dplyr 常用函数 [介绍篇]
常用的5个函数
mutate() adds new variables that are functions of existing variables 根据已有变量添加新变量
select() picks variables based on their names. 根据变量名提取变量
filter() picks cases based on their values. 根据变量的值提取
summarise() reduces multiple values down to a single summary. 精简多个变量到单个的总结
arrange() changes the ordering of the rows. 改变行的顺序
以上函数都可结合group_by,允许分组操作。更多的学习日志可通过vignette("dplyr")查看。除了这些单张表外,dplyr 还可执行双表操作,可通过bignette("two-table")进一步查看。
dplyr是根据数据的存储特性的来设计的,这意味着在操作本地数据框的同时,你还可以通过额外的R带代码操作远程的数据表格。安装dbplyr包后,阅读vignette("databases", package = "dbplyr")。
如果是新接触dplyr,最好从《R for data science》的 data import chapter开始。
安装
# 获得dplyr的最简单途径是安装整个tidyverse:
install.packages("tidyverse")
# 也可直接安装dplyr:
install.packages("dplyr")
开发者版本
为了使用bug及时修复,或者使用开发版本的特征,可以从GitHub安装dplyr。
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("tidyverse/dplyr")
备忘单
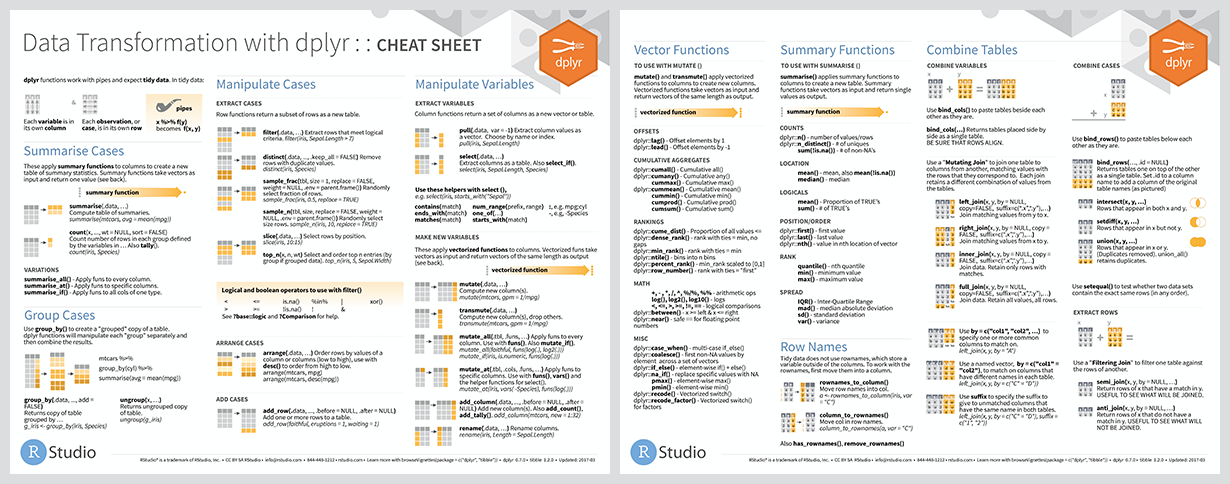
使用方法
library(dplyr)
starwars %>%
filter(species == "Droid")
#> # A tibble: 5 x 13
#> name height mass hair_color skin_color eye_color birth_year gender
#> <chr> <int> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr>
#> 1 C-3PO 167 75 <NA> gold yellow 112 <NA>
#> 2 R2-D2 96 32 <NA> white, bl… red 33 <NA>
#> 3 R5-D4 97 32 <NA> white, red red NA <NA>
#> 4 IG-88 200 140 none metal red 15 none
#> 5 BB8 NA NA none none black NA none
#> # … with 5 more variables: homeworld <chr>, species <chr>, films <list>,
#> # vehicles <list>, starships <list>
starwars %>%
select(name, ends_with("color"))
#> # A tibble: 87 x 4
#> name hair_color skin_color eye_color
#> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 Luke Skywalker blond fair blue
#> 2 C-3PO <NA> gold yellow
#> 3 R2-D2 <NA> white, blue red
#> 4 Darth Vader none white yellow
#> 5 Leia Organa brown light brown
#> # … with 82 more rows
starwars %>%
mutate(name, bmi = mass / ((height / 100) ^ 2)) %>%
select(name:mass, bmi)
#> # A tibble: 87 x 4
#> name height mass bmi
#> <chr> <int> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 Luke Skywalker 172 77 26.0
#> 2 C-3PO 167 75 26.9
#> 3 R2-D2 96 32 34.7
#> 4 Darth Vader 202 136 33.3
#> 5 Leia Organa 150 49 21.8
#> # … with 82 more rows
starwars %>%
arrange(desc(mass))
#> # A tibble: 87 x 13
#> name height mass hair_color skin_color eye_color birth_year gender
#> <chr> <int> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr>
#> 1 Jabb… 175 1358 <NA> green-tan… orange 600 herma…
#> 2 Grie… 216 159 none brown, wh… green, y… NA male
#> 3 IG-88 200 140 none metal red 15 none
#> 4 Dart… 202 136 none white yellow 41.9 male
#> 5 Tarf… 234 136 brown brown blue NA male
#> # … with 82 more rows, and 5 more variables: homeworld <chr>,
#> # species <chr>, films <list>, vehicles <list>, starships <list>
starwars %>%
group_by(species) %>%
summarise(
n = n(),
mass = mean(mass, na.rm = TRUE)
) %>%
filter(n > 1,
mass > 50)
#> # A tibble: 8 x 3
#> species n mass
#> <chr> <int> <dbl>
#> 1 Droid 5 69.8
#> 2 Gungan 3 74
#> 3 Human 35 82.8
#> 4 Kaminoan 2 88
#> 5 Mirialan 2 53.1
#> # … with 3 more rows
获取帮助
如果很明确的遇到bug,去github上反馈。如果要提问或者套路,可通过rstudio社区或者邮箱




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号