OpenGL渲染时必要数据的简单总结,Assimp数据结构&模型文件导入
渲染时必要数据:
- shader是 最终执行渲染的程序,检查shader的input接口,可以得到渲染所需数据:
- vertexShader: 具体代码详见 > UV坐标,2D贴图,冯氏光照模型和材质
- layout (location = 0) in vec3 vertexPos
- layout (location = 1) in vec3 Normal;
-
layout (location = 2) in vec2 TexCoords;
- 来自 vertexArrayBuffer,以顶点为单位,一次仅汇入一个顶点的相关数据
- vertexShader: 具体代码详见 > UV坐标,2D贴图,冯氏光照模型和材质
-
-
- uniform mat4 modelTransMatrix
- uniform mat4 viewTransMatrix
- uniform mat4 projectionTransMatrix
- 直接来自 [外部代码] ,通过:glUniform1i(glGetUniformLocation(shaderID, name.c_str()), value);
- 此处使用 的glUniform1i,仅支持灌入一个int值,如需灌入mat4,则需使用:
-
-
-
-
-
- glUniformMatrix4fv(glGetUniformLocation(ID, name.c_str()), 1, GL_FALSE, &mat[0][0]);
- 不同于单一int值,Matrix4是聚合值,需要给出首地址。
-
-
-
-
-
-
- 向shaderID标识的shaderProgram中的 名为name.c_str()的uniform栏位灌入值。
-
-
-
- fragmentShader: 具体代码详见 > UV坐标,2D贴图,冯氏光照模型和材质
-
-
- in vec3 FragPos > 经变换后的 vertexPos,来自vertexShader
- in vec3 Normal > 经变换 [防止缩放后走形] 后的 Normal,来自vertexShader
- in vec2 TexCoord > 来自vertexShader的UV值,因为UV值来自vertexArrayBuffer,所以只能先由vertexShader代为缓冲。
- uniform vec3 viewPos > 摄像机在 [世界空间坐标系] 中的坐标。
-
-
-
- uniform Material material;
-
struct Material {sampler2D diffuse;sampler2D specular;float shininess;};
- 本次所绘制片元的材质,如果此片元没有specular材质,则无需装填specular
- 相应的,若specular默认为空,则【specular光照渲染值 = 0】不生效。
-
-
-
-
- 当一个网格拥有多个贴图时(多个片元共用一个贴图,可以是共取贴图的不同部分)
- 需要的specular&diffuseTexture,就不止一个,当然,shininess也可能会有不同。
- struct Material {
- sampler2D diffuse;
- sampler2D diffuse2;
- sampler2D ...
- sampler2D specular;
- float shininess;
- sampler2D specular2;
- float shininess;
- ...
- };
- 但本次仅考虑一组的情况。
-
-
-
-
- uniform Light light;
-
struct Light {vec3 position;
vec3 ambient;vec3 diffuse;vec3 specular;}; - 此片元受到的光照,无论此片元是否有 specularTexture,都应装填 specularLight(vec3)
- 因为,虚拟现实与真实世界>理应是一样 光源是的公用的,仅在材质上做区分即可。
-
- uniform Light light;
-
Assimp数据结构:
- 如图:
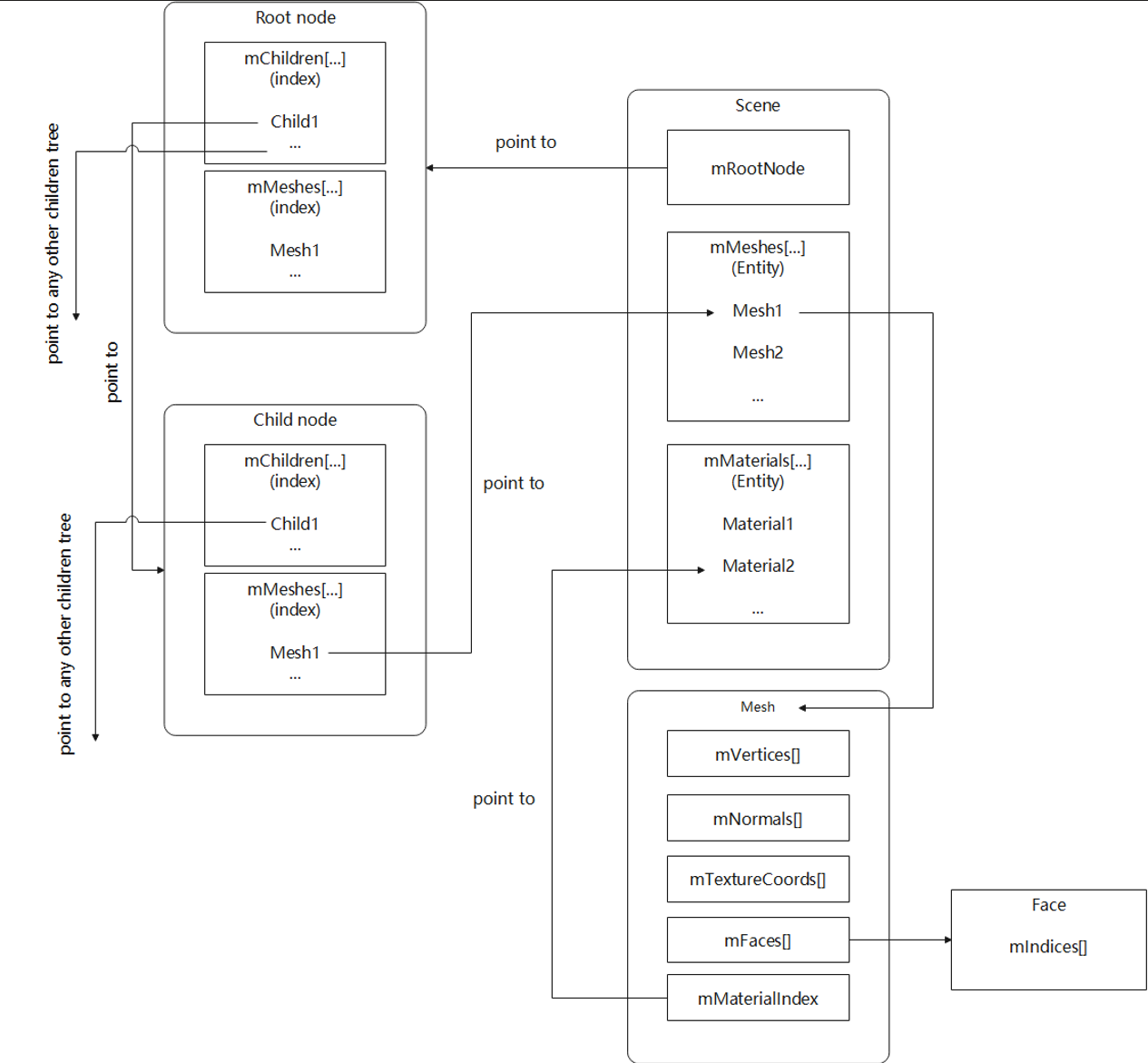
- Assimp数据结构解释:
- Scene | aiScene* > 指向场景内全部数据的指针
-
-
- mRootNode | aiNode* > 场景内所有节点的父节点的 指针
-
-
-
-
- mChildren | aiNode** > 子节点指针 的聚合体
- mChildren* (其中一个子节点指针)
- mChildren | aiNode** > 子节点指针 的聚合体
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- mChildren | aiNode** >子节点指针的聚合体
- mChildren* > 其中一个子节点指针
- 。。。
- mMeshes | unsigned int*
- mChildren | aiNode** >子节点指针的聚合体
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- mMeshes | unsigned int* 每个子节点指针 对应网格的 [线性索引]。
- 使用这个索引对应在Scene -> mMeshes内查找 该节点层级所包含的网格数据 的地址。
- mMeshes | unsigned int* 每个子节点指针 对应网格的 [线性索引]。
-
-
-
-
- mMeshes | aiMesh** > 网格数据指针 的聚合体。
- aiMesh:
- mVertices | aiVector3D*(aiVector3t<float>*)
- mNormals | aiVector3D*(aiVector3t<float>*)
- mTextureCoords | aiVector3D*(aiVector3t<float>*)
- 因为存在 3D贴图,所以预置 3个维度:UVT
- 2D贴图时,仅前两个分量有值,载入时,也仅使用前两个分量。
- mFaces | aiFace*
- 顶点索引。
- mIndices | unsigned int*
- mNumIndices | unsigned int
- mMaterialIndex > 材质信息索引,来自Scene > mMaterials
- aiMesh:
- mMeshes | aiMesh** > 网格数据指针 的聚合体。
-
-
-
- mMaterials | aiMaterial** > 材质信息指针 的聚合体
- aiMaterial:
- mNumAllocated | unsigned int
- mNumProperties | unsigned int
- mProperties | aiMaterialProperty**
- aiMateralProperty:
- mData | char*
- mDataLength | unsigned int
- mIndex | unsigned int > 索引
- mKey | aiString
- mSemantic | unsigned int > 贴图文件
- mType | aiPropertyTypeInfo > 贴图文件类型
- aiMateralProperty:
- aiMaterial:
- mMaterials | aiMaterial** > 材质信息指针 的聚合体
-
- 使用Assimp加载数据:
-
// read file via ASSIMP Assimp::Importer importer; const aiScene* scene = importer.ReadFile( /*-------模型文件路径-------*/ path, /*-------aiPostProcessSteps(enums)--------*/ /*此标志存在的目的是:如果模型文件成功加载,则按照以下flags执行操作*/ aiProcess_Triangulate //将所有的索引模式,都转化为三角形片元模式 | aiProcess_GenSmoothNormals //为所有顶点创建平滑法线,如果源文件中已经存在法线,则忽略此标志 | aiProcess_FlipUVs //沿Y轴翻转所有UV坐标,主要是为了防止贴图方向加载出错,如果方向正确,则不要使用此flags | aiProcess_CalcTangentSpace //为导入的网格计算切线和双切线,此处暂时还未用到,洒家也不懂,以后再说吧。 ); // check for errors if(!scene || scene->mFlags & AI_SCENE_FLAGS_INCOMPLETE || !scene->mRootNode) // if is Not Zero { cout << "ERROR::ASSIMP:: " << importer.GetErrorString() << endl; return; }
- aiPostProcessSteps的详细信息见 AssimpDoc_AiPostProcessSteps
- 加载Assimp数据到代码文件中:
- 自定义vertexDatapack_Single:用以封装单个顶点的相关数据
-
struct Vertex { glm::vec3 Position; glm::vec3 Normal; glm::vec2 TexCoords; };
-
- 自定义textureDatapack_Single:用以封装单个贴图的相关数据
-
struct Texture { unsigned int id; //textureID string type; //Specular | Diffuse };
- 自定义mesh类型:
-
1 class Mesh { 2 public: 3 /* 网格数据 */ 4 vector<Vertex> vertices; 5 vector<unsigned int> indices; 6 vector<Texture> textures; 7 /* 函数 */ 8 Mesh(vector<Vertex> vertices, vector<unsigned int> indices, vector<Texture> textures); 9 void Draw(Shader shader); 10 private: 11 /* 渲染数据 */ 12 unsigned int VAO, VBO, EBO; 13 /* 函数 */ 14 void setupMesh(); 15 }; 16 17 Mesh(vector<Vertex> vertices, vector<unsigned int> indices, vector<Texture> textures) 18 { 19 this->vertices = vertices; 20 this->indices = indices; 21 this->textures = textures; 22 23 setupMesh(); 24 } 25 26 void setupMesh() 27 { 28 glGenVertexArrays(1, &VAO); 29 glGenBuffers(1, &VBO); 30 glGenBuffers(1, &EBO); 31 32 glBindVertexArray(VAO); 33 34 glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO); 35 glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertices.size() * sizeof(Vertex), &vertices[0], GL_STATIC_DRAW); 36 37 glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, EBO); 38 glBufferData(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, indices.size() * sizeof(unsigned int), 39 &indices[0], GL_STATIC_DRAW); 40 41 // 顶点位置 42 glEnableVertexAttribArray(0); 43 glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, sizeof(Vertex), (void*)0); 44 // 顶点法线 45 glEnableVertexAttribArray(1); 46 glVertexAttribPointer(1, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, sizeof(Vertex), (void*)offsetof(Vertex, Normal)); 47 // 顶点纹理坐标 48 glEnableVertexAttribArray(2); 49 glVertexAttribPointer(2, 2, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, sizeof(Vertex), (void*)offsetof(Vertex, TexCoords)); 50 51 glBindVertexArray(0); 52 } 53 54 void Draw(Shader shader) 55 { 56 unsigned int diffuseNr = 1; 57 unsigned int specularNr = 1; 58 for(unsigned int i = 0; i < textures.size(); i++) 59 { 60 glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0 + i); // 在绑定之前激活相应的纹理单元 61 62 // 获取纹理序号(diffuse_textureN 中的 N) 63 string number; 64 string name = textures[i].type; 65 if(name == "texture_diffuse") 66 number = std::to_string(diffuseNr++); 67 else if(name == "texture_specular") 68 number = std::to_string(specularNr++); 69 70 shader.setFloat(("material." + name + number).c_str(), i); 71 glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, textures[i].id); 72 } 73 glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0); 74 75 // 绘制网格 76 glBindVertexArray(VAO); 77 glDrawElements(GL_TRIANGLES, indices.size(), GL_UNSIGNED_INT, 0); 78 glBindVertexArray(0); 79 }
- mesh是model中的一个层级,可视为 [子model] 是模型文件的最小单位。
- 你也可以认为model就是一个巨型mesh,而此mesh可以分块绘制。
- 此处的mesh仅考虑自身仅包含 specularTexture | diffuseTexture 的情况。
-
- 自定义model类型:
-
1 class Model 2 { 3 public: 4 /* 函数 */ 5 Model(char *path) 6 { 7 loadModel(path); 8 } 9 void Draw(Shader shader); 10 private: 11 vector<Texture> textures_loaded; 12 /* 模型数据 */ 13 vector<Mesh> meshes; 14 string directory; 15 /* 函数 */ 16 void loadModel(string path); 17 void processNode(aiNode *node, const aiScene *scene); 18 Mesh processMesh(aiMesh *mesh, const aiScene *scene); 19 vector<Texture> loadMaterialTextures(aiMaterial *mat, aiTextureType type, 20 string typeName); 21 }; 22 23 Mesh processMesh(aiMesh *mesh, const aiScene *scene) 24 { 25 // data to fill 26 vector<Vertex> vertices; 27 vector<unsigned int> indices; 28 vector<Texture> textures; 29 30 // walk through each of the mesh's vertices 31 for(unsigned int i = 0; i < mesh->mNumVertices; i++) 32 { 33 Vertex vertex; 34 glm::vec3 vector; 35 // positions 36 vector.x = mesh->mVertices[i].x; 37 vector.y = mesh->mVertices[i].y; 38 vector.z = mesh->mVertices[i].z; 39 vertex.Position = vector; 40 // normals 41 if (mesh->HasNormals()) 42 { 43 vector.x = mesh->mNormals[i].x; 44 vector.y = mesh->mNormals[i].y; 45 vector.z = mesh->mNormals[i].z; 46 vertex.Normal = vector; 47 } 48 // texture coordinates 49 if(mesh->mTextureCoords[0]) // does the mesh contain texture coordinates? 50 { 51 glm::vec2 vec; 52 // a vertex can contain up to 8 different texture coordinates. We thus make the assumption that we won't 53 // use models where a vertex can have multiple texture coordinates so we always take the first set (0). 54 vec.x = mesh->mTextureCoords[0][i].x; 55 vec.y = mesh->mTextureCoords[0][i].y; 56 vertex.TexCoords = vec; 57 // tangent 58 vector.x = mesh->mTangents[i].x; 59 vector.y = mesh->mTangents[i].y; 60 vector.z = mesh->mTangents[i].z; 61 vertex.Tangent = vector; 62 // bitangent 63 vector.x = mesh->mBitangents[i].x; 64 vector.y = mesh->mBitangents[i].y; 65 vector.z = mesh->mBitangents[i].z; 66 vertex.Bitangent = vector; 67 } 68 else 69 vertex.TexCoords = glm::vec2(0.0f, 0.0f); 70 71 vertices.push_back(vertex); 72 } 73 // now wak through each of the mesh's faces (a face is a mesh its triangle) and retrieve the corresponding vertex indices. 74 for(unsigned int i = 0; i < mesh->mNumFaces; i++) 75 { 76 aiFace face = mesh->mFaces[i]; 77 // retrieve all indices of the face and store them in the indices vector 78 for(unsigned int j = 0; j < face.mNumIndices; j++) 79 indices.push_back(face.mIndices[j]); 80 } 81 // process materials 82 aiMaterial* material = scene->mMaterials[mesh->mMaterialIndex]; 83 // we assume a convention for sampler names in the shaders. Each diffuse texture should be named 84 // as 'texture_diffuseN' where N is a sequential number ranging from 1 to MAX_SAMPLER_NUMBER. 85 // Same applies to other texture as the following list summarizes: 86 // diffuse: texture_diffuseN 87 // specular: texture_specularN 88 // normal: texture_normalN 89 90 // 1. diffuse maps 91 vector<Texture> diffuseMaps = loadMaterialTextures(material, aiTextureType_DIFFUSE, "texture_diffuse"); 92 textures.insert(textures.end(), diffuseMaps.begin(), diffuseMaps.end()); 93 // 2. specular maps 94 vector<Texture> specularMaps = loadMaterialTextures(material, aiTextureType_SPECULAR, "texture_specular"); 95 textures.insert(textures.end(), specularMaps.begin(), specularMaps.end()); 96 // 3. normal maps 97 std::vector<Texture> normalMaps = loadMaterialTextures(material, aiTextureType_HEIGHT, "texture_normal"); 98 textures.insert(textures.end(), normalMaps.begin(), normalMaps.end()); 99 // 4. height maps 100 std::vector<Texture> heightMaps = loadMaterialTextures(material, aiTextureType_AMBIENT, "texture_height"); 101 textures.insert(textures.end(), heightMaps.begin(), heightMaps.end()); 102 103 // return a mesh object created from the extracted mesh data 104 return Mesh(vertices, indices, textures); 105 } 106 107 // checks all material textures of a given type and loads the textures if they're not loaded yet. 108 // the required info is returned as a Texture struct. 109 vector<Texture> loadMaterialTextures(aiMaterial *mat, aiTextureType type, string typeName) 110 { 111 vector<Texture> textures; 112 for(unsigned int i = 0; i < mat->GetTextureCount(type); i++) 113 { 114 aiString str; 115 mat->GetTexture(type, i, &str); 116 // check if texture was loaded before and if so, continue to next iteration: skip loading a new texture 117 bool skip = false; 118 for(unsigned int j = 0; j < textures_loaded.size(); j++) 119 { 120 if(std::strcmp(textures_loaded[j].path.data(), str.C_Str()) == 0) 121 { 122 textures.push_back(textures_loaded[j]); 123 skip = true; // a texture with the same filepath has already been loaded, continue to next one. (optimization) 124 break; 125 } 126 } 127 if(!skip) 128 { // if texture hasn't been loaded already, load it 129 Texture texture; 130 texture.id = TextureFromFile(str.C_Str(), this->directory); 131 texture.type = typeName; 132 texture.path = str.C_Str(); 133 textures.push_back(texture); 134 textures_loaded.push_back(texture); // store it as texture loaded for entire model, to ensure we won't unnecesery load duplicate textures. 135 } 136 } 137 return textures; 138 } 139 }; 140 141 142 unsigned int TextureFromFile(const char *path, const string &directory, bool gamma) 143 { 144 string filename = string(path); 145 filename = directory + '/' + filename; 146 147 unsigned int textureID; 148 glGenTextures(1, &textureID); 149 150 int width, height, nrComponents; 151 unsigned char *data = stbi_load(filename.c_str(), &width, &height, &nrComponents, 0); 152 if (data) 153 { 154 GLenum format; 155 if (nrComponents == 1) 156 format = GL_RED; 157 else if (nrComponents == 3) 158 format = GL_RGB; 159 else if (nrComponents == 4) 160 format = GL_RGBA; 161 162 glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, textureID); 163 glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, format, width, height, 0, format, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, data); 164 glGenerateMipmap(GL_TEXTURE_2D); 165 166 glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT); 167 glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT); 168 glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR_MIPMAP_LINEAR); 169 glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR); 170 171 stbi_image_free(data); 172 } 173 else 174 { 175 std::cout << "Texture failed to load at path: " << path << std::endl; 176 stbi_image_free(data); 177 } 178 179 return textureID; 180 }
- 加载贴图时,尚考虑了 法线贴图 和 高程贴图(高程纹理),但这些都暂时未使用。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号