[算法][几何计算]固定半径最少圆覆盖问题
引题:固定半径最少圆覆盖问题
背景:二维坐标轴中,给出n个点以及每个点的坐标(坐标为浮点型),和一个长度r(r为浮点型),求至少需要多个半径为r的圆可以把所有点覆盖。其中,0 < n <= 20。
输入:第一行输入n和m,以下2 ~ n + 1行中第 i + 1 行 输入 x_i, y_i 表示第 i 个点的坐标
输出:一个数,表示圆的个数
样例(样例改编自链接):
input:
15 135 -144 -45 -72 -45 0 -45 72 -45 144 -45 -144 -135 -72 -135 0 -135 72 -135 144 -135 -144 135 -72 135 0 135 72 135 144 135
output:
3
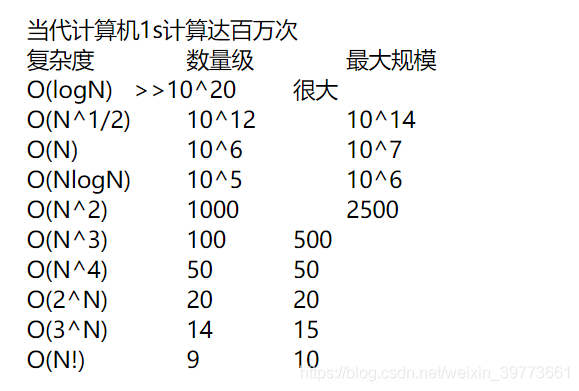
根据上表,可以支持O(2n)的算法
博客更新日志:
2022/12/08 提出问题,给出最原始的错误思路(由于是最小生成树+dij算法思路,很明显是错误的,防止误导已被删除)
2022/12/13 参考大量论文,写出了不同思路
2022/12/19 基本解决
2022/12/23 改正状态压缩dp错误
2023/01/01 大幅度优化状态压缩dp,并讨论了优化后的时间复杂程度
介绍 & 论文:
· 最少几何圆覆盖问题(MGDC)
Given a set P of n points in the Euclidean plane, the minimum geometric disk cover (MGDC) problem is to identify a minimally sized set of congruent disks with prescribed radius r that cover all the points in P. It is known that the MGDC problem is NP-complete. (Chang et al., 2013)
翻译:最小几何圆覆盖问题是 在个数为n的欧几里得平面上的点的集合P中,得出能覆盖所有P集合中的点的半径为r的圆的最小集合(与本文问题完全一致)。这是一个NP-complete问题。
虽然给出了解决方案,但是得买啊!好贵啊!
论文链接:链接
· 离散单位圆盘覆盖问题(Discrete unit disk cover (DUDC))
(Basappa et al., 2015)
翻译:离散单位圆覆盖问题(DUDC)是在平面中给定一个n个点的集合P和m个单位长度半径的圆的集合D,得出一个最小集合子集D'⊆D覆盖所有的点。
与MGDC问题不同的是,MGDC取圆的范围更广泛。
论文链接:链接
思路:
思路零:(整活)AI组简单粗暴算法(错误算法):
首先看看AI组给我们的代码是什么:
#include <stdio.h> int main(){ int n; float r; scanf("%d %f", &n, &r); float x[n], y[n]; for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){ scanf("%f %f", &x[i], &y[i]); } int count = 0; float cx[n], cy[n]; for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){ int flag = 0; for(int k = 0; k < count; k++){ float distance = (x[j] - cx[k]) * (x[j] - cx[k]) + (y[j] - cy[k]) * (y[j] - cy[k]); if(distance <= r * r){ flag = 1; break; } } if(flag == 0){ cx[count] = x[j]; cy[count] = y[j]; count++; } } printf("%d", count); return 0; }
时间复杂程度是O(n2),思路很简单:枚举每一个点,求每一个已经记录的圆心到该点的距离,如果在半径内则把这个点跳过;否则就将该点作为新的圆心记录。
AI的思路非常简单粗暴,但是很明显的错误点就是把每个点都作为圆心来求解,很明显这个思路是不正确的,举个例子:如果半径长r = 1,两个点(0,0),(0,2)很明显只需要一个圆心在(0,1)的圆就可以完全覆盖,但是如果用以上算法得出的结果是2,具体为什么自己可以思考一下。
这个算法也是大部分人第一时间会想到的算法,很明显是错误。
思路一:暴力枚举 + 状态压缩dp (最小覆盖圆 (The Smallest Circle))可以枚举所有的情况 时间复杂度很高:O(3n / 2)
- 思路总线:等价圆思想。“等价圆”是同一个圆心、所覆盖点完全相同的圆的集合,集合中不同圆唯一的不同就是半径不同,那么这个集合中半径最小的等价圆一定是这些被覆盖点中某三个点形成三角形的外接圆,或者是以某两个点为直径的圆,这个圆被称为这个集合中的最小等价圆。我们只需要找到这些半径不超过r的最小等价圆的最少数量即可。
- 状态压缩:维护多个最小覆盖圆的数据结构,将每个点是否构成同一个圆状态压缩(0为不在该圆中,1为在该圆中),然后对每个状态进行枚举初始化:半径长度超过m的圆初始化为0 (dp[ i ] = 0),半径长度小于等于m的初始化为1 (dp[ i ] = 1),时间复杂程度为 O(2n)。
- 优化:可以进行剪枝,当某一个状态得到的圆半径超过r,则不再加点枚举,例如状态 0011中的圆已经超过半径r,则不再枚举0111、1011、1111的状态。
- 动态规划:按照状态压缩后1的数量从少到多枚举每一个状态(2n个),如果该状态已经为1则跳过;如果为0则枚举两个子状态,相加进行状态转移,取所有情况的最小值;最终答案为 dp[2n-1]
- 状态转移方程:dp[i]= min(dp[j] + dp[i - j]),~i & j == 0,j < i
- 解释:
- 假设我们规定 j∈i 的情况为,j状态转化为二进制后,所有为1的位在i上对应也是1,如 可以被i = 1011包含的数有 j = 0001, 0010, 0011, 1000, 1001,那么很明显i的状态肯定是由j推出来的,可以得到 dp[i] = min( dp[j_0] +dp[j_1] +....),其中所有j加起来等于i。由于我们是从 0 到 i 开始枚举,那么被i包含的所有状态的dp[j]都已经得到答案,并且由于这些状态有互相包含的关系,因此我们只需要枚举出一个数j∈i来让dp[i] = min(dp[j]+dp[i-j])即可。
- 为什么?如果j, k ∈ i,并且j & k = 0,那么一定有(j + k) ∈ i。假设dp[i] = dp[j] + dp[k] + dp[i - j - k]、此时j、k使得dp[i]成为最小值,此时一定有j & k = 0,那么也可以让dp[i] = dp[j + k] + dp[i - (j + k)] 使得dp[i]成为最小值。也就是说,如果状态i的答案由多个子状态相加转移过来的,那么这些子状态可以互相相加形成一个更大的子状态(因为子状态一定小于i,我们是从1到i开始枚举的,那么这个更大的子状态的答案一定是确定的),最终状态i的值是由其中两个子状态相加枚举出来的。
- 另一个难题就是,怎么找出 j ∈ i,根据上述的定义我们可以知道,j转化为二进制后,所对应为1的位上 i 也必须为1。我们可以写一个真值表,把所有状态枚举出来,令合法的状态为0,不合法的状态为1,那么j ∈ i 就等价于 ~( i → j ),也就是 ~( i → j ) == 0 为合法,等价于 (j & ~i) == 0 为合法。实际上,这个也可以等价于 (i & j) == j为合法,(i - j) == (i ^ j)为合法(^为异或),具体为什么可以自己想一下。
- 进一步优化:
- 跳位:当第一次枚举到 j ∉ i ( ~i & j != 0)的时候,也就是j存在某一位为1 i为0的情况时,根据二进制+1只会导致一个0变成1的定律可以知道这一位的后面一定都为0,也就是这一位是lowbit。举个例子,二进制 11011 中,如果枚举到第一个j ∉ i的时候j = 00100,那么我们可以不再枚举后面的 00101、00110、00111,而是把这一位跳过(j += lowbit(j)),让 j = 01000继续判断、枚举。同理,下次再枚举到j ∉ i的时 j = 01100,那么可以直接把这一位跳过(j+=lowbit(j)),让j = 10000继续枚举。
- 折半:可知状态是成对出现的,所以只需要枚举到 (i / 2)即可,也就是判断条件为 j <= (i / 2)
- 时间复杂程度:由于跳位,所以每个状态的枚举子状态的个数只与其1的个数有关。假设一共n个点,第ik个状态1的个数为k个,那么对于n来说1的个数为k个一共有Cnk种情况。对于每一种情况,我们都需要分别枚举出其子状态,也就是枚举点的个数为(1~(k - 1))的状态,一共有(Ck1+Ck2+Ck3+... ) = (2k - 2) 个状态。考虑折半,所以对于n个点来说一共要计算
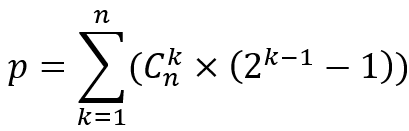 次。
次。
- 根据公式可以打印出以下的表,根据表可以得知p≈3n / 2(顺序分别为点的个数n、计算次数p、p*2、3n):
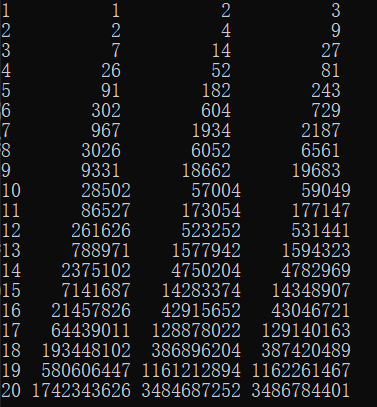
- 对于百万级计算机,20个点要计算大约29分钟,对于亿级计算机,20个点大约要计算17s
- 根据公式可以打印出以下的表,根据表可以得知p≈3n / 2(顺序分别为点的个数n、计算次数p、p*2、3n):
cpp代码及使用事项:
- 使用方法:先输入个数n,再输入半径r,然后输入n个点的坐标
- 输出情况:第一行为需要的圆的个数,从第二行开始往下都是圆心的坐标(注意坐标只是一种有效坐标,可以多种)
- 家用计算机一般都是亿级计算机,所以20个点基本15s左右可以计算出来。但是对于机房来说,有可能非常快也可能非常慢,取决于计算机配置
- 请使用cmake编译,gcc/g++可能无法编译
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <algorithm> 3 #include <vector> 4 #include <cmath> 5 6 #define cout std::cout 7 #define cin std::cin 8 #define endl std::endl 9 10 struct point { // 点 11 double x,y; 12 13 point():x(0.0),y(0.0) {} 14 point(double x, double y): x(x),y(y) {} 15 16 point operator + (const point &p) const { // (x1+x2), (y1+y2) 17 return {this->x + p.x, this->y + p.y}; 18 } 19 point operator - (const point &p) const { // (x1-x2), (y1-y2) 20 return {this->x - p.x, this->y - p.y}; 21 } 22 point operator / (const double &number) const { // (x / n), (y / n) 23 return {this->x / number, this->y / number}; 24 } 25 double distance (const point &p) const { // sq_distance = ((x1 - x2)^2 + (y1 - y2)^2) = distance^2 26 return (this->x - p.x) * (this->x - p.x) + (this->y - p.y) * (this->y - p.y); 27 } 28 point circumcenter (const point &p1, const point &p2) const { // The center of the circumscribed circle of three points 29 double x1 = this->x, x2 = p1.x, x3 = p2.x; 30 double y1 = this->y, y2 = p1.y, y3 = p2.y; 31 if ( (y2 - y1) * (x3 - x1) == (x2 - x1) * (y3 - y1)) { 32 double d1 = this->distance(p1); // this and p1 33 double d2 = this->distance(p2); // this and p2 34 double d3 = p1.distance(p2); // p1 and p3 35 if (d1 > d2 && d1 > d3) { 36 return (*this + p1) / 2.0; 37 } else if (d2 > d3) { 38 return (*this + p2) / 2.0; 39 } else { 40 return (p1 + p2) / 2.0; 41 } 42 } 43 double new_x = ((y2-y1)*(y3*y3-y1*y1+x3*x3-x1*x1)-(y3-y1)*(y2*y2-y1*y1+x2*x2-x1*x1)) / (2.0*((x3-x1)*(y2-y1)-(x2-x1)*(y3-y1))); 44 double new_y = ((x2-x1)*(x3*x3-x1*x1+y3*y3-y1*y1)-(x3-x1)*(x2*x2-x1*x1+y2*y2-y1*y1)) / (2.0*((y3-y1)*(x2-x1)-(y2-y1)*(x3-x1))); 45 return {new_x, new_y}; 46 } 47 }; 48 struct circle { // 最小覆盖圆数据结构 49 point center; 50 double radius; 51 std::vector< point > all_points; 52 53 circle (): center(point()), radius(0.0) {} 54 55 bool inside_point (const point &p) const { // if distance <= radius, return true; 56 return p.distance(this->center) <= this->radius; 57 } 58 59 void push_point (const point &p) { 60 this->all_points.push_back(p); 61 62 if(this->inside_point(p)) return; 63 64 this->center = p; 65 this->radius = 0.0; 66 67 for (auto i = 0; i < this->all_points.size() - 1; i++) { 68 if( this->inside_point(this->all_points[i]) ) continue; 69 70 this->center = (p + this->all_points[i]) / 2.0; 71 this->radius = p.distance(this->center); 72 73 for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) { 74 if(this->inside_point(this->all_points[j])) continue; 75 76 this->center = p.circumcenter(this->all_points[i], this->all_points[j]); 77 this->radius = p.distance(this->center); 78 } 79 } 80 } 81 }; 82 std::vector <circle> qwq[1 << 21]; 83 void initialization (int state, circle cir, int n, int max_n, point data[], double r, short dp[]) { // dp初始化 84 if (n == max_n) return; 85 circle copy_cir = cir; 86 cir.push_point(data[n]); 87 if (cir.radius <= r) { 88 int new_state = state + (1 << n); 89 dp[new_state] = 1; 90 qwq[new_state].clear(); 91 qwq[new_state].push_back(cir); 92 initialization(new_state, cir, n + 1, max_n, data, r, dp); 93 } 94 initialization(state, copy_cir, n + 1, max_n, data, r, dp); 95 } 96 void workDp (int max_n, short dp[]) { // dp 97 for (int i = 3; i <= max_n; i++) { 98 if(dp[i]) continue; 99 int tem = 0; 100 dp[i] = 20; 101 for (int j = 1; j <= (i >> 1);) { 102 if ( (~i & j) ) { // 不符合条件 103 j += ((-j) & j); // += lowbit(j) 104 continue; 105 } 106 if (dp[i] > dp[j] + dp[i - j]) { 107 tem = j; 108 dp[i] = dp[j] + dp[i - j]; 109 } 110 j++; 111 } 112 qwq[i].clear(); // 圆心坐标初始化 113 for (const auto& k : qwq[tem]) { 114 qwq[i].push_back(k); 115 } 116 for (const auto& k : qwq[i - tem]) { 117 qwq[i].push_back(k); 118 } 119 } 120 } 121 short dp[1 << 21]; 122 int main() { 123 int n; 124 double r; 125 cin >> n >> r; 126 const int numberOfCircles = 1 << n; 127 point data[21]; 128 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { 129 cin >> data[i].x >> data[i].y; 130 } 131 initialization(0, circle(), 0, n, data, r * r, dp); 132 workDp(numberOfCircles - 1, dp); 133 cout << dp[numberOfCircles - 1] << endl; 134 for (const auto& k : qwq[numberOfCircles - 1]) { 135 cout << k.center.x << " " << k.center.y << endl; 136 } 137 return 0; 138 }
思路二:暴力枚举 + 最小集合覆盖问题 (Set Cover) (转化到了另一个NP-hard问题)
- 暴力枚举两个点,求出半径为r、圆弧上有这两个点的圆,将每个圆的覆盖的点记录其中,表示一个点的集合(复杂程度为O(n*(n2)) = O(n3))
- 利用最小集合覆盖解决,是一个NP-hard的问题
由于集合覆盖问题比较困难,这里不再过多展开
思路三:覆盖最大点数圆 (Unit disk cover 详细算法(思路二))(贪心思想,有错误情况,也就是近似算法)(时间复杂程度:O(n3logn))
-
思路总线:利用单位圆覆盖最大点数来创建半径为r的圆,每次创建一个圆则将覆盖点记录,并标记为“已覆盖”,直到所有圆都覆盖(总时间复杂程度O(n*n2logn) = O(n3logn))
- 单位圆覆盖最大点数思路:(该算法详细流程:链接(思路二))把每个点都当成圆心,使每一个圆半径为r。枚举这些圆覆盖区域最多的一块,这一块区域的任意一点为圆心半径r的圆都是覆盖最多点数的圆。基本思想就是扫描线,扫描每个区域的初始和结束的区域来判断覆盖点的个数。
- 算法流程:
- 1 将所有的点初始化为“未标记”
- 2 在目前没有被标记“已覆盖”的点中,以每个点为圆心建立一个半径为r的圆,初始化一个数组用来记录覆盖区域的初始和结束点。
- 3 将自己的区域置为覆盖区域(极角为-2π和2π),再求出每个圆与其他圆的覆盖区域(也就是两个交点和圆心的向量为初始和结束点)。如果从极角小的开始扫描,那么很明显极角小的线为区域的起始线,极角大的为结束线,要记录这个线是起始线还是结束线。
- 4 根据极角进行升序排序(O(nlogn)),扫描线从最小的角开始扫描,进入区域(起始线)就将当前覆盖的点数+1,退出区域(结束线)就-1。取这个过程中的覆盖点数最大值时的交点坐标,表示可以最大覆盖点数圆的坐标之一(实际上覆盖最多的区域内的任意一点都可以为圆心,取此时的交点更方便,但是要注意精度判0) (由于每枚举第一个圆都要排序一次,所以寻找覆盖最多点数的圆的复杂程度为O(n2logn))
- 5 将覆盖点数最大的圆所覆盖的所有点标记
- 6 判断是否所有点的已标记,如果没有则返回2 (该部分时间复杂程度为O(n * n2logn))
- 7 最终结果为2操作的次数。
错误的情况也很好想,假设半径长度为0.5,有四个点A(0,0),B(1,0),C(2,0),D(3,0),很明显应该A、B组成一个圆,C、D组成一个圆,答案为2。但是如果第一次形成的圆为B和C,那么很明显会导致错误答案3。这种情况一般点的个数越少、点的排序越整齐、圆的直径长度越接近两个点的直线距离越容易出现。
怎么避免? 最简单的思路就是打乱数组跑多次。假设一个计算机是1s跑百万次,由于时间复杂程度是O(n3logn),那么可以根据n来判断出跑多少次,很明显公式 k = 106 / n3logn
注意n <= 3的时候只需要跑一次就可以了,也就是n <= 3的时候结果一定与输入的顺序无关了,至于为什么?从n=3举例,首先无论怎么打乱,最大覆盖数都是固定的,假如跑出来最大覆盖数为3,那么答案就是1;假如覆盖数为2,那么答案就是2;假如覆盖数为1,那么答案就是3,无论枚举哪一种情况答案都是固定的。但是如果n = 4,跑出来的最大覆盖数为2,那么就无法准确判断出答案了,正如上面所描述的。
cpp代码:
食用方法类似于思路一,唯一区别就是不输出圆心坐标(如果想要输出坐标也可以,只需要让函数输出一个pair类型即可。注意输出坐标只是一种有效坐标):
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <algorithm> 3 #include <vector> 4 #include <utility> 5 #include <cmath> 6 7 #define cout std::cout 8 #define cin std::cin 9 #define endl std::endl 10 #define string std::string 11 12 const double eps = 1e-8; 13 const double pi = acos(-1.0); 14 const int max_number = 501; 15 16 int cmpDouble (double x) { 17 if (fabs(x) <= eps) return 0; 18 return x < 0 ? -1 : 1; 19 } 20 21 struct Point { 22 double x, y; 23 Point () : x(0.0), y(0.0) {} 24 Point (double x, double y) : x(x), y(y){} 25 26 Point operator + (const Point& p) const { 27 return {x + p.x, y + p.y}; 28 } 29 Point operator - (const Point& p) const { 30 return {x - p.x, y - p.y}; 31 } 32 Point operator * (const double& n) const { 33 return {x * n, y * n}; 34 } 35 Point operator / (const double& n) const { 36 return {x / n, y / n}; 37 } 38 double operator * (const Point& p) const { // dot product 39 return x * p.x + y * p.y; 40 } 41 double operator ^ (const Point& p) const { // cross product 42 return x * p.y - p.x * y; 43 } 44 bool operator == (const Point& p) const { 45 return (cmpDouble(x - p.x) == 0 && cmpDouble(y - p.y) == 0); 46 } 47 double distance (const Point& p) const { // sqrt( (x2 - x1)^2 + (y2 - y1)^2 ) 48 return sqrt( (x - p.x) * (x - p.x) + (y - p.y) * (y - p.y) ); 49 } 50 double angle () const { 51 return atan2(y, x); 52 } 53 Point transfer (const double& angle, const double& dist) const { 54 return {x + dist * cos(angle), y + dist * sin(angle)}; 55 } 56 }; 57 typedef Point Vector; 58 struct Circle { 59 Point center; 60 double radius; 61 Circle () : center(Point()), radius(0.0) {} 62 Circle (Point c, double r) : center(c), radius(r) {} 63 64 bool operator == (const Circle& c) const { 65 return center == c.center && cmpDouble(radius - c.radius) == 0; 66 } 67 bool apart (const Circle& c) const { 68 return cmpDouble(center.distance(c.center) - (radius + c.radius)) > 0; 69 } 70 bool contain (const Point& p) const { 71 return cmpDouble(radius - p.distance(center)) >= 0; 72 } 73 }; 74 struct Scanline { 75 Point intersection; 76 double polarAngle; 77 int value; 78 Scanline () : intersection(Point()), polarAngle(0.0), value(0) {} 79 bool operator < (const Scanline& l) const { // The smaller angle or greater value comes first 80 if (cmpDouble(polarAngle - l.polarAngle) != 0) return polarAngle < l.polarAngle; 81 return value > l.value; 82 } 83 }; 84 class numberOfMinCircle { 85 private: 86 static std::pair < Scanline, Scanline > getScanline (const Circle& a, const Circle& b) { 87 Scanline inLine, outLine; 88 inLine.value = 1, outLine.value = -1; 89 if (a == b) { // Initialization of the same circle 90 inLine.polarAngle = -2 * pi; 91 inLine.intersection = a.center; 92 outLine.polarAngle = 2 * pi; 93 outLine.intersection = a.center; 94 } else { // two intersections 95 Vector AB = b.center - a.center; 96 double dist = a.center.distance((b.center)); 97 double r = a.radius; 98 double angleAB = AB.angle(); 99 double angleAI = acos( dist / (2 * r) ); 100 101 inLine.polarAngle = angleAB - angleAI; 102 inLine.intersection = a.center.transfer(inLine.polarAngle, r); 103 104 outLine.polarAngle = angleAB + angleAI; 105 outLine.intersection = a.center.transfer(outLine.polarAngle, r); 106 } 107 return std::make_pair(inLine, outLine); 108 } 109 static Circle getMostNumberCircle (const std::vector <Point>& p, const double r) { 110 int ans = 0; 111 Circle ansCircle; 112 ansCircle.radius = r; 113 for (auto i : p) { 114 int temNumber = 0; 115 Circle circleI = Circle(i, r); 116 std::vector <Scanline> lines; 117 118 for (auto j : p) { 119 Circle circleJ = Circle(j, r); 120 if ( circleI.apart(circleJ) ) continue; // Two circles apart 121 std::pair <Scanline, Scanline> pairLine = getScanline(circleI, circleJ); 122 lines.push_back(pairLine.first); 123 lines.push_back(pairLine.second); 124 } 125 if (lines.size() / 2 < ans) continue; // prune 126 std::sort(lines.begin(), lines.end()); 127 for (auto k : lines) { 128 temNumber += k.value; 129 if (temNumber > ans) { 130 ans = temNumber; 131 ansCircle.center = k.intersection; 132 } 133 } 134 } 135 return ansCircle; 136 } 137 static int getNumberOfCircle (std::vector <Point> p, const double r) { 138 int ans = 0; 139 while (!p.empty()) { 140 Circle temCircle = getMostNumberCircle(p, r); 141 for (auto i = p.begin(); i != p.end();) { 142 if (temCircle.contain(*i)) { 143 p.erase(i); 144 continue; 145 } 146 i++; 147 } 148 ans++; 149 } 150 return ans; 151 } 152 public: 153 static int solve (std::vector <Point>& p, const double r) { 154 int len = (int) p.size(); 155 int ans = max_number; 156 int numberOfWork = (int) floor( 1e7 / ( len * len * len * log(len) ) ); 157 while (numberOfWork--) { 158 std::random_shuffle(p.begin(), p.end()); 159 int tem = getNumberOfCircle(p, r); 160 ans = std::min(ans, tem); 161 } 162 return ans; 163 } 164 }; 165 166 int main() { 167 int n; 168 double r; 169 Point p; 170 std::vector< Point > points; 171 cin >> n >> r; 172 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { 173 cin >> p.x >> p.y; 174 points.push_back(p); 175 } 176 cout << numberOfMinCircle:: solve(points, r); 177 return 0; 178 }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号