Linux通过systemctl管理服务
介绍
systemd:Linux系统初始化工具,负责系统启动、进程管理和服务调度;
- system是系统,systemd是系统的守护进程
systemd 管理的对象: 单元(Unit),包括服务(.service)、挂载点(.mount)、设备(.device)等;
systemd 日志服务:journalctl(systemd-journald的命令行工具)
systemctl:systemd的命令行工具,用于管理systemd单元(Unit)
服务管理
常见服务
- systemd-udevd.service:识别设备(USB、硬盘)
- sshd.service:SSH服务(远程登录、文件传输)
- ufw.service或者firewalld.service:防火墙
- httpd.service:Apache
服务目录
- /lib = /usr/lib

系统服务:/usr/lib/systemd/system/(低优先级、不建议手动修改)
自定义服务:/etc/systemd/system/ (高优先级)
- systemctl enable nginx.service(在指定的*.target.wants/目录下创建符号链接、/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/nginx.service)
- 开机后自动读取 multi-user.target.wants 目录下的服务进行启动
- multi-user.target.wants:系统进入多用户模式,需要启动的服务
- network-online.target.wants:系统的网络连接正常后,需要启动的服务
- 服务文件配置启动模式:[Install]、WantedBy=multi-user.target(服务需要随哪个 target 启动)
启动/停止/重启服务
systemctl list-unit-files --type=service # 查看所有服务(--state=failed、查看失败的)
systemctl list-units --type=service # 查看所有已启动的服务
systemctl start <service> # 启动服务(如ssh)
systemctl stop <service> # 停止服务
systemctl restart <service> # 重启服务
systemctl reload <service> # 重新加载配置(不重启服务)
查看服务状态
systemctl status <service>
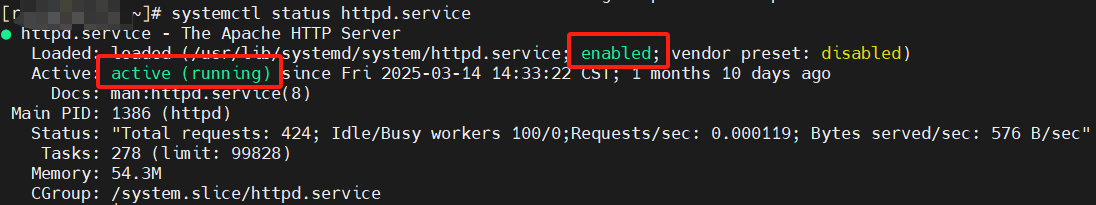
enabled:开机自启动
active(running):运行中
启用/禁用开机自启
systemctl enable <service> # 启用开机自启
systemctl disable <service> # 禁用开机自启
本文来自博客园,作者:Fēngwèi,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/fengwei-blogs/p/18839114




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号