PTA作业(java)总结(第一次博客作业)
1. 前言
2. 设计与分析
3. 踩坑心得
4. 改进建议
5. 总结
前言:
(总结三次题目集的知识点、题量、难度等情况)
这三次练习题的题目量并不是很大,但是题目难度对我来说还是相当具有挑战性的。
这三次题目集所涉及的知识点在我看来有以下几点:
1.如何定义类以及如何用类来制造对象。
2.对象的识别与交互。
3.封装以及类变量和类函数。
4.如何将字符串以数组的形式进行存储以及输出。
5.java中对数据的精度调控以及强制类型转化。
设计与分析:
(重点对题目的提交源码进行分析,可参考SourceMonitor的生成报表内容以及PowerDesigner的相应类图,要有相应的解释和心得(做到有图有真相),本次Blog必须分析题目集2的7-2以及题目集3的7-1、7-2、7-3)
1.题目集2 7—2
该题的主要考察知识点为奇偶效验:
(奇偶校验(Parity Check)是一种校验代码传输正确性的方法。根据被传输的一组二进制代码的数位中"1"的个数是奇数或偶数来进行校验。采用奇数的称为奇校验,反之,称为偶校验。采用何种校验是事先规定好的。通常专门设置一个奇偶校验位,用它使这组代码中"1"的个数为奇数或偶数。若用奇校验,则当接收端收到这组代码时,校验"1"的个数是否为奇数,从而确定传输代码的正确性。奇偶校验需要一位校验位,即使用串口通信的方式2或方式3(8位数据位+1位校验位)。奇校验(odd parity):让传输的数据(包含校验位)中1的个数为奇数。即:如果传输字节中1的个数是偶数,则校验位为“1”,奇数相反。)
我在该题存在失分情况
主要原因是对奇偶效验理解存在问题(我一开始以为只要奇效验通过即可未考虑偶效验情况)
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 public class Main { 3 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 6 //奇效验:代码中1出现的个数为奇数 7 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); 8 String sc = in.nextLine(); 9 char[] a = sc.toCharArray(); 10 boolean f = false; 11 boolean t = false; 12 boolean k = false; 13 int cnt = 0; 14 int c = 1; 15 if (sc.length() < 11) { 16 System.out.println("null data"); 17 return; 18 } else { 19 for (int i = 0; i < sc.length(); i++) { 20 if (a[i] == '0') { 21 f = true; 22 } 23 } 24 } 25 if (f) { 26 for (int i = 0; i < sc.length(); i++) { 27 if (a[i] == '0') { 28 k = false; 29 t = false; 30 while (i < sc.length()) { 31 int s; 32 s = i; 33 if (a[s + 9] == '1') { 34 k = true; 35 } 36 while (s < i + 9) { 37 s += 1; 38 if (a[s] == '1') { 39 cnt += 1; 40 } 41 } 42 if ((cnt % 2 == 0&&a[i + 10] == '0')||(cnt % 2 != 0&&a[i + 10] == '1')) { 43 t = true; 44 } 45 if (k==true&&t==true) { 46 System.out.println(c + ":" + a[i + 1] + a[i + 2] + a[i + 3] + a[i + 4] + a[i + 5] + a[i + 6] + a[i + 7] + a[i + 8]); 47 c += 1; 48 } 49 else if(k==false) 50 { 51 System.out.println(c + ":" + "validate error"); 52 c += 1; 53 } 54 else if(k==true&&t==false){ 55 System.out.println(c + ":" + "parity check error"); 56 c += 1; 57 } 58 else 59 { 60 System.out.println(c + ":" + "validate error"); 61 c += 1; 62 } 63 i += 11; 64 } 65 } 66 } 67 } else { 68 System.out.println("null data"); 69 } 70 } 71 }
2.题目集3 7—1
该题思路较为清晰(一遍过了)
唯一需要注意的是在进行一元二次方程类的编辑时要注意类中a,b,c三个变量在类中的私有性即private.
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class Main { 4 public static void main(String[] args){ 5 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 6 7 double a = Double.parseDouble(input.next()); 8 double b = Double.parseDouble(input.next()); 9 double c = Double.parseDouble(input.next()); 10 11 if(a == 0){ 12 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 13 System.exit(0); 14 } 15 16 //create a QuadraticEquation object 17 QuadraticEquation equation = new QuadraticEquation(a, b, c); 18 //get value of b * b - 4 * a * c 19 double discriminant = equation.getDiscriminant(); 20 21 System.out.println("a=" + equation.getA() + 22 ",b=" + equation.getB() + 23 ",c=" + equation.getC()+":"); 24 25 if (discriminant < 0) { 26 System.out.println("The equation has no roots."); 27 } 28 else if (discriminant == 0) 29 { 30 System.out.println("The root is " + 31 String.format("%.2f", equation.getRoot1())); 32 } 33 else // (discriminant >= 0) 34 { 35 System.out.println("The roots are " + 36 String.format("%.2f", equation.getRoot1()) 37 + " and " + String.format("%.2f", equation.getRoot2())); 38 } 39 } 40 } 41 42 class QuadraticEquation{ 43 double a; 44 double b; 45 double c; 46 47 public QuadraticEquation(double a, double b, double c) { 48 this.a = a; 49 this.b = b; 50 this.c = c; 51 } 52 53 double getDiscriminant() 54 { 55 double x; 56 x = b*b - 4*a*c; 57 return x; 58 } 59 60 double getRoot1() 61 { 62 double x1; 63 x1 = (-b+Math.sqrt(b*b-4*a*c))/(2*a); 64 return x1; 65 } 66 double getRoot2() 67 { 68 double x2; 69 x2 = (-b-Math.sqrt(b*b-4*a*c))/(2*a); 70 return x2; 71 } 72 73 public double getA() { 74 a = a*1.0; 75 return a; 76 } 77 public double getB() { 78 b = b*1.0; 79 return b; 80 } 81 public double getC() { 82 c = c*1.0; 83 return c; 84 } 85 }
3.题目集3 7—2
该题是对之前日期题目的改编需要将之前的一个函数转换为多种方法。
我认为该题的主要的难点在于对方法之间的数据衔接处理。日期之间的正确循环及在满足什么条件是月数进一,
在满足什么条件时年数进一,以及对闰年的循环问题,是本题对逻辑思维能力以及代码衔接能力最大的考察。
我在写该题时为了找到正确的循环计算方法花费了大量时间。这对我以后的编程习惯有了重大提醒。以后在进行
逻辑思维强的题目一定要先构建好程序框架,再进行程序编写。
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 public class Main { 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 5 int year; 6 int month; 7 int day; 8 9 int choice = input.nextInt(); 10 11 if (choice == 1) { // test getNextNDays method 12 int m; 13 year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 14 month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 15 day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 16 17 DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day); 18 19 if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { 20 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 21 System.exit(0); 22 } 23 24 m = input.nextInt(); 25 26 if (m < 0) { 27 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 28 System.exit(0); 29 } 30 31 System.out.print(date.getYear() + "-" + date.getMonth() + "-" + date.getDay() + " next " + m + " days is:"); 32 System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate()); 33 } else if (choice == 2) { // test getPreviousNDays method 34 int n; 35 year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 36 month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 37 day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 38 39 DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day); 40 41 if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { 42 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 43 System.exit(0); 44 } 45 46 n = input.nextInt(); 47 48 if (n < 0) { 49 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 50 System.exit(0); 51 } 52 53 System.out.print( 54 date.getYear() + "-" + date.getMonth() + "-" + date.getDay() + " previous " + n + " days is:"); 55 System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate()); 56 } else if (choice == 3) { //test getDaysofDates method 57 year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 58 month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 59 day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 60 61 int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 62 int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 63 int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 64 65 DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(year, month, day); 66 DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherYear, anotherMonth, anotherDay); 67 68 if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) { 69 System.out.println("The days between " + fromDate.showDate() + 70 " and " + toDate.showDate() + " are:" 71 + fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate)); 72 } else { 73 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 74 System.exit(0); 75 } 76 } 77 else{ 78 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 79 System.exit(0); 80 } 81 } 82 } 83 class DateUtil { 84 public DateUtil(int year, int month, int day) { 85 this.year = year; 86 this.month = month; 87 this.day = day; 88 } 89 public DateUtil(DateUtil d) { 90 this(d.year, d.month, d.day); 91 } 92 public String showDate() 93 { 94 return year + "-" + month + "-" + day; 95 } 96 public int getYear() { 97 return year; 98 } 99 100 public int getMonth() { 101 return month; 102 } 103 104 public int getDay() { 105 return day; 106 } 107 108 int year; 109 int month; 110 int day; 111 public boolean checkInputValidity() 112 { 113 if(this.year<1820||this.year>2020||this.month<1||this.month>12||this.day<1||this.day>31){ 114 return false; 115 } 116 else { 117 if(this.month == 2){ 118 if(isLeapYear(this.year)){ 119 if(this.day>29){ 120 return false; 121 } 122 } 123 else{ 124 if(this.day>28){ 125 return false; 126 } 127 } 128 } 129 if(this.month == 4 || this.month == 6 || this.month == 9 || this.month == 11){ 130 return this.day < 31; 131 } 132 } 133 return true; 134 } 135 public boolean isLeapYear(int year) 136 { 137 boolean isLeapYear; 138 isLeapYear=((year%4==0&&year%100!=0)||year%400==0); 139 return isLeapYear; 140 } 141 142 public DateUtil getNextNDays(int days) 143 { 144 DateUtil date=new DateUtil(this); 145 if(days==0) 146 return date; 147 do { 148 if (days > 31 && date.day < 29) { 149 days -= isLastDays(date.year, date.month); 150 nextMonth(date); 151 } 152 153 date = nextDay(date); 154 days--; 155 } while (days > 0); 156 return date; 157 } 158 159 private void nextMonth(DateUtil date) { 160 date.month++; 161 if(date.month == 13) 162 { 163 date.month = 1; 164 date.year++; 165 } 166 } 167 168 public DateUtil nextDay(DateUtil date) 169 { 170 if(date.day == isLastDays(date.year,date.month)) 171 { 172 date.day = 1; 173 nextMonth(date); 174 } 175 else 176 date.day++; 177 return date; 178 } 179 public int isLastDays(int year,int month) 180 { 181 if(isLeapYear(year) && month == 2){ 182 return 29; 183 } 184 if(month == 2){ 185 return 28;} 186 if(month == 4 || month == 6 || month == 9 || month == 11) 187 return 30; 188 return 31; 189 } 190 public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int days) 191 { 192 DateUtil date=new DateUtil(this); 193 if(days==0)return date; 194 do { 195 if (days > 31 && date.day < 29) { 196 days -= isStartDays(date.year, date.month); 197 nextPMonth(date); 198 } 199 lastDay(date); 200 days--; 201 202 } while (days > 0); 203 return date; 204 } 205 206 private void nextPMonth(DateUtil date) { 207 date.month--; 208 if(date.month == 0) 209 { 210 date.month = 12; 211 date.year--; 212 } 213 } 214 215 private void lastDay(DateUtil date) { 216 if(date.day == 1) 217 { 218 date.day = isStartDays(date.year,date.month); 219 nextPMonth(date); 220 } 221 else 222 date.day--; 223 } 224 private int isStartDays(int year, int month) { 225 if(isLeapYear(year) && month == 3){ 226 return 29;} 227 if(month == 3) 228 return 28; 229 if(month == 4 || month == 6 || month == 9 || month == 11||month==1||month==8||month==2) 230 return 31; 231 return 30; 232 } 233 public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date) 234 { 235 while (!equalTwoDates(date)){ 236 if(this.year>date.year) return true; 237 else if (this.year<date.year)return false; 238 else 239 { 240 if(this.month>date.month) return true; 241 else if(this.month<date.month) return false; 242 else { 243 return this.day > date.day; 244 } 245 } 246 } 247 return false; 248 249 } 250 public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date) 251 { 252 return this.day == date.day && this.year == date.year && this.month == date.month; 253 } 254 public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date) 255 { 256 if(this.equalTwoDates(date)){ 257 return 0; 258 } 259 else { 260 if(this.compareDates(date)){ 261 int i; 262 i=iS(date); 263 while (true){ 264 if(this.getPreviousNDays(i).equalTwoDates(date)){ 265 return i; 266 } 267 i++; 268 } 269 } 270 else { 271 int i; 272 i=iS(date); 273 while (true){ 274 if(this.getNextNDays(i).equalTwoDates(date)){ 275 return i; 276 } 277 i++; 278 } 279 } 280 } 281 } 282 private int iS(DateUtil date) { 283 int i; 284 if(this.year==date.year&&this.month==date.month){ 285 return 1; 286 } 287 else if(this.year==date.year){ 288 289 if(this.month>date.month){ 290 i=(this.month-1-date.month)*28+1; 291 return i; 292 } 293 else { 294 295 i=(date.month-1-this.month)*28+1; 296 return i; 297 } 298 } 299 else { 300 if(this.year>date.year){ 301 i=((this.year-1-date.year)*365); 302 return i; 303 } 304 else { 305 i=((date.year-this.year-1)*365); 306 return i; 307 } 308 } 309 310 } 311 }
4.题目集3 7—3
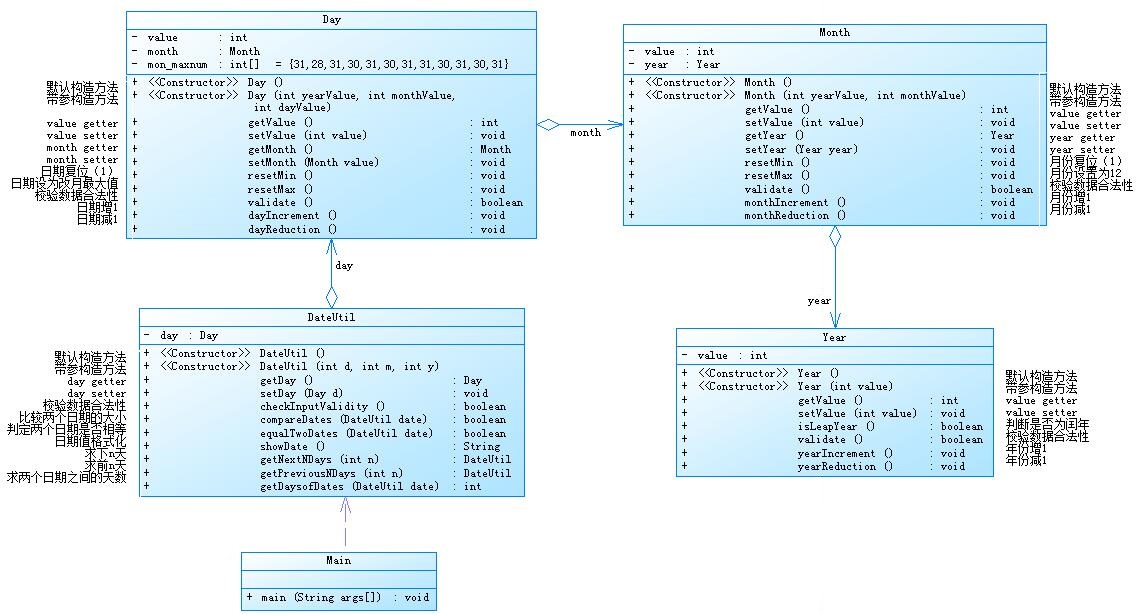
这题是对上一题的改造,即需要按照已提供的类图对题目进行重新编写。
虽然在主体逻辑思路上并未发生改变,但是在构造类的过程中就容易发现:这实际上将原有的编排完全打乱了,
需要按照新的类图对各个方法进行重构以及重新确定调用关系。
因此在该题上依旧要花费与上一题几乎同等的时间。
不过通过该题也可以很好的锻炼自己对题目的编码能力,以及更深入的了解类间关系。
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 public class Main { 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); 5 int year; 6 int month; 7 int day; 8 int choice=input.nextInt(); 9 if(choice==1){ 10 int m; 11 year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 12 month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 13 day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 14 DateUtil date=new DateUtil(year,month,day); 15 if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { 16 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 17 System.exit(0); 18 } 19 20 m = input.nextInt(); 21 22 if (m < 0) { 23 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 24 System.exit(0); 25 } 26 System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate()); 27 } 28 else if(choice==2){ 29 int n;//输入n 30 year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 31 month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 32 day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 33 34 DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day); 35 36 if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { 37 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 38 System.exit(0); 39 } 40 41 n = input.nextInt(); 42 43 if (n < 0) { 44 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 45 System.exit(0); 46 } 47 System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate()); 48 } 49 else if(choice==3){ 50 year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 51 month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 52 day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 53 54 int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 55 int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 56 int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 57 DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(year, month, day); 58 DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherYear, anotherMonth, anotherDay); 59 60 if(!fromDate.checkInputValidity() || !toDate.checkInputValidity()){//如果数据不合法 61 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 62 System.exit(0); 63 } 64 else 65 System.out.println(fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate)); 66 } 67 else 68 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 69 } 70 } 71 class Year{ 72 int value; 73 74 public Year(){ 75 } 76 77 public Year(int value){ 78 this.value=value; 79 } 80 81 public int getValue(){ 82 return value; 83 } 84 85 public void setValue(int value){ 86 this.value=value; 87 } 88 89 public boolean isLeapYear(){ 90 if((value%4==0&&value%100!=0)||value%400==0) 91 return true; 92 else 93 return false; 94 } 95 96 public boolean validate(){ 97 if(value<=2050&&value>=1900) 98 return true; 99 else 100 return false; 101 } 102 103 public void yearIncrement(){ 104 value+=1; 105 } 106 107 public void yearReduction(){ 108 value-=1; 109 } 110 } 111 112 class Month{ 113 int value; 114 Year year; 115 116 public Month(){ 117 } 118 119 public Month(int yearValue,int monthValue){ 120 this.year=new Year(yearValue); 121 this.value=monthValue; 122 } 123 124 public int getValue(){ 125 return value; 126 } 127 128 public void setValue(int value){ 129 this.value=value; 130 } 131 public Year getYear(){ 132 return year; 133 } 134 public void setYear(Year year){ 135 this.year=year; 136 } 137 138 public void resetMin(){ 139 value=1; 140 } 141 142 public void resetMax(){ 143 value=12; 144 } 145 146 public boolean validate(){ 147 if(value>=1&&value<=12) 148 return true; 149 else 150 return false; 151 } 152 153 public void dayIncrement(){ 154 value+=1; 155 } 156 157 public void dayReduction(){ 158 value-=1; 159 } 160 } 161 162 class Day{ 163 int value; 164 Month month; 165 int[] a ={31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; 166 167 public Day(){ 168 } 169 170 public Day(int yearValue,int monthValue,int dayValue){ 171 this.month=new Month(yearValue,monthValue); 172 this.value=dayValue; 173 } 174 175 public int getValue(){ 176 return value; 177 } 178 179 public void setValue(int value){ 180 this.value=value; 181 } 182 public Month getMonth(){ 183 return month; 184 } 185 public void setMonth(Month value){ 186 this.month=value; 187 } 188 189 public void resetMin(){ 190 value=1; 191 } 192 193 public void resetMax(){ 194 value=a[month.getValue()-1]; 195 } 196 197 public boolean validate(){ 198 if(this.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) 199 a[1]=29; 200 return value >= 1 && value <= a[month.getValue() - 1]; 201 } 202 203 public void dayIncrement() { 204 value+=1; 205 } 206 207 public void dayReduction() { 208 value-=1; 209 } 210 } 211 212 class DateUtil { 213 Day day; 214 215 public DateUtil() { 216 } 217 218 public DateUtil(int d, int m, int y) { 219 this.day = new Day(d, m, y); 220 } 221 222 public Day getDay() { 223 return day; 224 } 225 226 public void setDay(Day d) { 227 this.day = d; 228 } 229 230 231 public boolean checkInputValidity() { 232 return this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().validate() && this.getDay().getMonth().validate() && day.validate(); 233 } 234 235 public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date) { 236 if(date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()<this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) 237 return false; 238 else if(date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()==this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&date.getDay().getMonth().getValue()<this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()) 239 return false; 240 else return date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() != this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() || date.getDay().getMonth().getValue() != this.getDay().getMonth().getValue() || date.getDay().getValue() >= this.getDay().getValue(); 241 } 242 243 public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date) { 244 return this.getDay().getValue() == date.getDay().getValue() && this.getDay().getMonth().getValue() == date.getDay().getMonth().getValue() && this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() == date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue(); 245 } 246 public String showDate() { 247 return this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() + "-" + this.getDay().getMonth().getValue() + "-" + this.getDay().getValue(); 248 } 249 250 public int sets(DateUtil d) { 251 int[] a = {0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31}; 252 int b = 0, i; 253 i = d.getDay().getMonth().getValue() + 1; 254 while( i <= 12) { 255 b = b + a[i]; 256 i++; 257 } 258 b = b + a[d.getDay().getMonth().getValue()] - d.getDay().getValue(); 259 if (d.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear() && d.getDay().getMonth().getValue() <= 2)//闰年 260 b++; 261 return b; 262 } 263 264 265 public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n) { 266 int[] a = {0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31}; 267 int y1, m1, d1; 268 int i; 269 int b = sets(this); 270 if (b > n) { 271 y1 = this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue(); 272 if (this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) { 273 a[2] = 29; 274 } 275 int e = a[this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()]; 276 e = e - this.getDay().getValue(); 277 if (e >= n) { 278 m1 = this.getDay().getMonth().getValue(); 279 d1 = n + this.getDay().getValue(); 280 } else { 281 n = n - e; 282 m1 = this.getDay().getMonth().getValue() + 1; 283 i = m1; 284 while (n - a[i] > 0) { 285 n = n - a[i]; 286 m1++; 287 i++; 288 } 289 d1 = n; 290 } 291 } else { 292 n = n - b; 293 y1 = this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() + 1; 294 int c = 365; 295 if (new Year(y1).isLeapYear()) { 296 c++; 297 } 298 while (n - c > 0) { 299 n = n - c; 300 y1++; 301 c = 365; 302 if (new Year(y1).isLeapYear()) 303 c++; 304 } 305 i = 1; 306 for(;n - a[i] > 0;i++) { 307 n = n - a[i]; 308 } 309 m1 = i; 310 d1 = n; 311 } 312 return new DateUtil(y1, m1, d1); 313 } 314 315 public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n) { 316 int[] a = {0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31}; 317 int y2, m2, d2; 318 int i, b; 319 b = 365 - sets(this); 320 if (this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) { 321 b++; 322 } 323 if (b > n) { 324 y2 = this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue(); 325 int e = this.getDay().getValue(); 326 if (e > n) { 327 m2 = this.getDay().getMonth().getValue(); 328 d2 = e - n; 329 } else { 330 n = n - e; 331 m2 = this.getDay().getMonth().getValue() - 1; 332 i = m2; 333 while (n - a[i] > 0) { 334 n = n - a[i]; 335 m2--; 336 i--; 337 } 338 d2 = a[i] - n; 339 if (new Year(y2).isLeapYear() && m2 == 2) { 340 d2++; 341 } 342 } 343 } else { 344 n = n - b; 345 y2 = this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() - 1; 346 int f = 365; 347 if (new Year(y2).isLeapYear()) { 348 f++; 349 } 350 while (n - f > 0) { 351 n = n - f; 352 y2--; 353 f = 365; 354 if (new Year(y2).isLeapYear()) 355 f++; 356 } 357 i = 12; 358 for(;n - a[i] > 0;i--) { 359 n = n - a[i]; 360 } 361 m2 = i; 362 d2 = a[i] - n; 363 if (new Year(f).isLeapYear() && m2 == 2) { 364 d2++; 365 } 366 } 367 return new DateUtil(y2, m2, d2); 368 } 369 370 public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date) { 371 DateUtil s1 = this; 372 DateUtil s2 = date; 373 if (this.equalTwoDates(date)) { 374 return 0; 375 } else if (!this.compareDates(date)) { 376 s1 = date; 377 s2 = this; 378 } 379 int[] a = {0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31}; 380 int i; 381 int j; 382 int s = 0; 383 i = s1.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() + 1; 384 while(i < s2.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) { 385 s = s + 365; 386 if (new Year(i).isLeapYear()){ 387 s++; 388 } 389 i++; 390 } 391 if (s1.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() == s2.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() && s1.getDay().getMonth().getValue() == s2.getDay().getMonth().getValue()) { 392 s = s2.getDay().getValue() - s1.getDay().getValue(); 393 } else if (s1.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() == s2.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() && s1.getDay().getMonth().getValue() != s2.getDay().getMonth().getValue()) { 394 if (s1.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) 395 a[2] = 29; 396 s = s + a[s1.getDay().getMonth().getValue()] - s1.getDay().getValue(); 397 s = s + s2.getDay().getValue(); 398 j = s1.getDay().getMonth().getValue() + 1; 399 while(j <= s2.getDay().getMonth().getValue() - 1){ 400 s += a[j]; 401 j++; 402 } 403 } else if (s1.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() != s2.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) { 404 s = s + a[s1.getDay().getMonth().getValue()] - s1.getDay().getValue(); 405 s = s + s2.getDay().getValue(); 406 j = s1.getDay().getMonth().getValue() + 1; 407 while(j <= 12){ 408 s = s + a[j]; 409 j++; 410 } 411 j = s2.getDay().getMonth().getValue() - 1; 412 while(j > 0){ 413 s = s + a[j]; 414 j--; 415 } 416 if (s1.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear() && s1.getDay().getMonth().getValue() <= 2) 417 s++; 418 if (s2.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear() && s2.getDay().getMonth().getValue() > 2) 419 s++; 420 } 421 return s; 422 } 423 }
踩坑心得:
(对源码的提交过程中出现的问题及心得进行总结,务必做到详实,拿数据、源码及测试结果说话,切忌假大空)
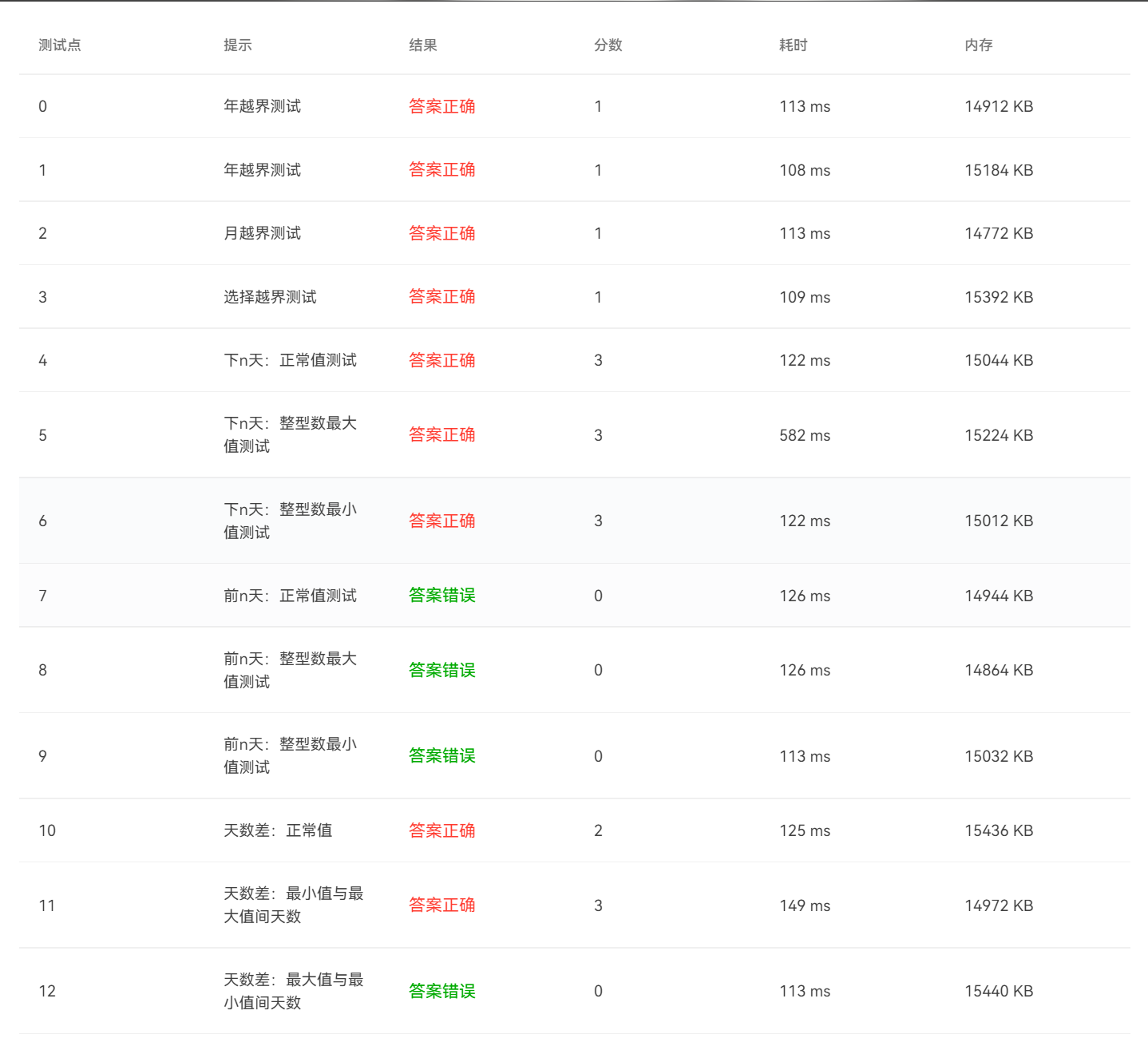
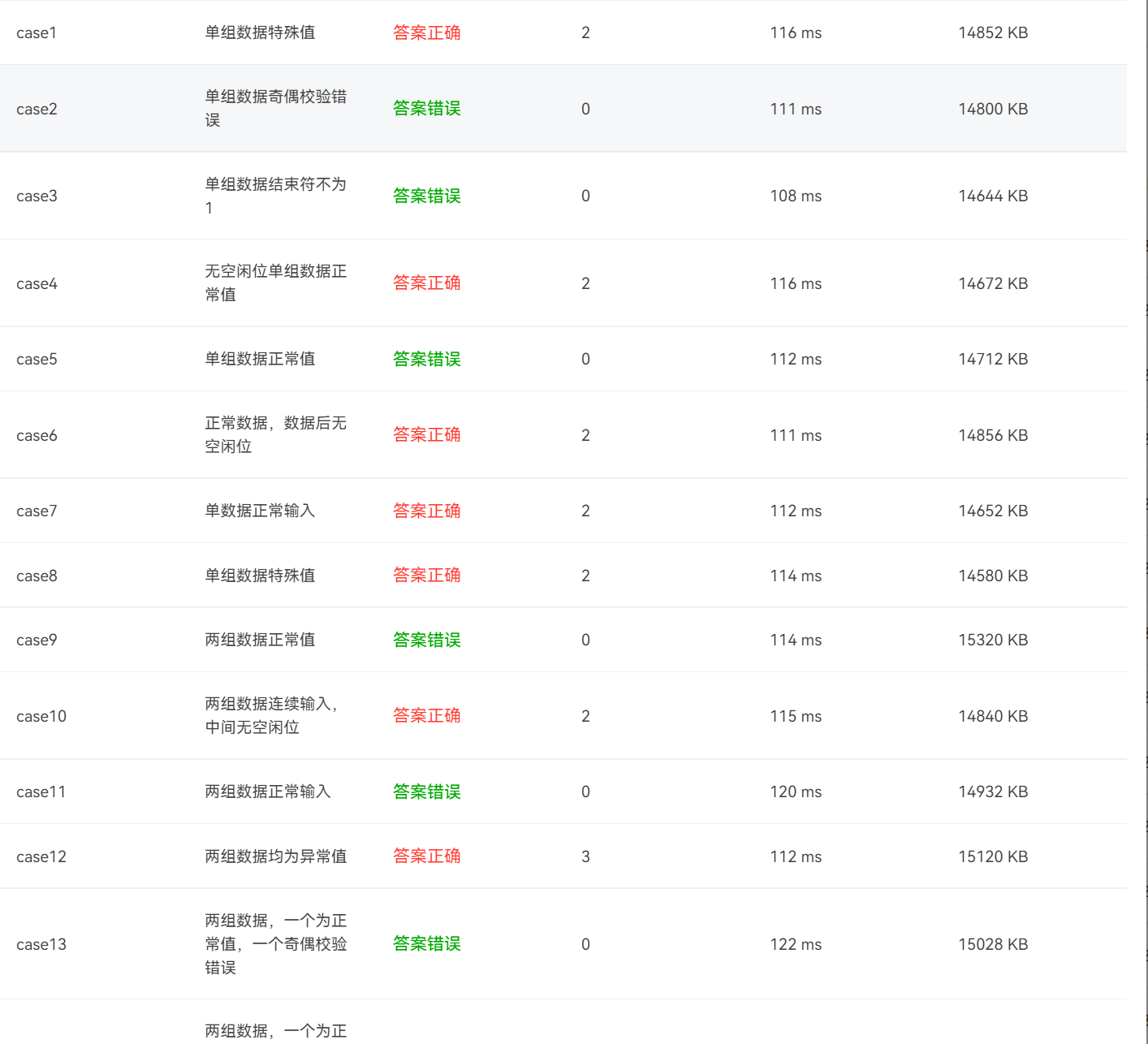
在源码的提交过程中,我经常会出现格式错误,以及输出问题有误,
格式错误一般都是浮点数的精度问题和一些错误输入的判断问题,
很多错误输入的判断,经常没有能考虑到,导致一些错误数据也能得出答案。
所以我认为进行代码提交之前,在尽可能地测试一些难以估测的边界值,以及非常大或非常小的数值,
在字符串的输入中,也应该输入一些带空格或者其他非数字型符号的输入。
同时在测试的过程中,我们可以进行设计测试用例,
每一个无效等价类都设计一个测试用例,遵循但缺陷原则或者设计一个测试用例,使其尽可能多的覆盖有效等价类。
改进建议:
(对相应题目的编码改进给出自己的见解,做到可持续改进)
具体怎么改进,我自己本身也不是很清楚,但我觉得代码风格一定要简约,
同时对函数的构造以及类的分类必须清晰,要不然一旦出现格式错误,
很难在短时间内发现自己代内部的问题,
在构造类的过程中,命名尽量贴合实际,切记不要随意命名,变量名也应尽量切合题意,
这样做可以极大程度的方便后续代码的维护以及修改。
同时在书写代码的时候,量在关键处,尤其是逻辑紧密的地方加上一定量的注释,
这样做既可以方便自己后续的阅读,也可以方便别人对代码进行理解
总结:
(对本阶段三次题目集的综合性总结,学到了什么,哪些地方需要进一步学习及研究,对教师、课程、作业、实验、课上及课下组织方式等方面的改进建议及意见。在截止时间之前将发布的Blog正文网址链接(非编辑网址链接)直接发到超星系统即可)
通过对本阶段三次题目集的综合练习,我学会了如何对类进行设计,
如何降低耦合性,提高内聚性。以及类设计的7大法则,对字符串的输入输出以及对字符串的处理,也有了更深的理解。
同时也学到了如何进行设计测试用例。
在对类的封装,以及如何对类进行设计,需要进一步的学习及研究。
同时还需要建立良好的代码习惯。
对老师的授课方式无任何异议。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号