spring security (史上最全)
文章很长,且持续更新,建议收藏起来,慢慢读!疯狂创客圈总目录 博客园版 为您奉上珍贵的学习资源 :
免费赠送 :《尼恩Java面试宝典》 持续更新+ 史上最全 + 面试必备 2000页+ 面试必备 + 大厂必备 +涨薪必备
免费赠送 :《尼恩技术圣经+高并发系列PDF》 ,帮你 实现技术自由,完成职业升级, 薪酬猛涨!加尼恩免费领
免费赠送 经典图书:《Java高并发核心编程(卷1)加强版》 面试必备 + 大厂必备 +涨薪必备 加尼恩免费领
免费赠送 经典图书:《Java高并发核心编程(卷2)加强版》 面试必备 + 大厂必备 +涨薪必备 加尼恩免费领
免费赠送 经典图书:《Java高并发核心编程(卷3)加强版》 面试必备 + 大厂必备 +涨薪必备 加尼恩免费领
免费赠送 资源宝库: Java 必备 百度网盘资源大合集 价值>10000元 加尼恩领取
认证与授权(Authentication and Authorization)
一般意义来说的应用访问安全性,都是围绕认证(Authentication)和授权(Authorization)这两个核心概念来展开的。
即:
- 首先需要确定用户身份,
- 再确定这个用户是否有访问指定资源的权限。
认证这块的解决方案很多,主流的有CAS、SAML2、OAUTH2等(不巧这几个都用过-_-),我们常说的单点登录方案(SSO)说的就是这块,
授权的话主流的就是spring security和shiro。
shiro比较轻量级,相比较而言spring security确实架构比较复杂。但是shiro与 ss,掌握一个即可。
什么是OAuth2 ?
OAuth2是一个关于授权的开放标准,核心思路是通过各类认证手段(具体什么手段OAuth2不关心)认证用户身份,
并颁发token(令牌),使得第三方应用可以使用该令牌在限定时间、限定范围访问指定资源。
主要涉及的RFC规范有【RFC6749(整体授权框架)】、【RFC6750(令牌使用)】、【RFC6819(威胁模型)】这几个,一般我们需要了解的就是RFC6749。
获取令牌的方式主要有四种,分别是授权码模式、简单模式、密码模式、客户端模式,
总之:OAuth2是一个授权(Authorization)协议。
认证(Authentication)证明的你是不是这个人,
而授权(Authorization)则是证明这个人有没有访问这个资源(Resource)的权限。
下面这张图来源于OAuth 2.0 authorization framework RFC Document,是OAuth2的一个抽象流程。
+--------+ +---------------+
| |--(A)- Authorization Request ->| Resource |
| | | Owner |
| |<-(B)-- Authorization Grant ---| |
| | +---------------+
| |
| | +---------------+
| |--(C)-- Authorization Grant -->| Authorization |
| Client | | Server |
| |<-(D)----- Access Token -------| |
| | +---------------+
| |
| | +---------------+
| |--(E)----- Access Token ------>| Resource |
| | | Server |
| |<-(F)--- Protected Resource ---| |
+--------+ +---------------+
先来解释一下上图的名词:
Resource Owner:资源所有者,即用户
Client:客户端应用程序(Application)
Authorization Server:授权服务器
Resource Server:资源服务器
再来解释一下上图的大致流程:
(A) 用户连接客户端应用程序以后,客户端应用程序要求用户给予授权
(B) 用户同意给予客户端应用程序授权
(C) 客户端应用程序使用上一步获得的授权(Grant),向授权服务器申请令牌
(D) 授权服务器对客户端应用程序的授权(Grant)进行验证后,确认无误,发放令牌
(E) 客户端应用程序使用令牌,向资源服务器申请获取资源
(F) 资源服务器确认令牌无误,同意向客户端应用程序开放资源
从上面的流程可以看出,如何获取授权(Grant)才是关键。
在OAuth2中有4种授权类型:
- Authorization Code(授权码模式):
功能最完整、流程最严密的授权模式。通过第三方应用程序服务器与认证服务器进行互动。广泛用于各种第三方认证。
- Implicit(简化模式):
不通过第三方应用程序服务器,直接在浏览器中向认证服务器申请令牌,更加适用于移动端的App及没有服务器端的第三方单页面应用。
- Resource Owner Password(密码模式):
用户向客户端服务器提供自己的用户名和密码,用户对客户端高度信任的情况下使用,比如公司、组织的内部系统,SSO。
- Client Credentials(客户端模式):
客户端服务器以自己的名义,而不是以用户的名义,向认证服务器进行认证。
下面主要讲最常用的(1)和(3)。此外,还有一个模式叫Refresh Token,也会在下面介绍。
Resource Owner Password(密码模式)
+----------+
| Resource |
| Owner |
| |
+----------+
v
| Resource Owner
(A) Password Credentials
|
v
+---------+ +---------------+
| |>--(B)---- Resource Owner ------->| |
| | Password Credentials | Authorization |
| Client | | Server |
| |<--(C)---- Access Token ---------<| |
| | (w/ Optional Refresh Token) | |
+---------+ +---------------+
Figure 5: Resource Owner Password Credentials Flow
它的步骤如下:
(A) 用户(Resource Owner)向客户端(Client)提供用户名和密码。
(B) 客户端将用户名和密码发给认证服务器(Authorization Server),向后者请求令牌。
(C) 认证服务器确认无误后,向客户端提供访问令牌。
Authorization Code(授权码模式)
+----------+
| Resource |
| Owner |
| |
+----------+
^
|
(B)
+----|-----+ Client Identifier +---------------+
| -+----(A)-- & Redirection URI ---->| |
| User- | | Authorization |
| Agent -+----(B)-- User authenticates --->| Server |
| | | |
| -+----(C)-- Authorization Code ---<| |
+-|----|---+ +---------------+
| | ^ v
(A) (C) | |
| | | |
^ v | |
+---------+ | |
| |>---(D)-- Authorization Code ---------' |
| Client | & Redirection URI |
| | |
| |<---(E)----- Access Token -------------------'
+---------+ (w/ Optional Refresh Token)
Note: The lines illustrating steps (A), (B), and (C) are broken into
two parts as they pass through the user-agent.
它的步骤如下:
(A) 用户(Resource Owner)通过用户代理(User-Agent)访问客户端(Client),客户端索要授权,并将用户导向认证服务器(Authorization Server)。
(B) 用户选择是否给予客户端授权。
(C) 假设用户给予授权,认证服务器将用户导向客户端事先指定的"重定向URI"(redirection URI),同时附上一个授权码。
(D) 客户端收到授权码,附上早先的"重定向URI",向认证服务器申请令牌。这一步是在客户端的后台的服务器上完成的,对用户不可见。
(E) 认证服务器核对了授权码和重定向URI,确认无误后,向客户端发送访问令牌(access token)和更新令牌(refresh token)。这一步也对用户不可见。
令牌刷新(refresh token)
+--------+ +---------------+
| |--(A)------- Authorization Grant --------->| |
| | | |
| |<-(B)----------- Access Token -------------| |
| | & Refresh Token | |
| | | |
| | +----------+ | |
| |--(C)---- Access Token ---->| | | |
| | | | | |
| |<-(D)- Protected Resource --| Resource | | Authorization |
| Client | | Server | | Server |
| |--(E)---- Access Token ---->| | | |
| | | | | |
| |<-(F)- Invalid Token Error -| | | |
| | +----------+ | |
| | | |
| |--(G)----------- Refresh Token ----------->| |
| | | |
| |<-(H)----------- Access Token -------------| |
+--------+ & Optional Refresh Token +---------------+
当我们申请token后,Authorization Server不仅给了我们Access Token,还有Refresh Token。
当Access Token过期后,我们用Refresh Token访问/refresh端点就可以拿到新的Access Token了。
我们要和Spring Security的认证(Authentication)区别开来,
什么是Spring Security?
Spring Security是一套安全框架,可以基于RBAC(基于角色的权限控制)对用户的访问权限进行控制,
核心思想是通过一系列的filter chain来进行拦截过滤,对用户的访问权限进行控制,
spring security 的核心功能主要包括:
-
认证 (你是谁)
-
授权 (你能干什么)
-
攻击防护 (防止伪造身份)
其核心就是一组过滤器链,项目启动后将会自动配置。最核心的就是 Basic Authentication Filter 用来认证用户的身份,一个在spring security中一种过滤器处理一种认证方式。
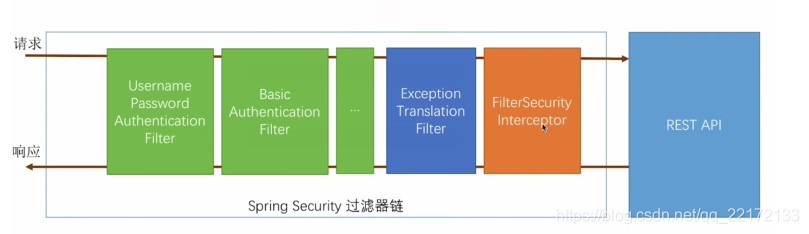
比如,对于username password认证过滤器来说,
会检查是否是一个登录请求;
是否包含username 和 password (也就是该过滤器需要的一些认证信息) ;
如果不满足则放行给下一个。
下一个按照自身职责判定是否是自身需要的信息,basic的特征就是在请求头中有 Authorization:Basic eHh4Onh4 的信息。中间可能还有更多的认证过滤器。**最后一环是 FilterSecurityInterceptor**,这里会判定该请求是否能进行访问rest服务,判断的依据是 BrowserSecurityConfig中的配置,如果被拒绝了就会抛出不同的异常(根据具体的原因)。Exception Translation Filter 会捕获抛出的错误,然后根据不同的认证方式进行信息的返回提示。
注意:绿色的过滤器可以配置是否生效,其他的都不能控制。
二、入门项目
首先创建spring boot项目HelloSecurity,其pom主要依赖如下:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
然后在src/main/resources/templates/目录下创建页面:
home.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org" xmlns:sec="http://www.thymeleaf.org/thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity3">
<head>
<title>Spring Security Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome!</h1>
<p>Click <a th:href="@{/hello}">here</a> to see a greeting.</p>
</body>
</html>
我们可以看到, 在这个简单的视图中包含了一个链接: “/hello”. 链接到了如下的页面,Thymeleaf模板如下:
hello.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"
xmlns:sec="http://www.thymeleaf.org/thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity3">
<head>
<title>Hello World!</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello world!</h1>
</body>
</html>
Web应用程序基于Spring MVC。 因此,你需要配置Spring MVC并设置视图控制器来暴露这些模板。 如下是一个典型的Spring MVC配置类。在src/main/java/hello目录下(所以java都在这里):
@Configuration
public class MvcConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController("/home").setViewName("home");
registry.addViewController("/").setViewName("home");
registry.addViewController("/hello").setViewName("hello");
registry.addViewController("/login").setViewName("login");
}
}
addViewControllers()方法(覆盖WebMvcConfigurerAdapter中同名的方法)添加了四个视图控制器。 两个视图控制器引用名称为“home”的视图(在home.html中定义),另一个引用名为“hello”的视图(在hello.html中定义)。 第四个视图控制器引用另一个名为“login”的视图。 将在下一部分中创建该视图。此时,可以跳过来使应用程序可执行并运行应用程序,而无需登录任何内容。然后启动程序如下:
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Throwable {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
2、加入Spring Security
假设你希望防止未经授权的用户访问“/ hello”。 此时,如果用户点击主页上的链接,他们会看到问候语,请求被没有被拦截。 你需要添加一个障碍,使得用户在看到该页面之前登录。您可以通过在应用程序中配置Spring Security来实现。 如果Spring Security在类路径上,则Spring Boot会使用“Basic认证”来自动保护所有HTTP端点。 同时,你可以进一步自定义安全设置。首先在pom文件中引入:
<dependencies>
...
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
...
</dependencies>
如下是安全配置,使得只有认证过的用户才可以访问到问候页面:
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/", "/home").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login")
.permitAll()
.and()
.logout()
.permitAll();
}
@Autowired
public void configureGlobal(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth
.inMemoryAuthentication()
.withUser("user").password("password").roles("USER");
}
}
WebSecurityConfig类使用了@EnableWebSecurity注解 ,以**启用Spring Security的Web安全支持**,并提供Spring MVC集成。它还扩展了WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter,并覆盖了一些方法来设置Web安全配置的一些细节。
**configure(HttpSecurity)方法定义了哪些URL路径应该被保护**,哪些不应该。具体来说,“/”和“/ home”路径被配置为不需要任何身份验证。所有其他路径必须经过身份验证。
当用户成功登录时,它们将被重定向到先前请求的需要身份认证的页面。有一个由 loginPage()指定的自定义“/登录”页面,每个人都可以查看它。
对于configureGlobal(AuthenticationManagerBuilder) 方法,它将单个用户设置在内存中。该用户的用户名为“user”,密码为“password”,角色为“USER”。
现在我们需要创建登录页面。前面我们已经配置了“login”的视图控制器,因此现在只需要创建登录页面即可:
login.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"
xmlns:sec="http://www.thymeleaf.org/thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity3">
<head>
<title>Spring Security Example </title>
</head>
<body>
<div th:if="${param.error}">
Invalid username and password.
</div>
<div th:if="${param.logout}">
You have been logged out.
</div>
<form th:action="@{/login}" method="post">
<div><label> User Name : <input type="text" name="username"/> </label></div>
<div><label> Password: <input type="password" name="password"/> </label></div>
<div><input type="submit" value="Sign In"/></div>
</form>
</body>
</html>
你可以看到,这个Thymeleaf模板只是提供一个表单来获取用户名和密码,并将它们提交到“/ login”。 根据配置,Spring Security提供了一个拦截该请求并验证用户的过滤器。 如果用户未通过认证,该页面将重定向到“/ login?error”,并在页面显示相应的错误消息。 注销成功后,我们的应用程序将发送到“/ login?logout”,我们的页面显示相应的登出成功消息。最后,我们需要向用户提供一个显示当前用户名和登出的方法。 更新hello.html 向当前用户打印一句hello,并包含一个“注销”表单,如下所示:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"
xmlns:sec="http://www.thymeleaf.org/thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity3">
<head>
<title>Hello World!</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1 th:inline="text">Hello [[${#httpServletRequest.remoteUser}]]!</h1>
<form th:action="@{/logout}" method="post">
<input type="submit" value="Sign Out"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
三、参数详解
1、注解 @EnableWebSecurity
在 Spring boot 应用中使用 Spring Security,用到了 @EnableWebSecurity注解,官方说明为,该注解和 @Configuration 注解一起使用, 注解 WebSecurityConfigurer 类型的类,或者利用@EnableWebSecurity 注解继承 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter的类,这样就构成了 Spring Security 的配置。
2、抽象类 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter
一般情况,会选择继承 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 类,其官方说明为:WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 提供了一种便利的方式去创建 WebSecurityConfigurer的实例,只需要重写 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 的方法,即可配置拦截什么URL、设置什么权限等安全控制。
3、方法 configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) 和 configure(HttpSecurity http)
Demo 中重写了 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 的两个方法:
/**
* 通过 {@link #authenticationManager()} 方法的默认实现尝试获取一个 {@link AuthenticationManager}.
* 如果被复写, 应该使用{@link AuthenticationManagerBuilder} 来指定 {@link AuthenticationManager}.
*
* 例如, 可以使用以下配置在内存中进行注册公开内存的身份验证{@link UserDetailsService}:
*
* // 在内存中添加 user 和 admin 用户
* @Override
* protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) {
* auth
* .inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("user").password("password").roles("USER").and()
* .withUser("admin").password("password").roles("USER", "ADMIN");
* }
*
* // 将 UserDetailsService 显示为 Bean
* @Bean
* @Override
* public UserDetailsService userDetailsServiceBean() throws Exception {
* return super.userDetailsServiceBean();
* }
*
*/
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
this.disableLocalConfigureAuthenticationBldr = true;
}
/**
* 复写这个方法来配置 {@link HttpSecurity}.
* 通常,子类不能通过调用 super 来调用此方法,因为它可能会覆盖其配置。 默认配置为:
*
* http.authorizeRequests().anyRequest().authenticated().and().formLogin().and().httpBasic();
*
*/
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
logger.debug("Using default configure(HttpSecurity). If subclassed this will potentially override subclass configure(HttpSecurity).");
http
.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin().and()
.httpBasic();
}
4、final 类 HttpSecurity
HttpSecurity 常用方法及说明:
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
openidLogin() |
用于基于 OpenId 的验证 |
headers() |
将安全标头添加到响应 |
cors() |
配置跨域资源共享( CORS ) |
sessionManagement() |
允许配置会话管理 |
portMapper() |
允许配置一个PortMapper(HttpSecurity#(getSharedObject(class))),其他提供SecurityConfigurer的对象使用 PortMapper 从 HTTP 重定向到 HTTPS 或者从 HTTPS 重定向到 HTTP。默认情况下,Spring Security使用一个PortMapperImpl映射 HTTP 端口8080到 HTTPS 端口8443,HTTP 端口80到 HTTPS 端口443 |
jee() |
配置基于容器的预认证。 在这种情况下,认证由Servlet容器管理 |
x509() |
配置基于x509的认证 |
rememberMe |
允许配置“记住我”的验证 |
authorizeRequests() |
允许基于使用HttpServletRequest限制访问 |
requestCache() |
允许配置请求缓存 |
exceptionHandling() |
允许配置错误处理 |
securityContext() |
在HttpServletRequests之间的SecurityContextHolder上设置SecurityContext的管理。 当使用WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter时,这将自动应用 |
servletApi() |
将HttpServletRequest方法与在其上找到的值集成到SecurityContext中。 当使用WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter时,这将自动应用 |
csrf() |
添加 CSRF 支持,使用WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter时,默认启用 |
logout() |
添加退出登录支持。当使用WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter时,这将自动应用。默认情况是,访问URL”/ logout”,使HTTP Session无效来清除用户,清除已配置的任何#rememberMe()身份验证,清除SecurityContextHolder,然后重定向到”/login?success” |
anonymous() |
允许配置匿名用户的表示方法。 当与WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter结合使用时,这将自动应用。 默认情况下,匿名用户将使用org.springframework.security.authentication.AnonymousAuthenticationToken表示,并包含角色 “ROLE_ANONYMOUS” |
formLogin() |
指定支持基于表单的身份验证。如果未指定FormLoginConfigurer#loginPage(String),则将生成默认登录页面 |
oauth2Login() |
根据外部OAuth 2.0或OpenID Connect 1.0提供程序配置身份验证 |
requiresChannel() |
配置通道安全。为了使该配置有用,必须提供至少一个到所需信道的映射 |
httpBasic() |
配置 Http Basic 验证 |
addFilterAt() |
在指定的Filter类的位置添加过滤器 |
5、类 AuthenticationManagerBuilder
/**
* {@link SecurityBuilder} used to create an {@link AuthenticationManager}. Allows for
* easily building in memory authentication, LDAP authentication, JDBC based
* authentication, adding {@link UserDetailsService}, and adding
* {@link AuthenticationProvider}'s.
*/
意思是,AuthenticationManagerBuilder 用于创建一个 AuthenticationManager,让我能够轻松的实现内存验证、LADP验证、基于JDBC的验证、添加UserDetailsService、添加AuthenticationProvider。
使用yaml文件定义的用户名、密码登录
在application.yaml中定义用户名密码:
spring:
security:
user:
name: root
password: root
使用root/root登录,可以正常访问/hello。
使用代码中指定的用户名、密码登录
- 使用configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder) 添加认证。
- 使用configure(httpSecurity) 添加权限
@Configuration
public class MySecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth
.inMemoryAuthentication()
.withUser("admin") // 添加用户admin
.password("{noop}admin") // 不设置密码加密
.roles("ADMIN", "USER")// 添加角色为admin,user
.and()
.withUser("user") // 添加用户user
.password("{noop}user")
.roles("USER")
.and()
.withUser("tmp") // 添加用户tmp
.password("{noop}tmp")
.roles(); // 没有角色
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/product/**").hasRole("USER") //添加/product/** 下的所有请求只能由user角色才能访问
.antMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN") //添加/admin/** 下的所有请求只能由admin角色才能访问
.anyRequest().authenticated() // 没有定义的请求,所有的角色都可以访问(tmp也可以)。
.and()
.formLogin().and()
.httpBasic();
}
}
添加AdminController、ProductController
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/admin")
public class AdminController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return "admin hello";
}
}
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/product")
public class ProductController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return "product hello";
}
}
通过上面的设置,访问http://localhost:8080/admin/hello只能由admin访问,http://localhost:8080/product/hello admin和user都可以访问,http://localhost:8080/hello 所有用户(包括tmp)都可以访问。
使用数据库的用户名、密码登录
添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
添加数据库配置
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/demo?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
username: root
password: root
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
配置spring-security认证和授权
@Configuration
public class MySecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsService)// 设置自定义的userDetailsService
.passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder());
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/product/**").hasRole("USER")
.antMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN")
.anyRequest().authenticated() //
.and()
.formLogin()
.and()
.httpBasic()
.and().logout().logoutUrl("/logout");
}
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance();// 使用不使用加密算法保持密码
// return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
}
如果需要使用BCryptPasswordEncoder,可以先在测试环境中加密后放到数据库中:
@Test
void encode() {
BCryptPasswordEncoder bCryptPasswordEncoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
String password = bCryptPasswordEncoder.encode("user");
String password2 = bCryptPasswordEncoder.encode("admin");
System.out.println(password);
System.out.println(password2);
}
配置自定义UserDetailsService来进行验证
@Component("userDetailsService")
public class CustomUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService {
@Autowired
UserRepository userRepository;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String login) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
// 1. 查询用户
User userFromDatabase = userRepository.findOneByLogin(login);
if (userFromDatabase == null) {
//log.warn("User: {} not found", login);
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("User " + login + " was not found in db");
//这里找不到必须抛异常
}
// 2. 设置角色
Collection<GrantedAuthority> grantedAuthorities = new ArrayList<>();
GrantedAuthority grantedAuthority = new SimpleGrantedAuthority(userFromDatabase.getRole());
grantedAuthorities.add(grantedAuthority);
return new org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User(login,
userFromDatabase.getPassword(), grantedAuthorities);
}
}
配置JPA中的UserRepository
@Repository
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
User findOneByLogin(String login);
}
添加数据库数据
CREATE TABLE `user` (
`id` int(28) NOT NULL,
`login` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci DEFAULT NULL,
`password` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci DEFAULT NULL,
`role` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_general_ci;
INSERT INTO `demo`.`user`(`id`, `login`, `password`, `role`) VALUES (1, 'user', 'user', 'ROLE_USER');
INSERT INTO `demo`.`user`(`id`, `login`, `password`, `role`) VALUES (2, 'admin', 'admin', 'ROLE_ADMIN');
默认角色前缀必须是
ROLE_,因为spring-security会在授权的时候自动使用match中的角色加上ROLE_后进行比较。
四:获取登录信息
@RequestMapping("/info")
public String info(){
String userDetails = null;
Object principal = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal();
if(principal instanceof UserDetails) {
userDetails = ((UserDetails)principal).getUsername();
}else {
userDetails = principal.toString();
}
return userDetails;
}
使用SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal();获取当前的登录信息。
五: Spring Security 核心组件
SecurityContext
SecurityContext是安全的上下文,所有的数据都是保存到SecurityContext中。
可以通过SecurityContext获取的对象有:
- Authentication
SecurityContextHolder
SecurityContextHolder用来获取SecurityContext中保存的数据的工具。通过使用静态方法获取SecurityContext的相对应的数据。
SecurityContext context = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();
Authentication
Authentication表示当前的认证情况,可以获取的对象有:
UserDetails:获取用户信息,是否锁定等额外信息。
Credentials:获取密码。
isAuthenticated:获取是否已经认证过。
Principal:获取用户,如果没有认证,那么就是用户名,如果认证了,返回UserDetails。
UserDetails
public interface UserDetails extends Serializable {
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities();
String getPassword();
String getUsername();
boolean isAccountNonExpired();
boolean isAccountNonLocked();
boolean isCredentialsNonExpired();
boolean isEnabled();
}
UserDetailsService
UserDetailsService可以通过loadUserByUsername获取UserDetails对象。该接口供spring security进行用户验证。
通常使用自定义一个CustomUserDetailsService来实现UserDetailsService接口,通过自定义查询UserDetails。
AuthenticationManager
AuthenticationManager用来进行验证,如果验证失败会抛出相对应的异常。
PasswordEncoder
密码加密器。通常是自定义指定。
BCryptPasswordEncoder:哈希算法加密
NoOpPasswordEncoder:不使用加密
六:spring security session 无状态支持权限控制(前后分离)
spring security会在默认的情况下将认证信息放到HttpSession中。
但是对于我们的前后端分离的情况,如app,小程序,web前后分离等,httpSession就没有用武之地了。这时我们可以通过
configure(httpSecurity)设置spring security是否使用httpSession。
@Configuration
public class MySecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
// code...
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.sessionManagement()
//设置无状态,所有的值如下所示。
.sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS)
// code...
}
// code...
}
共有四种值,其中默认的是ifRequired。
- always – a session will always be created if one doesn’t already exist,没有session就创建。
- ifRequired – a session will be created only if required (default),如果需要就创建(默认)。
- never – the framework will never create a session itself but it will use one if it already exists
- stateless – no session will be created or used by Spring Security 不创建不使用session
由于前后端不通过保存session和cookie来进行判断,所以为了保证spring security能够记录登录状态,所以需要传递一个值,让这个值能够自我验证来源,同时能够得到数据信息。选型我们选择JWT。对于java客户端我们选择使用jjwt。
添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId>
<artifactId>jjwt-api</artifactId>
<version>0.11.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId>
<artifactId>jjwt-impl</artifactId>
<version>0.11.2</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId>
<artifactId>jjwt-jackson</artifactId> <!-- or jjwt-gson if Gson is preferred -->
<version>0.11.2</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
创建工具类JWTProvider
JWTProvider需要至少提供两个方法,一个用来创建我们的token,另一个根据token获取Authentication。
provider需要保证Key密钥是唯一的,使用init()构建,否则会抛出异常。
@Component
@Slf4j
public class JWTProvider {
private Key key; // 私钥
private long tokenValidityInMilliseconds; // 有效时间
private long tokenValidityInMillisecondsForRememberMe; // 记住我有效时间
@Autowired
private JJWTProperties jjwtProperties; // jwt配置参数
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
byte[] keyBytes;
String secret = jjwtProperties.getSecret();
if (StringUtils.hasText(secret)) {
log.warn("Warning: the JWT key used is not Base64-encoded. " +
"We recommend using the `jhipster.security.authentication.jwt.base64-secret` key for optimum security.");
keyBytes = secret.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
} else {
log.debug("Using a Base64-encoded JWT secret key");
keyBytes = Decoders.BASE64.decode(jjwtProperties.getBase64Secret());
}
this.key = Keys.hmacShaKeyFor(keyBytes); // 使用mac-sha算法的密钥
this.tokenValidityInMilliseconds =
1000 * jjwtProperties.getTokenValidityInSeconds();
this.tokenValidityInMillisecondsForRememberMe =
1000 * jjwtProperties.getTokenValidityInSecondsForRememberMe();
}
public String createToken(Authentication authentication, boolean rememberMe) {
long now = (new Date()).getTime();
Date validity;
if (rememberMe) {
validity = new Date(now + this.tokenValidityInMillisecondsForRememberMe);
} else {
validity = new Date(now + this.tokenValidityInMilliseconds);
}
User user = userRepository.findOneByLogin(authentication.getName());
Map<String ,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("sub",authentication.getName());
map.put("user",user);
return Jwts.builder()
.setClaims(map) // 添加body
.signWith(key, SignatureAlgorithm.HS512) // 指定摘要算法
.setExpiration(validity) // 设置有效时间
.compact();
}
public Authentication getAuthentication(String token) {
Claims claims = Jwts.parserBuilder()
.setSigningKey(key)
.build()
.parseClaimsJws(token).getBody(); // 根据token获取body
User principal;
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities;
principal = userRepository.findOneByLogin(claims.getSubject());
authorities = principal.getAuthorities();
return new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(principal, token, authorities);
}
}
注意这里我们创建的User需要实现UserDetails对象,这样我们可以根据
principal.getAuthorities()获取到权限,如果不实现UserDetails,那么需要自定义authorities并添加到UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken中。
@Data
@Entity
@Table(name="user")
public class User implements UserDetails {
@Id
@Column
private Long id;
@Column
private String login;
@Column
private String password;
@Column
private String role;
@Override
// 获取权限,这里就用简单的方法
// 在spring security中,Authorities既可以是ROLE也可以是Authorities
public Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities() {
return Collections.singleton(new SimpleGrantedAuthority(role));
}
@Override
public String getUsername() {
return login;
}
@Override
public boolean isAccountNonExpired() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isAccountNonLocked() {
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean isCredentialsNonExpired() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isEnabled() {
return true;
}
}
创建登录成功,登出成功处理器
登录成功后向前台发送jwt。
认证成功,返回jwt:
public class MyAuthenticationSuccessHandler implements AuthenticationSuccessHandler{
void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException{
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.println(jwtProvider.createToken(authentication, true));
}
}
登出成功:
public class MyLogoutSuccessHandler implements LogoutSuccessHandler {
void onLogoutSuccess(HttpServletRequest var1, HttpServletResponse var2, Authentication var3) throws IOException, ServletException{
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.println("logout success");
writer.flush();
}
}
设置登录、登出、取消csrf防护
登出无法对token进行失效操作,可以使用数据库保存token,然后在登出时删除该token。
@Configuration
public class MySecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
// code...
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
// code...
// 添加登录处理器
.formLogin().loginProcessingUrl("/login").successHandler((request, response, authentication) -> {
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.println(jwtProvider.createToken(authentication, true));
})
// 取消csrf防护
.and().csrf().disable()
// code...
// 添加登出处理器
.and().logout().logoutUrl("/logout").logoutSuccessHandler((HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) -> {
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.println("logout success");
writer.flush();
})
// code...
}
// code...
}
使用JWT集成spring-security
添加Filter供spring-security解析token,并向securityContext中添加我们的用户信息。
在UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class之前我们需要执行根据token添加authentication。关键方法是从jwt中获取authentication,然后添加到securityContext中。
在SecurityConfiguration中需要设置Filter添加的位置。
创建自定义Filter,用于jwt获取authentication:
@Slf4j
public class JWTFilter extends GenericFilterBean {
private final static String HEADER_AUTH_NAME = "auth";
private JWTProvider jwtProvider;
public JWTFilter(JWTProvider jwtProvider) {
this.jwtProvider = jwtProvider;
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
try {
HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest;
String authToken = httpServletRequest.getHeader(HEADER_AUTH_NAME);
if (StringUtils.hasText(authToken)) {
// 从自定义tokenProvider中解析用户
Authentication authentication = this.jwtProvider.getAuthentication(authToken);
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authentication);
}
// 调用后续的Filter,如果上面的代码逻辑未能复原“session”,SecurityContext中没有想过信息,后面的流程会检测出"需要登录"
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest, servletResponse);
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
}
}
向HttpSecurity添加Filter和设置Filter位置:
public class MySecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
// code...
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.sessionManagement()
//设置添加Filter和位置
.and().addFilterBefore(new JWTFilter(jwtProvider), UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
// code...
}
// code...
}
MySecurityConfiguration代码
@Configuration
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)
public class MySecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
@Autowired
private JWTProvider jwtProvider;
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsService)// 设置自定义的userDetailsService
.passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder());
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.sessionManagement()
.sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS)//设置无状态
.and()
.authorizeRequests() // 配置请求权限
.antMatchers("/product/**").hasRole("USER") // 需要角色
.antMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN")
.anyRequest().authenticated() // 所有的请求都需要登录
.and()
// 配置登录url,和登录成功处理器
.formLogin().loginProcessingUrl("/login").successHandler((request, response, authentication) -> {
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.println(jwtProvider.createToken(authentication, true));
})
// 取消csrf防护
.and().csrf().disable()
.httpBasic()
// 配置登出url,和登出成功处理器
.and().logout().logoutUrl("/logout")
.logoutSuccessHandler((HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) -> {
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.println("logout success");
writer.flush();
})
// 在UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter之前执行我们添加的JWTFilter
.and().addFilterBefore(new JWTFilter(jwtProvider), UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
}
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance();
}
@Override
public void configure(WebSecurity web) {
// 添加不做权限的URL
web.ignoring()
.antMatchers("/swagger-resources/**")
.antMatchers("/swagger-ui.html")
.antMatchers("/webjars/**")
.antMatchers("/v2/**")
.antMatchers("/h2-console/**");
}
}
使用注解对方法进行权限管理
需要在
MySecurityConfiguration上添加@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)注解,prePostEnabled默认为false,需要设置为true后才能全局的注解权限控制。
prePostEnabled设置为true后,可以使用四个注解:
添加实体类School:
@Data
public class School implements Serializable {
private Long id;
private String name;
private String address;
}
-
@PreAuthorize
在访问之前就进行权限判断
@RestController public class AnnoController { @Autowired private JWTProvider jwtProvider; @RequestMapping("/annotation") // @PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')") @PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('ROLE_ADMIN')") public String info(){ return "拥有admin权限"; } }hasRole和hasAuthority都会对UserDetails中的getAuthorities进行判断区别是hasRole会对字段加上
ROLE_后再进行判断,上例中使用了hasRole('ADMIN'),那么就会使用ROLE_ADMIN进行判断,如果是hasAuthority('ADMIN'),那么就使用ADMIN进行判断。 -
@PostAuthorize
在请求之后进行判断,如果返回值不满足条件,会抛出异常,但是方法本身是已经执行过了的。
@RequestMapping("/postAuthorize") @PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')") @PostAuthorize("returnObject.id%2==0") public School postAuthorize(Long id) { School school = new School(); school.setId(id); return school; }returnObject是内置对象,引用的是方法的返回值。
如果
returnObject.id%2==0为 true,那么返回方法值。如果为false,会返回403 Forbidden。 -
@PreFilter
在方法执行之前,用于过滤集合中的值。
@RequestMapping("/preFilter") @PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')") @PreFilter("filterObject%2==0") public List<Long> preFilter(@RequestParam("ids") List<Long> ids) { return ids; }filterObject是内置对象,引用的是集合中的泛型类,如果有多个集合,需要指定filterTarget。@PreFilter(filterTarget="ids", value="filterObject%2==0") public List<Long> preFilter(@RequestParam("ids") List<Long> ids,@RequestParam("ids") List<User> users,) { return ids; }filterObject%2==0会对集合中的值会进行过滤,为true的值会保留。第一个例子返回的值在执行前过滤返回2,4。
-
@PostFilter
会对返回的集合进行过滤。
@RequestMapping("/postFilter") @PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')") @PostFilter("filterObject.id%2==0") public List<School> postFilter() { List<School> schools = new ArrayList<School>(); School school; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { school = new School(); school.setId((long)i); schools.add(school); } return schools; }上面的方法返回结果为:id为0,2,4,6,8的School对象。
七、原理讲解
1、校验流程图
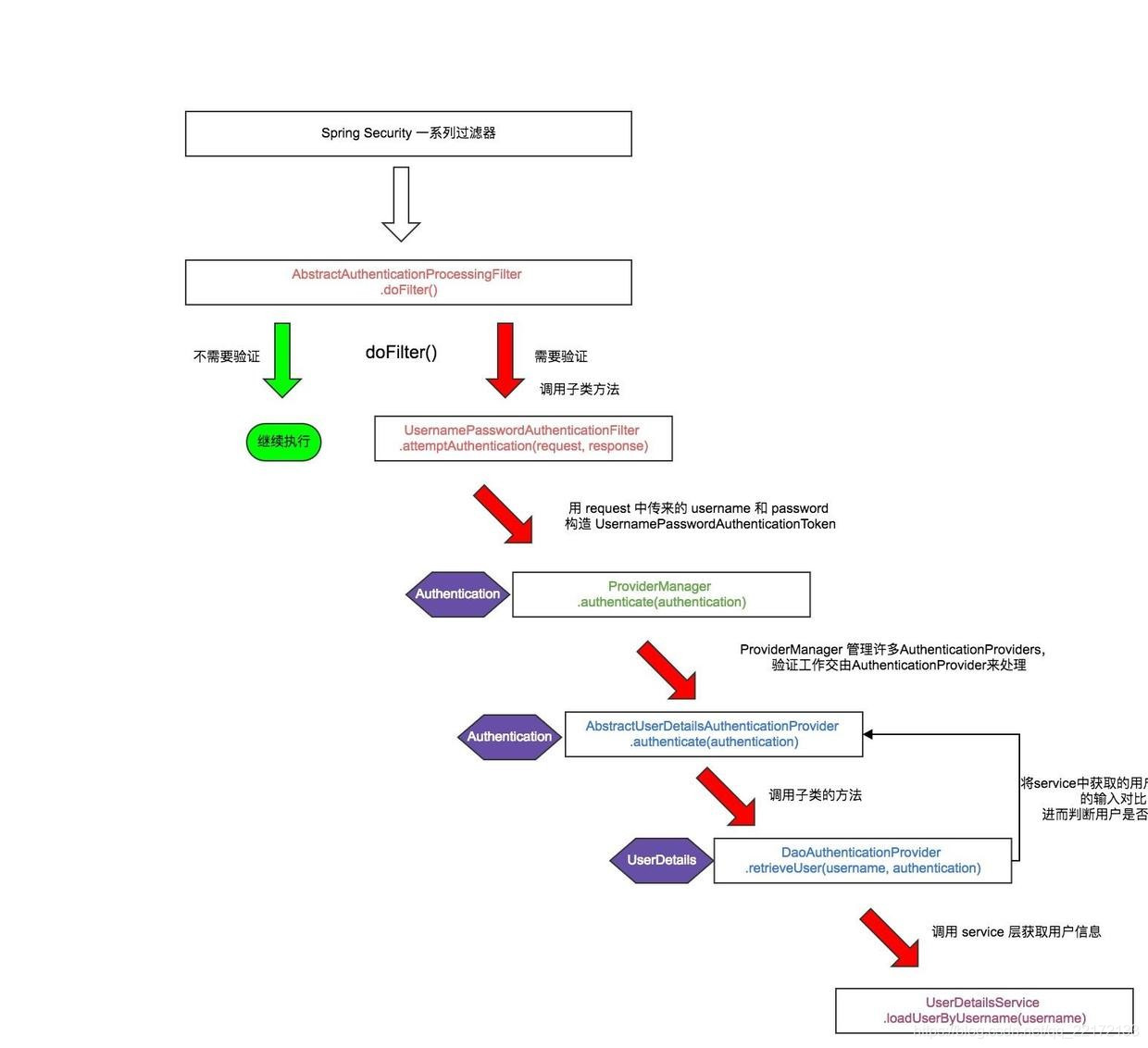
2、源码分析
- AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter 抽象类
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
if (!requiresAuthentication(request, response)) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Request is to process authentication");
}
Authentication authResult;
try {
authResult = attemptAuthentication(request, response);
if (authResult == null) {
// return immediately as subclass has indicated that it hasn't completed
// authentication
return;
}
sessionStrategy.onAuthentication(authResult, request, response);
}
catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException failed) {
logger.error(
"An internal error occurred while trying to authenticate the user.",
failed);
unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed);
return;
}
catch (AuthenticationException failed) {
// Authentication failed
unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed);
return;
}
// Authentication success
if (continueChainBeforeSuccessfulAuthentication) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
successfulAuthentication(request, response, chain, authResult);
}
**调用 requiresAuthentication(HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse) 决定是否需要进行验证操作**。如果需要验证,则会调用 attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse) 方法,有三种结果:
- 返回一个 Authentication 对象。配置的 SessionAuthenticationStrategy` 将被调用,然后 然后调用 successfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest,HttpServletResponse,FilterChain,Authentication) 方法。
- 验证时发生 AuthenticationException。unsuccessfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse, AuthenticationException) 方法将被调用。
- 返回Null,表示身份验证不完整。假设子类做了一些必要的工作(如重定向)来继续处理验证,方法将立即返回。假设后一个请求将被这种方法接收,其中返回的Authentication对象不为空。
- UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter(AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter的子类)
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException {
if (postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException(
"Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
}
String username = obtainUsername(request);
String password = obtainPassword(request);
if (username == null) {
username = "";
}
if (password == null) {
password = "";
}
username = username.trim();
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
username, password);
// Allow subclasses to set the "details" property
setDetails(request, authRequest);
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}
**attemptAuthentication () 方法将 request 中的 username 和 password 生成 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 对象**,用于 AuthenticationManager 的验证(即 this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest) )。默认情况下注入 Spring 容器的 AuthenticationManager 是 ProviderManager。
- ProviderManager(AuthenticationManager的实现类)
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
Class<? extends Authentication> toTest = authentication.getClass();
AuthenticationException lastException = null;
Authentication result = null;
boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
for (AuthenticationProvider provider : getProviders()) {
if (!provider.supports(toTest)) {
continue;
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Authentication attempt using "
+ provider.getClass().getName());
}
try {
result = provider.authenticate(authentication);
if (result != null) {
copyDetails(authentication, result);
break;
}
}
catch (AccountStatusException e) {
prepareException(e, authentication);
// SEC-546: Avoid polling additional providers if auth failure is due to
// invalid account status
throw e;
}
catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException e) {
prepareException(e, authentication);
throw e;
}
catch (AuthenticationException e) {
lastException = e;
}
}
if (result == null && parent != null) {
// Allow the parent to try.
try {
result = parent.authenticate(authentication);
}
catch (ProviderNotFoundException e) {
// ignore as we will throw below if no other exception occurred prior to
// calling parent and the parent
// may throw ProviderNotFound even though a provider in the child already
// handled the request
}
catch (AuthenticationException e) {
lastException = e;
}
}
if (result != null) {
if (eraseCredentialsAfterAuthentication
&& (result instanceof CredentialsContainer)) {
// Authentication is complete. Remove credentials and other secret data
// from authentication
((CredentialsContainer) result).eraseCredentials();
}
eventPublisher.publishAuthenticationSuccess(result);
return result;
}
// Parent was null, or didn't authenticate (or throw an exception).
if (lastException == null) {
lastException = new ProviderNotFoundException(messages.getMessage(
"ProviderManager.providerNotFound",
new Object[] { toTest.getName() },
"No AuthenticationProvider found for {0}"));
}
prepareException(lastException, authentication);
throw lastException;
}
**尝试验证 Authentication 对象**。AuthenticationProvider 列表将被连续尝试,直到 AuthenticationProvider 表示它能够认证传递的过来的Authentication 对象。然后将使用该 AuthenticationProvider 尝试身份验证。如果有多个 AuthenticationProvider 支持验证传递过来的Authentication 对象,那么由第一个来确定结果,覆盖早期支持AuthenticationProviders 所引发的任何可能的AuthenticationException。 成功验证后,将不会尝试后续的AuthenticationProvider。如果最后所有的 AuthenticationProviders 都没有成功验证 Authentication 对象,将抛出 AuthenticationException。从代码中不难看出,由 provider 来验证 authentication, 核心点方法是:
Authentication result = provider.authenticate(authentication);
此处的 provider 是 AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider,AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider 是AuthenticationProvider的实现,看看它的 authenticate(authentication) 方法:
// 验证 authentication
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
Assert.isInstanceOf(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.class, authentication,
messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.onlySupports",
"Only UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken is supported"));
// Determine username
String username = (authentication.getPrincipal() == null) ? "NONE_PROVIDED"
: authentication.getName();
boolean cacheWasUsed = true;
UserDetails user = this.userCache.getUserFromCache(username);
if (user == null) {
cacheWasUsed = false;
try {
user = retrieveUser(username,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
}
catch (UsernameNotFoundException notFound) {
logger.debug("User '" + username + "' not found");
if (hideUserNotFoundExceptions) {
throw new BadCredentialsException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials",
"Bad credentials"));
}
else {
throw notFound;
}
}
Assert.notNull(user,
"retrieveUser returned null - a violation of the interface contract");
}
try {
preAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
additionalAuthenticationChecks(user,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
}
catch (AuthenticationException exception) {
if (cacheWasUsed) {
// There was a problem, so try again after checking
// we're using latest data (i.e. not from the cache)
cacheWasUsed = false;
user = retrieveUser(username,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
preAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
additionalAuthenticationChecks(user,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
}
else {
throw exception;
}
}
postAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
if (!cacheWasUsed) {
this.userCache.putUserInCache(user);
}
Object principalToReturn = user;
if (forcePrincipalAsString) {
principalToReturn = user.getUsername();
}
return createSuccessAuthentication(principalToReturn, authentication, user);
}
AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider 内置了缓存机制,从缓存中获取不到的 UserDetails 信息的话,就调用如下方法获取用户信息,然后和 用户传来的信息进行对比来判断是否验证成功。
// 获取用户信息
UserDetails user = retrieveUser(username,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
retrieveUser() 方法在 DaoAuthenticationProvider 中实现,DaoAuthenticationProvider 是 AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider的子类。具体实现如下:
protected final UserDetails retrieveUser(String username,
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
UserDetails loadedUser;
try {
loadedUser = this.getUserDetailsService().loadUserByUsername(username);
}
catch (UsernameNotFoundException notFound) {
if (authentication.getCredentials() != null) {
String presentedPassword = authentication.getCredentials().toString();
passwordEncoder.isPasswordValid(userNotFoundEncodedPassword,
presentedPassword, null);
}
throw notFound;
}
catch (Exception repositoryProblem) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException(
repositoryProblem.getMessage(), repositoryProblem);
}
if (loadedUser == null) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException(
"UserDetailsService returned null, which is an interface contract violation");
}
return loadedUser;
}
可以看到此处的返回对象 userDetails 是由 UserDetailsService 的 #loadUserByUsername(username) 来获取的。
八、玩转自定义登录
1. form 登录的流程
下面是 form 登录的基本流程:

只要是 form 登录基本都能转化为上面的流程。接下来我们看看 Spring Security 是如何处理的。
3. Spring Security 中的登录
默认它提供了三种登录方式:
formLogin()普通表单登录oauth2Login()基于OAuth2.0认证/授权协议openidLogin()基于OpenID身份认证规范
以上三种方式统统是 AbstractAuthenticationFilterConfigurer 实现的,
4. HttpSecurity 中的 form 表单登录
启用表单登录通过两种方式一种是通过 HttpSecurity 的 apply(C configurer) 方法自己构造一个 AbstractAuthenticationFilterConfigurer 的实现,这种是比较高级的玩法。 另一种是我们常见的使用 HttpSecurity 的 formLogin() 方法来自定义 FormLoginConfigurer 。我们先搞一下比较常规的第二种。
4.1 FormLoginConfigurer
该类是 form 表单登录的配置类。它提供了一些我们常用的配置方法:
- loginPage(String loginPage) : 登录 页面而并不是接口,对于前后分离模式需要我们进行改造 默认为
/login。 - loginProcessingUrl(String loginProcessingUrl) 实际表单向后台提交用户信息的
Action,再由过滤器UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter拦截处理,该Action其实不会处理任何逻辑。 - usernameParameter(String usernameParameter) 用来自定义用户参数名,默认
username。 - passwordParameter(String passwordParameter) 用来自定义用户密码名,默认
password - failureUrl(String authenticationFailureUrl) 登录失败后会重定向到此路径, 一般前后分离不会使用它。
- failureForwardUrl(String forwardUrl) 登录失败会转发到此, 一般前后分离用到它。 可定义一个
Controller(控制器)来处理返回值,但是要注意RequestMethod。 - defaultSuccessUrl(String defaultSuccessUrl, boolean alwaysUse) 默认登陆成功后跳转到此 ,如果
alwaysUse为true只要进行认证流程而且成功,会一直跳转到此。一般推荐默认值false - successForwardUrl(String forwardUrl) 效果等同于上面
defaultSuccessUrl的alwaysUse为true但是要注意RequestMethod。 - successHandler(AuthenticationSuccessHandler successHandler) 自定义认证成功处理器,可替代上面所有的
success方式 - failureHandler(AuthenticationFailureHandler authenticationFailureHandler) 自定义失败成功处理器,可替代上面所有的
failure方式 - permitAll(boolean permitAll) form 表单登录是否放开
知道了这些我们就能来搞个定制化的登录了。
5. Spring Security 聚合登录 实战
接下来是我们最激动人心的实战登录操作。 有疑问的可认真阅读 Spring 实战 的一系列预热文章。
5.1 简单需求
我们的接口访问都要通过认证,登陆错误后返回错误信息(json),成功后前台可以获取到对应数据库用户信息(json)(实战中记得脱敏)。
我们定义处理成功失败的控制器:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/login")
public class LoginController {
@Resource
private SysUserService sysUserService;
/**
* 登录失败返回 401 以及提示信息.
*
* @return the rest
*/
@PostMapping("/failure")
public Rest loginFailure() {
return RestBody.failure(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED.value(), "登录失败了,老哥");
}
/**
* 登录成功后拿到个人信息.
*
* @return the rest
*/
@PostMapping("/success")
public Rest loginSuccess() {
// 登录成功后用户的认证信息 UserDetails会存在 安全上下文寄存器 SecurityContextHolder 中
User principal = (User) SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal();
String username = principal.getUsername();
SysUser sysUser = sysUserService.queryByUsername(username);
// 脱敏
sysUser.setEncodePassword("[PROTECT]");
return RestBody.okData(sysUser,"登录成功");
}
}
然后 我们自定义配置覆写 void configure(HttpSecurity http) 方法进行如下配置(这里需要禁用crsf):
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter.class)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = ConditionalOnWebApplication.Type.SERVLET)
public class CustomSpringBootWebSecurityConfiguration {
@Configuration
@Order(SecurityProperties.BASIC_AUTH_ORDER)
static class DefaultConfigurerAdapter extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
super.configure(auth);
}
@Override
public void configure(WebSecurity web) throws Exception {
super.configure(web);
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf().disable()
.cors()
.and()
.authorizeRequests().anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginProcessingUrl("/process")
.successForwardUrl("/login/success").
failureForwardUrl("/login/failure");
}
}
}
使用 Postman 或者其它工具进行 Post 方式的表单提交 http://localhost:8080/process?username=Felordcn&password=12345 会返回用户信息:
{
"httpStatus": 200,
"data": {
"userId": 1,
"username": "Felordcn",
"encodePassword": "[PROTECT]",
"age": 18
},
"msg": "登录成功",
"identifier": ""
}
把密码修改为其它值再次请求认证失败后 :
{
"httpStatus": 401,
"data": null,
"msg": "登录失败了,老哥",
"identifier": "-9999"
}
6. 多种登录方式的简单实现
就这么完了了么?现在登录的花样繁多。常规的就有短信、邮箱、扫码 ,第三方是以后我要讲的不在今天范围之内。 如何应对想法多的产品经理? 我们来搞一个可扩展各种姿势的登录方式。我们在上面 2. form 登录的流程 中的 用户 和 判定 之间增加一个适配器来适配即可。 我们知道这个所谓的 判定就是 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 。
我们只需要保证 uri 为上面配置的/process 并且能够通过 getParameter(String name) 获取用户名和密码即可 。
我突然觉得可以模仿 DelegatingPasswordEncoder 的搞法, 维护一个注册表执行不同的处理策略。当然我们要实现一个 GenericFilterBean 在 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 之前执行。同时制定登录的策略。
6.1 登录方式定义
定义登录方式枚举 ``。
public enum LoginTypeEnum {
/**
* 原始登录方式.
*/
FORM,
/**
* Json 提交.
*/
JSON,
/**
* 验证码.
*/
CAPTCHA
}
6.2 定义前置处理器接口
定义前置处理器接口用来处理接收的各种特色的登录参数 并处理具体的逻辑。这个借口其实有点随意 ,重要的是你要学会思路。我实现了一个 默认的 form' 表单登录 和 通过RequestBody放入json` 的两种方式,篇幅限制这里就不展示了。具体的 DEMO 参见底部。
public interface LoginPostProcessor {
/**
* 获取 登录类型
*
* @return the type
*/
LoginTypeEnum getLoginTypeEnum();
/**
* 获取用户名
*
* @param request the request
* @return the string
*/
String obtainUsername(ServletRequest request);
/**
* 获取密码
*
* @param request the request
* @return the string
*/
String obtainPassword(ServletRequest request);
}
6.3 实现登录前置处理过滤器
该过滤器维护了 LoginPostProcessor 映射表。 通过前端来判定登录方式进行策略上的预处理,最终还是会交给 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 。通过 HttpSecurity 的 addFilterBefore(preLoginFilter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class)方法进行前置。
package cn.felord.spring.security.filter;
import cn.felord.spring.security.enumation.LoginTypeEnum;
import org.springframework.security.web.util.matcher.AntPathRequestMatcher;
import org.springframework.security.web.util.matcher.RequestMatcher;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;
import org.springframework.web.filter.GenericFilterBean;
import javax.servlet.FilterChain;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.ServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.ServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import static org.springframework.security.web.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.SPRING_SECURITY_FORM_PASSWORD_KEY;
import static org.springframework.security.web.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.SPRING_SECURITY_FORM_USERNAME_KEY;
/**
* 预登录控制器
*
* @author Felordcn
* @since 16 :21 2019/10/17
*/
public class PreLoginFilter extends GenericFilterBean {
private static final String LOGIN_TYPE_KEY = "login_type";
private RequestMatcher requiresAuthenticationRequestMatcher;
private Map<LoginTypeEnum, LoginPostProcessor> processors = new HashMap<>();
public PreLoginFilter(String loginProcessingUrl, Collection<LoginPostProcessor> loginPostProcessors) {
Assert.notNull(loginProcessingUrl, "loginProcessingUrl must not be null");
requiresAuthenticationRequestMatcher = new AntPathRequestMatcher(loginProcessingUrl, "POST");
LoginPostProcessor loginPostProcessor = defaultLoginPostProcessor();
processors.put(loginPostProcessor.getLoginTypeEnum(), loginPostProcessor);
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(loginPostProcessors)) {
loginPostProcessors.forEach(element -> processors.put(element.getLoginTypeEnum(), element));
}
}
private LoginTypeEnum getTypeFromReq(ServletRequest request) {
String parameter = request.getParameter(LOGIN_TYPE_KEY);
int i = Integer.parseInt(parameter);
LoginTypeEnum[] values = LoginTypeEnum.values();
return values[i];
}
/**
* 默认还是Form .
*
* @return the login post processor
*/
private LoginPostProcessor defaultLoginPostProcessor() {
return new LoginPostProcessor() {
@Override
public LoginTypeEnum getLoginTypeEnum() {
return LoginTypeEnum.FORM;
}
@Override
public String obtainUsername(ServletRequest request) {
return request.getParameter(SPRING_SECURITY_FORM_USERNAME_KEY);
}
@Override
public String obtainPassword(ServletRequest request) {
return request.getParameter(SPRING_SECURITY_FORM_PASSWORD_KEY);
}
};
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
ParameterRequestWrapper parameterRequestWrapper = new ParameterRequestWrapper((HttpServletRequest) request);
if (requiresAuthenticationRequestMatcher.matches((HttpServletRequest) request)) {
LoginTypeEnum typeFromReq = getTypeFromReq(request);
LoginPostProcessor loginPostProcessor = processors.get(typeFromReq);
String username = loginPostProcessor.obtainUsername(request);
String password = loginPostProcessor.obtainPassword(request);
parameterRequestWrapper.setAttribute(SPRING_SECURITY_FORM_USERNAME_KEY, username);
parameterRequestWrapper.setAttribute(SPRING_SECURITY_FORM_PASSWORD_KEY, password);
}
chain.doFilter(parameterRequestWrapper, response);
}
}
6.4 验证
通过 POST 表单提交方式 http://localhost:8080/process?username=Felordcn&password=12345&login_type=0 可以请求成功。或者以下列方式也可以提交成功:
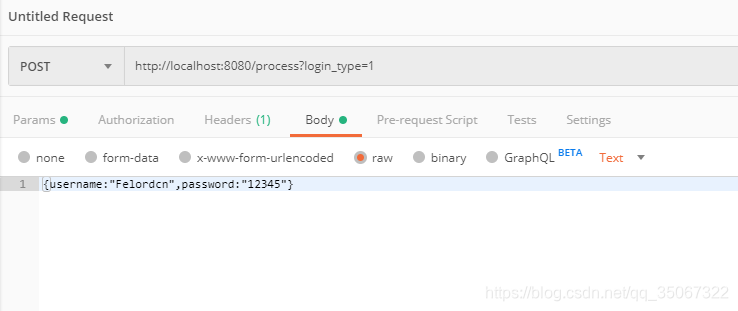
更多的方式 只需要实现接口 LoginPostProcessor 注入 PreLoginFilter
九 整合JWT做登录认证
JWT是JSON Web Token的缩写,是目前最流行的跨域认证解决方法。
互联网服务认证的一般流程是:
- 用户向服务器发送账号、密码
- 服务器验证通过后,将用户的角色、登录时间等信息保存到当前会话中
- 同时,服务器向用户返回一个session_id(一般保存在cookie里)
- 用户再次发送请求时,把含有session_id的cookie发送给服务器
- 服务器收到session_id,查找session,提取用户信息
上面的认证模式,存在以下缺点:
- cookie不允许跨域
- 因为每台服务器都必须保存session对象,所以扩展性不好
JWT认证原理是:
- 用户向服务器发送账号、密码
- 服务器验证通过后,生成token令牌返回给客户端(token可以包含用户信息)
- 用户再次请求时,把token放到请求头
Authorization里 - 服务器收到请求,验证token合法后放行请求
JWT token令牌可以包含用户身份、登录时间等信息,这样登录状态保持者由服务器端变为客户端,服务器变成无状态了;token放到请求头,实现了跨域
JWT的组成
eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJzdWIiOiIxMjM0NTY3ODkwIiwibmFtZSI6IkpvaG4gRG9lIiwiaWF0IjoxNTE2MjM5MDIyfQ.SflKxwRJSMeKKF2QT4fwpMeJf36POk6yJV_adQssw5c
JWT由三部分组成:
- Header(头部)
- Payload(负载)
- Signature(签名)
表现形式为:Header.Payload.Signature
Header 部分是一个 JSON 对象,描述 JWT 的元数据,通常是下面的样子:
{
"alg": "HS256",
"typ": "JWT"
}
上面代码中,alg属性表示签名的算法(algorithm),默认是 HMAC SHA256(写成 HS256);typ属性表示这个令牌(token)的类型(type),JWT 令牌统一写为JWT。
上面的 JSON 对象使用 Base64URL 算法转成字符串
Payload
Payload 部分也是一个 JSON 对象,用来存放实际需要传递的数据。JWT 规定了7个官方字段:
- iss (issuer):签发人
- exp (expiration time):过期时间
- sub (subject):主题
- aud (audience):受众
- nbf (Not Before):生效时间
- iat (Issued At):签发时间
- jti (JWT ID):编号
当然,用户也可以定义私有字段。
这个 JSON 对象也要使用 Base64URL 算法转成字符串
Signature
Signature 部分是对前两部分的签名,防止数据篡改
签名算法如下:
HMACSHA256(
base64UrlEncode(header) + "." +
base64UrlEncode(payload),
your-256-bit-secret
)
算出签名以后,把 Header、Payload、Signature 三个部分拼成一个字符串,每个部分之间用"."分隔
JWT认证和授权
Security是基于AOP和Servlet过滤器的安全框架,为了实现JWT要重写那些方法、自定义那些过滤器需要首先了解security自带的过滤器。security默认过滤器链如下:
- org.springframework.security.web.context.request.async.WebAsyncManagerIntegrationFilter
- org.springframework.security.web.context.SecurityContextPersistenceFilter
- org.springframework.security.web.header.HeaderWriterFilter
- org.springframework.security.web.authentication.logout.LogoutFilter
- org.springframework.security.web.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter
- org.springframework.security.web.savedrequest.RequestCacheAwareFilter
- org.springframework.security.web.servletapi.SecurityContextHolderAwareRequestFilter
- org.springframework.security.web.authentication.AnonymousAuthenticationFilter
- org.springframework.security.web.session.SessionManagementFilter
- org.springframework.security.web.access.ExceptionTranslationFilter
- org.springframework.security.web.access.intercept.FilterSecurityInterceptor
SecurityContextPersistenceFilter
这个过滤器有两个作用:
- 用户发送请求时,从session对象提取用户信息,保存到SecurityContextHolder的securitycontext中
- 当前请求响应结束时,把SecurityContextHolder的securitycontext保存的用户信息放到session,便于下次请求时共享数据;同时将SecurityContextHolder的securitycontext清空
由于禁用session功能,所以该过滤器只剩一个作用即把SecurityContextHolder的securitycontext清空。举例来说明为何要清空securitycontext:用户1发送一个请求,由线程M处理,当响应完成线程M放回线程池;用户2发送一个请求,本次请求同样由线程M处理,由于securitycontext没有清空,理应储存用户2的信息但此时储存的是用户1的信息,造成用户信息不符
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter继承自AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter,处理逻辑在doFilter方法中:
- 当请求被
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter拦截时,判断请求路径是否匹配登录URL,若不匹配继续执行下个过滤器;否则,执行步骤2 - 调用
attemptAuthentication方法进行认证。UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter重写了attemptAuthentication方法,负责读取表单登录参数,委托AuthenticationManager进行认证,返回一个认证过的token(null表示认证失败) - 判断token是否为null,非null表示认证成功,null表示认证失败
- 若认证成功,调用
successfulAuthentication。该方法把认证过的token放入securitycontext供后续请求授权,同时该方法预留一个扩展点(AuthenticationSuccessHandler.onAuthenticationSuccess方法),进行认证成功后的处理 - 若认证失败,同样可以扩展
uthenticationFailureHandler.onAuthenticationFailure进行认证失败后的处理 - 只要当前请求路径匹配登录URL,那么无论认证成功还是失败,当前请求都会响应完成,不再执行过滤器链
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter的attemptAuthentication方法,执行逻辑如下:
- 从请求中获取表单参数。因为使用
HttpServletRequest.getParameter方法获取参数,它只能处理Content-Type为application/x-www-form-urlencoded或multipart/form-data的请求,若是application/json则无法获取值 - 把步骤1获取的账号、密码封装成
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken对象,创建未认证的token。UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken有两个重载的构造方法,其中public UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(Object principal, Object credentials)创建未经认证的token,public UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(Object principal, Object credentials, Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities)创建已认证的token - 获取认证管理器
AuthenticationManager,其缺省实现为ProviderManager,调用其authenticate进行认证 ProviderManager的authenticate是个模板方法,它遍历所有AuthenticationProvider,直至找到支持认证某类型token的AuthenticationProvider,调用AuthenticationProvider.authenticate方法认证,AuthenticationProvider.authenticate加载正确的账号、密码进行比较验证AuthenticationManager.authenticate方法返回一个已认证的token
AnonymousAuthenticationFilter
AnonymousAuthenticationFilter负责创建匿名token:
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
if (SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() == null) {
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(this.createAuthentication((HttpServletRequest)req));
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace(LogMessage.of(() -> {
return "Set SecurityContextHolder to " + SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
}));
} else {
this.logger.debug("Set SecurityContextHolder to anonymous SecurityContext");
}
} else if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace(LogMessage.of(() -> {
return "Did not set SecurityContextHolder since already authenticated " + SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
}));
}
chain.doFilter(req, res);
}
如果当前用户没有认证,会创建一个匿名token,用户是否能读取资源交由FilterSecurityInterceptor过滤器委托给决策管理器判断是否有权限读取
实现思路
JWT认证思路:
- 利用Security原生的表单认证过滤器验证用户名、密码
- 验证通过后自定义
AuthenticationSuccessHandler认证成功处理器,由该处理器生成token令牌
JWT授权思路:
- 使用JWT目的是让服务器变成无状态,不用session共享数据,所以要禁用security的session功能(http.sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS))
- token令牌数据结构设计时,payload部分要储存用户名、角色信息
- token令牌有两个作用:
- 认证, 用户发送的token合法即代表认证成功
- 授权,令牌验证成功后提取角色信息,构造认证过的token,将其放到securitycontext,具体权限判断交给security框架处理
- 自己实现一个过滤器,拦截用户请求,实现(3)中所说的功能
代码实现 创建JWT工具类
<dependency>
<groupId>com.auth0</groupId>
<artifactId>java-jwt</artifactId>
<version>3.12.0</version>
</dependency>
我们对java-jwt提供的API进行封装,便于创建、验证、提取claim
@Slf4j
public class JWTUtil {
// 携带token的请求头名字
public final static String TOKEN_HEADER = "Authorization";
//token的前缀
public final static String TOKEN_PREFIX = "Bearer ";
// 默认密钥
public final static String DEFAULT_SECRET = "mySecret";
// 用户身份
private final static String ROLES_CLAIM = "roles";
// token有效期,单位分钟;
private final static long EXPIRE_TIME = 5 * 60 * 1000;
// 设置Remember-me功能后的token有效期
private final static long EXPIRE_TIME_REMEMBER = 7 * 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000;
// 创建token
public static String createToken(String username, List role, String secret, boolean rememberMe) {
Date expireDate = rememberMe ? new Date(System.currentTimeMillis() + EXPIRE_TIME_REMEMBER) : new Date(System.currentTimeMillis() + EXPIRE_TIME);
try {
// 创建签名的算法实例
Algorithm algorithm = Algorithm.HMAC256(secret);
String token = JWT.create()
.withExpiresAt(expireDate)
.withClaim("username", username)
.withClaim(ROLES_CLAIM, role)
.sign(algorithm);
return token;
} catch (JWTCreationException jwtCreationException) {
log.warn("Token create failed");
return null;
}
}
// 验证token
public static boolean verifyToken(String token, String secret) {
try{
Algorithm algorithm = Algorithm.HMAC256(secret);
// 构建JWT验证器,token合法同时pyload必须含有私有字段username且值一致
// token过期也会验证失败
JWTVerifier verifier = JWT.require(algorithm)
.build();
// 验证token
DecodedJWT decodedJWT = verifier.verify(token);
return true;
} catch (JWTVerificationException jwtVerificationException) {
log.warn("token验证失败");
return false;
}
}
// 获取username
public static String getUsername(String token) {
try {
// 因此获取载荷信息不需要密钥
DecodedJWT jwt = JWT.decode(token);
return jwt.getClaim("username").asString();
} catch (JWTDecodeException jwtDecodeException) {
log.warn("提取用户姓名时,token解码失败");
return null;
}
}
public static List<String> getRole(String token) {
try {
// 因此获取载荷信息不需要密钥
DecodedJWT jwt = JWT.decode(token);
// asList方法需要指定容器元素的类型
return jwt.getClaim(ROLES_CLAIM).asList(String.class);
} catch (JWTDecodeException jwtDecodeException) {
log.warn("提取身份时,token解码失败");
return null;
}
}
}
代码实现认证
验证账号、密码交给UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter,不用修改代码
认证成功后,需要生成token返回给客户端,我们通过扩展AuthenticationSuccessHandler.onAuthenticationSuccess方法实现
@Component
public class JWTAuthenticationSuccessHandler implements AuthenticationSuccessHandler {
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException {
ResponseData responseData = new ResponseData();
responseData.setCode("200");
responseData.setMessage("登录成功!");
// 提取用户名,准备写入token
String username = authentication.getName();
// 提取角色,转为List<String>对象,写入token
List<String> roles = new ArrayList<>();
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities = authentication.getAuthorities();
for (GrantedAuthority authority : authorities){
roles.add(authority.getAuthority());
}
// 创建token
String token = JWTUtil.createToken(username, roles, JWTUtil.DEFAULT_SECRET, true);
httpServletResponse.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
// 为了跨域,把token放到响应头WWW-Authenticate里
httpServletResponse.setHeader("WWW-Authenticate", JWTUtil.TOKEN_PREFIX + token);
// 写入响应里
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
mapper.writeValue(httpServletResponse.getWriter(), responseData);
}
}
为了统一返回值,我们封装了一个ResponseData对象
代码实现 授权
自定义一个过滤器JWTAuthorizationFilter,验证token,token验证成功后认为认证成功
@Slf4j
public class JWTAuthorizationFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
String token = getTokenFromRequestHeader(request);
Authentication verifyResult = verefyToken(token, JWTUtil.DEFAULT_SECRET);
if (verifyResult == null) {
// 即便验证失败,也继续调用过滤链,匿名过滤器生成匿名令牌
chain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
} else {
log.info("token令牌验证成功");
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(verifyResult);
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
}
// 从请求头获取token
private String getTokenFromRequestHeader(HttpServletRequest request) {
String header = request.getHeader(JWTUtil.TOKEN_HEADER);
if (header == null || !header.startsWith(JWTUtil.TOKEN_PREFIX)) {
log.info("请求头不含JWT token, 调用下个过滤器");
return null;
}
String token = header.split(" ")[1].trim();
return token;
}
// 验证token,并生成认证后的token
private UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken verefyToken(String token, String secret) {
if (token == null) {
return null;
}
// 认证失败,返回null
if (!JWTUtil.verifyToken(token, secret)) {
return null;
}
// 提取用户名
String username = JWTUtil.getUsername(token);
// 定义权限列表
List<GrantedAuthority> authorities = new ArrayList<>();
// 从token提取角色
List<String> roles = JWTUtil.getRole(token);
for (String role : roles) {
log.info("用户身份是:" + role);
authorities.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority(role));
}
// 构建认证过的token
return new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(username, null, authorities);
}
}
OncePerRequestFilter`保证当前请求中,此过滤器只被调用一次,执行逻辑在`doFilterInternal
代码实现 security配置
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private AjaxAuthenticationEntryPoint ajaxAuthenticationEntryPoint;
@Autowired
private JWTAuthenticationSuccessHandler jwtAuthenticationSuccessHandler;
@Autowired
private AjaxAuthenticationFailureHandler ajaxAuthenticationFailureHandler;
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf().disable()
.authorizeRequests().anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.successHandler(jwtAuthenticationSuccessHandler)
.failureHandler(ajaxAuthenticationFailureHandler)
.permitAll()
.and()
.addFilterAfter(new JWTAuthorizationFilter(), UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class)
.sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS)
.and()
.exceptionHandling().authenticationEntryPoint(ajaxAuthenticationEntryPoint);
}
}
配置里取消了session功能,把我们定义的过滤器添加到过滤链中;同时,定义ajaxAuthenticationEntryPoint处理未认证用户访问未授权资源时抛出的异常
@Component
public class AjaxAuthenticationEntryPoint implements AuthenticationEntryPoint {
@Override
public void commence(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, AuthenticationException e) throws IOException, ServletException {
ResponseData responseData = new ResponseData();
responseData.setCode("401");
responseData.setMessage("匿名用户,请先登录再访问!");
httpServletResponse.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
mapper.writeValue(httpServletResponse.getWriter(), responseData);
}
}
过滤器链(filter chain)的介绍
上一节中,主要讲了Spring Security认证和授权的核心组件及核心方法。但是,什么时候调用这些方法呢?答案就是Filter和AOP。Spring Security在我们进行用户认证以及授予权限的时候,通过各种各样的拦截器来控制权限的访问。
对于基于HttpRequest的方式对端点进行保护,我们使用一个Filter Chain来保护;对于基于方法调用进行保护,我们使用AOP来保护。本篇重点讲Spring Security中过滤器链的种类及过滤器中如何实现的认证和授权。
Spring Security会默认为我们添加15个过滤器,我们可以从WebSecurity(WebSecurity是Spring Security加载的一个重要对象,将在下节具体讲述)的performBuild()方法中看到过滤器链SecurityFilterChain的构建过程,并交由FilterChainProxy对象代理。我们从SecurityFilterChain的默认实现类DefaultSecurityFilterChain中的log看出,Spring Security由以下过滤器组成了过滤器链:
Creating filter chain: any request, [
org.springframework.security.web.context.request.async.WebAsyncManagerIntegrationFilter@7f353a0f,
org.springframework.security.web.context.SecurityContextPersistenceFilter@4735d6e5,
org.springframework.security.web.header.HeaderWriterFilter@314a31b0,
org.springframework.security.web.csrf.CsrfFilter@4ef2ab73,
org.springframework.security.web.authentication.logout.LogoutFilter@57efc6fd,
org.springframework.security.web.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter@d88f893,
org.springframework.security.web.authentication.ui.DefaultLoginPageGeneratingFilter@2cd388f5,
org.springframework.security.web.authentication.ui.DefaultLogoutPageGeneratingFilter@7ea2412c,
org.springframework.security.web.authentication.www.BasicAuthenticationFilter@2091833,
org.springframework.security.web.savedrequest.RequestCacheAwareFilter@4dad0eed,
org.springframework.security.web.servletapi.SecurityContextHolderAwareRequestFilter@16132f21,
org.springframework.security.web.authentication.AnonymousAuthenticationFilter@1c93b51e,
org.springframework.security.web.session.SessionManagementFilter@59edb4f5,
org.springframework.security.web.access.ExceptionTranslationFilter@104dc1a2,
org.springframework.security.web.access.intercept.FilterSecurityInterceptor@1de0641b
]
下面就是各个过滤器的功能,
其中SecurityContextPersistenceFilter,UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter及FilterSecurityInterceptor分别对应了SecurityContext,AuthenticationManager,AccessDecisionManager的处理。
[WebAsyncManagerIntegrationFilter] (异步方式)提供了对securityContext和WebAsyncManager的集成。
方式是通过SecurityContextCallableProcessingInterceptor的beforeConcurrentHandling(NativeWebRequest, Callable)方法来将SecurityContext设置到Callable上。
其实就是把SecurityContext设置到异步线程中,使其也能获取到用户上下文认证信息。
[SecurityContextPersistenceFilter] (同步方式)在请求之前从SecurityContextRepository(默认实现是HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository)获取信息并填充SecurityContextHolder(如果没有,则创建一个新的ThreadLocal的SecurityContext),并在请求完成并清空SecurityContextHolder并更新SecurityContextRepository。
在Spring Security中,虽然安全上下文信息被存储于Session中,但实际的Filter中不应直接操作Session(过滤器一般负责核心的处理流程,而具体的业务实现,通常交给其中聚合的其他实体类),而是用如HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository中loadContext(),saveContext()来存取session。
[HeaderWriterFilter] 用来给http响应添加一些Header,比如X-Frame-Options,X-XSS-Protection*,X-Content-Type-Options。
[CsrfFilter] 默认开启,用于防止csrf攻击的过滤器
[LogoutFilter] 处理注销的过滤器
[UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter] 表单提交了username和password,被封装成UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken对象进行一系列的认证,便是主要通过这个过滤器完成的,即调用AuthenticationManager.authenticate()。在表单认证的方法中,这是最最关键的过滤器。具体过程是:
(1)调用AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter.doFilter()方法执行过滤器
(2)调用UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.attemptAuthentication()方法
(3)调用AuthenticationManager.authenticate()方法(实际上委托给AuthenticationProvider的实现类来处理)
[DefaultLoginPageGeneratingFilter] & [DefaultLogoutPageGeneratingFilter] 如果没有配置/login及login page, 系统则会自动配置这两个Filter。
[BasicAuthenticationFilter] Processes a HTTP request's BASIC authorization headers, putting the result into the SecurityContextHolder.
[RequestCacheAwareFilter] 内部维护了一个RequestCache,用于缓存request请求
[SecurityContextHolderAwareRequestFilter] 此过滤器对ServletRequest进行了一次包装,使得request具有更加丰富的API(populates the ServletRequest with a request wrapper which implements servlet API security methods)
[AnonymousAuthenticationFilter] 匿名身份过滤器,spring security为了兼容未登录的访问,也走了一套认证流程,只不过是一个匿名的身份。它位于身份认证过滤器(e.g. UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter)之后,意味着只有在上述身份过滤器执行完毕后,SecurityContext依旧没有用户信息,AnonymousAuthenticationFilter该过滤器才会有意义。
[SessionManagementFilter] 和session相关的过滤器,内部维护了一个SessionAuthenticationStrategy来执行任何与session相关的活动,比如session-fixation protection mechanisms or checking for multiple concurrent logins。
[ExceptionTranslationFilter] 异常转换过滤器,这个过滤器本身不处理异常,而是将认证过程中出现的异常(AccessDeniedException and AuthenticationException)交给内部维护的一些类去处理。它
位于整个springSecurityFilterChain的后方,用来转换整个链路中出现的异常,将其转化,顾名思义,转化以意味本身并不处理。一般其只处理两大类异常:AccessDeniedException访问异常和AuthenticationException认证异常。
它将Java中的异常和HTTP的响应连接在了一起,这样在处理异常时,我们不用考虑密码错误该跳到什么页面,账号锁定该如何,只需要关注自己的业务逻辑,抛出相应的异常便可。如果该过滤器检测到AuthenticationException,则将会交给内部的AuthenticationEntryPoint去处理,如果检测到AccessDeniedException,需要先判断当前用户是不是匿名用户,如果是匿名访问,则和前面一样运行AuthenticationEntryPoint,否则会委托给AccessDeniedHandler去处理,而AccessDeniedHandler的默认实现,是AccessDeniedHandlerImpl。
[FilterSecurityInterceptor] 这个过滤器决定了访问特定路径应该具备的权限,这些受限的资源访需要什么权限或角色,这些判断和处理都是由该类进行的。
(1)调用FilterSecurityInterceptor.invoke()方法执行过滤器
(2)调用AbstractSecurityInterceptor.beforeInvocation()方法
(3)调用AccessDecisionManager.decide()方法决策判断是否有该权限
参考
JSON Web Token 入门教程
Spring Security-5-认证流程梳理
Spring Security3源码分析(5)-SecurityContextPersistenceFilter分析
Spring Security addFilter() 顺序问题
前后端联调之Form Data与Request Payload,你真的了解吗?
Spring Boot 2 + Spring Security 5 + JWT 的单页应用 Restful 解决方案
SpringBoot实战派-第十章源码
https://www.cnblogs.com/cjsblog/p/9184173.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/storml/p/10937486.html
技术自由的实现路径:
实现你的 架构自由:
《阿里二面:千万级、亿级数据,如何性能优化? 教科书级 答案来了》
《峰值21WQps、亿级DAU,小游戏《羊了个羊》是怎么架构的?》
… 更多架构文章,正在添加中
实现你的 响应式 自由:
这是老版本 《Flux、Mono、Reactor 实战(史上最全)》
实现你的 spring cloud 自由:
《Spring cloud Alibaba 学习圣经》 PDF
《分库分表 Sharding-JDBC 底层原理、核心实战(史上最全)》
《一文搞定:SpringBoot、SLF4j、Log4j、Logback、Netty之间混乱关系(史上最全)》
实现你的 linux 自由:
实现你的 网络 自由:
《网络三张表:ARP表, MAC表, 路由表,实现你的网络自由!!》
实现你的 分布式锁 自由:
实现你的 王者组件 自由:
《队列之王: Disruptor 原理、架构、源码 一文穿透》
《缓存之王:Caffeine 源码、架构、原理(史上最全,10W字 超级长文)》
《Java Agent 探针、字节码增强 ByteBuddy(史上最全)》
实现你的 面试题 自由:
免费获取11个技术圣经PDF:





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号