A trie (pronounced as "try") or prefix tree is a tree data structure used to efficiently store and retrieve keys in a dataset of strings. There are various applications of this data structure, such as autocomplete and spellchecker.
Implement the Trie class:
Trie()Initializes the trie object.void insert(String word)Inserts the stringwordinto the trie.boolean search(String word)Returnstrueif the stringwordis in the trie (i.e., was inserted before), andfalseotherwise.boolean startsWith(String prefix)Returnstrueif there is a previously inserted stringwordthat has the prefixprefix, andfalseotherwise.
Example 1:
Input
["Trie", "insert", "search", "search", "startsWith", "insert", "search"]
[[], ["apple"], ["apple"], ["app"], ["app"], ["app"], ["app"]]
Output
[null, null, true, false, true, null, true]
Explanation
Trie trie = new Trie();
trie.insert("apple");
trie.search("apple"); // return True
trie.search("app"); // return False
trie.startsWith("app"); // return True
trie.insert("app");
trie.search("app"); // return True
Constraints:
1 <= word.length, prefix.length <= 2000wordandprefixconsist only of lowercase English letters.- At most
3 * 104calls in total will be made toinsert,search, andstartsWith.
My Solution:
class Trie: def __init__(self): self.words = set() def insert(self, word: str) -> None: self.words.add(word) def search(self, word: str) -> bool: return word in self.words def startsWith(self, prefix: str) -> bool: for word in self.words: if word.startswith(prefix): return True return False # Your Trie object will be instantiated and called as such: # obj = Trie() # obj.insert(word) # param_2 = obj.search(word) # param_3 = obj.startsWith(prefix)
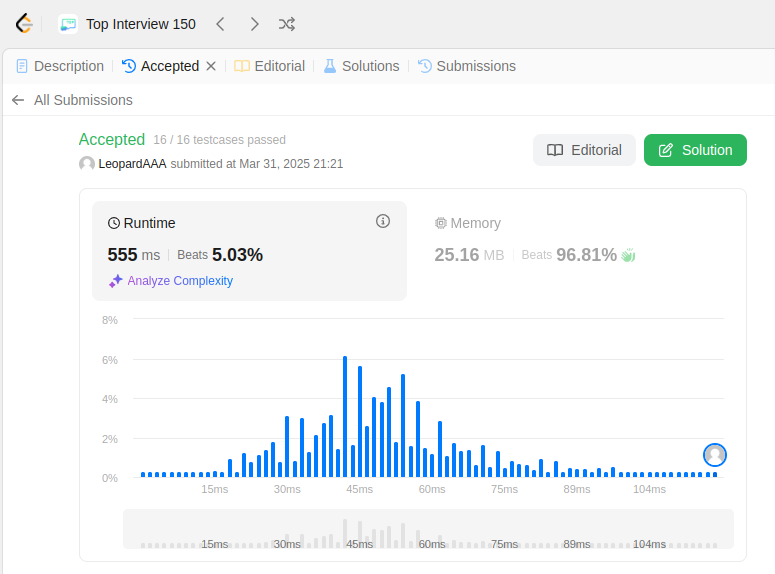
ChatGPT's Solution:
class TrieNode: def __init__(self): # Each node stores a dictionary of children and a boolean for end of word. self.children = {} self.is_end_of_word = False class Trie: def __init__(self): # Initialize the trie with a root node. self.root = TrieNode() def insert(self, word: str) -> None: # Insert a word into the trie. node = self.root for char in word: if char not in node.children: node.children[char] = TrieNode() node = node.children[char] node.is_end_of_word = True def search(self, word: str) -> bool: # Return true if the word is in the trie, otherwise false. node = self.root for char in word: if char not in node.children: return False node = node.children[char] return node.is_end_of_word def startsWith(self, prefix: str) -> bool: # Return true if there is a word in the trie that starts with the given prefix. node = self.root for char in prefix: if char not in node.children: return False node = node.children[char] return True # Your Trie object will be instantiated and called as such: # obj = Trie() # obj.insert(word) # param_2 = obj.search(word) # param_3 = obj.startsWith(prefix)
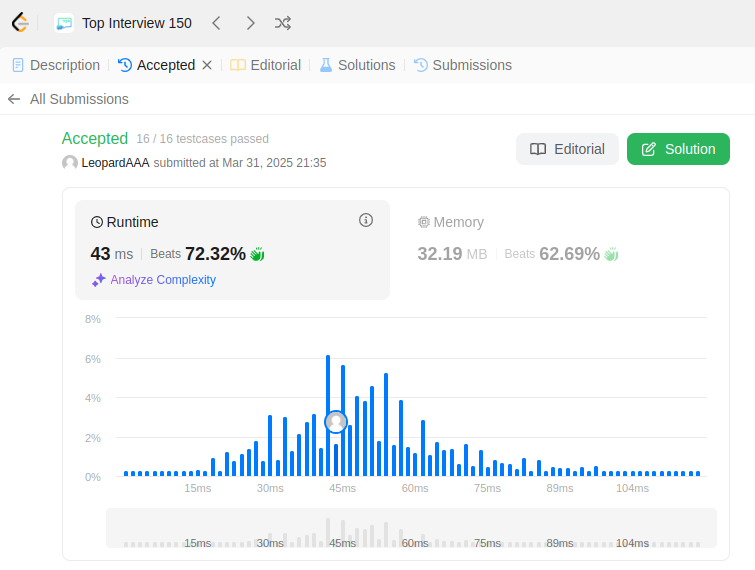
Explanation:
-
TrieNode class:
-
It has a dictionary
childrento store the next characters of the word. -
is_end_of_wordis a boolean flag to indicate whether the current node marks the end of a word.
-
-
Trie class:
-
insert(word): This method inserts a word into the trie. It traverses the trie, adding new nodes if necessary. -
search(word): This method checks if the word exists in the trie by traversing through the nodes. -
startsWith(prefix): This method checks if any word in the trie starts with the given prefix.
-
Example Usage:
trie = Trie() trie.insert("apple") print(trie.search("apple")) # Returns True print(trie.search("app")) # Returns False print(trie.startsWith("app")) # Returns True trie.insert("app") print(trie.search("app")) # Returns True




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号