基础 | 并发编程 - [不安全集合 & 写时复制]
List
不安全示例
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0 ;i <10;i++){
new Thread(()->{
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(new Random().nextInt(10));
list.add(UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0,8));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(list);
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
list.forEach(System.out::println);
}
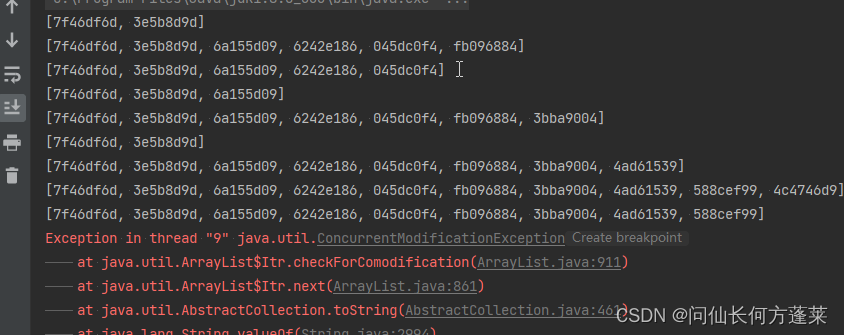
解决
- 业务上,避免将 list 作为成员变量时出现并发操作(这也是为什么通常使用 ArrayList 不会出错)
- 使用 Vector
- 使用 Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>())
- 使用 new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>()
适用于读远多于写的小集合
写时复制
写时复制的设计初衷是优先保证读的效率
因此,基于读写分离的思路,读的时候不加锁
为了保证读的安全(防止读时写),需要将写操作的生效变为一瞬间
这通过类似下面流程实现
- 从旧 list 中读(其实是从它内部的数组中读,下同)
- 开始写(锁还是要加的,防止并发写)
- 从旧 list 中复制一个新 list,新 list 长度 + 1
长度 + 1 是因为下面的复制不走 add 方法
而是直接在新 list 的对应位置插值
这可能因因为旧 list 满了,所以新 list 复制出来也满了,进而数组角标越界
先 + 1,在复制时就会自动完成数组的扩容 - 此时,依然从旧 list 里读值
- 新 list 的对应位置插入新值
- 此时,依然从旧 list 里读值
- 新 list 替换旧 list,此时,瞬间完成新旧 list 的切换
public boolean add(E e) {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
Object[] elements = getArray();
int len = elements.length;
Object[] newElements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, len + 1);
newElements[len] = e;
setArray(newElements);
return true;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
写时复制的限制
- 只适合用于小集合
因为有数组 copy,且 copy 也是有时间空间成本的 - 从其设计初衷,适合读远高于写的场景
Set
不安全示例
同 List ,集合改为 HashSet 即可
// Dummy value to associate with an Object in the backing Map
// 删元素时,返回元素值,因此默认值不是 null 以区分是否删成功
private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();
public HashSet() {
map = new HashMap<>();
}
public boolean add(E e) {
return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
写时复制
//1 查重
public boolean addIfAbsent(E e) {
Object[] snapshot = getArray();
return indexOf(e, snapshot, 0, snapshot.length) >= 0 ? false :
addIfAbsent(e, snapshot);
}
private boolean addIfAbsent(E e, Object[] snapshot) {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
Object[] current = getArray();
int len = current.length;
if (snapshot != current) {
// 防止查重时,其他线程操作
// 先判断新旧 set 的前半截得一致,后判断另一个线程是否塞了和当前值一样的值进去
// Optimize for lost race to another addXXX operation
int common = Math.min(snapshot.length, len);
for (int i = 0; i < common; i++)
if (current[i] != snapshot[i] && eq(e, current[i]))
return false;
if (indexOf(e, current, common, len) >= 0)
return false;
}
Object[] newElements = Arrays.copyOf(current, len + 1);
newElements[len] = e;
setArray(newElements);
return true;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
Map
不安全示例
略
写时复制
使用 ConcurrentHashMap



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号