C. Domino
维护当前能推倒的右边界
代码实现
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define rep(i, n) for (int i = 0; i < (n); ++i)
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a(n);
rep(i, n) cin >> a[i];
int ans = 0;
int r = 0;
rep(i, n) {
if (i > r) break;
r = max(r, i+a[i]-1);
ans++;
}
cout << ans << '\n';
return 0;
}
D. Reachability Query 2
建反图,从点 \(v\) 开始跑 \(\text{bfs}\) 把所有能遍历到的点都染上黑色
代码实现
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define rep(i, n) for (int i = 0; i < (n); ++i)
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<vector<int>> to(n);
rep(i, m) {
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
--a; --b;
to[b].push_back(a);
}
int q;
cin >> q;
vector<bool> black(n);
rep(qi, q) {
int type, v;
cin >> type >> v;
--v;
if (type == 1) {
queue<int> q;
auto push = [&](int v) {
if (black[v]) return;
black[v] = true;
q.push(v);
};
push(v);
while (q.size()) {
int v = q.front(); q.pop();
for (int u : to[v]) push(u);
}
}
else {
if (black[v]) puts("Yes");
else puts("No");
}
}
return 0;
}
E. Cover query
只需维护一个数据结构:
- 插入区间
- 删除 \([l, r]\) 里覆盖的区间
可以用 std::set 来实现,另外这实际上就是珂朵莉树
代码实现
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define rep(i, n) for (int i = 0; i < (n); ++i)
using namespace std;
using P = pair<int, int>;
int main() {
int n, q;
cin >> n >> q;
int ans = n;
set<P> s;
rep(qi, q) {
int l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
--l;
auto it = s.lower_bound(P(l, -1));
if (it != s.begin() and prev(it)->second >= l) it--;
while (it != s.end() and it->first <= r) {
ans += it->second - it->first;
l = min(l, it->first);
r = max(r, it->second);
s.erase(it++);
}
s.emplace(l, r);
ans -= r-l;
cout << ans << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
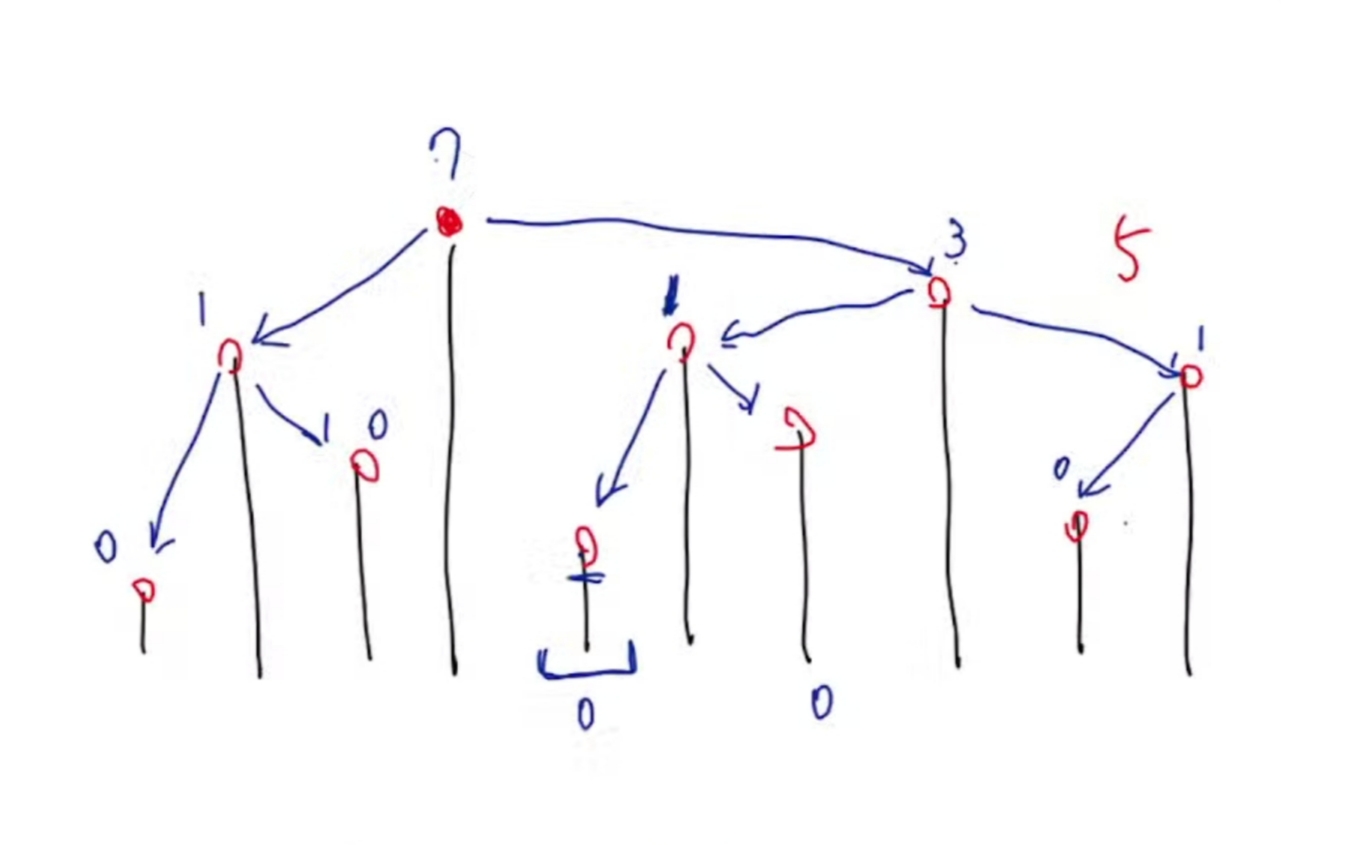
F. Cat exercise
显然每次移除猫所在的塔是最优的
一旦猫跳到某个位置就不能再往回跳了
笛卡尔树上 \(\text{dp}\)
代码实现
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define rep(i, n) for (int i = 0; i < (n); ++i)
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
template<class T=long long>
struct CartesianTree {
int n, root;
vector<int> l, r;
CartesianTree() {}
CartesianTree(const vector<T>& a, bool _max=true) {
n = a.size();
l = r = vector<int>(n, -1);
vector<int> st;
rep(i, n) {
int p = -1;
while (st.size() and !((a[st.back()] < a[i]) ^ _max)) {
int j = st.back(); st.pop_back();
r[j] = p; p = j;
}
l[i] = p;
st.push_back(i);
}
rep(i, st.size()-1) r[st[i]] = st[i+1];
root = st[0];
}
};
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> p(n);
rep(i, n) cin >> p[i];
CartesianTree t(p);
auto f = [&](auto& f, int v) -> ll {
int l = t.l[v], r = t.r[v];
ll res = 0;
if (l != -1) res = max(res, f(f, l) + (v-l));
if (r != -1) res = max(res, f(f, r) + (r-v));
return res;
};
cout << f(f, t.root) << '\n';
return 0;
}
G. Domino Arrangement
参考 StarSilk



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号