PyTorch基础
红圈圈里的数据类型比较重要
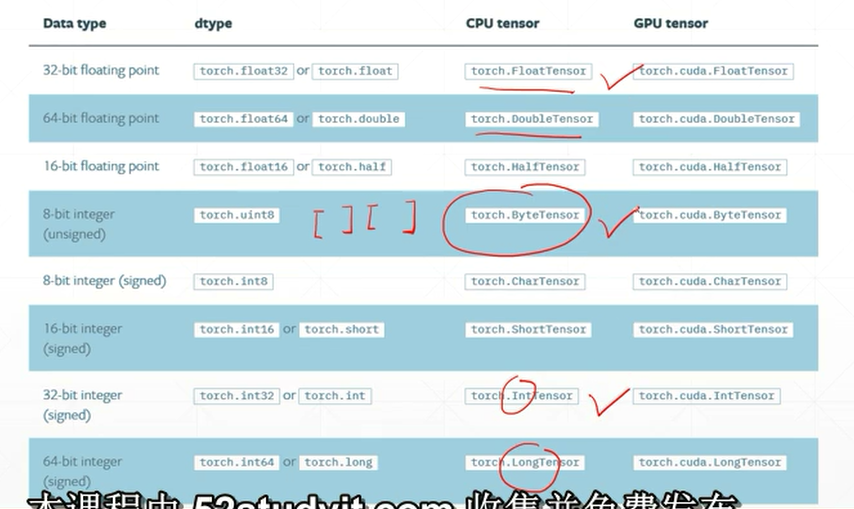
瞎贴一波:
一、数据类型
a = torch.randn(2,3) print(a) print(type(a)) print(isinstance(a, torch.FloatTensor))#合法化检验 print(isinstance(a, torch.cuda.FloatTensor))#合法化检验 a = a.cuda()#返回一个GPU上的引用 print(isinstance(a, torch.cuda.FloatTensor))#合法化检验 >>> tensor([[ 1.0300, -0.7234, -0.5679], [-0.7928, -0.2508, -0.9085]]) <class 'torch.Tensor'> True False True
torch.tensor(1.) >>>tensor(1.) torch.tensor(1.3) >>>tensor(1.3000) torch.tensor([1.]) #torch.tensor([1.]) >>>tensor([1.]) a = torch.tensor(2.2) a.shape >>>torch.Size([]) len(a.shape) >>>0 a.size() >>>torch.Size([]) torch.tensor([1.1]) >>>tensor([1.1000]) torch.tensor([1.1,2.2]) >>>tensor([1.1000, 2.2000]) torch.FloatTensor(1) >>>tensor([1.4574e-43]) torch.FloatTensor(2) >>>tensor([0., 0.]) data = np.ones(2) data >>>array([1., 1.]) torch.from_numpy(data) >>>tensor([1., 1.], dtype=torch.float64) a = torch.ones(2) a.shape >>>torch.Size([2])
a = torch.randn(2,3) a >>>tensor([[ 0.5736, 0.4078, -0.8879], [-0.0126, 0.4756, -0.0214]]) a.shape >>>torch.Size([2, 3]) a.size(0) >>>2 a.size(1) >>>3
a = torch.rand(2,1,4,4) a >>>tensor([[[[0.4224, 0.5601, 0.3603, 0.7440], [0.2749, 0.4182, 0.5837, 0.1956], [0.9536, 0.9231, 0.6720, 0.4501], [0.0255, 0.0731, 0.7247, 0.3907]]], [[[0.0651, 0.7923, 0.1018, 0.3250], [0.7650, 0.5583, 0.5320, 0.9807], [0.2130, 0.2525, 0.7932, 0.0258], [0.7981, 0.6380, 0.1390, 0.2147]]]]) a.numel() #元素个数 >>>32 a.dim() #维度 >>>4
二、创建Tensor
1.import from numpy,从numpy数据中载入
a = np.array([2,3.3]) torch.from_numpy(a) >>>tensor([2.0000, 3.3000], dtype=torch.float64) a = np.ones([2,3]) torch.from_numpy(a) >>>tensor([[1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1.]], dtype=torch.float64)
2.import from List,从列表类型数据中载入
torch.tensor([2., 3.2]) #直接接受数据,经常使用,注意是小写 >>>tensor([2.0000, 3.2000]) torch.FloatTensor(4,3)#设定维度,经常使用 >>>tensor([[0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0.]]) torch.FloatTensor([2.,3.2]) #不轻易用,容易和小写的tensor混淆 >>>tensor([2.0000, 3.2000]) torch.IntTensor(2,3) #未初始化,数据分布差异太大 >>>tensor([[0, 0, 1], [0, 1, 0]], dtype=torch.int32) torch.FloatTensor(2,3) #未初始化 >>>tensor([[7.4715e+37, 6.6001e-43, 8.4078e-45], [0.0000e+00, 1.4013e-45, 0.0000e+00]]) torch.tensor([1.2, 3]).type() >>>'torch.FloatTensor' #默认情况是FloatTensor torch.set_default_tensor_type(torch.DoubleTensor) #修改默认情况 torch.tensor([1.2, 3]).type() >>>'torch.DoubleTensor'
3. rand/rand_like,randint
torch.rand(3,3) #采样(0,1)之间的分布 >>>tensor([[0.2816, 0.4244, 0.1964], [0.5480, 0.6377, 0.2992], [0.4763, 0.4480, 0.1515]]) a = torch.rand(3,3) torch.rand_like(a)#读出a的维度后再送到函数里 >>>tensor([[0.4966, 0.2000, 0.9064], [0.8584, 0.1375, 0.7557], [0.2186, 0.9776, 0.8252]]) torch.randint(1,10,[3,3]) #(min,max,[size[0],size[1]]) >>>tensor([[2, 1, 7], [7, 7, 6], [8, 5, 3]]) ###正态分布的采样,均值为0,方差为1 torch.randn(3,3) >>>tensor([[-0.3037, 1.2203, -0.2857], [ 0.4289, 0.3293, 0.6834], [-0.5883, 0.6679, -0.1545]]) torch.normal(mean=torch.full([10],0), std=torch.arange(1, 0, -0.1)) >>>tensor([-0.1700, -1.2166, 0.0035, -0.4357, -0.0571, -0.9798, -0.1286, 0.1009, 0.2687, -0.1457]) torch.full([2,3],7) >>>'torch.DoubleTensor' #之前修改了默认数据类型 torch.full([],7) #表示生成标量 >>>'torch.DoubleTensor' torch.full([1],7) #生成维度为1的vector >>>tensor([7.]) torch.arange(0,10) >>>tensor([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]) torch.arange(0,10,2) >>>tensor([0, 2, 4, 6, 8]) torch.linspace(0,10,steps=4) >>>tensor([ 0.0000, 3.3333, 6.6667, 10.0000]) torch.linspace(0,10,steps=10) >>>tensor([ 0.0000, 1.1111, 2.2222, 3.3333, 4.4444, 5.5556, 6.6667, 7.7778, 8.8889, 10.0000]) torch.linspace(0,10,steps=11) >>>tensor([ 0., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., 7., 8., 9., 10.]) torch.logspace(0,-1,steps=10) #10^0,...,10^(-1) >>>tensor([1.0000, 0.7743, 0.5995, 0.4642, 0.3594, 0.2783, 0.2154, 0.1668, 0.1292, 0.1000]) torch.logspace(0,1,steps=10) #10^0,...,10^1 >>>tensor([ 1.0000, 1.2915, 1.6681, 2.1544, 2.7826, 3.5938, 4.6416, 5.9948, 7.7426, 10.0000]) torch.ones(3,3) >>>tensor([[1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1.]]) torch.zeros(3,3) >>>tensor([[0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0.]]) torch.eye(3,4) >>>tensor([[1., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 1., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 1., 0.]]) a = torch.zeros(3,3) torch.ones_like(a) #读取tensor维度再生成 >>>tensor([[1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1.]])
4. shuffle方法
a = torch.rand(2,3) b = torch.rand(2,2) a,b >>>(tensor([[0.3372, 0.5688, 0.9331], [0.6488, 0.4826, 0.6608]]), tensor([[0.4330, 0.8487], [0.0610, 0.5291]])) idx = torch.randperm(2) idx >>>tensor([1, 0]) #表示经过了一次shuffle,从0,1->1,0 a[idx] >>>tensor([[0.6488, 0.4826, 0.6608], [0.3372, 0.5688, 0.9331]]) b[idx] >>>tensor([[0.0610, 0.5291], [0.4330, 0.8487]])
三、索引与切片
1、给定索引号
a = torch.rand(4,3,28,28) a[0].shape #第0张图 >>>torch.Size([3, 28, 28]) a[0,0].shape #第0张图,第0个通道 >>>torch.Size([28, 28]) a[0,0,2,4] #第0张图,第0个通道,第2行第4列的像素点 >>>tensor(0.7300) a.shape >>>torch.Size([4, 3, 28, 28]) a[:2].shape #第0,1张图 >>>torch.Size([2, 3, 28, 28]) a[:2,:1,:,:].shape #第0,1张图的第1个通道上的数据 >>>torch.Size([2, 1, 28, 28]) a[:2,1:,:,:].shape #第0,1张图的(第一个通道,末尾通道)上的数据 >>>torch.Size([2, 2, 28, 28]) a[:2,-1:,:,:].shape #第0,1张图的末尾通道的数据 >>>torch.Size([2, 1, 28, 28]) a[:,:,0:28:2,0:28:2].shape #隔行采样 torch.Size([4, 3, 14, 14]) a[:,:,::2,::2].shape #同上 >>>torch.Size([4, 3, 14, 14])
2、具体索引
a.shape >>>torch.Size([4, 3, 28, 28]) a.index_select(0,torch.tensor([0,2])).shape #0表示对第一个维度,也就是图片张数进行操作,[0,2]表示第0和第2张图片 >>>torch.Size([2, 3, 28, 28]) a.index_select(1,torch.tensor([1,2])).shape #1表示对第二个维度,在通道数上,取第1和第2个通道,当然图片数就是全部了 >>>torch.Size([4, 2, 28, 28]) a.index_select(2, torch.arange(14)).shape >>>torch.Size([4, 3, 14, 28]) a[...].shape #表示所有维度都取 >>>torch.Size([4, 3, 28, 28]) a[0,...,::2].shape #第一个维度取0,中间一个维度全取(...表示任意多的维度),最后一个维度取步长为2 >>>torch.Size([3, 28, 14]) a[:,1,...].shape >>>torch.Size([4, 28, 28]) a[...,:2].shape >>>torch.Size([4, 3, 28, 2]) ###select by mask x = torch.randn(3, 4) x >>>tensor([[ 1.1194, -0.5518, -0.2115, -1.4508], [ 1.3920, 1.0053, -1.2985, -1.2529], [-1.0730, 1.4239, 0.1493, -0.2288]]) mask = x.ge(0.5) #把元素大于0.5的设为1,小于0.5为0 mask >>>tensor([[1, 0, 0, 0], [1, 1, 0, 0], [0, 1, 0, 0]], dtype=torch.uint8) torch.masked_select(x, mask) >>>tensor([1.1194, 1.3920, 1.0053, 1.4239]) torch.masked_select(x, mask).shape >>>torch.Size([4]) #select by flatten index src = torch.tensor([[4,3,5], [6,7,8]]) torch.take(src, torch.tensor([0,2,5])) >>>tensor([4, 5, 8])
三、维度变换
1、view/reshape
#view和reshape a = torch.rand(4,1,28,28) a.shape >>>torch.Size([4, 1, 28, 28]) a.view(4, 28*28) #把后面三个维度合并到一起,每张图片都用一个784维的向量表示 >>>tensor([[0.1820, 0.8625, 0.2687, ..., 0.2841, 0.4331, 0.6522], [0.4611, 0.7675, 0.7003, ..., 0.9976, 0.9174, 0.2024], [0.7160, 0.8296, 0.7346, ..., 0.6240, 0.6848, 0.3391], [0.3076, 0.6013, 0.2066, ..., 0.2345, 0.5690, 0.2885]]) a.view(4,28*28).shape >>>torch.Size([4, 784]) a.view(4*28,28).shape #所有照片的所有行都放到一个行向量中 >>>torch.Size([112, 28]) a.view(4*1, 28, 28).shape #所有照片的通道数进行合并 >>>torch.Size([4, 28, 28]) b = a.view(4, 784) b.view(4, 1, 28, 28).shape >>>torch.Size([4, 1, 28, 28])
2、unsqueeze/squeeze
a.shape >>>torch.Size([4, 1, 28, 28]) a.unsqueeze(0).shape #在第0维度前插入一个维度 >>>torch.Size([1, 4, 1, 28, 28]) a.unsqueeze(-1).shape #对应于4 >>>torch.Size([4, 1, 28, 28, 1]) a.unsqueeze(-4).shape #对应于1 >>>torch.Size([4, 1, 1, 28, 28]) a.unsqueeze(4).shape >>>torch.Size([4, 1, 28, 28, 1]) a.unsqueeze(-5).shape #对应于0 >>>torch.Size([1, 4, 1, 28, 28])
实际数据
a = torch.tensor([1.2,2.3]) a.shape >>>torch.Size([2]) a.unsqueeze(-1) #[2] -> [2,1] >>>tensor([[1.2000], [2.3000]]) a.unsqueeze(-1).shape >>>torch.Size([2, 1]) a.unsqueeze(0) #[2] -> [1,2] >>>tensor([[1.2000, 2.3000]]) a.unsqueeze(0).shape >>>torch.Size([1, 2]) #For example b = torch.rand(32) f = torch.rand(4,32,14,14) b = b.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(2).unsqueeze(0) b.shape >>>torch.Size([1, 32, 1, 1])
squeeze
b.shape >>>torch.Size([1, 32, 1, 1]) b.squeeze().shape #不给参数,全部解压 >>>torch.Size([32]) b.squeeze(0).shape >>>torch.Size([32, 1, 1]) b.squeeze(-1).shape >>>torch.Size([1, 32, 1]) b.squeeze(-1).shape >>>torch.Size([1, 32, 1]) b.squeeze(1).shape >>>torch.Size([1, 32, 1, 1]) b.squeeze(-4).shape >>>torch.Size([32, 1, 1])
expand
a = torch.rand(4,32,14,14) b.shape >>>torch.Size([1, 32, 1, 1]) b.expand(4,32,14,14).shape #仅限于1->N >>>torch.Size([4, 32, 14, 14]) b.expand(-1,32,-1,-1).shape #-1表示该维度保持不变 >>>torch.Size([1, 32, 1, 1]) b.expand(-1,32,-1,4).shape >>>torch.Size([1, 32, 1, 4])
repeat#维度拷贝
b.shape >>>torch.Size([1, 32, 1, 1]) b.repeat(4,32,1,1).shape #每一个维度需要拷贝的次数 >>>torch.Size([4, 1024, 1, 1]) b.repeat(4,1,1,1).shape >>>torch.Size([4, 32, 1, 1]) b.repeat(4,1,32,32).shape >>>torch.Size([4, 32, 32, 32])
矩阵转置
a = torch.randn(3,4) a.t() #只能用于二维 >>>tensor([[ 1.4149, -1.2417, 0.4027], [-0.3130, 1.0590, 0.1123], [-1.3699, -0.3791, -1.0308], [-0.8360, -0.2011, -0.4700]]) a = torch.randn(4, 3, 32, 32) a1 = a.transpose(1,3).contiguous().view(4,3*32*32).view(4,3,32,32) >>>#[b c H W] ->[b w H C] ->[b C W H] a2 = a.transpose(1,3).contiguous().view(4,3*32*32).view(4,32,32,3).transpose(1,3) # [b c H W] -> [b W H c] -> [b WHc] -> [b W H c] -> [b c H W] a1.shape, a2.shape >>>(torch.Size([4, 3, 32, 32]), torch.Size([4, 3, 32, 32])) torch.all(torch.eq(a,a1)) >>>tensor(0, dtype=torch.uint8) torch.all(torch.eq(a,a2)) >>>tensor(1, dtype=torch.uint8)
a.transpose(1,3).shape >>>torch.Size([4, 28, 28, 3]) b = torch.rand(4,3,28,32) b.transpose(1,3).shape >>>torch.Size([4, 32, 28, 3]) b.transpose(1,3).transpose(1,2).shape >>>torch.Size([4, 28, 32, 3]) b.permute(0,2,3,1).shape #直接干,[b c H W] -> [b H W c] >>>torch.Size([4, 28, 32, 3])
人生苦短,何不用python


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号