多项式例题1
Golf Bot

利用生成函数维护可达性,可以达到的点设为 \(1\),卷一下就可以知道打两次可以到哪些点。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define ld long double
#define ull unsigned long long
#define PII pair<ll, ll>
#define pb push_back
#define clr(f, n) memset(f, 0, sizeof(int) * (n))
#define cpy(f, g, n) memcpy(f, g, sizeof(int) * (n))
#define rev(f, n) reverse(f, f + (n))
const int N = 1.5e6 + 10, _G = 3, mod = 998244353;
ll qpow(ll a, ll k = mod - 2) {
ll res = 1;
while (k) {
if (k & 1) res = res * a % mod;
k >>= 1;
a = a * a % mod;
}
return res;
}
const int invG = qpow(_G);
int rev[N << 1], rev_len;
void rev_init(int n) {
if (rev_len == n) return;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) rev[i] = (rev[i >> 1] >> 1) | (i & 1 ? n >> 1 : 0);
rev_len = n;
}
void NTT(int *g, int op, int n) {
rev_init(n);
static ull f[N << 1], Gk[N << 1] = {1};
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) f[i] = g[rev[i]];
for (int k = 1; k < n; k <<= 1) {
int G1 = qpow(~op ? _G : invG, (mod - 1) / (k << 1));
for (int i = 1; i < k; i ++ ) Gk[i] = Gk[i - 1] * G1 % mod;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i += k << 1) {
for (int j = 0; j < k; j ++ ) {
int tmp = Gk[j] * f[i | j | k] % mod;
f[i | j | k] = f[i | j] + mod - tmp;
f[i | j] += tmp;
}
}
if (k == (1 << 10)) for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) f[i] %= mod;
}
if (~op) for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) g[i] = f[i] % mod;
else {
int invn = qpow(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) g[i] = f[i] % mod * invn % mod;
}
}
void px(int *f, int *g, int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) f[i] = 1ll * f[i] * g[i] % mod;
}
void covolution(int *f, int *g, int len, int lim) {
static int sav[N << 1];
int n; for (n = 1; n < len << 1; n <<= 1);
clr(sav, n); cpy(sav, g, n);
NTT(sav, 1, n); NTT(f, 1, n);
px(f, sav, n); NTT(f, -1, n);
clr(f + lim, n - lim), clr(sav, n);
}
int n, m, a[N], b[N], F[N << 1];
int ans, maxn = 200001;
void solve() {
cin >> n;
F[0] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) cin >> a[i], F[a[i]] = 1;
cin >> m;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i ++ ) cin >> b[i];
covolution(F, F, maxn, (maxn << 1) - 1);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i ++ ) if (F[b[i]]) ans ++ ;
cout << ans << "\n";
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int T = 1;
// cin >> T;
while (T -- ) solve();
return 0;
}
ADAMATCH - Ada and Nucleobase
Ada the Ladybug is helping her friend who is biologist. He examines DNA. Actually he has a long DNA of one bug, consisting of adenine, cytosine, guanine and thymine and he wants to know whether another bug might be relative to first bug. A bug is relative to another bug if his his DNA has very low Hamming Distance with some substring of the first bug.
Your job is to find the lowest hamming distance between second DNA and any substring of first DNA.
Input
Input contains only two lines: first DNA (s) and second DNA (r).
It is true that 0 < |r| ≤ |s| ≤ 5*10^5
|s| means length of string s.
All strings contains only A, C, T, and G .
Output
Print minimal Hamming Distance (the number of mismatched nucleobases) of any substring of s and r (the substring MUST have length |r|)
考虑不匹配的位置等于总数减去匹配的位置,我们想知道
如果改写为
那么有答案是 \(s\) 与 \(r\) 在 \(i\) 处的卷积值,分四个字母分别卷积即可。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define clr(f, n) memset(f, 0, sizeof(int) * (n))
#define cpy(f, g, n) memcpy(f, g, sizeof(int) * (n))
#define rev(f, n) reverse(f, f + (n))
const int N = 2e6 + 10, _G = 3, mod = 998244353;
ll qpow(ll a, ll k = mod - 2) {
ll res = 1;
while (k) {
if (k & 1) res = res * a % mod;
k >>= 1;
a = a * a % mod;
}
return res;
}
const int invG = qpow(_G);
int rev[N << 1], rev_len;
void rev_init(int n) {
if (rev_len == n) return;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) rev[i] = (rev[i >> 1] >> 1) | (i & 1 ? n >> 1 : 0);
rev_len = n;
}
void NTT(int *g, int op, int n) {
rev_init(n);
static ull f[N << 1], Gk[N << 1] = {1};
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) f[i] = g[rev[i]];
for (int k = 1; k < n; k <<= 1) {
int G1 = qpow(~op ? _G : invG, (mod - 1) / (k << 1));
for (int i = 1; i < k; i ++ ) Gk[i] = Gk[i - 1] * G1 % mod;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i += k << 1) {
for (int j = 0; j < k; j ++ ) {
int tmp = Gk[j] * f[i | j | k] % mod;
f[i | j | k] = f[i | j] + mod - tmp;
f[i | j] += tmp;
}
}
if (k == (1 << 10)) for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) f[i] %= mod;
}
if (~op) for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) g[i] = f[i] % mod;
else {
int invn = qpow(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) g[i] = f[i] % mod * invn % mod;
}
}
void px(int *f, int *g, int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) f[i] = 1ll * f[i] * g[i] % mod;
}
void covolution(int *f, int *g, int len, int lim) {
static int sav[N << 1];
int n; for (n = 1; n < len << 1; n <<= 1);
clr(sav, n); cpy(sav, g, n);
NTT(sav, 1, n); NTT(f, 1, n);
px(f, sav, n); NTT(f, -1, n);
clr(f + lim, n - lim), clr(sav, n);
}
int n, m; string s, r;
int f[4][N << 1], g[4][N << 1];
int reflect(char c) {
if (c == 'A') return 0;
if (c == 'C') return 1;
if (c == 'T') return 2;
if (c == 'G') return 3;
}
void solve() {
cin >> s >> r;
n = s.length(), m = r.length();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) f[reflect(s[i])][i] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i ++ ) g[reflect(r[i])][i] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++ ) rev(g[i], m), covolution(f[i], g[i], n, n);
int ans = m;
for (int i = m - 1; i < n; i ++ ) ans = min(m - (f[0][i] + f[1][i] + f[2][i] + f[3][i]), ans);
cout << ans << "\n";
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int T = 1;
// cin >> T;
while (T -- ) solve();
return 0;
}
MAXMATCH - Maximum Self-Matching
You're given a string s consisting of letters 'a', 'b' and 'c'.
The matching function ms( i ) is defined as the number of matching characters of s and its i-shift. In other words, ms( i ) is the number of characters that are matched when you align the 0-th character of s with the i-th character of its copy.
You are asked to compute the maximum of ms( i ) for all i ( 1 <= i <= |s| ). To make it a bit harder, you should also output all the optimal i's in increasing order.
Input
The first and only line of input contains the string s. 2 <= |s| <= 10^5.
Output
The first line of output contains the maximal ms( i ) over all i.
The second line of output contains all the i's for which ms( i ) reaches maximum.
和上面那个题可以说是完全一样,唯一需要注意的是第一个位置不能匹配。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define clr(f, n) memset(f, 0, sizeof(int) * (n))
#define cpy(f, g, n) memcpy(f, g, sizeof(int) * (n))
#define rev(f, n) reverse(f, f + (n))
const int N = 150000, _G = 3, mod = 998244353;
ll qpow(ll a, ll k = mod - 2) {
ll res = 1;
while (k) {
if (k & 1) res = res * a % mod;
k >>= 1;
a = a * a % mod;
}
return res;
}
const int invG = qpow(_G);
int rev[N << 1], rev_len;
void rev_init(int n) {
if (rev_len == n) return;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) rev[i] = (rev[i >> 1] >> 1) | (i & 1 ? n >> 1 : 0);
rev_len = n;
}
void NTT(int *g, int op, int n) {
rev_init(n);
static ull f[N << 1], Gk[N << 1] = {1};
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) f[i] = g[rev[i]];
for (int k = 1; k < n; k <<= 1) {
int G1 = qpow(~op ? _G : invG, (mod - 1) / (k << 1));
for (int i = 1; i < k; i ++ ) Gk[i] = Gk[i - 1] * G1 % mod;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i += k << 1) {
for (int j = 0; j < k; j ++ ) {
int tmp = Gk[j] * f[i | j | k] % mod;
f[i | j | k] = f[i | j] + mod - tmp;
f[i | j] += tmp;
}
}
if (k == (1 << 10)) for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) f[i] %= mod;
}
if (~op) for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) g[i] = f[i] % mod;
else {
int invn = qpow(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) g[i] = f[i] % mod * invn % mod;
}
}
void px(int *f, int *g, int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) f[i] = 1ll * f[i] * g[i] % mod;
}
void covolution(int *f, int *g, int len, int lim) {
static int sav[N << 1];
int n; for (n = 1; n < len << 1; n <<= 1);
clr(sav, n); cpy(sav, g, n);
NTT(sav, 1, n); NTT(f, 1, n);
px(f, sav, n); NTT(f, -1, n);
clr(f + lim, n - lim), clr(sav, n);
}
int n; string s;
int f[3][N << 1], g[3][N << 1];
void solve() {
cin >> s, n = s.length();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) f[s[i] - 'a'][i] = g[s[i] - 'a'][i] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i ++ ) rev(g[i], n), covolution(f[i], g[i], n, n << 1);
int ans = 0;
vector<int> pos;
for (int i = n; i < n << 1; i ++ ) {
if (ans < f[0][i] + f[1][i] + f[2][i]) {
ans = f[0][i] + f[1][i] + f[2][i];
pos.clear();
pos.push_back(i - (n - 1));
} else if (ans == f[0][i] + f[1][i] + f[2][i]) pos.push_back(i - (n - 1));
}
cout << ans << "\n";
for (auto i : pos) cout << i << " ";
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int T = 1;
// cin >> T;
while (T -- ) solve();
return 0;
}
K-Inversions
You are given a string s consisting only of upper case letters A and B. For an integer k, a pair of indices i and j (1≤i<j≤n) is called a k-inversion if and only if s[i]=B, s[j]=A and j−i=k.
Consider the string BABA. It has two 1-inversions and one 3-inversion. It has no 2-inversions.
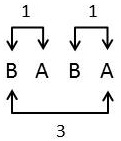
For each k between 1 and n−1 (inclusive), print the number of k-inversions in the string s.
Input
Each input will consist of a single test case. Note that your program may be run multiple times on different inputs. The input will consist of a single line with a string s, which consists of only upper case As and Bs. The string s will be between 1 and 1,000,000 characters long. There will be no spaces.
Output
n−1 lines, each with a single integer. The first line’s integer should be the number of 1-inversions, the second should be the number of 2-inversions, and so on.
按照题意,我们想知道 \(a_i - b_j = k\) 的数量,我们构造两个多项式 \(F(x) = \sum_{i = 0}^n[s_i = \textbf{A}]x^i, \, G(x) = \sum_{i = 0}^n[s_i = \textbf{B}]x^i\),我们将 \(G(x)\) 取反再卷积可以得到 \(H(x) = \left(\sum_{i = 0}^n[s_i = \textbf{A}]x^i\right)\left(\sum_{i = 0}^n[s_i = \textbf{B}]x^{n-i}\right)\),那么 \(k\) 的答案显然是 \([x^{n + k}]H(x)\)。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define ld long double
#define ull unsigned long long
#define PII pair<ll, ll>
#define pb push_back
#define clr(f, n) memset(f, 0, sizeof(int) * (n))
#define cpy(f, g, n) memcpy(f, g, sizeof(int) * (n))
#define rev(f, n) reverse(f, f + (n))
const int N = 1.5e6 + 10, _G = 3, mod = 998244353;
ll qpow(ll a, ll k = mod - 2) {
ll res = 1;
while (k) {
if (k & 1) res = res * a % mod;
k >>= 1;
a = a * a % mod;
}
return res;
}
const int invG = qpow(_G);
int rev[N << 1], rev_len;
void rev_init(int n) {
if (rev_len == n) return;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) rev[i] = (rev[i >> 1] >> 1) | (i & 1 ? n >> 1 : 0);
rev_len = n;
}
void NTT(int *g, int op, int n) {
rev_init(n);
static ull f[N << 1], Gk[N << 1] = {1};
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) f[i] = g[rev[i]];
for (int k = 1; k < n; k <<= 1) {
int G1 = qpow(~op ? _G : invG, (mod - 1) / (k << 1));
for (int i = 1; i < k; i ++ ) Gk[i] = Gk[i - 1] * G1 % mod;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i += k << 1) {
for (int j = 0; j < k; j ++ ) {
int tmp = Gk[j] * f[i | j | k] % mod;
f[i | j | k] = f[i | j] + mod - tmp;
f[i | j] += tmp;
}
}
if (k == (1 << 10)) for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) f[i] %= mod;
}
if (~op) for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) g[i] = f[i] % mod;
else {
int invn = qpow(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) g[i] = f[i] % mod * invn % mod;
}
}
void px(int *f, int *g, int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) f[i] = 1ll * f[i] * g[i] % mod;
}
void covolution(int *f, int *g, int len, int lim) {
static int sav[N << 1];
int n; for (n = 1; n < len << 1; n <<= 1);
clr(sav, n); cpy(sav, g, n);
NTT(sav, 1, n); NTT(f, 1, n);
px(f, sav, n); NTT(f, -1, n);
clr(f + lim, n - lim), clr(sav, n);
}
int n; string s;
int f[N << 1], g[N << 1];
void solve() {
cin >> s; n = s.length();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) f[i] = s[i] == 'A', g[i] = s[i] == 'B';
rev(g, n), covolution(f, g, n, n << 1);
for (int i = n; i < (n << 1) - 1; i ++ ) cout << f[i] << "\n";
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int T = 1;
// cin >> T;
while (T -- ) solve();
return 0;
}
Kattis - aplusb A+B Problem
Given N integers in the range [−50000,50000], how many ways are there to pick three integers ai, aj, ak, such that i, j, k are pairwise distinct and ai+aj=ak? Two ways are different if their ordered triples (i,j,k) of indices are different.
Input
The first line of input consists of a single integer N
(1≤N≤200000). The next line consists of N space-separated integers a1,a2,…,aN
Output
Output an integer representing the number of ways.
为了构造 \(a_i + a_j = a_k\),我们把数放到幂上,相当于我们只需要卷一下 \(\sum\limits_{i = 1}^nx^{a_i}\),然后去重之后并除以而保证偏序。
枚举 \(a_k\),去重只有少数情况:
-
\(i = k\) 或 \(j = k\),相当于 \(0 + a_i = a_i\),这种情况有 \(2\) 种。
-
\(i = j\),也就只有 \(a_i + a_i = a_k\) 的这种情况。
-
对于 \(0 + 0 = 0\) 的情况,由于上面两种情况减了 \(3\) 次 \(i = j = k\),所以我们还要加回来 \(2\) 次。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define ld long double
#define ull unsigned long long
#define PII pair<ll, ll>
#define pb push_back
#define clr(f, n) memset(f, 0, sizeof(int) * (n))
#define cpy(f, g, n) memcpy(f, g, sizeof(int) * (n))
#define rev(f, n) reverse(f, f + (n))
const int N = 4e5 + 10, mod = 998244353;
const ld Pi = acos(-1);
struct Complex {
ld x, y;
Complex (ld xx = 0, ld yy = 0) {x = xx, y = yy;}
Complex operator+ (Complex const &C) const {return Complex(x + C.x, y + C.y);}
Complex operator+ (ld R) {return Complex(x + R, y);}
Complex operator- (Complex const &C) const {return Complex(x - C.x, y - C.y);}
Complex operator- (ld R) {return Complex(x - R, y);}
Complex operator* (Complex const &C) const {return Complex(x * C.x - y * C.y, x * C.y + y * C.x);}
Complex operator/ (const ld &R) const {return Complex(x / R, y / R);}
Complex operator~ () {return Complex(x, -y);}
};
int rev[N << 1], rev_len;
void rev_init(int n) {
if (rev_len == n) return;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) rev[i] = (rev[i >> 1] >> 1) | (i & 1 ? n >> 1 : 0);
rev_len = n;
}
void FFT(Complex *f, int op, int n) {
rev_init(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) if (i < rev[i]) swap(f[i], f[rev[i]]);
for (int k = 1; k < n; k <<= 1) {
Complex w1 = Complex(cos(Pi / k), op * sin(Pi / k));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i += k << 1) {
Complex wk = Complex(1, 0);
for (int j = 0; j < k; j ++ , wk = wk * w1) {
Complex x = f[i + j], y = wk * f[i + j + k];
f[i + j] = x + y, f[i + j + k] = x - y;
}
}
}
if (op == -1) for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) f[i] = f[i] / n;
}
void px(Complex *f, Complex *g, int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) f[i] = f[i] * g[i];
}
void covolution(Complex *f, Complex *g, int len, int lim) {
static Complex sav[N << 1];
int n; for (n = 1; n < len << 1; n <<= 1);
clr(sav, n); cpy(sav, g, n);
FFT(sav, 1, n); FFT(f, 1, n);
px(f, sav, n); FFT(f, -1, n);
clr(f + lim, n - lim), clr(sav, n);
}
const int limit = 50000;
int n, a[N], cnt[N];
Complex F[N << 1];
ll get(Complex C) { return (ll)(C.y / 2 + 0.5); }
void solve() {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) cin >> a[i], cnt[a[i] + limit] ++ ;
for (int i = 0; i <= limit << 1; i ++ ) F[i] = Complex(cnt[i], cnt[i]);
int m; for (m = 1; m <= limit << 2; m <<= 1);
FFT(F, 1, m); px(F, F, m); FFT(F, -1, m);
ll ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
ans += get(F[a[i] + limit * 2]);
if (!(a[i] & 1)) ans -= cnt[(a[i] >> 1) + limit];
ans -= cnt[limit] << 1;
if (!a[i]) ans += 2;
}
cout << ans << "\n";
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int T = 1;
// cin >> T;
while (T -- ) solve();
return 0;
}
[ABC392G] Fine Triplets
当三个整数 \(A,B,C\)(满足 \(A < B < C\))满足 \(B - A = C - B\) 时,称 \((A,B,C)\) 为好的三元组。
给定一个包含 \(N\) 个元素的正整数集合 \(S = \{\ S_1, S_2, \dots, S_N\ \}\),求满足 \(A,B,C \in S\) 的好的三元组的个数。
输入格式
输入通过标准输入给出,格式如下:
\(N\)
\(S_1\) \(S_2\) \(\dots\) \(S_N\)
输出格式
输出答案作为整数。
限制
- 输入均为整数
- \(1 \leq N \leq 10^6\)
- \(1 \leq S_i \leq 10^6\)
- \(S\) 中的元素互不相同
移项之后可发现 \(A + C = 2B\),我们自卷积并去重后,枚举所有符合条件的 \(S_i\) 即可。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
const int N = 4e6 + 10;
const double Pi = acos(-1);
int n, m = 2e6 + 2, s, a[N], rev[N];
struct Complex {
double x, y;
Complex (double xx = 0, double yy = 0) {x = xx, y = yy;}
Complex operator+ (Complex const &Z) const {
return Complex(x + Z.x, y + Z.y);
}
Complex operator- (Complex const &Z) const {
return Complex(x - Z.x, y - Z.y);
}
Complex operator* (Complex const &Z) const {
return Complex(x * Z.x - y * Z.y, x * Z.y + y * Z.x);
}
}f[N];
void fft(Complex *f, int op) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
if (i < rev[i]) {
swap(f[i], f[rev[i]]);
}
}
for (int k = 1; k < n; k <<= 1) {
Complex w1 = Complex(cos(Pi / k), op * sin(Pi / k));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i += k << 1) {
Complex wk = Complex(1, 0);
for (int j = 0; j < k; j ++ , wk = wk * w1) {
Complex x = f[i + j], y = wk * f[i + j + k];
f[i + j] = x + y, f[i + j + k] = x - y;
}
}
}
if (op == -1) for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) f[i].x /= n, f[i].y /= n;
}
void solve() {
cin >> n, s = n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) cin >> a[i], f[a[i]] = Complex(1, 1);
for (n = 1; n <= m; n <<= 1);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i ++ ) rev[i] = (rev[i >> 1] >> 1) | (i & 1 ? n >> 1 : 0);
fft(f, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) f[i] = f[i] * f[i];
fft(f, -1);
ll ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= s; i ++ ) ans += (round(f[a[i] * 2].y / 2) - 1) / 2;
cout << ans;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int T = 1;
// cin >> T;
while (T -- ) solve();
return 0;
}
TSUM - Triple Sums
You're given a sequence s of N distinct integers. Consider all the possible sums of three integers from the sequence at three different indices. For each obtainable sum output the number of different triples of indices that generate it.
Constraints
N ≤ 40000, |si| ≤ 20000
Input
The first line of input contains a single integer N. Each of the next N lines contain an element of s.
Output
Print the solution for each possible sum in the following format:
sum_value : number_of_triples
Smaller sum values should be printed first.
考虑把数字放到多项式上,先不限制 \(i < j < k\),我们需要找出所有不同数的组合,为了避免重复,考虑容斥,设 \(A_{i, j}\) 表示第 \(i\) 位和第 \(j\) 位相同:
于是,设多项式
那么答案为 \(F^3(x) - 3F(x)G(x) + 2H(x)\),由于负数存在,我们先平移 \(20000\) 位即可。
本题用 FFT 实现,注意精度。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ld long double
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e6 + 10;
const double Pi = acos(-1);
struct Complex {
ld x, y;
Complex (ld xx = 0, ld yy = 0) {x = xx, y = yy;}
Complex operator+ (Complex const &C) const {return Complex(x + C.x, y + C.y);}
Complex operator- (Complex const &C) const {return Complex(x - C.x, y - C.y);}
Complex operator* (Complex const &C) const {return Complex(x * C.x - y * C.y, x * C.y + y * C.x);}
Complex operator/ (const ld &C) const {return Complex(x / C, y / C);}
}f[N << 1];
int rev[N << 1], rev_len;
void rev_init(int n) {
if (rev_len == n) return;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) rev[i] = (rev[i >> 1] >> 1) | (i & 1 ? n >> 1 : 0);
rev_len = n;
}
void fft(Complex *f, int op, int n) {
rev_init(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) if (i < rev[i]) swap(f[i], f[rev[i]]);
for (int k = 1; k < n; k <<= 1) {
Complex w1 = Complex(cos(Pi / k), op * sin(Pi / k));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i += k << 1) {
Complex wk = Complex(1, 0);
for (int j = 0; j < k; j ++ , wk = wk * w1) {
Complex x = f[i + j], y = wk * f[i + j + k];
f[i + j] = x + y, f[i + j + k] = x - y;
}
}
}
if (op == -1) for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) f[i].x /= n, f[i].y /= n;
}
int n, limit = 20000, sz = 40001, a[N];
Complex F[N << 1], G[N << 1], H[N << 1];
void solve() {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
cin >> a[i]; a[i] += limit;
F[a[i]].x += 1; G[a[i] * 2].x += 1; H[a[i] * 3].x += 2;
}
int m; for (m = 1; m < sz * 3; m <<= 1);
fft(F, 1, m); fft(G, 1, m);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i ++ ) G[i] = F[i] * G[i] * 3;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i ++ ) F[i] = F[i] * F[i] * F[i];
fft(F, -1, m), fft(G, -1, m);
for (int i = 0; i < sz * 3; i ++ ) F[i] = (F[i] - G[i] + H[i]) / 6;
for (int i = 0; i < sz * 3; i ++ ) {
ll cnt = F[i].x + 0.5;
if (cnt > 0) cout << i - limit * 3 << " : " << cnt << "\n";
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int T = 1;
// cin >> T;
while (T -- ) solve();
return 0;
}
CF993E Nikita and Order Statistics
Nikita likes tasks on order statistics, for example, he can easily find the $ k $ -th number in increasing order on a segment of an array. But now Nikita wonders how many segments of an array there are such that a given number $ x $ is the $ k $ -th number in increasing order on this segment. In other words, you should find the number of segments of a given array such that there are exactly $ k $ numbers of this segment which are less than $ x $ .
Nikita wants to get answer for this question for each $ k $ from $ 0 $ to $ n $ , where $ n $ is the size of the array.
Input
The first line contains two integers $ n $ and $ x $ $ (1 \le n \le 2 \cdot 10^5, -10^9 \le x \le 10^9) $ .
The second line contains $ n $ integers $ a_1, a_2, \ldots, a_n $ $ (-10^9 \le a_i \le 10^9) $ — the given array.
Output
Print $ n+1 $ integers, where the $ i $ -th number is the answer for Nikita's question for $ k=i-1 $ .
我们只关系小于 \(x\) 的数的个数,所以将所有小数改为 \(1\),大数改为 \(0\),我们做前缀和可以得到
考虑把 \(s_i\) 放到多项式上,那么有
为了求出所有 \(Ans_{i - j} = \sum\limits_{i = 0}^n[x^i]F(x) \times [x^j]F(x)\),将 \(G(x)\) 定义为 \(F(x)\) 的翻转,则
也就是
为 \(0\) 时需要特判,因为此时不满足 \(i > j\),同时,由于答案超过 \(2^{32}\),我们选取了一个 \(2^{63}\) 级别的模数,并用 int128 实现,当然,FFT 也是可接受的。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define i128 __int128
#define clr(f, n) memset(f, 0, sizeof(ll) * (n))
#define cpy(f, g, n) memcpy(f, g, sizeof(ll) * (n))
#define rev(f, n) reverse(f, f + (n))
const int N = 4e5 + 10, _G = 3;
const ll mod = 1337006139375617;
ll qpow(i128 a, i128 k = mod - 2) {
i128 res = 1;
while (k) {
if (k & 1) res = res * a % mod;
k >>= 1;
a = a * a % mod;
}
return res;
}
const ull invG = qpow(_G);
int rev[N << 1], rev_len;
void rev_init(int n) {
if (rev_len == n) return;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) rev[i] = (rev[i >> 1] >> 1) | (i & 1 ? n >> 1 : 0);
rev_len = n;
}
void NTT(ll *g, int op, int n) {
rev_init(n);
static __int128 f[N << 1], Gk[N << 1] = {1};
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) f[i] = g[rev[i]];
for (int k = 1; k < n; k <<= 1) {
ull G1 = qpow(~op ? _G : invG, (mod - 1) / (k << 1));
for (int i = 1; i < k; i ++ ) Gk[i] = (__int128)Gk[i - 1] * G1 % mod;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i += k << 1) {
for (int j = 0; j < k; j ++ ) {
ull tmp = (__int128)Gk[j] * f[i | j | k] % mod;
f[i | j | k] = f[i | j] + mod - tmp;
f[i | j] += tmp;
}
}
if (k == (1 << 10)) for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) f[i] %= mod;
}
if (~op) for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) g[i] = f[i] % mod;
else {
ull invn = qpow(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) g[i] = f[i] % mod * invn % mod;
}
}
void px(ll *f, ll *g, int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) f[i] = (__int128)f[i] * g[i] % mod;
}
void covolution(ll *f, ll *g, int len, int lim) {
static ll sav[N << 1];
int n; for (n = 1; n < len << 1; n <<= 1);
clr(sav, n); cpy(sav, g, n);
NTT(sav, 1, n); NTT(f, 1, n);
px(f, sav, n); NTT(f, -1, n);
clr(f + lim, n - lim), clr(sav, n);
}
int n, x, a[N];
ll F[N << 1], G[N << 1];
ll get0() {
int last = 0;
ll res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
if (a[last] != a[i]) last = i;
else res += i - last;
}
return res;
}
void solve() {
cin >> n >> x;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) cin >> a[i], a[i] = a[i - 1] + (a[i] < x);
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i ++ ) F[a[i]] ++ ;
cpy(G, F, n + 1); rev(G, n + 1);
covolution(F, G, n + 1, (n << 1) + 1);
cout << get0() << " ";
for (int i = n + 1; i <= n << 1; i ++ ) cout << F[i] << " \n"[i == (n << 1)];
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int T = 1;
// cin >> T;
while (T -- ) solve();
return 0;
}
CF1398G Running Competition
A running competition is going to be held soon. The stadium where the competition will be held can be represented by several segments on the coordinate plane:
- two horizontal segments: one connecting the points $ (0, 0) $ and $ (x, 0) $ , the other connecting the points $ (0, y) $ and $ (x, y) $ ;
- $ n + 1 $ vertical segments, numbered from $ 0 $ to $ n $ . The $ i $ -th segment connects the points $ (a_i, 0) $ and $ (a_i, y) $ ; $ 0 = a_0 < a_1 < a_2 < \dots < a_{n - 1} < a_n = x $ .
For example, here is a picture of the stadium with $ x = 10 $ , $ y = 5 $ , $ n = 3 $ and $ a = [0, 3, 5, 10] $ :
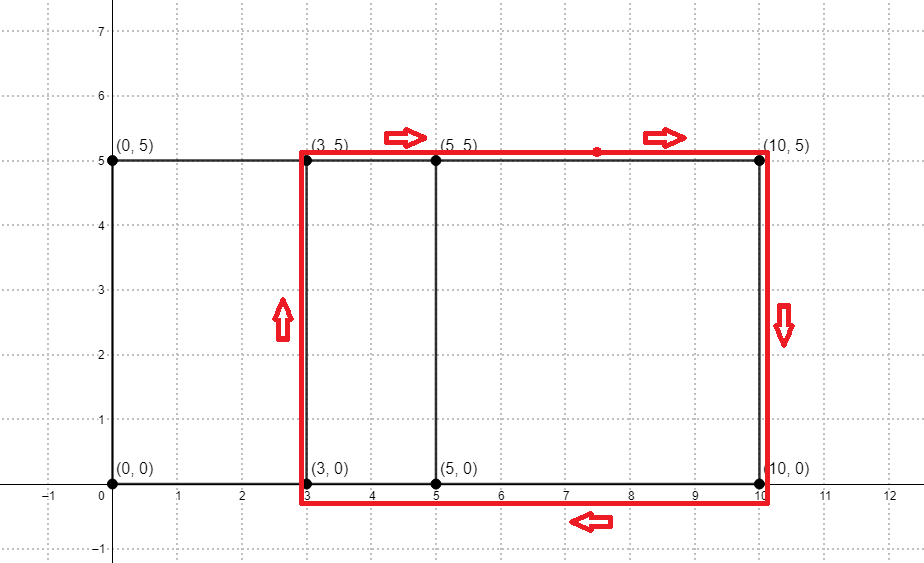 A lap is a route that goes along the segments, starts and finishes at the same point, and never intersects itself (the only two points of a lap that coincide are its starting point and ending point). The length of a lap is a total distance travelled around it. For example, the red route in the picture representing the stadium is a lap of length $ 24 $ .
A lap is a route that goes along the segments, starts and finishes at the same point, and never intersects itself (the only two points of a lap that coincide are its starting point and ending point). The length of a lap is a total distance travelled around it. For example, the red route in the picture representing the stadium is a lap of length $ 24 $ .
The competition will be held in $ q $ stages. The $ i $ -th stage has length $ l_i $ , and the organizers want to choose a lap for each stage such that the length of the lap is a divisor of $ l_i $ . The organizers don't want to choose short laps for the stages, so for each stage, they want to find the maximum possible length of a suitable lap.
Help the organizers to calculate the maximum possible lengths of the laps for the stages! In other words, for every $ l_i $ , find the maximum possible integer $ L $ such that $ l_i \bmod L = 0 $ , and there exists a lap of length exactly $ L $ .
If it is impossible to choose such a lap then print $ -1 $ .
Input
The first line contains three integers $ n $ , $ x $ and $ y $ ( $ 1 \le n, x, y \le 2 \cdot 10^5 $ , $ n \le x $ ).
The second line contains $ n + 1 $ integers $ a_0 $ , $ a_1 $ , ..., $ a_n $ ( $ 0 = a_0 < a_1 < a_2 < \dots < a_{n - 1} < a_n = x $ ).
The third line contains one integer $ q $ ( $ 1 \le q \le 2 \cdot 10^5 $ ) — the number of stages.
The fourth line contains $ q $ even integers $ l_1 $ , $ l_2 $ , ..., $ l_q $ ( $ 4 \le l_i \le 10^6 $ ) — the lengths of the stages.
Output
Print $ q $ numbers. The $ i $ -th number should be equal to the maximum possible length of a suitable lap for the $ i $ -th stage, or $ -1 $ if it is impossible to choose a lap for that stage.
这个题本质上事项让我们求出所有合法的 \(a_i - a_j\),构造生成函数 \(F(x) = \sum_{i = 0}^nx^{a_i}\),我们可以将生成函数的系数反向,即 \(G(x) = \sum_{i = 0}^nx^{M - a_i}\),把两个生成函数卷起来就可以得到哪些位置是合法的。
本题还需要处理的是输出 \(L \mid l_i\) 的最大合法 \(L\),我们可以找出所有的 \(L\) 之后,枚举它的倍数更新合法数组,总体复杂度是 \(O(n\log{n} + L\ln{L})\) 的,跑起来很快。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define ld long double
#define ull unsigned long long
#define PII pair<ll, ll>
#define pb push_back
#define clr(f, n) memset(f, 0, sizeof(int) * (n))
#define cpy(f, g, n) memcpy(f, g, sizeof(int) * (n))
#define rev(f, n) reverse(f, f + (n))
const int N = 1e6 + 10, _G = 3, mod = 998244353;
ll qpow(ll a, ll k = mod - 2) {
ll res = 1;
while (k) {
if (k & 1) res = res * a % mod;
k >>= 1;
a = a * a % mod;
}
return res;
}
const int invG = qpow(_G);
int rev[N << 1], rev_len;
void rev_init(int n) {
if (rev_len == n) return;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) rev[i] = (rev[i >> 1] >> 1) | (i & 1 ? n >> 1 : 0);
rev_len = n;
}
void NTT(int *g, int op, int n) {
rev_init(n);
static ull f[N << 1], Gk[N << 1] = {1};
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) f[i] = g[rev[i]];
for (int k = 1; k < n; k <<= 1) {
int G1 = qpow(~op ? _G : invG, (mod - 1) / (k << 1));
for (int i = 1; i < k; i ++ ) Gk[i] = Gk[i - 1] * G1 % mod;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i += k << 1) {
for (int j = 0; j < k; j ++ ) {
int tmp = Gk[j] * f[i | j | k] % mod;
f[i | j | k] = f[i | j] + mod - tmp;
f[i | j] += tmp;
}
}
if (k == (1 << 10)) for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) f[i] %= mod;
}
if (~op) for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) g[i] = f[i] % mod;
else {
int invn = qpow(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) g[i] = f[i] % mod * invn % mod;
}
}
void px(int *f, int *g, int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) f[i] = 1ll * f[i] * g[i] % mod;
}
void covolution(int *f, int *g, int len, int lim) {
static int sav[N << 1];
int n; for (n = 1; n < len << 1; n <<= 1);
clr(sav, n); cpy(sav, g, n);
NTT(sav, 1, n); NTT(f, 1, n);
px(f, sav, n); NTT(f, -1, n);
clr(f + lim, n - lim), clr(sav, n);
}
int n, q, x, y, a[N], cnt[N];
int F[N << 1], G[N << 1], maxn = 1e6;
void solve() {
cin >> n >> x >> y;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i ++ ) cin >> a[i], F[a[i]] = 1, G[x - a[i]] = 1;
covolution(F, G, x + 1, (x << 1) + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= x; i ++ ) cnt[i + y << 1] = (!!F[x + i]) * (i + y << 1);
for (int i = y << 1; i <= maxn; i += 2) {
if (!cnt[i]) continue;
for (int j = i; j <= maxn; j += i) {
if (cnt[j] < cnt[i]) cnt[j] = cnt[i];
}
}
cin >> q;
for (int i = 1, l; i <= q; i ++ ) {
cin >> l;
if (cnt[l]) cout << cnt[l] << " ";
else cout << "-1 ";
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int T = 1;
// cin >> T;
while (T -- ) solve();
return 0;
}
P3723 [AH2017/HNOI2017] 礼物 - 洛谷
我的室友最近喜欢上了一个可爱的小女生。马上就要到她的生日了,他决定买一对情侣手环,一个留给自己,一个送给她。每个手环上各有 \(n\) 个装饰物,并且每个装饰物都有一定的亮度。
但是在她生日的前一天,我的室友突然发现他好像拿错了一个手环,而且已经没时间去更换它了!他只能使用一种特殊的方法,将其中一个手环中所有装饰物的亮度增加一个相同的非负整数 \(c\)。并且由于这个手环是一个圆,可以以任意的角度旋转它,但是由于上面装饰物的方向是固定的,所以手环不能翻转。需要在经过亮度改造和旋转之后,使得两个手环的差异值最小。
在将两个手环旋转且装饰物对齐了之后,从对齐的某个位置开始逆时针方向对装饰物编号 \(1 \sim n\),其中 \(n\) 为每个手环的装饰物个数, 第 \(1\) 个手环的 \(i\) 号位置装饰物亮度为 \(x_i\),第 \(2\) 个手环的 \(i\) 号位置装饰物亮度为 \(y_i\),两个手环之间的差异值为(参见输入输出样例和样例解释):
麻烦你帮他计算一下,进行调整(亮度改造和旋转),使得两个手环之间的差异值最小,这个最小值是多少呢?
输入格式
输入数据的第一行有两个数 \(n,m\),代表每条手环的装饰物的数量为 \(n\),每个装饰物的初始亮度小于等于 \(m\)。
接下来两行,每行各有 \(n\) 个数,分别代表第一条手环和第二条手环上从某个位置开始逆时针方向上各装饰物的亮度。
输出格式
输出一个数,表示两个手环能产生的最小差异值。注意在将手环改造之后,装饰物的亮度可以大于 \(m\)。
数据范围
对于 \(30\%\) 的数据,\(n \le 500\),\(m \le 10\);
对于 \(70\%\) 的数据,\(n \le 5000\);
对于 \(100\%\) 的数据,\(1 \le n \le 50000\), \(1 \le x_i,y_i \le m \le 100\)。
首先我们把式子的最终形态写为
通过展开式子我们可以得到
事实上我们容易发现常数很多
鉴于手环可以旋转,我们的 \(x_i\) 需要被看做 \(x_{i + j}\),但是 \(\sum\limits_{i = 1}^n(x_i^2 + y_i^2)\) 和 \(\sum\limits_{i = 1}^n(x_i - y_i)\) 在旋转中始终为定值,\(\sum\limits_{i = 1}^nx_{i + j}y_i\) 可以通过翻转 \(y\) 卷积求出,于是,我们可以枚举 \(c\) 找到最小值。
卷积中最大不超过 \(100 \times 50000 = 5 \times 10^6\),用 NTT 即可。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define ld long double
#define ull unsigned long long
#define PII pair<ll, ll>
#define pb push_back
#define clr(f, n) memset(f, 0, sizeof(int) * (n))
#define cpy(f, g, n) memcpy(f, g, sizeof(int) * (n))
#define rev(f, n) reverse(f, f + (n))
const int N = 4e5 + 10, _G = 3, mod = 998244353;
ll qpow(ll a, ll k = mod - 2) {
ll res = 1;
while (k) {
if (k & 1) res = res * a % mod;
k >>= 1;
a = a * a % mod;
}
return res;
}
const int invG = qpow(_G);
int rev[N << 1], rev_len;
void rev_init(int n) {
if (rev_len == n) return;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) rev[i] = (rev[i >> 1] >> 1) | (i & 1 ? n >> 1 : 0);
rev_len = n;
}
void NTT(int *g, int op, int n) {
rev_init(n);
static ull f[N << 1], Gk[N << 1] = {1};
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) f[i] = g[rev[i]];
for (int k = 1; k < n; k <<= 1) {
int G1 = qpow(~op ? _G : invG, (mod - 1) / (k << 1));
for (int i = 1; i < k; i ++ ) Gk[i] = Gk[i - 1] * G1 % mod;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i += k << 1) {
for (int j = 0; j < k; j ++ ) {
int tmp = Gk[j] * f[i | j | k] % mod;
f[i | j | k] = f[i | j] + mod - tmp;
f[i | j] += tmp;
}
}
if (k == (1 << 10)) for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) f[i] %= mod;
}
if (~op) for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) g[i] = f[i] % mod;
else {
int invn = qpow(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) g[i] = f[i] % mod * invn % mod;
}
}
void px(int *f, int *g, int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) f[i] = 1ll * f[i] * g[i] % mod;
}
void covolution(int *f, int *g, int len, int lim) {
static int sav[N << 1];
int n; for (n = 1; n < len << 1; n <<= 1);
clr(sav, n); cpy(sav, g, n);
NTT(sav, 1, n); NTT(f, 1, n);
px(f, sav, n); NTT(f, -1, n);
clr(f + lim, n - lim), clr(sav, n);
}
int inv[N << 1], inv_len;
void inv_init(int n) {
if (n <= inv_len) return;
if (!inv_len) inv[0] = inv[1] = 1, inv_len = 1;
for (int i = inv_len + 1; i <= n; i ++ ) inv[i] = 1ll * inv[mod % i] * (mod - mod / i) % mod;
inv_len = n;
}
void Poly_d(int *f, int n) {
for (int i = 1; i < n; i ++ ) f[i - 1] = 1ll * f[i] * i % mod;
f[n - 1] = 0;
}
void Poly_int(int *f, int n) {
for (int i = n; i; i -- ) f[i] = 1ll * f[i - 1] * inv[i] % mod;
f[0] = 0;
}
void Poly_inv(int *f, int m) {
static int g1[N << 1], g2[N << 1], sav[N << 1];
int n; for (n = 1; n < m; n <<= 1);
g1[0] = qpow(f[0]);
for (int len = 2; len <= n; len <<= 1) {
cpy(g2, g1, len >> 1), cpy(sav, f, len);
NTT(g2, 1, len), NTT(sav, 1, len);
px(g2, sav, len); NTT(g2, -1, len);
clr(g2, len >> 1); cpy(sav, g1, len);
NTT(sav, 1, len); NTT(g2, 1, len);
px(g2, sav, len); NTT(g2, -1, len);
for (int i = len >> 1; i < len; i ++ ) g1[i] = (2ll * g1[i] - g2[i] + mod) % mod;
}
cpy(f, g1, m), clr(g1, n), clr(g2, n), clr(sav, n);
}
void Poly_ln(int *f, int n) {
static int sav[N << 1];
inv_init(n); cpy(sav, f, n);
Poly_d(sav, n); Poly_inv(f, n);
covolution(f, sav, n, n); Poly_int(f, n - 1);
clr(sav, n);
}
void Poly_exp(int *f, int m) {
static int b1[N << 1], b2[N << 1];
int n; for (n = 1; n < m; n <<= 1);
b1[0] = 1;
for (int len = 2; len <= n; len <<= 1) {
cpy(b2, b1, len >> 1); Poly_ln(b2, len);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i ++ ) b2[i] = (f[i] - b2[i] + mod) % mod;
b2[0] = (b2[0] + 1) % mod;
covolution(b1, b2, len, len);
}
cpy(f, b1, m); clr(b1, n); clr(b2, n);
}
int n, m, a[N], b[N];
ll res, coff, ans = 1e9;
void solve() {
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) cin >> a[i], a[i + n] = a[i];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) cin >> b[i];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) res += a[i] * a[i] + b[i] * b[i], coff += a[i] - b[i] << 1;
rev(b, n); covolution(a, b, n << 1, (n << 1) - 1);
for (int i = n; i < n << 1; i ++ ) {
for (int c = -m; c <= m; c ++ ) {
ans = min(res - (a[i] << 1) + n * c * c + coff * c, ans);
}
}
cout << ans << "\n";
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int T = 1;
// cin >> T;
while (T -- ) solve();
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号