SoftGLRender源码:配置面板(ConfigPanel)
Config类
特性
文件:Config.h
Config类管理着SoftGLRender的配置资源,主要包括资源路径、渲染设置、场景参数等.
Config对象由ViewManager管理,但由ConfigPanel使用. 因此,介绍ConfigPanel时,需要先了解Config.
常量定义
资源路径
// 资源路径
const std::string ASSERTS_DIR = "./assets"; // 模型、贴图等路径
const std::string SHADER_GLSL_DR = "./shader/GLSL"; // 着色器路径
抗锯齿类型
抗锯齿技术可减少图形中锯齿状边缘. 2种常见抗锯齿技术:
-
MSAA 多重采样抗锯齿,对多边形的边缘进行多重采样(如4x、8x),通过混合相邻像素的颜色平滑锯齿. 仅对几何边缘处理,不处理纹理内部的锯齿.
质量较好,但速度慢. -
FXAA 快速近似抗锯齿,后处理的全屏模糊技术,通过快速模糊整个画面中的高对比度区域(包括边缘和纹理)来消除锯齿.
质量一般,但速度快.
// 抗锯齿类型
enum AAType {
AAType_NONE, // 无抗锯齿
AAType_MSAA, // 多重采样抗锯齿
AAType_FXAA, // 快速近似抗锯齿
};
Config类定义
class Config {
public:
// resource paths
// 管理当前加载的3D模型和skybox资源
std::string modelName;
std::string modelPath;
std::string skyboxName;
std::string skyboxPath;
// 模型的三角形总数
size_t triangleCount_ = 0;
// 显示控制
bool wireFrame = false; // 是否启用线框模式
bool worldAxis = true; // 是否显示世界坐标系
bool showSkybox = false; // 是否显示天空盒
bool showFloor = false; // 是否显示地面
bool shadowMap = true; // 是否启用阴影贴图
bool pbrIbl = false; // 是否启用基于图像的PBR光照
bool mipmaps = false; // 是否生成纹理Mipmap
bool cullFace = true; // 是否启用背面剔除
bool depthTest = true; // 是否启用深度测试
bool reverseZ = false; // 反转Z缓冲
glm::vec4 clearColor = { 0.f, 0.f, 0.f, 0.f }; // 清屏颜色(RGBA)
glm::vec3 ambientColor = { 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f }; // 环境光颜色(RGB)
bool showLight = true;
glm::vec3 pointLightPosition = { 0.f, 0.f, 0.f }; // 点光源位置
glm::vec3 pointLightColor = { 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f }; // 点光源颜色
// render mode
int aaType = AAType_NONE; // 抗锯齿类型(默认关闭)
int renderType = Renderer_SOFT; // 渲染器类型(默认为软光栅化)
};
reverseZ 反转深度缓冲范围,可减少远距离物体的Z-fighting问题.
pbrIbl 基于物理的渲染(PBR),基于图像的光照(IBR).
ConfigPanel类
特性
文件:ConfigPanel.h, ConfigPanel.cpp
ConfigPanel是一个UI强相关的类,主要负责利用配置(Config)信息构建配置面板界面,同时为用户提供交换接口.
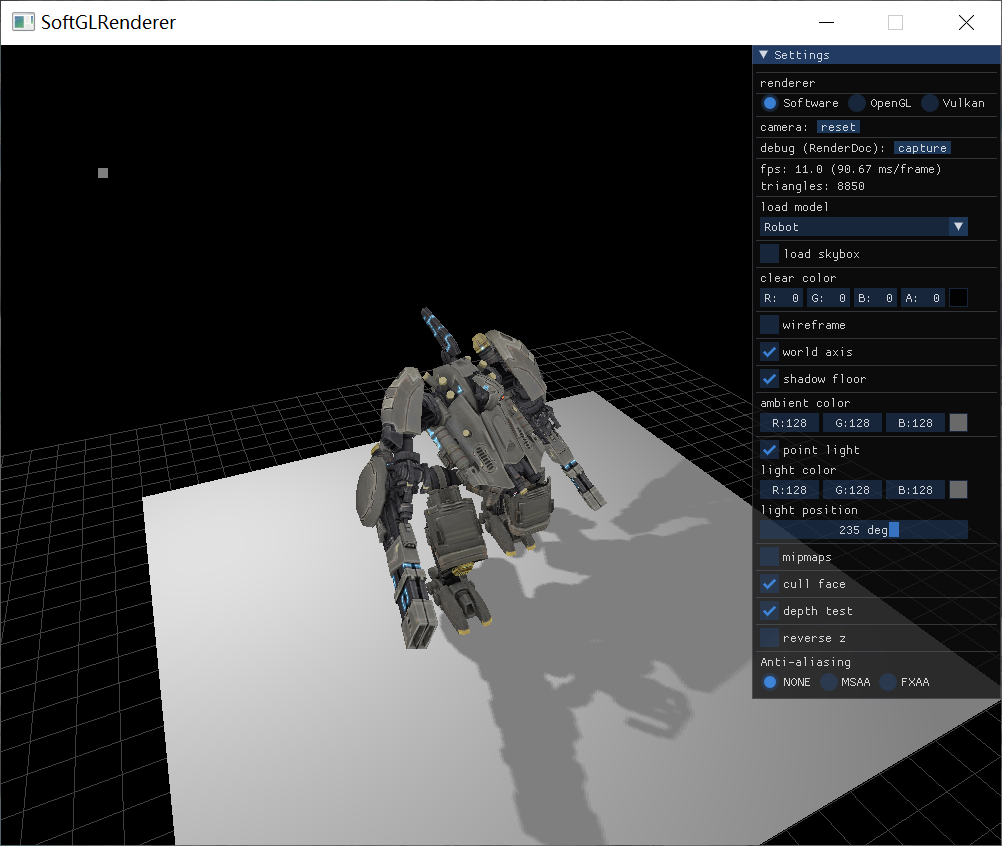
下图是SoftGLRender初始界面:
ConfigPanel数据成员
private:
Config &config_; // not the owner
// frame size
int frameWidth_ = 0;
int frameHeight_ = 0;
float lightPositionAngle_ = glm::radians(235.f); // 角度 -> 弧度
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> modelPaths_;
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> skyboxPaths_;
std::vector<const char*> modelNames_;
std::vector<const char*> skyboxNames_;
// callbacks
std::function<bool(const std::string& path)> reloadModelFunc_;
std::function<bool(const std::string& path)> reloadSkyboxFunc_;
std::function<void(glm::vec3& position, glm::vec3& color)> updateLightFunc_;
std::function<void(void)> resetCameraFunc_;
std::function<void(void)> resetMipmapFunc_;
std::function<void(void)> resetReverseZFunc_;
std::function<void(void)> frameDumpFunc_;
重用数据成员:
- config_,ConfigPanel类利用Config对象来配置界面,但本身并不持有Config对象,Config对象由ViewManager管理,同时,ConfigPanel对象也是被ViewManager管理,因此生存周期一致,只需要一个引用即可.
- lightPositionAngle_ 控制点光源位置的时候,是通过一个滑块控制角度lightPositionAngle_来实现的.
- modelPaths_, skyboxPaths_ 模型、天空盒资源路径. 路径和名称以json格式存放在json文件中.
- modelNames_, skyboxNames_ 模型、天空盒资源名称.
ConfigPanel函数成员
核心函数:
onDraw()主循环调用,绘制面板update()主循环调用,更新光源位置wantCaptureKeyboard()检测ImGUI是否希望捕获键盘输入wantCaptureMouse()检测ImGUI是否希望捕获鼠标输入loadConfig()根据Config模块信息,读取资源路径reloadModel()重载模型reloadSkybox()重载skyboxdrawSettings()负责实现绘制Settings面板内容
注意:ConfigPanel只负责读取资源路径,并转存给Config对象,并不直接读取模型文件. 也就是说,ConfigPanel不负责3D模型绘制.
构造与析构
ConfigPanel的构造函数很简单,从ViewManager接受Config对象,并绑定本地引用.
explicit ConfigPanel(Config &config) : config_(config) {}
ConfigPanel类的真正初始化,不是在ctor中,而是在init()中.
这部分主要工作:
1)初始化ImGui环境(见下文ImGui使用流程);
2)从Config模块加载资源路径;
注意:init不负责绘制界面
bool ConfigPanel::init(void* window, int width, int height) {
frameWidth_ = width;
frameHeight_ = height;
// 1. 创建上下文
// Setup Dear ImGui context
IMGUI_CHECKVERSION(); // 版本兼容性检查宏
ImGui::CreateContext();
ImGuiIO& io = ImGui::GetIO();
io.IniFilename = nullptr;
// 2. 设置样式
// Setup Dear ImGui style
ImGui::StyleColorsDark(); // Optional: Dark / Classic / Light
ImGuiStyle* style = &ImGui::GetStyle();
style->Alpha = 0.8f;
// 3. 初始化平台和渲染器绑定(示例: GLFW + OpenGL)
ImGui_ImplGlfw_InitForOpenGL((GLFWwindow *)window, true);
ImGui_ImplOpenGL3_Init("#version 330 core");
// load config
return loadConfig();
}
ConfigPanel::init()由ConfigPanel对象的拥有者ViewManager调用,这也是一种延迟初始化方式,可将类构造与初始化分离.
析构:主要回收在Init中申请的ImGui与OpenGL、glfw关联的资源
~ConfigPanel() { destroy(); };
void ConfigPanel::destroy() {
// 关闭后端
ImGui_ImplOpenGL3_Shutdown(); // 释放ImGui与OpenGL关联的资源, 与ImGui_ImplOpenGL3_Init配对
ImGui_ImplGlfw_Shutdown(); // 是否ImGui与glfw关联的资源,与ImGui_ImplGlfw_InitForOpenGL配对
// 销毁ImGui上下文
ImGui::DestroyContext();
}
加载资源路径
loadConfig 由init调用,主要负责从Config模块提供的信息加载资源路径.
bool ConfigPanel::loadConfig() {
auto configPath = ASSERTS_DIR + "assets.json"; // "./assets/assets.json"
auto configStr = FileUtils::readText(configPath); // 一次性读取所有文本
if (configStr.empty()) {
LOGE("load models failed: error read config file");
return false;
}
// 用json11库解析json文件
std::string err;
const auto json = json11::Json::parse(configStr, err);
// 找到 model 下所有路径
for (auto& kv : json["model"].object_items()) {
modelPaths_[kv.first] = ASSERTS_DIR + kv.second["path"].string_value();
}
// 找到 skybox 下所有路径
for (auto& kv : json["skybox"].object_items()) {
skyboxPaths_[kv.first] = ASSERTS_DIR + kv.second["path"].string_value();
}
if (modelPaths_.empty()) {
LOGE("load models failed: %s", err.c_str());
return false;
}
// 找到所有model路径下资源对应名称
for (const auto& kv : modelPaths_) {
modelNames_.emplace_back(kv.first.c_str());
}
// 找到所有skybox路径下资源对应名称
for (const auto& kv : skyboxPaths_) {
skyboxNames_.emplace_back(kv.first.c_str());
}
// load default model & skybox
return reloadModel(modelPaths_.begin()->first) && reloadSkybox(skyboxPaths_.begin()->first);
}
init中默认加载的model和skybox,是第一个从json文件读取到的资源.
"assets.json"文件,是以json格式存储了项目的模型(model)、天空盒(skybox)资源路径.
"assets.json"文件内容:
{
"model": {
"AfricanHead": {
"path": "AfricanHead/african_head.obj"
},
"Brickwall": {
"path": "Brickwall/brickwall.obj"
},
"Cube": {
"path": "Cube/Cube.gltf"
},
"DamagedHelmet": {
"path": "DamagedHelmet/DamagedHelmet.gltf"
},
"BoomBox": {
"path": "BoomBox/BoomBox.gltf"
},
"GlassTable": {
"path": "GlassTable/scene.gltf"
},
"Robot": {
"path": "Robot/scene.gltf"
}
},
"skybox": {
"Lake": {
"path": "Skybox/Lake/"
},
"Room": {
"path": "Skybox/Room.jpeg"
},
"Hotel": {
"path": "Skybox/Hotel.jpg"
}
}
}
加载model
加载model主要完成2个工作:
1)更新config配置中存放的mode name,model path信息;
2)回调用户定义的加载model函数;
// 加载指定名称的model
bool ConfigPanel::reloadModel(const std::string& name) {
if (name != config_.modelName) {
// 当前正在加载的model
config_.modelName = name;
config_.modelPath = modelPaths_[config_.modelName];
if (reloadModelFunc_) {
return reloadModelFunc_(config_.modelPath);
}
}
return true;
}
加载skybox
与加载model方式类似,不过加载资源的来源不同.
bool ConfigPanel::reloadSkybox(const std::string& name) {
if (name != config_.skyboxName) {
config_.skyboxName = name;
config_.skyboxPath = skyboxPaths_[config_.skyboxName];
if (reloadSkyboxFunc_) {
reloadModelFunc_(config_.skyboxPath);
}
}
return true;
}
绘制面板
main函数通过调用viewer->drawPanel();,进而调用configPanel_->onDraw();绘制配置面板.
也就是说,实际绘制工作由onDraw完成. 这部分ImGui的工作,可参考下文ImGui使用流程中的主循环渲染.
// 绘制面板,主循环调用
inline void drawPanel() {
if (showConfigPanel_) { // 如果启用了控制面板,则转发给onDraw()负责绘制工作
configPanel_->onDraw();
}
}
// 绘制面板
void ConfigPanel::onDraw() {
// 1. 启动新帧
// Start the Dear ImGui frame
ImGui_ImplOpenGL3_NewFrame(); // 渲染器绑定的 new frame
ImGui_ImplGlfw_NewFrame(); // 平台绑定的 new frame
ImGui::NewFrame(); // ImGui 本身的 new frame
// 2. 构建UI(核心逻辑)
// 开始一个窗口
ImGui::Begin(
"Settings",
nullptr,
ImGuiWindowFlags_NoSavedSettings | ImGuiWindowFlags_NoMove | ImGuiWindowFlags_NoResize);
drawSettings(); // 绘制设置菜单
ImGui::SetWindowPos(ImVec2(frameWidth_ - ImGui::GetWindowWidth(), 0));
ImGui::End(); // 结束窗口
// 3. 渲染UI
ImGui::Render();
ImGui_ImplOpenGL3_RenderDrawData(ImGui::GetDrawData());
}
其中,隐藏了一个重要的自定义函数drawSettings,用于专门绘制设置菜单内容.
绘制设置菜单
drawSettings 负责绘制菜单. 与onDraw主要区别:
onDraw绘制面板,同时为菜单绘制提供环境;drawSettings绘制面板中的菜单内容.
我们看下这个菜单包含哪些内容.
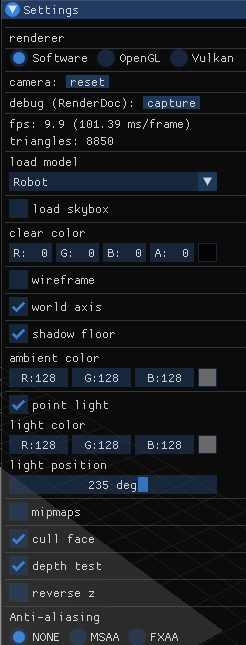
最上面窗口标题"Settings",是onDraw中设置的;从"renderer"文本开始,一直到最下面的"Aniti-aliasing"的3个选项,都由drawSettings负责.
renderer,包含3个单选选项{"Software","OpenGL","Vulkan"},用于选择渲染类型camera,包含1个reset按钮,用于重置相机debug,包含一个capture按钮,用于捕获画面(截图)fps,显示当前帧数triangles,显示当前模型的三角形总数load model,1个下拉框,选择要加载的当前模型(名称)load skybox,1个复选框,决定是否加载天空盒clear color,4个文本输入框,双击可以输入RGBA值,决定清除色(背景色);右键可以选择颜色模型、颜色范围wireframe,1个复选框,决定模型是否以网格形式显示world axis,1个复选框,决定是否显示世界坐标(地板上的网格)shadow floor,1个复选框,决定是否显示阴影地板ambient color,3个文本输入框、1个颜色选择按钮,双击可输入RGBA值,决定环境光颜色;单击颜色选择按钮,可从颜色图中选择颜色;右键可以选择颜色模型、颜色范围(类似于clear color部分)point light,1个复选框,决定是否使用场景中的点光源light color,点光源颜色. 设置方法类同ambient colorlight position,1个滑动条,设置光源角度,进而决定光源位置mipmaps,1个复选框,决定是否使用Mipmaps技术cull face,1个复选框,决定是否开启背面剔除depth test,1个复选框,决定是否开启深度测试reverse z,1个复选框,决定是否z缓冲反向Aniti-aliasing,3个单选框,决定使用哪种抗锯齿技术
// 绘制设置菜单
void ConfigPanel::drawSettings() {
// renderer
const char* rendererItems[] = {
"Software",
"OpenGL",
"Vulkan",
};
ImGui::Separator(); // UI中插入一条水平分隔线
ImGui::Text("renderer"); // UI中显示一段静态文本
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
if (ImGui::RadioButton(rendererItems[i], config_.renderType == i)) {
config_.renderType = i;
}
ImGui::SameLine(); // 将下一个控件放在同一行
}
ImGui::Separator();
// reset camera
ImGui::Separator();
ImGui::Text("camera");
ImGui::SameLine();
if (ImGui::SmallButton("reset")) {
if (resetCameraFunc_) {
resetCameraFunc_();
}
}
// frame dump
ImGui::Separator();
ImGui::Text("debug (RenderDoc):");
ImGui::SameLine();
if (ImGui::SmallButton("capture")) {
if (frameDumpFunc_) {
frameDumpFunc_();
}
}
// fps
ImGui::Separator();
ImGui::Text("fps: %.1f (%.2f ms/frame)", ImGui::GetIO().Framerate, 1000.f / ImGui::GetIO().Framerate);
// model
ImGui::Separator();
ImGui::Text("load model");
// find out current model
int modelIdx = 0;
for (; modelIdx < modelNames_.size(); modelIdx++) {
if (config_.modelName == modelNames_[modelIdx]) {
break;
}
}
// ImGui::Combo: 创建下拉选择框(类似于HTML <select>). 用户可以从预定义的选项列表中选择一个值
if (ImGui::Combo("##load model", &modelIdx, modelNames_.data(), (int)modelNames_.size())) {
reloadModel(modelNames_[modelIdx]);
}
// skybox
ImGui::Separator();
ImGui::Checkbox("load skybox", &config_.showSkybox);
if (config_.showSkybox) {
// pbr ibl
// PBR: Physically Based Rendering,基于物理的渲染
// IBL: Image-Based Lighting,基于图像的照明
int skyboxIdx = 0;
for (; skyboxIdx < skyboxNames_.size(); skyboxIdx++) {
reloadSkybox(skyboxNames_[skyboxIdx]);
}
}
// clear color
ImGui::Separator();
ImGui::Text("clear color");
// ImGui::ColorEdit4: 提供一个 颜色选择器,允许用户通过UI交互修改一个RGBA颜色值(4个float,范围 [0.0, 1.0])
// ImGuiColorEditFlags_NoLabel: 隐藏颜色选择器左侧的文本标签,仅保留颜色按钮和编辑区域
ImGui::ColorEdit4("clear color", (float*)&config_.clearColor, ImGuiColorEditFlags_NoLabel);
// wireframe
ImGui::Separator();
ImGui::Checkbox("wireframe", &config_.wireFrame);
// world axis
ImGui::Separator();
ImGui::Checkbox("world axis", &config_.worldAxis);
// shadow floor
ImGui::Separator();
ImGui::Checkbox("shadow floor", &config_.showFloor);
config_.shadowMap = config_.showFloor;
if (!config_.wireFrame) {
// light
ImGui::Separator();
ImGui::Text("ambient color");
// ImGui::ColorEdit3: 提供一个颜色选择器,用于编辑RGB颜色值(区别ImGui::ColorEdit4的RGBA值)
ImGui::ColorEdit3("ambient color", (float*)&config_.ambientColor, ImGuiColorEditFlags_NoLabel);
ImGui::Separator();
ImGui::Checkbox("point light", &config_.showLight);
if (config_.showLight) {
ImGui::Text("light color");
ImGui::ColorEdit3("light color", (float*)&config_.pointLightColor, ImGuiColorEditFlags_NoLabel);
ImGui::Text("light position");
// 通过滑块交互式地调整角度值(以弧度或度数为单位)
// 直观地显示角度范围(如 -180° 到 180°),适合旋转、方向控制等场景
ImGui::SliderAngle("##light position", &lightPositionAngle_, 0, 360.f);
}
// mipmaps
ImGui::Separator();
if (ImGui::Checkbox("mipmaps", &config_.mipmaps)) {
if (resetMipmapFunc_) {
resetMipmapFunc_();
}
}
}
// face cull
ImGui::Separator();
ImGui::Checkbox("cull face", &config_.cullFace);
// depth test
ImGui::Separator();
ImGui::Checkbox("depth test", &config_.depthTest);
// reverse Z
ImGui::Separator();
if (ImGui::Checkbox("reverse z", &config_.reverseZ)) {
if (resetReverseZFunc_) {
resetReverseZFunc_();
}
}
// Anti aliasing
const char* aaItems[] = {
"NONE",
"MSAA",
"FXAA",
};
ImGui::Separator();
ImGui::Text("Anti-aliasing");
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
if (ImGui::RadioButton(aaItems[i], config_.aaType == i)) {
config_.aaType = i;
}
ImGui::SameLine();
}
}
更新光源
update()负责更新光源位置,并回调用户更新光源的函数.
void ConfigPanel::update() {
// update light position
config_.pointLightPosition = 2.f * glm::vec3(
glm::sin(lightPositionAngle_),
1.2f,
glm::cos(lightPositionAngle_));
if (updateLightFunc_) {
updateLightFunc_(config_.pointLightPosition, config_.pointLightColor);
}
}
ConfigPanel从面板UI读取光源位置角度(滑块)、光源颜色(3个文本输入框),在update中转换为光源位置后,交给用户,根据用户自己的光照模型,对shading point进行着色.
设从滑块读取的光源位置角度\(α\in [0,360)deg\),则
可以看出,光源位置运行轨道是y=2.4的圆.
下面看看update的客户端是什么样的,即回调的是什么函数,客户如何更新光源的.
// ViewManager.h
void ViewManager::setupConfigPanelActions() {
...
// 更新光源时,同步更新场景点光源的属性
configPanel_->setUpdateLightFunc([&](glm::vec3& position, glm::vec3& color)->void {
auto& scene = modelLoader_->getScene();
scene.pointLight.vertexes[0].a_position = position; // 位置
scene.pointLight.UpdateVertexes(); // 同步GPU数据
scene.pointLight.material->baseColor = glm::vec4(color, 1.f); // 材质基础颜色
});
}
传入updateLightFunc_的是一个lambda表达式.
首先,利用ModelLoader对象获取场景Scene对象,然后用Scene设置点光源信息,接着将光源信息同步到GPU,最后将材质的基础颜色修改为光照颜色(update回调传入).
是否需要捕获IO事件
ImGui并不是随时随地都需要捕获鼠标、键盘等IO事件,有可能是其他程序需要捕获的事件. ImGui提供一组状态,用于判断鼠标、键盘等IO输入是否应由ImGui处理.
而ConfigPanel对这些状态用函数进行了包装:
wantCaptureKeyboard检查当前是否需要捕获键盘输入wantCaptureMouse检查当前是否需要捕获鼠标输入
// 检测ImGui 是否正在捕获键盘输入
// @return io.WantCaptureKeyboard,供外部逻辑判断是否屏蔽键盘输入
// - true:表示 ImGui 当前正在使用键盘输入(例如输入框聚焦、快捷键触发等),此时应禁止游戏/应用的键盘响应
// - false: 表示 ImGui 未占用键盘,游戏/应用可以处理键盘事件
bool ConfigPanel::wantCaptureKeyboard() {
ImGuiIO& io = ImGui::GetIO();
return io.WantCaptureKeyboard;
}
// 检测 ImGui 是否正在捕获鼠标输入
bool ConfigPanel::wantCaptureMouse() {
ImGuiIO& io = ImGui::GetIO();
return io.WantCaptureMouse;
}
可以看看ConfigPanel::wantCaptureMouse()的客户端,返回true时,直接忽略该事件;返回false,才处理.
// Main.cpp
// glfw: whenever the mouse moves, this callback is called
void mouseCallback(GLFWwindow* window, double xPos, double yPos) {
if (!viewer || viewer->wantCaptureMouse()) {
return;
}
...
}
ImGui
使用流程
ImGui使用流程:
- 初始化流程(GLFW+OpenGL3)
// 初始化GLFW和OpenGL上下文
glfwInit();
GLFWwindow* window = glfwCreateWindow(...);
// 初始化ImGui
IMGUI_CHECKVERSION();
ImGui::CreateContext();
ImGuiIO& io = ImGui::GetIO();
// 绑定后端
ImGui_ImplGlfw_InitForOpenGL(window, true);
ImGui_ImplOpenGL3_Init("#version 330"); // 匹配你的GLSL版本
// 设置样式
ImGui::StyleColorsDark();
- 主渲染循环
while (!glfwWindowShouldClose(window)) {
// draw frame use OpenGL
...
// 开始新帧
ImGui_ImplOpenGL3_NewFrame();
ImGui_ImplGlfw_NewFrame();
ImGui::NewFrame();
// 构建UI(示例:显示一个窗口)
ImGui::Begin("Demo Window");
ImGui::Text("Hello, OpenGL!");
if (ImGui::Button("Click Me")) { ... }
ImGui::End();
// 渲染
ImGui::Render();
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
// 实际绘制ImGui数据
ImGui_ImplOpenGL3_RenderDrawData(ImGui::GetDrawData());
glfwSwapBuffers(window);
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号