You are given two integer arrays nums1 and nums2 sorted in non-decreasing order and an integer k.
Define a pair (u, v) which consists of one element from the first array and one element from the second array.
Return the k pairs (u1, v1), (u2, v2), ..., (uk, vk) with the smallest sums.
Example 1:
Input: nums1 = [1,7,11], nums2 = [2,4,6], k = 3 Output: [[1,2],[1,4],[1,6]] Explanation: The first 3 pairs are returned from the sequence: [1,2],[1,4],[1,6],[7,2],[7,4],[11,2],[7,6],[11,4],[11,6]
Example 2:
Input: nums1 = [1,1,2], nums2 = [1,2,3], k = 2 Output: [[1,1],[1,1]] Explanation: The first 2 pairs are returned from the sequence: [1,1],[1,1],[1,2],[2,1],[1,2],[2,2],[1,3],[1,3],[2,3]
Constraints:
1 <= nums1.length, nums2.length <= 105-109 <= nums1[i], nums2[i] <= 109nums1andnums2both are sorted in non-decreasing order.1 <= k <= 104k <= nums1.length * nums2.length
ChatGPT's Solution:
import heapq class Solution: def kSmallestPairs(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int], k: int) -> List[List[int]]: if not nums1 or not nums2: return [] min_heap = [] result = [] # Initialize the heap with the first element of nums2 paired with tup to k elements of nums1 for i in range(min(k, len(nums1))): heapq.heappush(min_heap, (nums1[i] + nums2[0], i, 0)) while min_heap and len(result) < k: sum_val, i, j = heapq.heappop(min_heap) result.append((nums1[i], nums2[j])) # If there is a next element in nums2, push the next pair (i, j+1) into the heap if j + 1 < len(nums2): heapq.heappush(min_heap, (nums1[i] + nums2[j+1], i, j+1)) return result
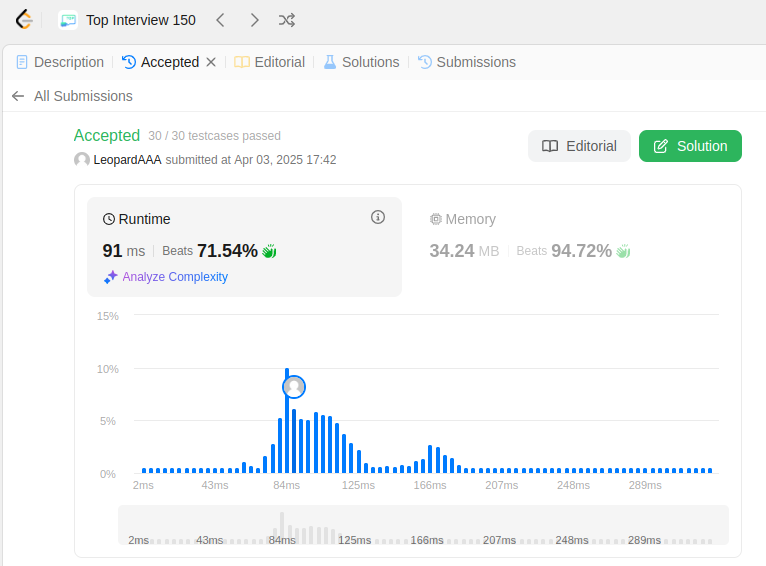
Explanation:
-
We use a min-heap to efficiently get the smallest sums.
-
We initialize the heap with the first element of
nums2paired with up tokelements ofnums1. -
We extract the smallest pair, then push the next potential pair by increasing the index in
nums2. -
We repeat this until we collect
kpairs or the heap is exhausted.
This approach ensures an efficient O(k log k) time complexity, making it suitable for large inputs.




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号