可持续的通用分割管线
Towards Continual Universal Segmentation --CVPR2025
CUE --- Continual Universal sEgmentation pipeline 可持续的通用分割管线
not only inherently tackles the stability-plasticity dilemma, but unifies any segmentation across tasks and models as well.
"stability-plasticity dilemma"(稳定性-可塑性困境),描述模型在保持已有知识稳定性和适应新知识可塑性之间的矛盾关系
Our key insight: any segmentation task can be reformulated as an understanding-then-refinement paradigm, which is inspired by humans’ visual perception system to first perform high-level semantic understanding, then focus on low-level vision cues。
"understanding-then-refinement paradigm" 理解-然后改进的范式
受人类视觉感知系统的启发,首先进行高层次的语义理解,然后专注于低层次的视觉线索。
We claim three desiderata for this design: Continuity by inherently avoiding the stability-plasticity dilemma via exploiting the natural differences between high-level and low-level knowledge. Generality by unifying and simplifying the landscape towards various segmentation tasks. Efficiency as an interesting by-product by significantly reducing the research effort. Our resulting model, built upon this pipeline by complementary expert models, shows significant improvements over previous state-of-the-arts across various segmentation tasks and datasets. We believe that our work is a significant step towards making continual segmentation more universal and practicable
我们为该设计提出了三大核心诉求: 可持续性;通用性;高效性
通过利用高层次与低层次知识的天然差异,从根本上规避稳定性-可塑性困境,实现设计的连续性;// 为什么利用高低层次知识的差异就能够规避困境?
通过整合简化知识图谱,提升各类分割任务的通用性;
通过显著降低研究成本,将效率作为重要副产品实现。
基于这一框架构建的互补型专家模型,在各类分割任务和数据集上均展现出显著优于现有前沿成果的性能。我们相信,这项研究为实现持续性分割技术的普适化与实用化迈出了关键一步。
Deep neural networks have shown great success in various computer vision tasks [23, 37, 48]. Conventionally, they are trained in a single-shot manner without considering further updates. As a result, they may lack the flexibility to handle situations that evolve over time. Typical solutions include either re-training the networks with both previous and new data or fine-tuning the networks solely on new data. Nevertheless, the former is computationally intensive, while the latter poses a great challenge of preserving previous knowledge and is known as the catastrophic forgetting [36].
"catastrophic forgetting"- 灾难性遗忘是机器学习领域的专业术语,指神经网络在学习新任务时丧失先前学到的知识这一现象
Recently, various approaches have been proposed for continual classification [17, 28, 39, 57, 60, 61, 72]. A few attempts extend their successes to the field of continual semantic segmentation [6, 8, 18, 53, 67, 69]. Typically, a cross-entropy loss is applied to handle new knowledge together with a regularization like knowledge distillation (KD) [27] to preserve old knowledge. How to carefully balance between stability (i.e., preserve previous states) and plasticity (i.e., incorporate new knowledge) becomes the main stream of current research.
通常采用交叉熵损失函数处理新知识,同时结合知识蒸馏(KD)[27]等正则化技术来保留原有知识。如何在稳定性(即保持先前状态)与可塑性(即整合新知识)之间取得平衡,已成为当前研究的主流方向。
Though groundbreaking, the stability-plasticity dilemma still poses a great challenge in segmentation tasks. To get a clearer understanding of why this dilemma happens, we start by examining how forgetting impacts the network in continual updates.
For the first time, we reveal that the high-level knowledge (i.e., semantic understanding) and the This CVPR paper is the Open Access version, provided by the Computer Vision Foundation. Except for this watermark, it is identical to the accepted version; the final published version of the proceedings is available on IEEE Xplore. low-level knowledge (i.e., boundary prediction) show distinctive sensitivity to forgetting. Specifically, we observe that the network preserves a holistic semantic understanding across steps by correctly identifying objects in a given scene while failing to predict faithful boundaries. This inherent difference reveals a crucial reason why stability and plasticity cannot be simultaneously achieved by previous arts: A regularization that enforces enough stability for low-level knowledge could be too restrictive for high-level knowledge, excessively sacrificing its plasticity; while a proper constraint for high-level knowledge could be too flexible to effectively preserve low-level knowledge.
本研究首次揭示:高层次知识(即语义理解)与低层次知识(即边界预测)对遗忘表现出显著差异。具体而言,网络在跨步骤保持整体语义理解方面表现优异——能准确识别场景中的物体,却难以忠实地预测边界。这种本质差异揭示了传统方法难以同时兼顾稳定性和可塑性的关键原因:若对低层次知识施加足够稳定性的约束,可能过度限制其可塑性;而对高层次知识施加适当约束时,又可能过于宽松导致无法有效保留底层知识。
Based on this understanding and motivated by humans’ visual perception system [9]. For the first time, we propose to decouple high-level and low-level knowledge by reformulating segmentation tasks into an understanding-thenrefinement pipeline. In this pipeline, the model first focuses on high-level semantic understanding by identifying ”what” and ”where” of objects in a scene, then grounds them to low-level vision cues for final predictions. By this design, we can achieve better Continuity by simultaneously attending to both plasticity and stability instead of naively balancing between each other. This is achieved by applying suitable constraints for high-level and low-level knowledge, respectively. On top of that, it simplifies the landscape of Generality by unifying any image segmentation task into a bio-inspired pipeline. This spans across semantic, instance and panoptic segmentation, as well as complex ones like language-guided segmentation and beyond, greatly promoting the reusability and transferability of techniques under the same pipeline. Notably as a by-product, it brings better Efficiency by utilizing the fast convergence speed of high-level knowledge (Sec. 3.3 and Fig. 2c) to significantly reduce the computational cost. This benefit helps to pave the way towards scaling to larger networks and datasets. Our resulting model follows this novel pipeline and leverages complementary expert models to handle semantic understanding and visual refinement.
基于这一认知,并受人类视觉感知系统[9]的启发,我们首次提出通过将分割任务重构为理解-精炼流程来解耦高层与低层知识。该流程中,模型首先专注于高层次语义理解,通过识别场景中物体的“是什么”和“在哪里”,再将其与低层视觉线索相结合进行最终预测。这种设计通过同时关注可塑性与稳定性而非简单权衡二者,实现了更好的连续性。这是通过为高层与低层知识分别施加适当约束实现的。此外,该方法通过将任何图像分割任务统一到生物启发式流程中,简化了通用性架构。这一框架覆盖语义分割、实例分割、全景分割以及语言引导分割等复杂场景,极大提升了同一流程下技术的复用性和迁移性。值得注意的是,作为副产品,该方法利用高层知识的快速收敛特性(第3.3节及图2c)显著降低计算成本,从而提高效率。这一优势为扩展至更大规模网络和数据集铺平了道路。我们最终构建的模型遵循这一创新流程,并通过互补专家模型处理语义理解与视觉精炼。
As an interesting by-product, we point out that this design helps in Efficiency by utilizing the fast convergence speed of high-level knowledge.
一个有趣的副产品是,我们指出,这种设计通过利用高层次知识的快速收敛速度来提高效率。
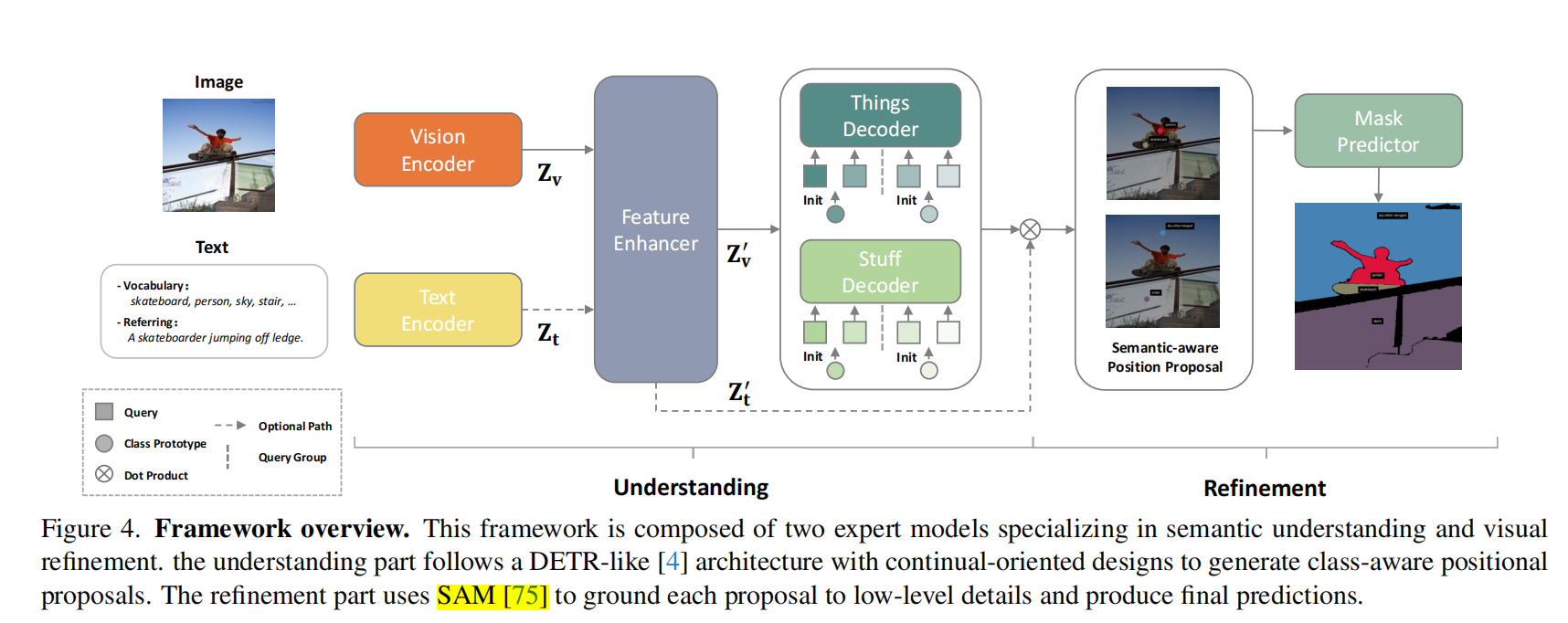
本节将基于图4所示的创新流程框架进行阐述。
首先介绍语义理解模块,该模块采用类似DETR[4]的设计架构(第4.1至4.3节)。
为实现持续更新,我们将其与物体与内容分离处理技术(第4.2节)、
语义感知查询初始化及分组匹配算法(第4.3节)相结合。
随后阐述视觉优化模块,通过融合图像特征与底层视觉线索生成最终预测结果(第4.4节)。
最后讨论该框架如何实现持续更新(第4.5节)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号