Given the root of a binary tree, flatten the tree into a "linked list":
- The "linked list" should use the same
TreeNodeclass where therightchild pointer points to the next node in the list and theleftchild pointer is alwaysnull. - The "linked list" should be in the same order as a pre-order traversal of the binary tree.
Example 1:
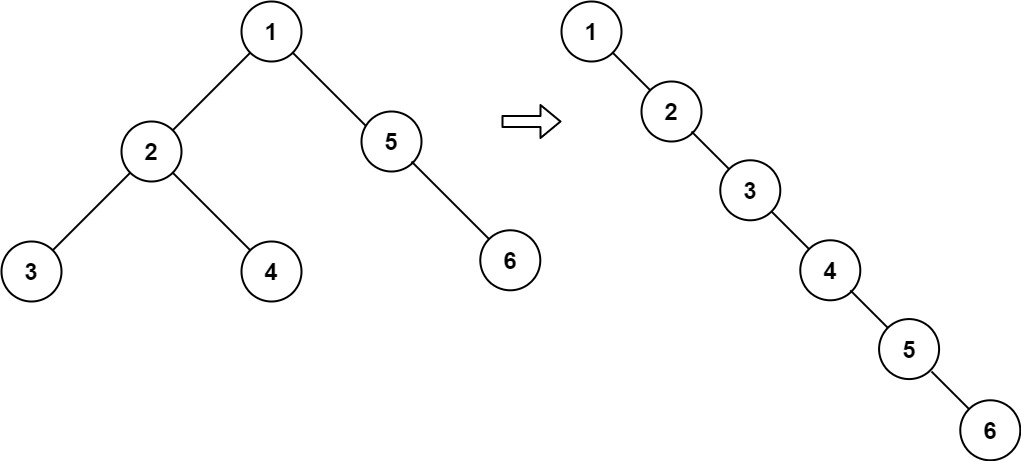
Input: root = [1,2,5,3,4,null,6] Output: [1,null,2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
Example 2:
Input: root = [] Output: []
Example 3:
Input: root = [0] Output: [0]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 2000]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
My Solution:
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def flatten(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> None: """ Do not return anything, modify root in-place instead. """ if not root or not root.left and not root.right: return root right_node = root.right root.right = self.flatten(root.left) root.left = None if right_node: node = root while node.right: node = node.right node.right = self.flatten(right_node) return root




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号