动手动脑01(续)
动手动脑01(续)
字符串加法
源码
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int X=100;
int Y=200;
System.out.println("X+Y="+X+Y);
System.out.println(X+Y+"=X+Y");
}
}
运行结果

结果分析
由于加法从左向右计算,第一行先计算为字符串加法,即将整数拼接到字段串上.第二行为先进行整数加法,然后进行拼接操作
出30道题
源代码
import java.util.Random;
public class AskQuestion {
final int NUMBER_OF_QUESTIONS=30;
boolean [][][]st=new boolean[501][501][4];
Random r=new Random();
String operation="+-*/";
public AskQuestion(){
int cnt=0;
while(cnt<NUMBER_OF_QUESTIONS){
int a=r.nextInt(500);
int b=r.nextInt(500)+1;
int o=r.nextInt(4);
char operat=operation.charAt(o);
if(st[a][b][o])continue;
st[a][b][o]=true;
System.out.println(a+" "+operat+" "+b+" "+"= ");
cnt++;
}
}
}
源码分析
(1)使用NUMBER_OF_QUESTIONS,来设定题目的数量,便于以后的维护
(2)是用三维的boolean数组来记录每一种可能出现的题目的状态,为false,为没出过,true为已经出过,第一维度表示第一个数,第二维度表示第二个数,第三维度表示加减乘除.这样做在空间上上复杂度提高很多,但是时间上会快很多,如果可以我想用hash表,这样可以大大降低空间复杂度,但是本人不会手搓hash,java又没有stl.
(3)在构造函数中出题,在测试类中直接创建变量就可以出题了,也可以给函数写成成静态函数,让这个类变成一个工具类.
结果展示
一共三十道题目而且没有重复

获取验证码
源码展示
import javax.sound.midi.Soundbank;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.util.Random;
public class Password extends JFrame implements KeyListener , ActionListener
{
Random r=new Random();
String s=new String();
JButton logIn=new JButton("登录");
JTextField registerText=new JTextField();
JButton res=new JButton();
Password(){
//初始化界面
initJFrame();
//初始化图像
initView();
//让当前界面显示出来
this.setVisible(true);
}
public void initJFrame() {
this.setSize(488, 430);//设置宽高
this.setTitle("拼图游戏 V1.0登录");//设置标题
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(3);//设置关闭模式
this.setLocationRelativeTo(null);//居中
this.setAlwaysOnTop(true);//置顶
this.setLayout(null);//取消内部默认布局
}
public void initView(){
//用户名
JLabel userNametext=new JLabel("用户名");
userNametext.setBounds(116, 135, 47, 17);
this.getContentPane().add(userNametext);
//定义密码
JLabel password=new JLabel("密码");
password.setBounds(116,185,47,17);
this.getContentPane().add(password);
//添加验证码
JLabel register=new JLabel("验证码");
register.setBounds(116,225,47,17);
this.getContentPane().add(register);
//输入框
//用户
JTextField userName=new JTextField();
userName.setBounds(166,135,100,17);
this.getContentPane().add(userName);
//密码
JTextField passwordText=new JTextField();
passwordText.setBounds(166,185,100,17);
this.getContentPane().add(passwordText);
//验证码
registerText.setBounds(166,225,60,17);
this.getContentPane().add(registerText);
//验证码提示
s=getRegister();
res=new JButton(s);
// JLabel res=new JLabel(s);
res.setBounds(236,225,80,20);
res.addActionListener(this);
this.getContentPane().add(res);
//登录
logIn.setBounds(175,260,60,20);
logIn.addKeyListener(this);
logIn.addActionListener(this);
this.getContentPane().add(logIn);
}
String getRegister(){
char []A=new char[4];
for(int i=0;i<4;i++ ){
int t=r.nextInt(62);
if(t<26)
A[i]=(char)(t+'a');
else if(t<52)A[i]=(char)(t+'A'-26);
else A[i]=(char)(t+'0'-52);
}
String se=new String(A);
return se;
}
@Override
public void keyTyped(KeyEvent e) {
System.out.println(registerText.getText());
System.out.println(s);
}
@Override
public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e) {
System.out.println(registerText.getText());
System.out.println(s);
}
@Override
public void keyReleased(KeyEvent e) {
System.out.println(registerText.getText());
System.out.println(s);
Object object=e.getSource();
if(object==logIn){
if(s.equals(registerText.getText()))
System.out.println("登录成功");
}
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
Object object=e.getSource();
if(object==logIn){
System.out.println("heihie");
// System.out.println(registerText.getText());
// System.out.println(s);
String str=registerText.getText();
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println(s);
// System.out.println(str);
if(s.equals(str)){
String string="登陆成功";
creatJDialog(string);
System.out.println();
}
else {
String string="验证码错误";
creatJDialog(string);
}
}
if(object==res){
s=getRegister();
// initView();
res.setText(s);
System.out.println("bushigemen");
// res=new JButton(s);
}
}
private static void creatJDialog(String string) {
//创建一弹窗
JDialog jDialog=new JDialog();
//设置大小
jDialog.setSize(200,150);
//设置置顶
jDialog.setAlwaysOnTop(true);
//不关无法下面操作
jDialog.setModal(true);
//居中
jDialog.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
//添加文字
JLabel j=new JLabel(string);
j.setBounds(0, 0, 200, 150);
jDialog.getContentPane().add(j);
//可见
jDialog.setVisible(true);
}
}
代码分析
(1)做一个界面对我是一个庞大的问题我准备对他进行分析细化,然后逐个解决
a.我要用java的图形化界面使用JFrame来做框架,Jlabel来填充文字,用JBotton来做按钮,用JFieldText来作输入用的文本框
b.获取验证码封装成一个get方法.用字符串来作返回值
c.需要对各个按钮加上事件监听,需要实现接口ActionListener
(2)大体框架和问题梳理完成,在细节上
a.对与JFrame,要设置大小,是否可见,位置,关闭方式
b.Jbotton 设置监听,设置大小位置,设置在顶部,设置不关闭无法其他操作
c.写一个弹窗函数,来实现对各种情况的回应比如验证码错误等等
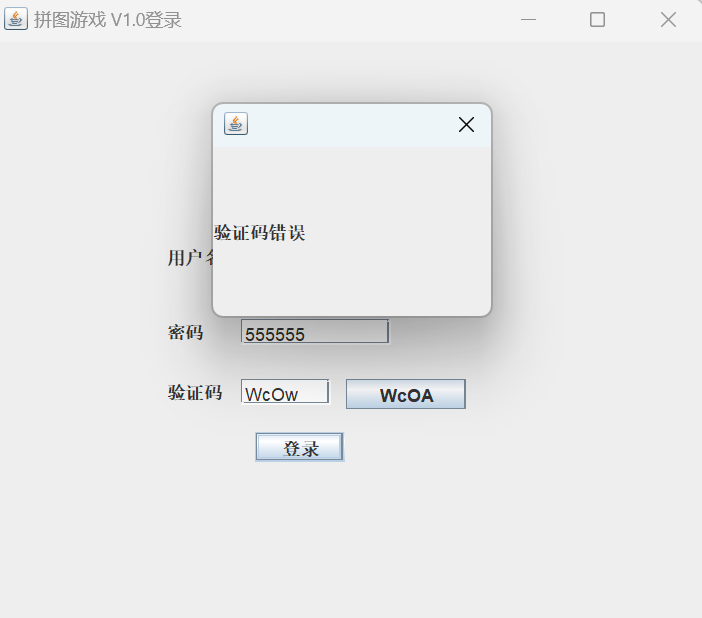
结果展示

点击按钮可以更新验证码

验证码正确显示登录成功

错误显示验证码错误



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号