树链剖分
定义
将一棵树划分为许多条重链,从而将树上问题转化为区间问题。
什么是重链?
对于树上节点 \(i\),我们定义其「重儿子」\(son_i\) 为 \(i\) 的所有儿子中子树大小最大的儿子节点,其「轻儿子」即为除去「重儿子」外的所有儿子节点。
进一步的,我们定义「重链」为从每个「轻儿子」出发,不断向下走「重儿子」直至叶子节点而形成的一条路径。如下图所示。
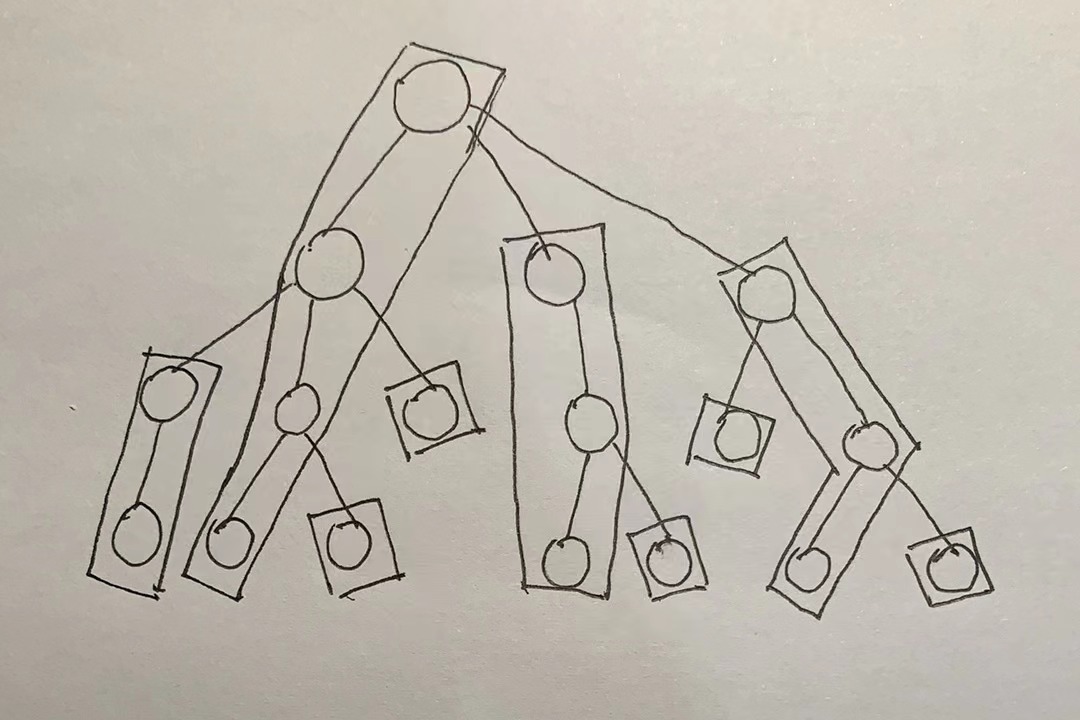
与 DSU on tree 类似,容易得知这样的重链至多 \(\log n\) 条。
实现时运用两个 dfs 即可完成划分。
void dfs(int cur,int f,int d){
siz[cur]=1,fa[cur]=f,dep[cur]=d;
for(int i:G[cur]){
if(!dep[i]){
dfs(i,cur,d+1);
siz[cur]+=siz[i];
if(siz[son[cur]]<siz[i])
son[cur]=i;
}
}
}
void DFS(int cur){
dfn[cur]=++tim,id[tim]=cur;
if(son[cur])
top[son[cur]]=top[cur],DFS(son[cur]);
for(int i:G[cur])
if(!top[i])
top[i]=i,DFS(i);
}
树上问题的处理
于是,对于树上每条简单路径,我们都可以通过将重链拼接的方式转化为区间问题,子树同理。
立题
P3384
模板。
实现
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int N=1e6+5;
int n,m,root,MOD,tim;
int a[N],siz[N],fa[N],dep[N],son[N],dfn[N],id[N],top[N];
vector<int> G[N];
struct TREE{
int sum,tag;
}tr[N];
//dfs
void dfs(int cur,int f,int d){
siz[cur]=1,fa[cur]=f,dep[cur]=d;
for(int i:G[cur]){
if(!dep[i]){
dfs(i,cur,d+1);
siz[cur]+=siz[i];
if(siz[son[cur]]<siz[i])
son[cur]=i;
}
}
}
void DFS(int cur){
dfn[cur]=++tim,id[tim]=cur;
if(son[cur])
top[son[cur]]=top[cur],DFS(son[cur]);
for(int i:G[cur])
if(!top[i])
top[i]=i,DFS(i);
}
//SGT
void pushup(int p){
tr[p].sum=tr[p<<1].sum+tr[p<<1|1].sum;
}
void addtag(int p,int lt,int rt,int val){
tr[p].tag+=val;
tr[p].sum+=val*(rt-lt+1);
}
void pushdown(int p,int lt,int rt){
if(!tr[p].tag)
return;
int mid=(lt+rt)>>1;
addtag(p<<1,lt,mid,tr[p].tag);
addtag(p<<1|1,mid+1,rt,tr[p].tag);
tr[p].tag=0;
}
void build(int p,int lt,int rt){
if(lt==rt){
tr[p].sum=a[id[lt]]%MOD;
return;
}
int mid=(lt+rt)>>1;
build(p<<1,lt,mid);
build(p<<1|1,mid+1,rt);
pushup(p);
}
void upd(int p,int lt,int rt,int ql,int qr,int val){
if(lt>qr||rt<ql)
return;
if(ql<=lt&&rt<=qr){
addtag(p,lt,rt,val);
return;
}
pushdown(p,lt,rt);
int mid=(lt+rt)>>1;
upd(p<<1,lt,mid,ql,qr,val);
upd(p<<1|1,mid+1,rt,ql,qr,val);
pushup(p);
}
int qry(int p,int lt,int rt,int ql,int qr){
if(lt>qr||rt<ql)
return 0;
if(ql<=lt&&rt<=qr)
return tr[p].sum%MOD;
pushdown(p,lt,rt);
int mid=(lt+rt)>>1;
return (qry(p<<1,lt,mid,ql,qr)+qry(p<<1|1,mid+1,rt,ql,qr))%MOD;
}
//Task
void upd_path(int x,int y,int val){
while(top[x]!=top[y]){
if(dep[top[x]]<dep[top[y]])
swap(x,y);
upd(1,1,n,dfn[top[x]],dfn[x],val);
x=fa[top[x]];
}
if(dep[y]>dep[x])
swap(x,y);
upd(1,1,n,dfn[y],dfn[x],val);
}
int qry_path(int x,int y){
int res=0;
while(top[x]!=top[y]){
if(dep[top[x]]<dep[top[y]])
swap(x,y);
res=(res+qry(1,1,n,dfn[top[x]],dfn[x]))%MOD;
x=fa[top[x]];
}
if(dep[y]>dep[x])
swap(x,y);
res=(res+qry(1,1,n,dfn[y],dfn[x]))%MOD;
return res;
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cin>>n>>m>>root>>MOD;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
cin>>a[i],a[i]%=MOD;
for(int i=1,u,v;i<n;i++)
cin>>u>>v,G[u].push_back(v),G[v].push_back(u);
dfs(root,0,1),top[root]=root,DFS(root);
build(1,1,n);
while(m--){
int op,x,y,z;
cin>>op>>x;
if(op==1)
cin>>y>>z,upd_path(x,y,z%MOD);
else if(op==2)
cin>>y,cout<<qry_path(x,y)<<'\n';
else if(op==3)
cin>>z,upd(1,1,n,dfn[x],dfn[x]+siz[x]-1,z);
else
cout<<qry(1,1,n,dfn[x],dfn[x]+siz[x]-1)<<'\n';
}
return 0;
}
P1505
总结:边权转点权,将边权赋值到它对应的较深端点上。
实现
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
//Var
const int N=1e6+5;
int n,m,root=1,tim;
int a[N],to[N];
int siz[N],fa[N],dep[N],son[N];
int dfn[N],id[N],top[N];
struct EDGE{
int v,w,id;
};
vector<EDGE> G[N];
struct TREE{
int sum,tag,max,min;
}tr[N];
//DFS
void dfs(int cur,int f,int d){
siz[cur]=1,fa[cur]=f,dep[cur]=d;
for(auto i:G[cur]){
if(!dep[i.v]){
a[i.v]=i.w,to[i.id]=i.v;
dfs(i.v,cur,d+1);
siz[cur]+=siz[i.v];
if(siz[son[cur]]<siz[i.v])
son[cur]=i.v;
}
}
}
void DFS(int cur){
dfn[cur]=++tim,id[tim]=cur;
if(son[cur])
top[son[cur]]=top[cur],DFS(son[cur]);
for(auto i:G[cur])
if(!top[i.v])
top[i.v]=i.v,DFS(i.v);
}
//SGT
void pushup(int p){
tr[p].sum=tr[p<<1].sum+tr[p<<1|1].sum;
tr[p].max=max(tr[p<<1].max,tr[p<<1|1].max);
tr[p].min=min(tr[p<<1].min,tr[p<<1|1].min);
}
void addtag(int p){
tr[p].sum*=-1,tr[p].max*=-1,tr[p].min*=-1;
swap(tr[p].max,tr[p].min),tr[p].tag^=1;
}
void pushdown(int p){
if(!tr[p].tag)
return;
addtag(p<<1),addtag(p<<1|1),tr[p].tag=0;
}
void build(int p,int lt,int rt){
if(lt==rt){
tr[p].sum=tr[p].max=tr[p].min=a[id[lt]];
return;
}
int mid=(lt+rt)>>1;
build(p<<1,lt,mid);
build(p<<1|1,mid+1,rt);
pushup(p);
}
void upd_val(int p,int lt,int rt,int qx,int val){
if(lt>qx||rt<qx)
return;
if(lt==rt){
tr[p].sum=tr[p].max=tr[p].min=val;
return;
}
pushdown(p);
int mid=(lt+rt)>>1;
upd_val(p<<1,lt,mid,qx,val);
upd_val(p<<1|1,mid+1,rt,qx,val);
pushup(p);
}
void upd_mul(int p,int lt,int rt,int ql,int qr){
if(lt>qr||rt<ql)
return;
if(ql<=lt&&rt<=qr){
addtag(p);
return;
}
pushdown(p);
int mid=(lt+rt)>>1;
upd_mul(p<<1,lt,mid,ql,qr);
upd_mul(p<<1|1,mid+1,rt,ql,qr);
pushup(p);
}
int qry_sum(int p,int lt,int rt,int ql,int qr){
if(lt>qr||rt<ql)
return 0;
if(ql<=lt&&rt<=qr)
return tr[p].sum;
pushdown(p);
int mid=(lt+rt)>>1;
return qry_sum(p<<1,lt,mid,ql,qr)+qry_sum(p<<1|1,mid+1,rt,ql,qr);
}
int qry_max(int p,int lt,int rt,int ql,int qr){
if(lt>qr||rt<ql)
return -1e9;
if(ql<=lt&&rt<=qr)
return tr[p].max;
pushdown(p);
int mid=(lt+rt)>>1;
return max(qry_max(p<<1,lt,mid,ql,qr),qry_max(p<<1|1,mid+1,rt,ql,qr));
}
int qry_min(int p,int lt,int rt,int ql,int qr){
if(lt>qr||rt<ql)
return 1e9;
if(ql<=lt&&rt<=qr)
return tr[p].min;
pushdown(p);
int mid=(lt+rt)>>1;
return min(qry_min(p<<1,lt,mid,ql,qr),qry_min(p<<1|1,mid+1,rt,ql,qr));
}
//Task
void upd_path_mul(int x,int y){
while(top[x]!=top[y]){
if(dep[top[x]]<dep[top[y]])
swap(x,y);
upd_mul(1,1,n,dfn[top[x]],dfn[x]);
x=fa[top[x]];
}
if(dep[y]>dep[x])
swap(x,y);
upd_mul(1,1,n,dfn[y]+1,dfn[x]);
}
int qry_path_sum(int x,int y){
int res=0;
while(top[x]!=top[y]){
if(dep[top[x]]<dep[top[y]])
swap(x,y);
res+=qry_sum(1,1,n,dfn[top[x]],dfn[x]);
x=fa[top[x]];
}
if(x==y)
return res;
if(dep[y]>dep[x])
swap(x,y);
res+=qry_sum(1,1,n,dfn[y]+1,dfn[x]);
return res;
}
int qry_path_max(int x,int y){
int res=-1e9;
while(top[x]!=top[y]){
if(dep[top[x]]<dep[top[y]])
swap(x,y);
res=max(res,qry_max(1,1,n,dfn[top[x]],dfn[x]));
x=fa[top[x]];
}
if(x==y)
return res;
if(dep[y]>dep[x])
swap(x,y);
res=max(res,qry_max(1,1,n,dfn[y]+1,dfn[x]));
return res;
}
int qry_path_min(int x,int y){
int res=1e9;
while(top[x]!=top[y]){
if(dep[top[x]]<dep[top[y]])
swap(x,y);
res=min(res,qry_min(1,1,n,dfn[top[x]],dfn[x]));
x=fa[top[x]];
}
if(x==y)
return res;
if(dep[y]>dep[x])
swap(x,y);
res=min(res,qry_min(1,1,n,dfn[y]+1,dfn[x]));
return res;
}
//Main
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cin>>n;
for(int i=1,u,v,w;i<n;i++)
cin>>u>>v>>w,u++,v++,
G[u].push_back({v,w,i}),
G[v].push_back({u,w,i});
dfs(root,0,1),top[root]=root,DFS(root);
build(1,1,n);
cin>>m;
while(m--){
string op; int x,y;
cin>>op>>x>>y,x++,y++;
if(op[0]=='C')
x--,y--,upd_val(1,1,n,dfn[to[x]],y);
else if(op[0]=='N')
upd_path_mul(x,y);
else if(op[0]=='S')
cout<<qry_path_sum(x,y)<<'\n';
else if(op=="MAX")
cout<<qry_path_max(x,y)<<'\n';
else
cout<<qry_path_min(x,y)<<'\n';
}
return 0;
}
P3313
考虑建颜色数棵线段树,那么这个题就是板子了。
时间没问题,但是空间开不下,于是采用动态开点线段树即可。(分块也行,但是我没写)。
总结:树剖完之后,不一定线段树维护,不要有思维定式。
实现
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
//Var
const int N=1e5+5,M=2e6+5;
int n,q,tim,root,tot;
int w[N],c[N];
int siz[N],fa[N],dep[N],son[N],dfn[N],id[N],top[N],rt[N];
vector<int> G[N];
struct TREE{
int ls,rs,sum,max;
}tr[M];
//SGT
void pushup(int p){
tr[p].sum=tr[tr[p].ls].sum+tr[tr[p].rs].sum;
tr[p].max=max(tr[tr[p].ls].max,tr[tr[p].rs].max);
}
void build(int &p){ if(!p) p=++tot; }
void upd(int &p,int lt,int rt,int qx,int val){
build(p);
if(lt>qx||rt<qx)
return;
if(lt==rt){
tr[p].sum=tr[p].max=val;
return;
}
int mid=(lt+rt)>>1;
build(tr[p].ls);
build(tr[p].rs);
upd(tr[p].ls,lt,mid,qx,val);
upd(tr[p].rs,mid+1,rt,qx,val);
pushup(p);
}
int qry_sum(int p,int lt,int rt,int ql,int qr){
if(lt>qr||rt<ql||!p)
return 0;
if(ql<=lt&&rt<=qr)
return tr[p].sum;
int mid=(lt+rt)>>1;
return qry_sum(tr[p].ls,lt,mid,ql,qr)+qry_sum(tr[p].rs,mid+1,rt,ql,qr);
}
int qry_max(int p,int lt,int rt,int ql,int qr){
if(lt>qr||rt<ql||!p)
return 0;
if(ql<=lt&&rt<=qr)
return tr[p].max;
int mid=(lt+rt)>>1;
return max(qry_max(tr[p].ls,lt,mid,ql,qr),qry_max(tr[p].rs,mid+1,rt,ql,qr));
}
//DFS
void dfs(int cur,int f,int d){
siz[cur]=1,fa[cur]=f,dep[cur]=d;
for(int i:G[cur]){
if(!dep[i]){
dfs(i,cur,d+1);
siz[cur]+=siz[i];
if(siz[son[cur]]<siz[i])
son[cur]=i;
}
}
}
void DFS(int cur){
dfn[cur]=++tim,id[tim]=cur;
if(son[cur])
top[son[cur]]=top[cur],DFS(son[cur]);
for(int i:G[cur])
if(!top[i])
top[i]=i,DFS(i);
}
//Tasks
int sum_path(int x,int y,int col){
int res=0;
while(top[x]!=top[y]){
if(dep[top[x]]<dep[top[y]])
swap(x,y);
res+=qry_sum(rt[col],1,n,dfn[top[x]],dfn[x]);
x=fa[top[x]];
}
if(dep[x]<dep[y])
swap(x,y);
res+=qry_sum(rt[col],1,n,dfn[y],dfn[x]);
return res;
}
int max_path(int x,int y,int col){
int res=0;
while(top[x]!=top[y]){
if(dep[top[x]]<dep[top[y]])
swap(x,y);
res=max(res,qry_max(rt[col],1,n,dfn[top[x]],dfn[x]));
x=fa[top[x]];
}
if(dep[x]<dep[y])
swap(x,y);
res=max(res,qry_max(rt[col],1,n,dfn[y],dfn[x]));
return res;
}
//Main
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cin>>n>>q;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
cin>>w[i]>>c[i];
for(int i=1,u,v;i<n;i++)
cin>>u>>v,G[u].push_back(v),G[v].push_back(u);
dfs(1,0,1),top[1]=1,DFS(1);
build(root);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
upd(rt[c[i]],1,n,dfn[i],w[i]);
while(q--){
string op; int x,y;
cin>>op>>x>>y;
if(op=="CC"){
int s=qry_sum(rt[c[x]],1,n,dfn[x],dfn[x]);
upd(rt[c[x]],1,n,dfn[x],0);
upd(rt[y],1,n,dfn[x],s);
c[x]=y;
}
else if(op=="CW")
upd(rt[c[x]],1,n,dfn[x],y);
else if(op=="QS")
cout<<sum_path(x,y,c[x])<<'\n';
else
cout<<max_path(x,y,c[x])<<'\n';
}
return 0;
}
注意事项(本文的精髓):
-
线段树方面:
-
\(tag\) 若初值不为 \(0\),要所有节点全赋值;
-
使用线段树时注意节点编号是否转为了时间戳。
-
-
树链剖分方面:
-
跳跃时比较 \(top_x\) 和 \(top_y\);
-
注意函数调用是否正确;
-
牢记:动态开点线段树空间复杂度为 \(O(n \log n)\)。
-



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号