Design a data structure that follows the constraints of a Least Recently Used (LRU) cache.
Implement the LRUCache class:
LRUCache(int capacity)Initialize the LRU cache with positive sizecapacity.int get(int key)Return the value of thekeyif the key exists, otherwise return-1.void put(int key, int value)Update the value of thekeyif thekeyexists. Otherwise, add thekey-valuepair to the cache. If the number of keys exceeds thecapacityfrom this operation, evict the least recently used key.
The functions get and put must each run in O(1) average time complexity.
Example 1:
Input
["LRUCache", "put", "put", "get", "put", "get", "put", "get", "get", "get"]
[[2], [1, 1], [2, 2], [1], [3, 3], [2], [4, 4], [1], [3], [4]]
Output
[null, null, null, 1, null, -1, null, -1, 3, 4]
Explanation
LRUCache lRUCache = new LRUCache(2);
lRUCache.put(1, 1); // cache is {1=1}
lRUCache.put(2, 2); // cache is {1=1, 2=2}
lRUCache.get(1); // return 1
lRUCache.put(3, 3); // LRU key was 2, evicts key 2, cache is {1=1, 3=3}
lRUCache.get(2); // returns -1 (not found)
lRUCache.put(4, 4); // LRU key was 1, evicts key 1, cache is {4=4, 3=3}
lRUCache.get(1); // return -1 (not found)
lRUCache.get(3); // return 3
lRUCache.get(4); // return 4
Constraints:
1 <= capacity <= 30000 <= key <= 1040 <= value <= 105- At most
2 * 105calls will be made togetandput.
My Solution:
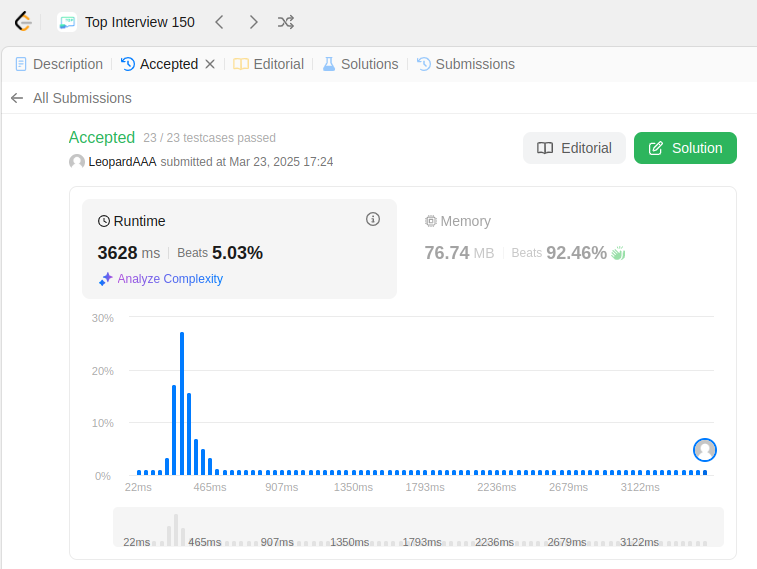
class LRUCache(object): def __init__(self, capacity): """ :type capacity: int """ self.capacity = capacity self._cache = {} self._used = [] def get(self, key): """ :type key: int :rtype: int """ try: res = self._cache[key] self._used.remove(key) self._used.append(key) except KeyError: return -1 return res def put(self, key, value): """ :type key: int :type value: int :rtype: None """ self._cache[key] = value if key in self._used: self._used.remove(key) self._used.append(key) if len(self._cache) > self.capacity: del self._cache[self._used[0]] self._used.pop(0) # Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such: # obj = LRUCache(capacity) # param_1 = obj.get(key) # obj.put(key,value)
ChatGPT's Solution:
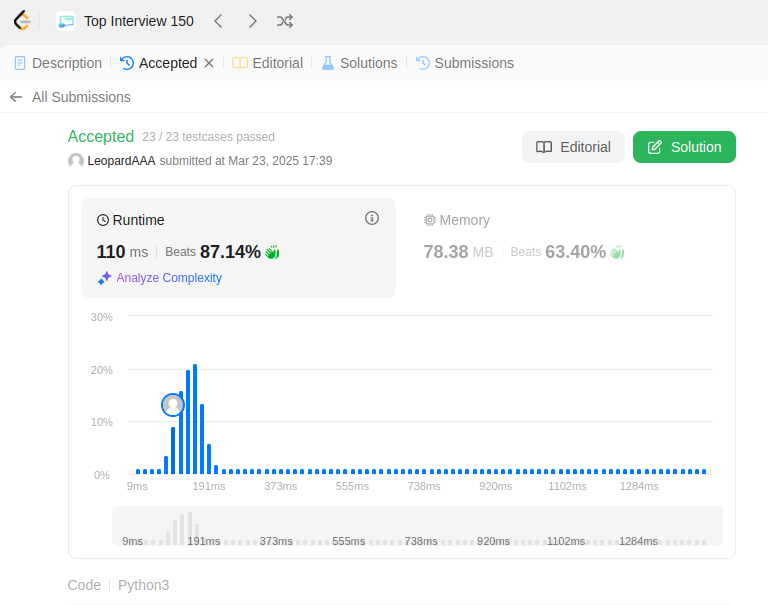
from collections import OrderedDict class LRUCache(object): def __init__(self, capacity): """ :type capacity: int """ self.cache = OrderedDict() self.capacity = capacity def get(self, key): """ :type key: int :rtype: int """ if key not in self.cache: return -1 # Move the accessed item to the end to mark it as recently used self.cache.move_to_end(key) return self.cache[key] def put(self, key, value): """ :type key: int :type value: int :rtype: None """ if key in self.cache: # Update the key and move it to the end self.cache.move_to_end(key) self.cache[key] = value if len(self.cache) > self.capacity: # Pop the least recently used item (first item) self.cache.popitem(last=False) # Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such: # obj = LRUCache(capacity) # param_1 = obj.get(key) # obj.put(key,value)




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号