数据结构与算法-栈、队列、堆
一、栈、队列
预备知识:
#include "pch.h" #include <iostream> #include <stdio.h> #include <stack> int main() { std::stack<int> S; if (S.empty()) { printf("S is empty"); } S.push(5); S.push(6); S.push(10); printf("S.top = %d\n", S.top()); S.pop(); S.pop(); printf("S.top = %d\n", S.top()); printf("S.size = %d\n", S.size()); return 0; } //S.top() 取出栈顶 //S.empty() 判断栈是否为空 //S.push(x) 把x压入栈 //S.pop() 弹出栈顶 //S.size() 栈的存储元素个数
#include "pch.h" #include <iostream> #include <stdio.h> #include <queue> int main() { std::queue<int> Q; if (Q.empty()) { printf("Q is empty!\n"); } Q.push(5); Q.push(6); Q.push(10); printf("Q.front = %d\n", Q.front()); Q.pop(); Q.pop(); printf("Q.front = %d\n", Q.front()); Q.push(1); printf("Q.back = %d\n", Q.back()); printf("Q.size = %d\n", Q.size()); return 0; } //Q.front() 取出队列头部元素 //Q.back() 取出队列尾部元素 //Q.empty() 判断队列是否为空 //Q.push(x) 把x添加至队列 //Q.pop() 弹出队列头部元素 //Q.size() 返回队列的存储元素个数
1.用队列实现栈
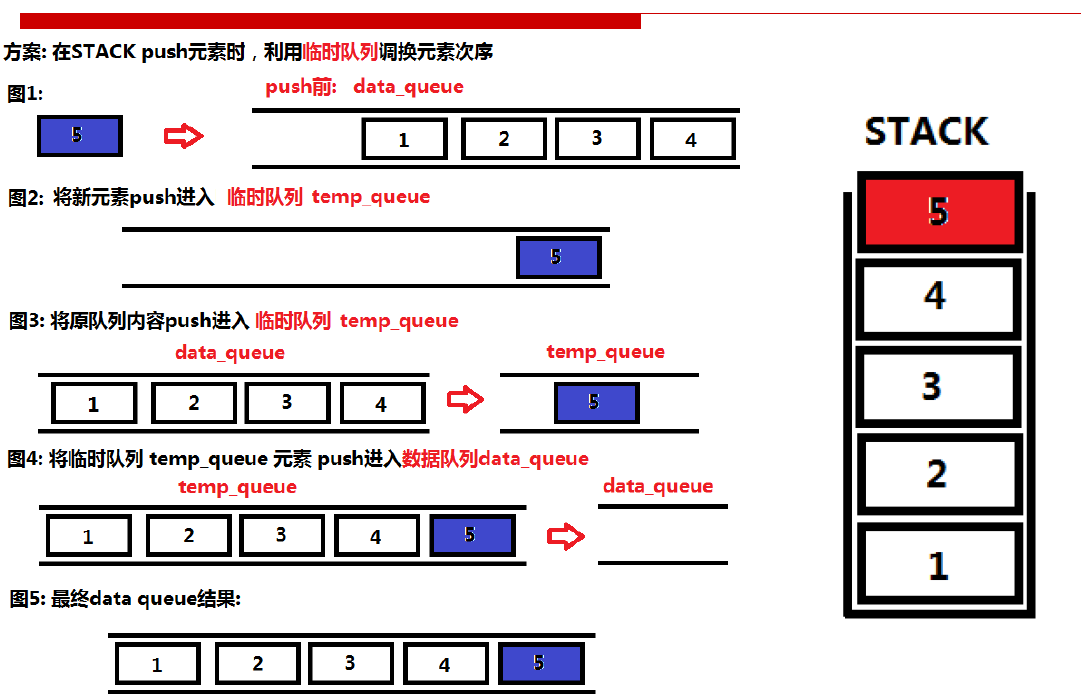
要求栈用队列实现,即在队列里面实现“后进先出”,所以把新进来的元素放入临时队列(temp_queue)中,再把原来的队列中的元素添加至临时队列中,形成了最后新进来的元素在最前面。
代码实现如下:
class MyStack { public: /** Initialize your data structure here. */ MyStack() { } /** Push element x onto stack. */ void push(int x) { std::queue<int> tem_queue; tem_queue.push(x); while(!_data.empty()) { tem_queue.push(_data.front()); _data.pop(); } while(!tem_queue.empty()) { _data.push(tem_queue.front()); tem_queue.pop(); } } /** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */ int pop() { int x =_data.front(); _data.pop(); return x; } /** Get the top element. */ int top() { return _data.front(); }
2.用栈实现队列
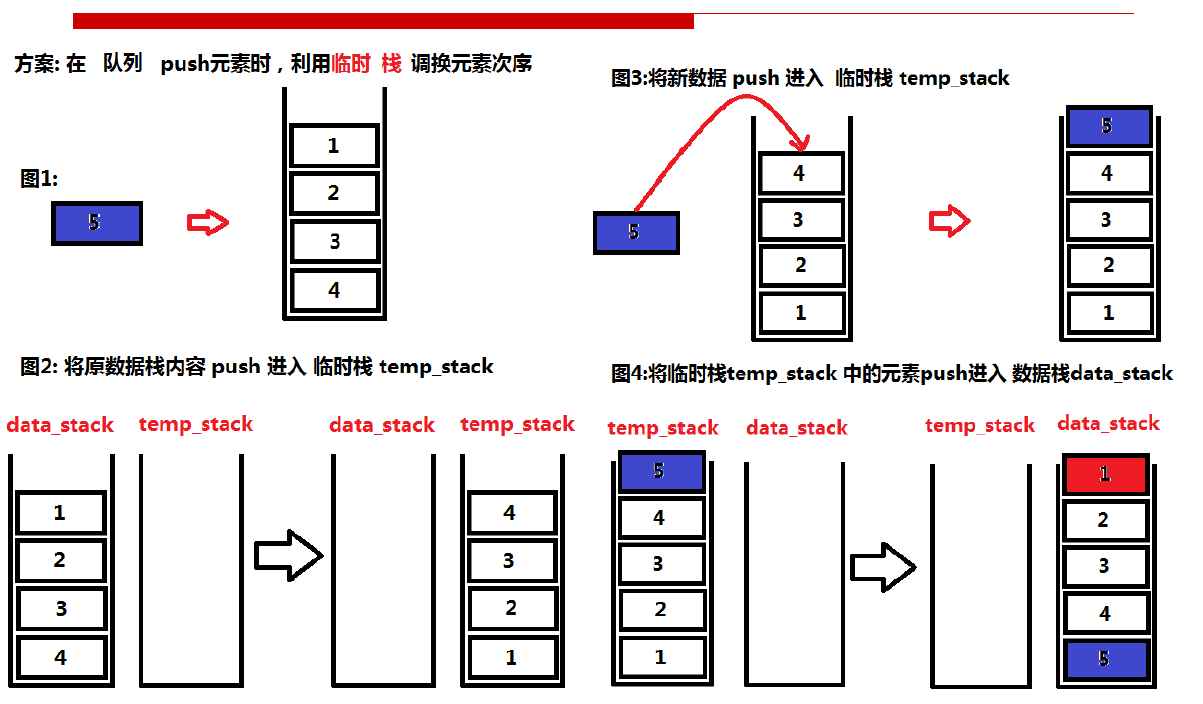
将原数据压入临时栈,再讲新数据压入临时栈,之后将临时栈数据压入原栈。
class MyQueue { public: /** Initialize your data structure here. */ MyQueue() { } /** Push element x to the back of queue. */ void push(int x) { std::stack<int>tem_stack; while(!_data.empty()) { tem_stack.push(_data.top()); _data.pop(); } tem_stack.push(x); while(!tem_stack.empty()) { _data.push(tem_stack.top()); tem_stack.pop(); } } /** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */ int pop() { int x = _data.top(); _data.pop(); return x; } /** Get the front element. */ int peek() { return _data.top(); } /** Returns whether the queue is empty. */ bool empty() { return _data.empty(); } private: std::stack<int>_data; };
3.包含min函数的栈
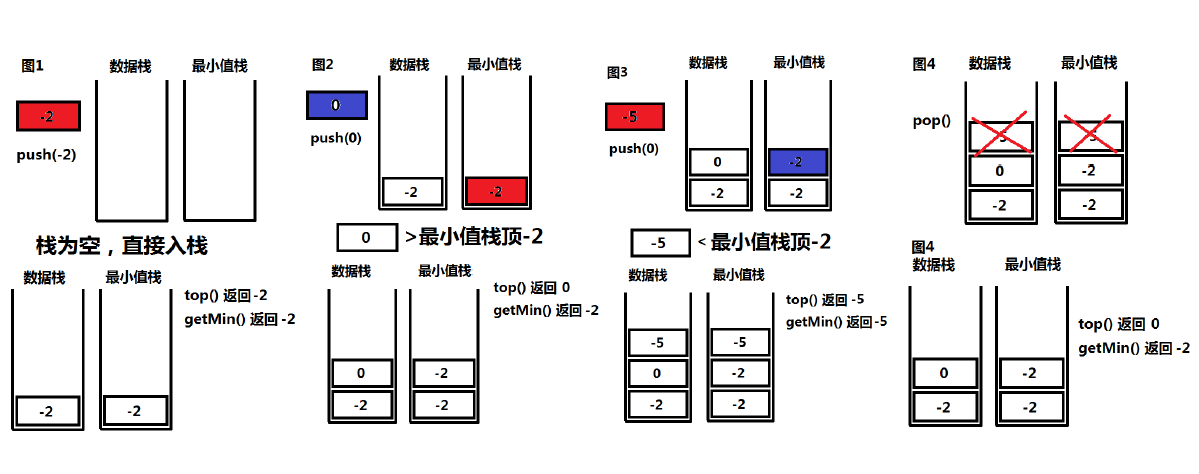
class MinStack { public: /** initialize your data structure here. */ MinStack() { } void push(int x) { _data.push(x); if (_min.empty()) { _min.push(x); } else { if(x > _min.top()) x = _min.top(); _min.push(x); } } void pop() { _data.pop(); _min.pop(); } int top() { return _data.top(); } int getMin() { return _min.top(); } private: std::stack<int>_data; std::stack<int>_min; };
4.合法的出栈序列
5.简单的计算器
二、堆
预备知识:
#include "pch.h" #include <iostream> #include <stdio.h> #include <queue> int main() { std::priority_queue<int>big_heap; std::priority_queue<int, std::vector<int>, std::greater<int>>small_heap; std::priority_queue<int, std::vector<int>, std::less<int>>big_heap2; if (big_heap.empty()) { printf("big_heap is empty!\n"); } int test[] = { 6, 10, 1, 7, 99, 4,33 }; for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) { big_heap.push(test[i]); } printf("big_heap.top = %d\n", big_heap.top()); big_heap.push(1000); printf("big_heap.top = %d\n", big_heap.top()); for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { big_heap.pop(); } printf("big_heap.top= %d\n", big_heap.top()); printf("big_heap.size = %d\n", big_heap.size()); }
1.数组中第K大的数


class Solution { public: int findKthLargest(vector<int>& nums, int k) { std::priority_queue<int, std::vector<int>, std::greater<int>> Q; for(int i = 0; i< nums.size(); i++) { if(i < k) #这里我觉得是i < k { Q.push(nums[i]); } else if(nums[i] > Q.top()) { Q.pop(); Q.push(nums[i]); } } return Q.top(); } };
2.寻找中位数
第一种情况:
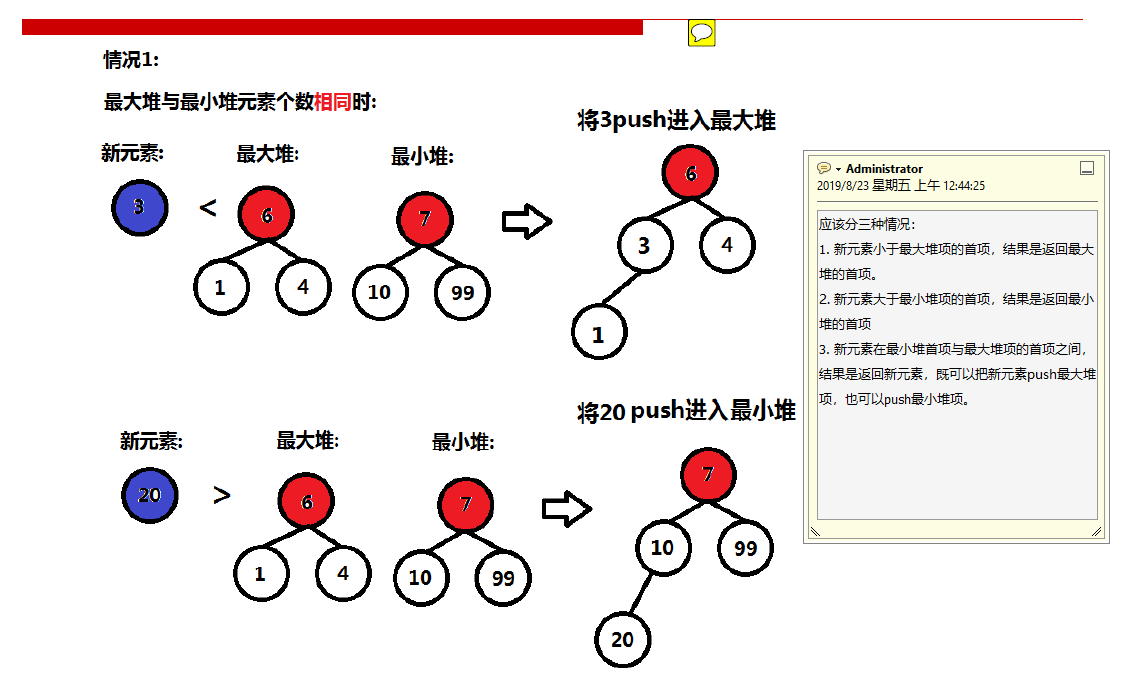
第二种情况:
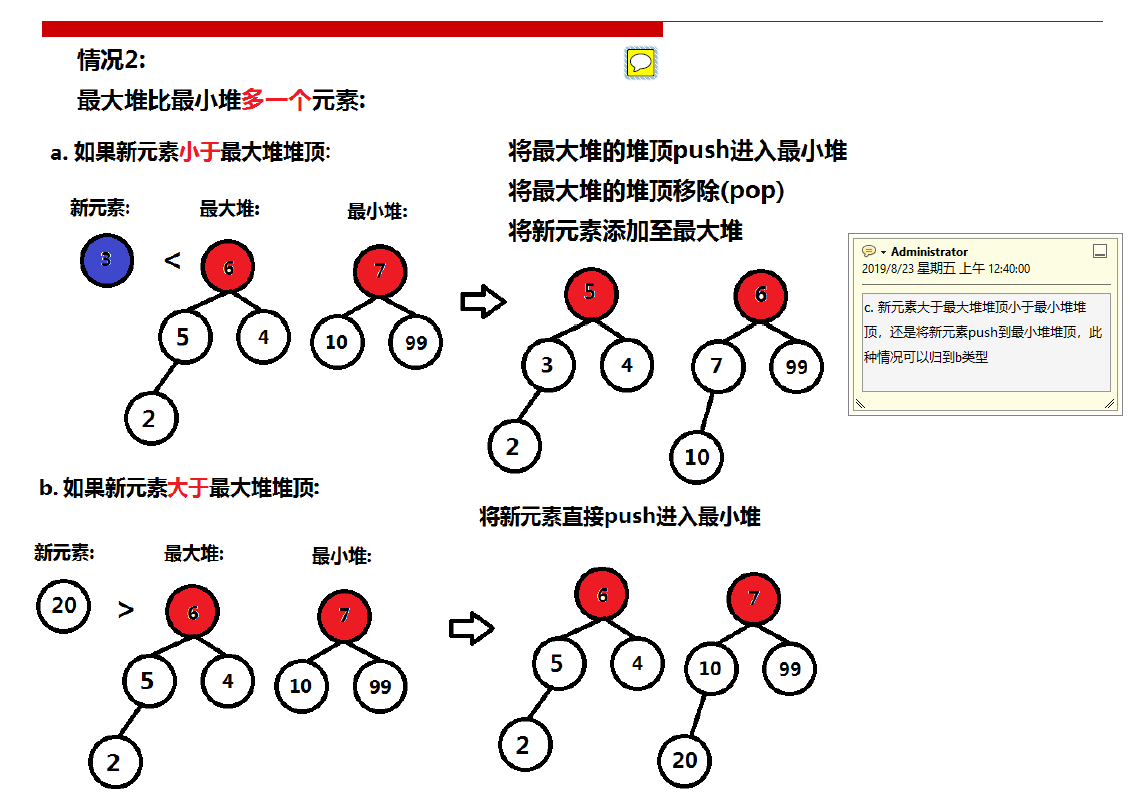
第三种情况:
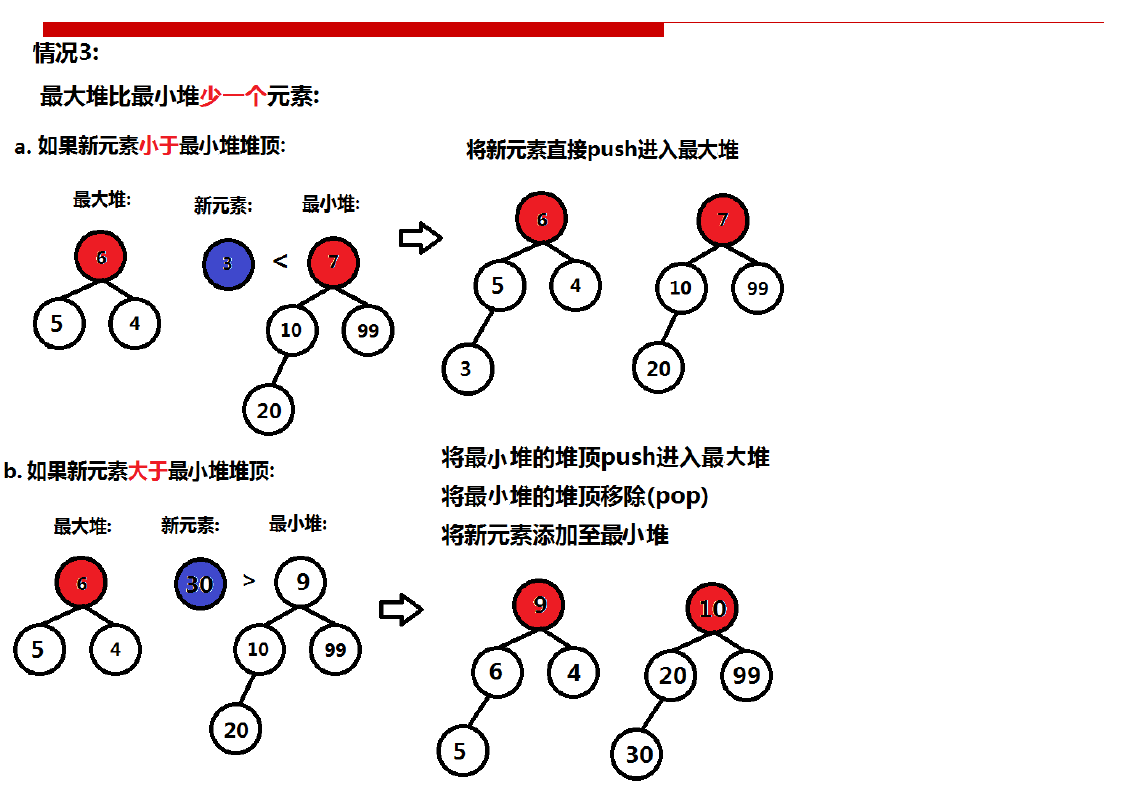
class MedianFinder { public: /** initialize your data structure here. */ std::priority_queue<int, std::vector<int>, std::greater<int>>small_queue; std::priority_queue<int, std::vector<int>, std::less<int>>big_queue; MedianFinder() { } void addNum(int num) { if (big_queue.empty()) { big_queue.push(num); return; } if (big_queue.size() == small_queue.size()) { if (num < big_queue.top()) { big_queue.push(num); } else{ small_queue.push(num); } } else if (big_queue.size() > small_queue.size() ) { if(num > big_queue.top()){ small_queue.push(num); } else{ small_queue.push(big_queue.top()); big_queue.pop(); big_queue.push(num); } } else if(small_queue.size() > big_queue.size() ) { if(num < small_queue.top()){ big_queue.push(num); } else{ big_queue.push(small_queue.top()); small_queue.pop(); small_queue.push(num); } } } double findMedian() { if(big_queue.size() == small_queue.size()){ return (float((big_queue.top()) + small_queue.top()) / 2); //注意需要进行浮点数转换 } else if(big_queue.size() > small_queue.size()){ return big_queue.top(); } return small_queue.top(); } };


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号