgs::Float64 flag_;
geometry_msgs::Pose pose_msg;
pose_msg.position.x = t[0]; // 示例位置
pose_msg.position.y = t[1];
pose_msg.position.z = t[2];
pose_msg.orientation.x = quat.x(); // 示例姿态
pose_msg.orientation.y = quat.y();
pose_msg.orientation.z = quat.z();
pose_msg.orientation.w = quat.w();
ROS_INFO("send Pose - x: %f, y: %f, z: %f",
pose_msg.position.x,
pose_msg.position.y,
pose_msg.position.z);
gaosi_img_pose_flag::PoseImgFlagMsg pose_img_flag_msg;
//pose_msg.image = *cv_bridge::CvImage(std_msgs::Header(), "bgr8", image_).toImageMsg();
pose_img_flag_msg.flag = flag_;
pose_img_flag_msg.pose = pose_msg;
// 设置当前时间戳
ros::Time current_time = ros::Time::now();
pose_img_flag_msg.timestamp = std_msgs::Time(); // 初始化时间戳
pose_img_flag_msg.timestamp.data = current_time; // 设置当前时间
// 发布PoseStamped消息
pose_pub.publish(pose_img_flag_msg);
}
// Callback function to handle incoming messages
void render_callback(const gaosi_img_pose_flag::PoseImgFlagMsg::ConstPtr& msg)
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(queue_mutex);
data_queue.push(msg);
}
// Thread function to process the queue
void processQueue()
{
while (ros::ok())
{
std::queue<gaosi_img_pose_flag::PoseImgFlagMsg::ConstPtr> local_queue;
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(queue_mutex);
std::swap(local_queue, data_queue); // Safely access the queue
}
while (!local_queue.empty())
{
auto msg = local_queue.front();
local_queue.pop();
// 将ROS图像消息转换为OpenCV图像
cv_bridge::CvImagePtr cv_ptr = cv_bridge::toCvCopy(msg->image, sensor_msgs::image_encodings::BGR8);
cv::imshow("Rec_Image", cv_ptr->image);
cv::waitKey(1);
// Process the message
ROS_INFO("Processing flag: %.2f", msg->flag.data);
ROS_INFO("Processing pose: Position(%.2f, %.2f, %.2f), Orientation(%.2f, %.2f, %.2f, %.2f)",
msg->pose.position.x, msg->pose.position.y, msg->pose.position.z,
msg->pose.orientation.x, msg->pose.orientation.y, msg->pose.orientation.z, msg->pose.orientation.w);
}
// Optional: Sleep to avoid busy waiting
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(100));
}
}
void spinThread()
{
ros::spin();// 处理回调函数积累消息
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
ros::init(argc, argv, "image_pose_processor");
ros::NodeHandle nh;
ros::Subscriber sub;
ros::Publisher pose_pub;
// Initialize the subscriber
sub = nh.subscribe("render/image_pose_topic", 10, render_callback);
pose_pub = nh.advertise<gaosi_img_pose_flag::PoseImgFlagMsg>("slam/image_pose_topic", 10);
// Start a thread to run ros::spin()
std::thread spin_thread(spinThread); // 处理rospin的线程
// Create a thread to process the queue
std::thread processing_thread(processQueue); // 处理接受消息的线程
Q_c2w = Eigen::Quaterniond::Identity();;
t_c2w={0,0,0.1};
std::string control_mode="auto";// 自动 auto 手动 hand
ros::Rate rate(1);// Hz 频率
if(control_mode=="auto"){
// 定时器每秒调用一次
ros::Rate rate(1);
double i =0;
while (ros::ok())
{
i=i+0.1;
if(i>3)i=0;
t_c2w={i,0,i};
std_msgs::Float64 Msg_id; // 创建 Float64 消息
Msg_id.data = i;// 将 double 值赋给消息的 data 成员
// todo 从slam获取想要的位姿
publishPose(pose_pub,Msg_id,Q_c2w,t_c2w);
rate.sleep();
}
}
// Join the processing thread before exiting
if (processing_thread.joinable())
{
processing_thread.join();
}
// Join the spin thread before exiting
if (spin_thread.joinable())
{
spin_thread.join();
}
return 0;
}
升级版本 发送端也可以手动漫游
image_pose_flag_subscriber.cpp
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include <ros/time.h>
#include <std_msgs/Time.h>
#include <queue>
#include <mutex>
#include <thread>
#include <iostream>
#include <sensor_msgs/Image.h>
#include <std_msgs/Float64.h>
#include <geometry_msgs/Pose.h>
#include <cv_bridge/cv_bridge.h>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <gaosi_img_pose_flag/PoseImgFlagMsg.h> // 更换为你包的名字
#include <Eigen/Dense>
#include <Eigen/Geometry> // For Quaterniond
// Global variables
std::queue<gaosi_img_pose_flag::PoseImgFlagMsg::ConstPtr> data_queue;
std::mutex queue_mutex;
int i = 0;
double x = 0, y = 0, z = 0;
double step_ = 0.1, step_theta = 1.0;
double theta_x = 0, theta_y = 0, theta_z = 0;
cv::Mat image_hand = cv::Mat::zeros(480, 640, CV_8UC3);
// 用于过于早位姿的节点
Eigen::Quaterniond Q_c2w ;
Eigen::Vector3d t_c2w;
Eigen::Quaterniond eulerToQuaternion(double pitch, double yaw, double roll) {
// 使用 Eigen 的四元数构造函数直接创建四元数
Eigen::Quaterniond q = Eigen::AngleAxisd(roll, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitX()) *
Eigen::AngleAxisd(pitch, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitY()) *
Eigen::AngleAxisd(yaw, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitZ());
return q;
}
Eigen::Matrix3d eulerToRotationMatrix(double pitch, double yaw, double roll) {
// 使用 Eigen 的四元数计算旋转矩阵
Eigen::Quaterniond q = eulerToQuaternion(pitch, yaw, roll);
return q.toRotationMatrix();
}
std::string rond_num(double value,int weishu) {
// Round the number to 2 decimal places
double roundedValue = std::round(value * 100.0) / 100.0;
// Use a string stream to format the number
std::ostringstream oss;
oss << std::fixed << std::setprecision(weishu) << roundedValue;
return oss.str();
}
int GetHandsPose(Eigen::Quaterniond &Q_c2w, Eigen::Vector3d &t_c2w){
int state_=0;
if (image_hand.empty()) {
return state_;
}
cv::namedWindow("cgg_hand_control", cv::WINDOW_NORMAL);
bool new_img = false;
// 设置文字的参数
double font_scale = 0.5; // 大小
int thickness = 1; // 粗细
cv::Scalar color1(255, 0, 0); // 文字颜色
cv::Scalar color2(0, 0, 255); // 文字颜色
// // 设置文字
std::string text1 = "position_xyz: " + (rond_num(x,2)) + " , " + (rond_num(y ,2)) + " , " + (rond_num(z,2));
cv::putText(image_hand, text1, cv::Point(10, 60), cv::FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, font_scale, color1, thickness);
std::string text2 = "theta_xyz: " + (rond_num(theta_x,2) ) + " , " + (rond_num(theta_y ,2)) + " , " + (rond_num(theta_z,2));
cv::putText(image_hand, text2, cv::Point(10, 120), cv::FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, font_scale, color2, thickness);
cv::imshow("cgg_hand_control", image_hand);
char key = (char)cv::waitKey(1);
if (key == 27) { // 按下 'ESC' 键
std::cout << "退出" << std::endl;
state_=-1;
new_img=false;
return state_;
//break;
} else if (key == 'w') { // 按下 'w' 键
std::cout << "x前进" << std::endl;
x += step_;
i++;
new_img = true;
} else if (key == 's') { // 按下 's' 键
std::cout << "x后退" << std::endl;
x -= step_;
i++;
new_img = true;
} else if (key == 'a') { // 按下 'a' 键
std::cout << "y前进" << std::endl;
y += step_;
i++;
new_img = true;
} else if (key == 'd') { // 按下 'd' 键
std::cout << "y后退" << std::endl;
y -= step_;
i++;
new_img = true;
} else if (key == 'q') { // 按下 'q' 键
std::cout << "z前进" << std::endl;
z += step_;
i++;
new_img = true;
} else if (key == 'e') { // 按下 'e' 键
std::cout << "z后退" << std::endl;
z -= step_;
i++;
new_img = true;
} else if (key == 'i') { // 按下 'i' 键
std::cout << "x旋转+" << std::endl;
theta_x += step_theta;
if (theta_x > 360 || theta_x < -360) theta_x = 0;
i++;
new_img = true;
} else if (key == 'k') { // 按下 'k' 键
std::cout << "x旋转-" << std::endl;
theta_x -= step_theta;
if (theta_x > 360 || theta_x < -360) theta_x = 0;
i++;
new_img = true;
} else if (key == 'j') { // 按下 'j' 键
std::cout << "y旋转+" << std::endl;
theta_y += step_theta;
if (theta_y > 360 || theta_y < -360) theta_y = 0;
i++;
new_img = true;
} else if (key == 'l') { // 按下 'l' 键
std::cout << "y旋转-" << std::endl;
theta_y -= step_theta;
if (theta_y > 360 || theta_y < -360) theta_y = 0;
i++;
new_img = true;
} else if (key == 'u') { // 按下 'u' 键
std::cout << "z旋转+" << std::endl;
theta_z += step_theta;
if (theta_z > 360 || theta_z < -360) theta_z = 0;
i++;
new_img = true;
} else if (key == 'o') { // 按下 'o' 键
std::cout << "z旋转-" << std::endl;
theta_z -= step_theta;
if (theta_z > 360 || theta_z < -360) theta_z = 0;
i++;
new_img = true;
}
else{
new_img = false;
state_=0;
}
if (new_img) {
state_=1;
// 示例角度(以弧度为单位)
double pitch = M_PI*(theta_x/180); // 30度
double yaw = M_PI*(theta_y/180); // 45度
double roll = M_PI*(theta_z/180); // 60度
Q_c2w = eulerToQuaternion(pitch, yaw, roll);
t_c2w={x,y,z};
}
return state_;
}
void publishPose(ros::Publisher& pose_pub, std_msgs::Float64 flag_,Eigen::Quaterniond &quat, Eigen::Vector3d &t)
{
cv::Mat image_;
//std_msgs::Float64 flag_;
geometry_msgs::Pose pose_msg;
pose_msg.position.x = t[0]; // 示例位置
pose_msg.position.y = t[1];
pose_msg.position.z = t[2];
pose_msg.orientation.x = quat.x(); // 示例姿态
pose_msg.orientation.y = quat.y();
pose_msg.orientation.z = quat.z();
pose_msg.orientation.w = quat.w();
ROS_INFO("send Pose - x: %f, y: %f, z: %f",
pose_msg.position.x,
pose_msg.position.y,
pose_msg.position.z);
gaosi_img_pose_flag::PoseImgFlagMsg pose_img_flag_msg;
//pose_msg.image = *cv_bridge::CvImage(std_msgs::Header(), "bgr8", image_).toImageMsg();
pose_img_flag_msg.flag = flag_;
pose_img_flag_msg.pose = pose_msg;
// 设置当前时间戳
ros::Time current_time = ros::Time::now();
pose_img_flag_msg.timestamp = std_msgs::Time(); // 初始化时间戳
pose_img_flag_msg.timestamp.data = current_time; // 设置当前时间
// 发布PoseStamped消息
pose_pub.publish(pose_img_flag_msg);
}
// Callback function to handle incoming messages
void render_callback(const gaosi_img_pose_flag::PoseImgFlagMsg::ConstPtr& msg)
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(queue_mutex);
data_queue.push(msg);
}
// Thread function to process the queue
void processQueue()
{
while (ros::ok())
{
std::queue<gaosi_img_pose_flag::PoseImgFlagMsg::ConstPtr> local_queue;
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(queue_mutex);
std::swap(local_queue, data_queue); // Safely access the queue
}
while (!local_queue.empty())
{
auto msg = local_queue.front();
local_queue.pop();
// 将ROS图像消息转换为OpenCV图像
cv_bridge::CvImagePtr cv_ptr = cv_bridge::toCvCopy(msg->image, sensor_msgs::image_encodings::BGR8);
cv::imshow("Rec_Image", cv_ptr->image);
cv::waitKey(1);
// Process the message
ROS_INFO("Processing flag: %.2f", msg->flag.data);
ROS_INFO("Processing pose: Position(%.2f, %.2f, %.2f), Orientation(%.2f, %.2f, %.2f, %.2f)",
msg->pose.position.x, msg->pose.position.y, msg->pose.position.z,
msg->pose.orientation.x, msg->pose.orientation.y, msg->pose.orientation.z, msg->pose.orientation.w);
}
// Optional: Sleep to avoid busy waiting
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(100));
}
}
void spinThread()
{
ros::spin();// 处理回调函数积累消息
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
ros::init(argc, argv, "image_pose_processor");
ros::NodeHandle nh;
ros::Subscriber sub;
ros::Publisher pose_pub;
// Initialize the subscriber
sub = nh.subscribe("render/image_pose_topic", 10, render_callback);
pose_pub = nh.advertise<gaosi_img_pose_flag::PoseImgFlagMsg>("slam/image_pose_topic", 10);
// Start a thread to run ros::spin()
std::thread spin_thread(spinThread); // 处理rospin的线程
// Create a thread to process the queue
std::thread processing_thread(processQueue); // 处理接受消息的线程
std_msgs::Float64 Msg_id; // 创建 Float64 消息
Msg_id.data =0;
Q_c2w = Eigen::Quaterniond::Identity();;
t_c2w={0,0,0.1};
std::string control_mode="hand";// 自动 auto 手动 hand
ros::Rate rate(1);// Hz 频率
if(control_mode=="hand"){
int state_=0;
while ( ros::ok()){
if(ros::ok() && state_==1){
Msg_id.data=Msg_id.data+1;
//ros::spinOnce(); // 不能执行太快 否则来不及处理回调 必须配合ros::Rate rate(10); rate.sleep(); 单独卡求一个线程处理
publishPose(pose_pub,Msg_id,Q_c2w,t_c2w);
}
else if(state_==-1) {break;}
//std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(20)); // 暂停以减少CPU使用率
rate.sleep();
state_= GetHandsPose(Q_c2w,t_c2w);
}
}
else if(control_mode=="auto"){
// 定时器每秒调用一次
double i =0;
while (ros::ok())
{
i=i+0.1;
if(i>3)i=0;
t_c2w={i,0,i};
Msg_id.data = i;// 将 double 值赋给消息的 data 成员
// todo 从slam获取想要的位姿
publishPose(pose_pub,Msg_id,Q_c2w,t_c2w);
rate.sleep();
}
}
// Join the processing thread before exiting
if (processing_thread.joinable())
{
processing_thread.join();
}
// Join the spin thread before exiting
if (spin_thread.joinable())
{
spin_thread.join();
}
return 0;
}
python接受位姿消息,渲染图像,返回图像,且可以手动漫游地图给与渲染图

v1_image_pose_subscriber.py
# sudo apt-get install python3-rosdep python3-rosinstall python3-rospkg
import rospy
import cv2
import numpy as np
from sensor_msgs.msg import Image as ImageMsg
from geometry_msgs.msg import PoseStamped,Pose
from cv_bridge import CvBridge, CvBridgeError
from collections import deque
from sensor_msgs.msg import Image
from std_msgs.msg import Float64
from geometry_msgs.msg import Pose
from gaosi_img_pose_flag.msg import PoseImgFlagMsg # 更换为你包的名字
import std_msgs.msg
# import sys
# directory = '/home/dongdong/2project/2_3DGaosi/reduced-3dgs/'
# sys.path.append(directory)
from API_render import *
pose_queue = deque() # Queue to store pose messages with timestamps
bridge = CvBridge()
def pose_callback(msg):
# Store the pose message with timestamp in the queue
pose_queue.append((msg.timestamp, msg))
#print("收到位姿 x", msg.pose.position.x, "y", msg.pose.position.y, "z", msg.pose.position.z)
# try:
# # Convert ROS image message to OpenCV image
# cv_image = bridge.imgmsg_to_cv2(msg.image, desired_encoding="bgr8")
# cv2.imshow("Received Image", cv_image)
# cv2.waitKey(1)
# except Exception as e:
# rospy.logerr("Failed to convert image: %s", str(e))
# rospy.loginfo("Received flag: %.2f", msg.flag.data)
# rospy.loginfo("Received pose: Position(%.2f, %.2f, %.2f), Orientation(%.2f, %.2f, %.2f, %.2f)",
# msg.pose.position.x, msg.pose.position.y, msg.pose.position.z,
# msg.pose.orientation.x, msg.pose.orientation.y, msg.pose.orientation.z, msg.pose.orientation.w)
# 继承模式 直接使用而非拷贝
def publish_image_with_pose_gaosi(dataset : ModelParams,
iteration : int,
pipeline : PipelineParams,
):
# ============ 3d 初始化 =================
with torch.no_grad():# 丢不更新 防止高斯模型数据修改
print("dataset._model_path 训练渲染保存的模型总路径",dataset.model_path)
print("dataset._source_path 原始输入SFM数据路径",dataset.source_path)
print("dataset.sh_degree 球谐系数",dataset.sh_degree)
print("dataset.white_background 是否白色背景",dataset.sh_degree)
cam_info = Read_caminfo_from_colmap(dataset.source_path)
height, width = cam_info["height"], cam_info["width"]
Fovx,Fovy = cam_info["FovX"], cam_info["FovY"]
img_opencv = np.ones((height, width, 3), dtype=np.uint8) * 0
cv2.namedWindow('python_Node_Rendering_Img', cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
# 加载渲染器
gaussians = GaussianModel(dataset.sh_degree)
bg_color = [1,1,1] if dataset.white_background else [0, 0, 0]
background = torch.tensor(bg_color, dtype=torch.float32, device="cuda")
# 加载什么精度模型
model = args.models
print("渲染实际加载的训练模型精度类型 (标准baseline 半精度quantised 半半精度half_float)",model)
name = models_configuration[model]['name']
quantised = models_configuration[model]['quantised']
half_float = models_configuration[model]['half_float']
try:
# 选择什么训练次数模型
model_path = dataset.model_path+"/point_cloud/iteration_"+str(iteration)+"/"
model_path=os.path.join(model_path,name)
print("渲染实际加载的训练模型",model_path)
gaussians.load_ply(model_path, quantised=quantised, half_float=half_float)
except:
raise RuntimeError(f"Configuration {model} with name {name} not found!")
# ============== rosros 节点 ===============
i=0
x,y,z=0,0,0 # 手动控制的位置
t_x,t_y,t_z=0,0,0 # ros 收到的位置 后期会更新给x,y,z 保证手动控制给的位置是从上次的位姿开始的,而不会突变。
step_=0.1
theta_x=0 # 旋转角度
theta_y=0
theta_z=0
step_theta=1
scale_c2w=1
t_c2w=np.array([0, 0, 0])
R_c2w = quaternion_to_rotation_matrix((0,0,0,1))
# 初始化消息
image = np.zeros((480, 640, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
flag_ = Float64()
flag_.data = 1.0
pose_=Pose()
pose_.position.x =0
pose_.position.y =0
pose_.position.z =0
pose_.orientation.x =0
pose_.orientation.y =0
pose_.orientation.z =0
pose_.orientation.w =1
ImagePoseFlag_Msg = PoseImgFlagMsg()
timestamp = rospy.Time.now()# 时间戳 同于数据同步
ImagePoseFlag_Msg.timestamp = std_msgs.msg.Time() # 初始化时间戳
ImagePoseFlag_Msg.timestamp.data = timestamp # 设置当前时间
ImagePoseFlag_Msg.image = bridge.cv2_to_imgmsg(image, encoding="bgr8")
ImagePoseFlag_Msg.flag.data = flag_
ImagePoseFlag_Msg.pose = pose_
# 用于构造渲染视角
view = Camera_view(img_id=i,
R=R_c2w,
t=t_c2w,
scale=scale_c2w,
FoVx=Fovx,
FoVy=Fovy,
image_width=width,
image_height=height)
#df = pd.DataFrame()
# 初期渲染一张
img_opencv = render_img( view, gaussians, pipeline, background)
# 用于增加文字信息后的可视化
image = img_opencv# 原始渲染图不能被污染 要发送slam回去,新创建图可视化 cv2.UMat转换后才可以 cv2.putText
new_img=0
rate = rospy.Rate(20) # 1 Hz
while not rospy.is_shutdown():
new_img=0
image = img_opencv# 原始渲染图不能被污染 要发送slam回去,新创建图可视化 cv2.UMat转换后才可以 cv2.putText
# 设置文字的参数
font_scale = 2 # 大小
thickness = 2 # 粗细
text1 ="position_xyz: " + str(round(t_x, 2))+" , "+str(round(t_y, 2)) +" , "+ str(round(t_z, 2))
position1 = (10, 60) # 文字的位置
cv2.putText(image, text1, position1, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, font_scale, (255, 0, 0), thickness)
text2 = "theta_xyz: " + str(round(theta_x, 2))+" , "+str(round(theta_y, 2)) +" , "+ str(round(theta_z, 2))
position2 = (10, 120) # 文字的位置
cv2.putText(image, text2, position2, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, font_scale, (0, 0, 255), thickness)
cv2.imshow('python_Node_Rendering_Img', image)
#cv2.imshow('Rendering_Img', img_opencv)# imshow 不需要额外 cv2.UMat转换
key = cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF
if pose_queue: # 收到渲染请求 位姿队列不为空
i=i+1 # 记录
new_img=1
timestamp, rec_pose_msg = pose_queue.popleft()
t_x = rec_pose_msg.pose.position.x
t_y = rec_pose_msg.pose.position.y
t_z = rec_pose_msg.pose.position.z
qx = rec_pose_msg.pose.orientation.x
qy = rec_pose_msg.pose.orientation.y
qz = rec_pose_msg.pose.orientation.z
qw = rec_pose_msg.pose.orientation.w
x,y,z=t_x,t_y,t_z# 将收到的位姿更新给按键变量 确保按键从现有位置开始运动
scale_c2w=1
t_c2w=np.array([t_x, t_y, t_z])
quaternion = (qx,qy,qz,qw)
R_c2w = quaternion_to_rotation_matrix(quaternion)
# # 从旋转矩阵获取欧拉角
roll, pitch, yaw = rotation_matrix_to_euler_angles(R_c2w)
theta_x,theta_y,theta_z = roll, pitch, yaw
flag_ = rec_pose_msg.flag
pose_ = rec_pose_msg.pose
#print(f"绕 X 轴的角度 滚转会使物体的左侧和右侧倾斜 (roll): {roll:.2f}°")
#print(f"绕 Y 轴的角度 俯仰会使物体的前端向上或向下移动 (pitch): {pitch:.2f}°")
#print(f"绕 Z 轴的角度 偏航会使物体的前端向左或向右转动 (yaw): {yaw:.2f}°")
else:# 如果没有收到渲染请求 是否手动给了渲染位姿
if key == 27: # 按下 'q' 键
print("退出")
break
elif key == ord('w'): # 按下 's' 键
print("x前进")
x=x+step_
i=i+1
new_img=1
elif key == ord('s'): # 按下 's' 键
print("x后退")
x=x-step_
i=i+1
new_img=1
elif key == ord('a'): # 按下 's' 键
print("y前进")
y=y+step_
i=i+1
new_img=1
elif key == ord('d'): # 按下 's' 键
print("y后退")
y=y-step_
i=i+1
new_img=1
elif key == ord('q'): # 按下 's' 键
print("z前进")
z=z+step_
i=i+1
new_img=1
elif key == ord('e'): # 按下 's' 键
print("z后退")
z=z-step_
i=i+1
new_img=1
elif key == ord('i'): # 按下 's' 键
print("x旋转+")
theta_x=theta_x+step_theta
if(theta_x>360 or theta_x<-360): theta_x=0
i=i+1
new_img=1
elif key == ord('k'): # 按下 's' 键
print("x旋转-")
theta_x=theta_x-step_theta
if(theta_x>360 or theta_x<-360): theta_x=0
i=i+1
new_img=1
elif key == ord('j'): # 按下 's' 键
print("y旋转+")
theta_y=theta_y+step_theta
if(theta_y>360 or theta_y<-360): theta_y=0
i=i+1
new_img=1
elif key == ord('l'): # 按下 's' 键
print("y旋转-")
theta_y=theta_y-step_theta
if(theta_y>360 or theta_y<-360): theta_y=0
i=i+1
new_img=1
elif key == ord('u'): # 按下 's' 键
print("z旋转+")
theta_z=theta_z+step_theta
if(theta_z>360 or theta_z<-360): theta_z=0
i=i+1
new_img=1
elif key == ord('o'): # 按下 's' 键
print("z旋转-")
theta_z=theta_z-step_theta
if(theta_z>360 or theta_z<-360): theta_z=0
i=i+1
new_img=1
if new_img==1:
t_x,t_y,t_z = x,y,z# 将按键变量更新给收到的位姿变量 确保图像可以显示刷新当前位置
# # 示例角度(以弧度为单位)
theta_x_pi = np.radians(theta_x) # 30度
theta_y_pi = np.radians(theta_y) # 45度
theta_z_pi = np.radians(theta_z) # 60度
# # 计算旋转矩阵
R_c2w = combined_rotation_matrix(theta_x_pi, theta_y_pi, theta_z_pi)
# 相机到世界的旋转矩阵
# R_c2w = np.array([
# [1.0, 0.0, 0.0],
# [0.0, 1.0, 0.0],
# [0.0, 0.0, 1.0]
# ])
# print("旋转矩阵 R:")
# print(R)
# 相机到世界的平移矩阵 也就是相机在世界坐标系下的位置
t_c2w=np.array([x, y, z])
scale_c2w=1
q_c2w=rotation_matrix_to_quaternion(R_c2w)
#timestamp = rospy.Time.now()
pose_.position.x =t_c2w[0]
pose_.position.y =t_c2w[1]
pose_.position.z =t_c2w[2]
pose_.orientation.x =q_c2w[0]
pose_.orientation.y =q_c2w[1]
pose_.orientation.z =q_c2w[2]
pose_.orientation.w =q_c2w[3]
if new_img==1:
view = Camera_view(img_id=i,
R=R_c2w,
t=t_c2w,
scale=scale_c2w,
FoVx=Fovx,
FoVy=Fovy,
image_width=width,
image_height=height)
#df = pd.DataFrame()
img_opencv = render_img( view, gaussians, pipeline, background)
#random_image = np.random.randint(0, 256, (480, 640, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
try:
ImagePoseFlag_Msg.timestamp.data = rospy.Time.now()
ImagePoseFlag_Msg.pose = pose_
ImagePoseFlag_Msg.flag.data = flag_.data
ImagePoseFlag_Msg.image = bridge.cv2_to_imgmsg(image, "bgr8")
pub_ImgPoseFlag.publish(ImagePoseFlag_Msg)
# Publish pose and image
#pose_pub.publish(pose_msg)
#image_pub.publish(image_msg)
print("图像数据发送", " 位姿xyz ", x, y, z)
except CvBridgeError as e:
rospy.logerr(f'CvBridge Error: {e}')
rate.sleep()
if __name__ == '__main__':
# ============ 3d 初始化 =================
parser = ArgumentParser(description="渲染测试脚本")
model = ModelParams(parser, sentinel=True)
pipeline = PipelineParams(parser)
parser.add_argument("--iteration", default=30000, type=int)
parser.add_argument("--models", default='baseline',type=str) #'baseline','quantised' 'quantised_half'
parser.add_argument("--quiet", action="store_true") #标记以省略写入标准输出管道的任何文本。
args = get_combined_args(parser) # 从cfg_args加载路径
safe_state(args.quiet)
#render_sets_handMode(model.extract(args), args.iteration, pipeline.extract(args))
# ============== rosros 节点初始化 ===============
rospy.init_node('node2', anonymous=True)
rospy.Subscriber('slam/image_pose_topic', PoseImgFlagMsg, pose_callback)
global pub_ImgPoseFlag
pub_ImgPoseFlag = rospy.Publisher('render/image_pose_topic', PoseImgFlagMsg, queue_size=10)
publish_image_with_pose_gaosi(model.extract(args), args.iteration, pipeline.extract(args))
API_render.py
修改自己的高斯渲染工程代码路径
import sys
directory = '/home/r9000k/v2_project/gaosi_slam/reduced-3dgs'
sys.path.append(directory)
import cv2
import numpy as np
import torch
from scene import Scene
import os
from tqdm import tqdm
from os import makedirs
from gaussian_renderer import render
import torchvision
from utils.general_utils import safe_state
from argparse import ArgumentParser
from arguments import ModelParams, PipelineParams, get_combined_args
from gaussian_renderer import GaussianModel
import pandas as pd
import torch
from torch import nn
import numpy as np
from utils.graphics_utils import getWorld2View2, getProjectionMatrix
from scene.colmap_loader import *
from scene.dataset_readers import *
# 要选的视角
class Camera_view(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, img_id, R, FoVx, FoVy, image_width,image_height,
t=np.array([0.0, 0.0, 0.0]), scale=1.0
):
super(Camera_view, self).__init__()
self.img_id = img_id
# 相机到世界 也就是相机在世界坐标系下的位姿
self.R = R # 相机到世界 源代码
self.t = t # 相机到世界
self.scale = scale # 尺度 展示没有
self.FoVx = FoVx
self.FoVy = FoVy
self.image_width = image_width
self.image_height = image_height
self.zfar = 100.0
self.znear = 0.01
# 相机到世界
sRt_c2w = np.zeros((4, 4)) #标准的矩阵转置
sRt_c2w[:3, :3] = self.R
sRt_c2w[:3, 3] = self.scale*self.t
sRt_c2w[3, 3] = 1.0
# 3D高斯渲染 需要的是 一个3D高斯球(x,y,z) 投影到相机像素画面 ,也就是世界到相机的变换矩阵, 所以需要对相机到世界矩阵sRt转置取逆
# 3D世界到3D相机坐标系 变换矩阵
# 高斯渲染 计算从世界坐标系到相机视图坐标系的变换矩阵,并将其移动到 GPU
sRt_w2c=np.linalg.inv(sRt_c2w) # 世界到相机
self.world_view_transform = torch.tensor(np.float32(sRt_w2c)).transpose(0, 1).cuda() # 世界到相机
'''
#将3D相机坐标投影到2D相机像素平面的投影矩阵
# 真实相机成像模型中 该矩阵是由 fx fy cx cy构造的
# 虚拟渲染相机模型中 该矩阵是由 znear 默认0.01 近平面 zfar 默认100 远平面 视场角FoVx FoVy构造的。计算视场角FoVx=fx/(W/2),FoVy=fy/(H/2)
# 两者关系:
# 虚拟渲染相机用fx和fy表示的话 ,最后都是变为统一的形式。
(相机前方为z正轴的坐标系)
u=fx*x/z-W/2
v=fy*y/z-H/2
w=-zfar*n/z (像素坐标不关心投影后的z值,无用舍去,所以最终znear和zfar对像素坐标u,v没有影响。)
# 真实采集相机参数 fx fy cx=实际物理值 cy=实际物理值 成像分辨率 W*H
# 渲染虚拟相机参数 fx fy cx=W/2 cy=H/2 成像分辨率 W*H
'''
self.projection_matrix = getProjectionMatrix(znear=self.znear, zfar=self.zfar, fovX=self.FoVx, fovY=self.FoVy).transpose(0, 1).cuda()
# 3D世界点投影到2D相机像素坐标 变换矩阵 world_view_transform 世界到相机 projection_matrix 相机到像素 合起来 世界到像素投影
'''
unsqueeze(0):为张量添加一个额外的维度,以便进行批量操作。
.bmm(...):执行批量矩阵乘法,将世界到视图的变换与投影矩阵相乘,得到一个合成的变换矩阵。
.squeeze(0):移除之前添加的额外维度。
'''
self.full_proj_transform = (self.world_view_transform.unsqueeze(0).bmm(self.projection_matrix.unsqueeze(0))).squeeze(0)
self.inverse_full_proj_transform = self.full_proj_transform.inverse()# 后面貌似没用到
self.camera_center = self.world_view_transform.inverse()[3, :3] # 先求逆矩阵 相机到世界 然后取出t 世界计算相机中心位置 世界坐标系下的
# 考虑到R在层层计算中精度损失行列式不为1,从而影响t的计算,可以考虑直接用原始传来的t。
# 但是得保证数据采集时候 相机姿态方向没有转动过。飞机即使垂直朝下,也会因为气流扰动相机云台抖动有轻微R的变化。
#self.world_view_transform_c2w = torch.tensor(np.float32(sRt_c2w)).transpose(0, 1).cuda() # 自己定义的 未必用到
#self.camera_center = self.world_view_transform_c2w[3, :3] # 如果要忽略R的计算导致的误差 直接用原始的t_c2w
def __del__(self):
# 如果几个数据使用.cuda() 创建的,会自动存到显卡内存,多次渲染积累造成内存爆满,每次用完需要指定回收释放。否则不会随着程序(cpu)关闭而销毁。
# 删除张量并释放 GPU 内存
del self.world_view_transform
del self.full_proj_transform
del self.inverse_full_proj_transform
del self.camera_center
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
#print("cuda占用回收.")
#训练中间只会保存 原始模型 。 训练结束最后一次会保存原始模型baseline 精度减半模型quantised 精度减半减半模型 quantised_half,三种不同模型供测试。
# 要测试的模型类型。标准的、基准的模型 “baseline”和将模型的权重或激活值量化为半精度(16-bit)格式“quantised_half”之间的选择
#功能:量化可以显著降低计算量和内存消耗,但可能会引入一些精度损失。具体来说,“quantised_half”可能指的是将模型参数或中间激活值量化为16-bit浮点数(half precision),从而减少存储需求并提高计算效率。
#半浮点量化 如果采用半浮点量化,则码本条目以及位置参数将以半精度存储。这意味着使用 16 位而不是 32 位,因此存储的是 float16 而不是 float32。
# #但是,由于格式.ply不允许 float16 类型的数字,因此参数将指针转换为 int16 并以此形式存储。
models_configuration = {
'baseline': {
'quantised': False,
'half_float': False,
'name': 'point_cloud.ply'
},
'quantised': {
'quantised': True,
'half_float': False,
'name': 'point_cloud_quantised.ply'
},
'quantised_half': {
'quantised': True,
'half_float': True,
'name': 'point_cloud_quantised_half.ply'
},
}
def measure_fps(iteration, views, gaussians, pipeline, background, pcd_name):
fps = 0
for _, view in enumerate(views):
render(view, gaussians, pipeline, background, measure_fps=False)
for _, view in enumerate(views):
fps += render(view, gaussians, pipeline, background, measure_fps=True)["FPS"]
fps *= 1000 / len(views)
return pd.Series([fps], index=["FPS"], name=f"{pcd_name}_{iteration}")
def rotation_matrix_x(theta_x):
""" 创建绕x轴旋转的旋转矩阵 """
c, s = np.cos(theta_x), np.sin(theta_x)
return np.array([
[1, 0, 0],
[0, c, -s],
[0, s, c]
])
def rotation_matrix_y(theta_y):
""" 创建绕y轴旋转的旋转矩阵 """
c, s = np.cos(theta_y), np.sin(theta_y)
return np.array([
[c, 0, s],
[0, 1, 0],
[-s, 0, c]
])
def rotation_matrix_z(theta_z):
""" 创建绕z轴旋转的旋转矩阵 """
c, s = np.cos(theta_z), np.sin(theta_z)
return np.array([
[c, -s, 0],
[s, c, 0],
[0, 0, 1]
])
def combined_rotation_matrix(theta_x, theta_y, theta_z):
""" 通过绕x、y、z轴的旋转角度创建组合旋转矩阵 """
Rx = rotation_matrix_x(theta_x)
Ry = rotation_matrix_y(theta_y)
Rz = rotation_matrix_z(theta_z)
# 旋转矩阵的组合顺序:绕z轴 -> 绕y轴 -> 绕x轴
R = Rz @ Ry @ Rx
return R
# # 示例角度(以弧度为单位)
# theta_x = np.radians(30) # 30度
# theta_y = np.radians(45) # 45度
# theta_z = np.radians(60) # 60度
# # 计算旋转矩阵
# R = combined_rotation_matrix(theta_x, theta_y, theta_z)
# print("旋转矩阵 R:")
# print(R)
def quaternion_to_rotation_matrix(q):
qx, qy, qz, qw = q
R = np.array([
[1 - 2*(qy**2 + qz**2), 2*(qx*qy - qz*qw), 2*(qx*qz + qy*qw)],
[2*(qx*qy + qz*qw), 1 - 2*(qx**2 + qz**2), 2*(qy*qz - qx*qw)],
[2*(qx*qz - qy*qw), 2*(qy*qz + qx*qw), 1 - 2*(qx**2 + qy**2)]
])
return R
def rotation_matrix_to_euler_angles(R):
sy = np.sqrt(R[0, 0]**2 + R[1, 0]**2)
singular = sy < 1e-6
if not singular:
x = np.arctan2(R[2, 1], R[2, 2])
y = np.arctan2(-R[2, 0], sy)
z = np.arctan2(R[1, 0], R[0, 0])
else:
x = np.arctan2(-R[1, 2], R[1, 1])
y = np.arctan2(-R[2, 0], sy)
z = 0
return np.degrees(x), np.degrees(y), np.degrees(z)
# # 示例四元数
# quaternion = (0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0) # 替换为你自己的四元数
# # 转换为旋转矩阵
# R = quaternion_to_rotation_matrix(quaternion)
# print("旋转矩阵 R:")
# print(R)
# # 从旋转矩阵获取欧拉角
# roll, pitch, yaw = rotation_matrix_to_euler_angles(R)
# print(f"绕 X 轴的角度 (roll): {roll:.2f}°")
# print(f"绕 Y 轴的角度 (pitch): {pitch:.2f}°")
# print(f"绕 Z 轴的角度 (yaw): {yaw:.2f}°")
def rotation_matrix_to_quaternion(R):
"""
Convert a rotation matrix to a quaternion.
Parameters:
R (numpy.ndarray): A 3x3 rotation matrix.
Returns:
numpy.ndarray: A quaternion in the form of [w, x, y, z].
"""
assert R.shape == (3, 3), "Input must be a 3x3 rotation matrix."
# Calculate the trace of the matrix
trace = np.trace(R)
if trace > 0:
s = np.sqrt(trace + 1.0) * 2 # s=4*qw
qw = 0.25 * s
qx = (R[2, 1] - R[1, 2]) / s
qy = (R[0, 2] - R[2, 0]) / s
qz = (R[1, 0] - R[0, 1]) / s
else:
# Find the largest diagonal element
if R[0, 0] > R[1, 1] and R[0, 0] > R[2, 2]:
s = np.sqrt(1.0 + R[0, 0] - R[1, 1] - R[2, 2]) * 2 # s=4*qx
qw = (R[2, 1] - R[1, 2]) / s
qx = 0.25 * s
qy = (R[0, 1] + R[1, 0]) / s
qz = (R[0, 2] + R[2, 0]) / s
elif R[1, 1] > R[2, 2]:
s = np.sqrt(1.0 + R[1, 1] - R[0, 0] - R[2, 2]) * 2 # s=4*qy
qw = (R[0, 2] - R[2, 0]) / s
qx = (R[0, 1] + R[1, 0]) / s
qy = 0.25 * s
qz = (R[1, 2] + R[2, 1]) / s
else:
s = np.sqrt(1.0 + R[2, 2] - R[0, 0] - R[1, 1]) * 2 # s=4*qz
qw = (R[1, 0] - R[0, 1]) / s
qx = (R[0, 2] + R[2, 0]) / s
qy = (R[1, 2] + R[2, 1]) / s
qz = 0.25 * s
return np.array([qw, qx, qy, qz])
# # 示例
# R = np.array([[0, -1, 0],
# [1, 0, 0],
# [0, 0, 1]]) # 90度绕Z轴旋转的矩阵
# quaternion = rotation_matrix_to_quaternion(R)
#print("Quaternion:", quaternion)
# 渲染单个视角图像并转化opencv图像
def render_img(view,
gaussians, # 模型
pipeline,
background,
):
#for idx, view in enumerate(tqdm(views, desc="Rendering progress")):
# view 拷贝 # gaussians 继承 pipeline 拷贝 background 继承
rendering = render(view, gaussians, pipeline, background)["render"]
#fps = render(view, gaussians, pipeline, background, measure_fps=True)["FPS"]
#gt = view.original_image[0:3, :, :]
# 将渲染图像转换为 NumPy 数组
rendering_np = rendering.cpu().numpy()
# 如果张量是 (C, H, W) 形式,需要调整为 (H, W, C)
if rendering_np.shape[0] == 3:
rendering_np = np.transpose(rendering_np, (1, 2, 0))
# 将 RGB 转换为 BGR
#opencv_img = rendering_np[..., ::-1] # 后续调用convert_image 一次性完成
#print("转化前 ",opencv_img.dtype)
opencv_img = convert_image(rendering_np) #高斯输出是 float32(imshow虽然可以直接显示出来) 但是opencv和ros发送需要8UC3 图像
#print("转化后",opencv_img.dtype)
# 及时清空显卡数据缓存
#del rendering
#del rendering_np
#torch.cuda.empty_cache()
# # 显示图像
# cv2.imshow('Rendering', opencv_img)
# cv2.waitKey(0) # 等待用户按键
return opencv_img
def convert_image(image_32fc3):
# 确保图像类型是 float32
if image_32fc3.dtype != np.float32:
raise TypeError("输入图像必须是 32FC3 类型")
# 将 32FC3 图像转换为 8UC3 图像
# 将浮点值缩放到 0-255 范围
image_8uc3 = cv2.convertScaleAbs(image_32fc3, alpha=(255.0 / np.max(image_32fc3)))
# 转换为 BGR 颜色空间
image_bgr8 = cv2.cvtColor(image_8uc3, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
return image_bgr8
# 从slam读取相机参数
def Read_caminfo_from_orbslam(path):
# wait to do
pass
# 从colmap读取相机参数
def Read_caminfo_from_colmap(path):
cam_intrinsics={}
cam_extrinsics={}
# 自带的代码
'''
from scene.colmap_loader import *
from scene.dataset_readers import *
'''
try:
cameras_extrinsic_file = os.path.join(path, "sparse/0", "images.bin")
cameras_intrinsic_file = os.path.join(path, "sparse/0", "cameras.bin")
cam_extrinsics = read_extrinsics_binary(cameras_extrinsic_file)
cam_intrinsics = read_intrinsics_binary(cameras_intrinsic_file)
except:
cameras_extrinsic_file = os.path.join(path, "sparse/0", "images.txt")
cameras_intrinsic_file = os.path.join(path, "sparse/0", "cameras.txt")
cam_extrinsics = read_extrinsics_text(cameras_extrinsic_file)
cam_intrinsics = read_intrinsics_text(cameras_intrinsic_file)
'''
加载相机内参 read_intrinsics_text()
# Camera list with one line of data per camera:
# CAMERA_ID, MODEL, WIDTH, HEIGHT, PARAMS[]
# Number of cameras: 1
1 PINHOLE 1920 1080 1114.0581411159471 1108.508409747483 960 540
'''
cam_id=1 # 从1开始。以一个相机模型 这里默认colmap一般只有一个相机. 但是可能存在GNSS照片和视频抽离的帧,2个相机模型参数
cam_parameters=cam_intrinsics[cam_id]
print("相机id",cam_parameters.id)
print("相机模型",cam_parameters.model)
print("图像宽度",cam_parameters.width)
print("图像高度",cam_parameters.height)
print("相机内参 fx ",cam_parameters.params[0])
print("相机内参 fy ",cam_parameters.params[1])
FovY=0
FovX=0
if cam_parameters.model=="SIMPLE_PINHOLE":
focal_length_x = cam_parameters.params[0]
FovY = focal2fov(focal_length_x, cam_parameters.height)
FovX = focal2fov(focal_length_x, cam_parameters.width)
elif cam_parameters.model=="PINHOLE":
focal_length_x = cam_parameters.params[0]
focal_length_y = cam_parameters.params[1]
FovY = focal2fov(focal_length_y, cam_parameters.height)
FovX = focal2fov(focal_length_x, cam_parameters.width)
else:
assert False, "Colmap camera model not handled: only undistorted datasets (PINHOLE or SIMPLE_PINHOLE cameras) supported!"
cam_info = {
"width": cam_parameters.width,
"height": cam_parameters.height,
"fx": cam_parameters.params[0],
"fy": cam_parameters.params[1],
"FovX": FovX,
"FovY": FovY
}
return cam_info
def render_sets_handMode(dataset : ModelParams,
iteration : int,
pipeline : PipelineParams,
):
with torch.no_grad():
print("dataset._model_path 训练渲染保存的模型总路径",dataset.model_path)
print("dataset._source_path 原始输入SFM数据路径",dataset.source_path)
print("dataset.sh_degree 球谐系数",dataset.sh_degree)
print("dataset.white_background 是否白色背景",dataset.sh_degree)
cam_info = Read_caminfo_from_colmap(dataset.source_path)
height, width = cam_info["height"], cam_info["width"]
Fovx,Fovy = cam_info["FovX"], cam_info["FovY"]
img_opencv = np.ones((height, width, 3), dtype=np.uint8) * 0
cv2.namedWindow('Rendering_Img', cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
# 加载渲染器
gaussians = GaussianModel(dataset.sh_degree)
bg_color = [1,1,1] if dataset.white_background else [0, 0, 0]
background = torch.tensor(bg_color, dtype=torch.float32, device="cuda")
# 加载什么精度模型
model = args.models
print("渲染实际加载的训练模型精度类型 (标准baseline 半精度quantised 半半精度half_float)",model)
name = models_configuration[model]['name']
quantised = models_configuration[model]['quantised']
half_float = models_configuration[model]['half_float']
try:
# 选择什么训练次数模型
model_path = dataset.model_path+"/point_cloud/iteration_"+str(iteration)+"/"
model_path=os.path.join(model_path,name)
print("渲染实际加载的训练模型",model_path)
gaussians.load_ply(model_path, quantised=quantised, half_float=half_float)
except:
raise RuntimeError(f"Configuration {model} with name {name} not found!")
i=0 # 渲染的图像计数 id
x=0 # 位置
y=0
z=0
step_=0.1
theta_x=0 # 旋转角度
theta_y=0
theta_z=0
step_theta=1
while True:
new_img=0
image = img_opencv # 原始渲染图不能被污染 要发送slam回去,新创建图可视化 cv2.UMat转换后才可以 cv2.putText
# 设置文字的参数
font_scale = 2 # 大小
thickness = 2 # 粗细
text1 ="position_xyz: " + str(round(x, 2))+" , "+str(round(y, 2)) +" , "+ str(round(z, 2))
position1 = (10, 60) # 文字的位置
cv2.putText(image, text1, position1, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, font_scale, (255, 0, 0), thickness)
text2 = "theta_xyz: " + str(round(theta_x, 2))+" , "+str(round(theta_y, 2)) +" , "+ str(round(theta_z, 2))
position2 = (10, 120) # 文字的位置
cv2.putText(image, text2, position2, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, font_scale, (0, 0, 255), thickness)
cv2.imshow('Rendering_Img', image)
#cv2.imshow('Rendering_Img', img_opencv)# imshow 不需要额外 cv2.UMat转换
key = cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF
if key == 27: # 按下 'q' 键
print("退出")
break
elif key == ord('w'): # 按下 's' 键
print("x前进")
x=x+step_
i=i+1
new_img=1
elif key == ord('s'): # 按下 's' 键
print("x后退")
x=x-step_
i=i+1
new_img=1
elif key == ord('a'): # 按下 's' 键
print("y前进")
y=y+step_
i=i+1
new_img=1
elif key == ord('d'): # 按下 's' 键
print("y后退")
y=y-step_
i=i+1
new_img=1
elif key == ord('q'): # 按下 's' 键
print("z前进")
z=z+step_
i=i+1
new_img=1
elif key == ord('e'): # 按下 's' 键
print("z后退")
z=z-step_
i=i+1
new_img=1
elif key == ord('i'): # 按下 's' 键
print("x旋转+")
theta_x=theta_x+step_theta
if(theta_x>360 or theta_x<-360): theta_x=0
i=i+1
new_img=1
elif key == ord('k'): # 按下 's' 键
print("x旋转-")
theta_x=theta_x-step_theta
if(theta_x>360 or theta_x<-360): theta_x=0
i=i+1
new_img=1
elif key == ord('j'): # 按下 's' 键
print("y旋转+")
theta_y=theta_y+step_theta
if(theta_y>360 or theta_y<-360): theta_y=0
i=i+1
new_img=1
elif key == ord('l'): # 按下 's' 键
print("y旋转-")
theta_y=theta_y-step_theta
if(theta_y>360 or theta_y<-360): theta_y=0
i=i+1
new_img=1
elif key == ord('u'): # 按下 's' 键
print("z旋转+")
theta_z=theta_z+step_theta
if(theta_z>360 or theta_z<-360): theta_z=0
i=i+1
new_img=1
elif key == ord('o'): # 按下 's' 键
print("z旋转-")
theta_z=theta_z-step_theta
if(theta_z>360 or theta_z<-360): theta_z=0
i=i+1
new_img=1
if new_img==1:
# # 示例角度(以弧度为单位)
theta_x_pi = np.radians(theta_x) # 30度
theta_y_pi = np.radians(theta_y) # 45度
theta_z_pi = np.radians(theta_z) # 60度
# # 计算旋转矩阵
R_c2w = combined_rotation_matrix(theta_x_pi, theta_y_pi, theta_z_pi)
# 相机到世界的旋转矩阵
# R_c2w = np.array([
# [1.0, 0.0, 0.0],
# [0.0, 1.0, 0.0],
# [0.0, 0.0, 1.0]
# ])
# print("旋转矩阵 R:")
# print(R)
# 相机到世界的平移矩阵 也就是相机在世界坐标系下的位置
t_c2w=np.array([x, y, z])
scale_c2w=1
view = Camera_view(img_id=i,
R=R_c2w,
t=t_c2w,
scale=scale_c2w,
FoVx=Fovx,
FoVy=Fovy,
image_width=width,
image_height=height)
#df = pd.DataFrame()
img_opencv = render_img( view, gaussians, pipeline, background)
# python ./render.py -m /home/dongdong/2project/0data/NWPU/gs_out/train1_out_sh1_num7000 --iteration 7010
# if __name__ == "__main__":
# # Set up command line argument parser
# parser = ArgumentParser(description="渲染测试脚本")
# model = ModelParams(parser, sentinel=True)
# pipeline = PipelineParams(parser)
# parser.add_argument("--iteration", default=30000, type=int)
# parser.add_argument("--models", default='baseline',type=str) #'baseline','quantised' 'quantised_half'
# parser.add_argument("--quiet", action="store_true") #标记以省略写入标准输出管道的任何文本。
# args = get_combined_args(parser) # 从cfg_args加载路径
# safe_state(args.quiet)
# render_sets_handMode(model.extract(args), args.iteration, pipeline.extract(args))



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号