对于吉司机线段树下传懒标记的顺序的解释
对于吉司机线段树下传懒标记的顺序的解释
哇,标题怎么这么长
吉司机线段树
是线段树的一种,可用于维护区间 \(\max/\min\) 操作,即把原数组 \(a_i\) 变为 \(\max(a_i,x)\) 或 \(\min(a_i,x)\)。
以洛谷题目P10639 最假女选手为例,需要存的 lazytag(懒标记)为加法、区间 \(\max\) 和 \(\min\)。
那么我们下传懒标记(pushdown)操作中,如何确定下传顺序?
首先显然地,对于 \(\min\) 和 \(\max\) 操作,它们是同级的,先后顺序无所谓。
下文以 \(M\) 操作代替 \(\min\) 和 \(\max\) 操作,因为这俩太长了,懒得打。
那么问题就是加法和 \(M\) 操作的下传顺序问题。
下传顺序的解释
以 \(M\) 操作中的 \(\max\) 为例子,即 \(a_i=\max(a_i,x)\)。
假设我们有两个操作:
- 加上 \(x\)
- \(a_i=\max(a_i,y)\)
当前元素为 \(a_i\)。
首先如果 \(a_i\ge y\),那么 \(\max\) 操作的结果是 \(a_i=\max(a_i,y)=a_i\),发现是无意义的,可以省略,直接加法。
现在考虑 \(\max\) 操作会影响元素的情况。
不难发现 \(x\) 与 \(a_i,y\) 的相对大小是不影响的,所以只要考虑 \(a_i\) 和 \(y\) 的大小关系。
而上文分析过了,所以只要考虑 \(a_i<y\) 的情况。
现在证明为什么先下传加法懒标记的顺序是对的。
我们以一种情况举例子,其他可以自行尝试。
我们假设 \(a_i<y<x\)。
我们画个数轴理解下。
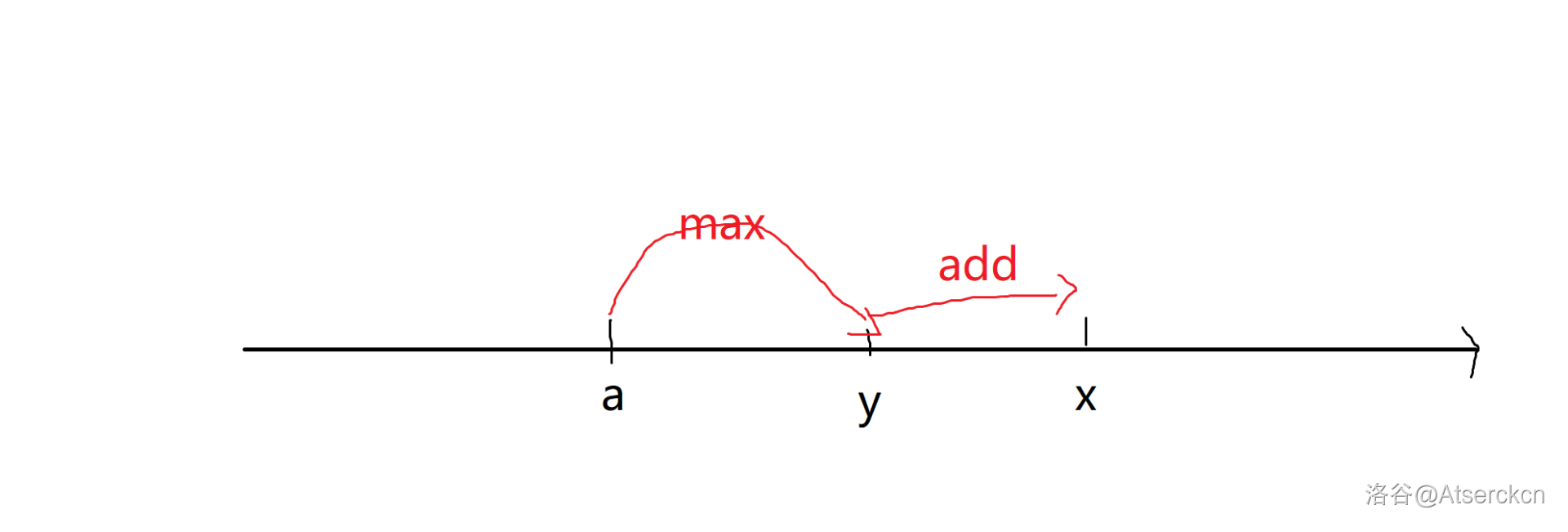
这是原操作先 \(\max\) 后加法的结果,发现最后位置在 \(x\) 那。
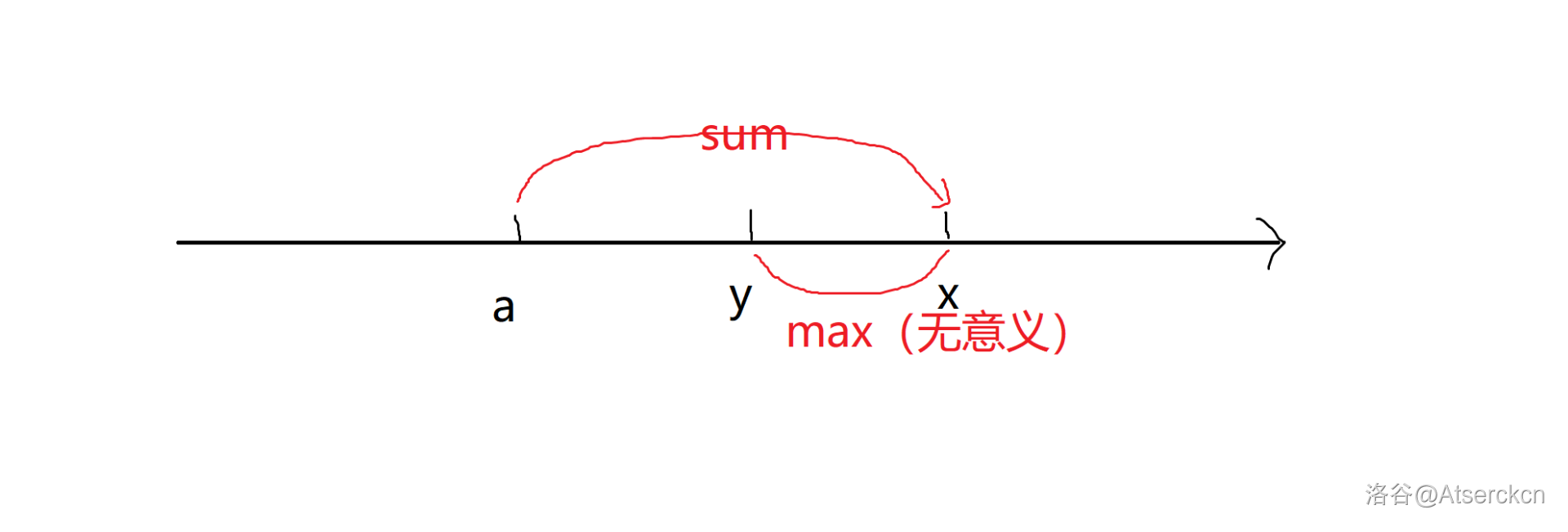
这是先加法再 \(\max\) 后的结果,发现最后结果是一样的。
所以先 pushdown 加法的 tag 再 pushdown \(M\) 操作的 tag 是对的。
例题都给了,就给个代码吧
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ljl;
#define FUP(i,x,y) for(auto (i)=(x);(i)<=(y);++(i))
#define FDW(i,x,y) for(auto (i)=(x);(i)>=(y);--(i))
inline void Rd(auto &num);
const int N=5e5+5;
const ljl inf=1e18;
int n,a[N],m;
namespace SMT{
#define lc (p<<1)
#define rc (p<<1|1)
struct NODE{
ljl sum,lz,mx,mx2,cmx,mn,mn2,cmn,tmx,tmn,l,r;
}node[N*4];
void pushup(int p)
{
node[p].sum=node[lc].sum+node[rc].sum;
if(node[lc].mx==node[rc].mx)
{
node[p].mx=node[lc].mx;node[p].cmx=node[lc].cmx+node[rc].cmx;
node[p].mx2=max(node[lc].mx2,node[rc].mx2);
}
else
{
if(node[lc].mx<node[rc].mx)
{
node[p].mx=node[rc].mx;node[p].cmx=node[rc].cmx;
node[p].mx2=max(node[lc].mx,node[rc].mx2);
}
else
{
node[p].mx=node[lc].mx;node[p].cmx=node[lc].cmx;
node[p].mx2=max(node[lc].mx2,node[rc].mx);
}
}
if(node[lc].mn==node[rc].mn)
{
node[p].mn=node[lc].mn;node[p].cmn=node[lc].cmn+node[rc].cmn;
node[p].mn2=min(node[lc].mn2,node[rc].mn2);
}
else
{
if(node[lc].mn<node[rc].mn)
{
node[p].mn=node[lc].mn;node[p].cmn=node[lc].cmn;
node[p].mn2=min(node[lc].mn2,node[rc].mn);
}
else
{
node[p].mn=node[rc].mn;node[p].cmn=node[rc].cmn;
node[p].mn2=min(node[rc].mn2,node[lc].mn);
}
}
return;
}
void bld(int l,int r,int p)
{
node[p].l=l;node[p].r=r;node[p].tmx=-inf;node[p].tmn=inf;
if(l==r)
{
node[p].mx=node[p].mn=node[p].sum=a[l];
node[p].cmn=node[p].cmx=1;
node[p].mx2=-inf;node[p].mn2=inf;
return;
}
int mid=(l+r)/2;
bld(l,mid,lc);bld(mid+1,r,rc);
pushup(p);
return;
}
void pushsum(int p,ljl val)
{
node[p].sum+=(node[p].r-node[p].l+1)*val;
node[p].mx+=val;node[p].mn+=val;
if(node[p].mx2!=-inf)node[p].mx2+=val;
if(node[p].mn2!=inf)node[p].mn2+=val;
if(node[p].tmx!=-inf)node[p].tmx+=val;
if(node[p].tmn!=inf)node[p].tmn+=val;
node[p].lz+=val;
return;
}
void pushmin(int p,ljl val)
{
if(node[p].mx<=val)return;
node[p].sum+=(val-node[p].mx)*node[p].cmx;
if(node[p].mn2==node[p].mx)
node[p].mn2=val;
if(node[p].mn==node[p].mx)node[p].mn=val;
node[p].tmx=min(val,node[p].tmx);node[p].mx=val;node[p].tmn=val;
return;
}
void pushmax(int p,ljl val)
{
if(node[p].mn>=val)return;
node[p].sum+=(val-node[p].mn)*node[p].cmn;
if(node[p].mx2==node[p].mn)
node[p].mx2=val;
if(node[p].mx==node[p].mn)node[p].mx=val;
node[p].tmn=max(node[p].tmn,val);node[p].mn=val;node[p].tmx=val;
return;
}
void pushdown(int p)
{
if(node[p].l==node[p].r)return;
if(node[p].lz)
{
pushsum(lc,node[p].lz);
pushsum(rc,node[p].lz);node[p].lz=0;
}
if(node[p].tmx!=-inf)
{
pushmax(lc,node[p].tmx);
pushmax(rc,node[p].tmx);node[p].tmx=-inf;
}
if(node[p].tmn!=inf)
{
pushmin(lc,node[p].tmn);
pushmin(rc,node[p].tmn);node[p].tmn=inf;
}
return;
}
void changesum(int l,int r,ljl val,int p)
{
if(l<=node[p].l&&node[p].r<=r)return pushsum(p,val);
int mid=(node[p].l+node[p].r)/2;
pushdown(p);
if(l<=mid)changesum(l,r,val,lc);
if(mid<r)changesum(l,r,val,rc);
pushup(p);
return;
}
void changemin(int l,int r,ljl val,int p)
{
if(node[p].mx<=val)return;
if(l<=node[p].l&&node[p].r<=r&&node[p].mx2<val)return pushmin(p,val);
int mid=(node[p].l+node[p].r)/2;
pushdown(p);
if(l<=mid)changemin(l,r,val,lc);
if(mid<r)changemin(l,r,val,rc);
pushup(p);
return;
}
void changemax(int l,int r,ljl val,int p)
{
if(node[p].mn>=val)return;
if(l<=node[p].l&&node[p].r<=r&&node[p].mn2>=val)return pushmax(p,val);
int mid=(node[p].l+node[p].r)/2;
pushdown(p);
if(l<=mid)changemax(l,r,val,lc);
if(mid<r)changemax(l,r,val,rc);
pushup(p);
return;
}
ljl querysum(int l,int r,int p)
{
if(l<=node[p].l&&node[p].r<=r)return node[p].sum;
pushdown(p);
int mid=(node[p].l+node[p].r)/2;ljl ans=0;
if(l<=mid)ans+=querysum(l,r,lc);
if(mid<r)ans+=querysum(l,r,rc);
return ans;
}
ljl querymin(int l,int r,int p)
{
if(l<=node[p].l&&node[p].r<=r)return node[p].mn;
pushdown(p);
int mid=(node[p].l+node[p].r)/2;ljl ans=inf;
if(l<=mid)ans=min(ans,querymin(l,r,lc));
if(mid<r)ans=min(ans,querymin(l,r,rc));
return ans;
}
ljl querymax(int l,int r,int p)
{
if(l<=node[p].l&&node[p].r<=r)return node[p].mx;
pushdown(p);
int mid=(node[p].l+node[p].r)/2;ljl ans=-inf;
if(l<=mid)ans=max(ans,querymax(l,r,lc));
if(mid<r)ans=max(ans,querymax(l,r,rc));
return ans;
}
}
using namespace SMT;
int main(){
Rd(n);
FUP(i,1,n)Rd(a[i]);
bld(1,n,1);
Rd(m);int op,l,r;ljl x;
while(m--)
{
Rd(op);Rd(l);Rd(r);
if(1<=op&&op<=3)
{
Rd(x);
if(op==1)changesum(l,r,x,1);
if(op==2)changemax(l,r,x,1);
if(op==3)changemin(l,r,x,1);
}
else
{
if(op==4)printf("%lld\n",querysum(l,r,1));
if(op==5)printf("%lld\n",querymax(l,r,1));
if(op==6)printf("%lld\n",querymin(l,r,1));
}
}
return 0;
}
inline void Rd(auto &num)
{
num=0;char ch=getchar();bool f=0;
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9')
{
if(ch=='-')f=1;
ch=getchar();
}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9')
{
num=(num<<1)+(num<<3)+(ch-'0');
ch=getchar();
}
if(f)num=-num;
return;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号