聚类-kmeans以及一些演变
一、作用
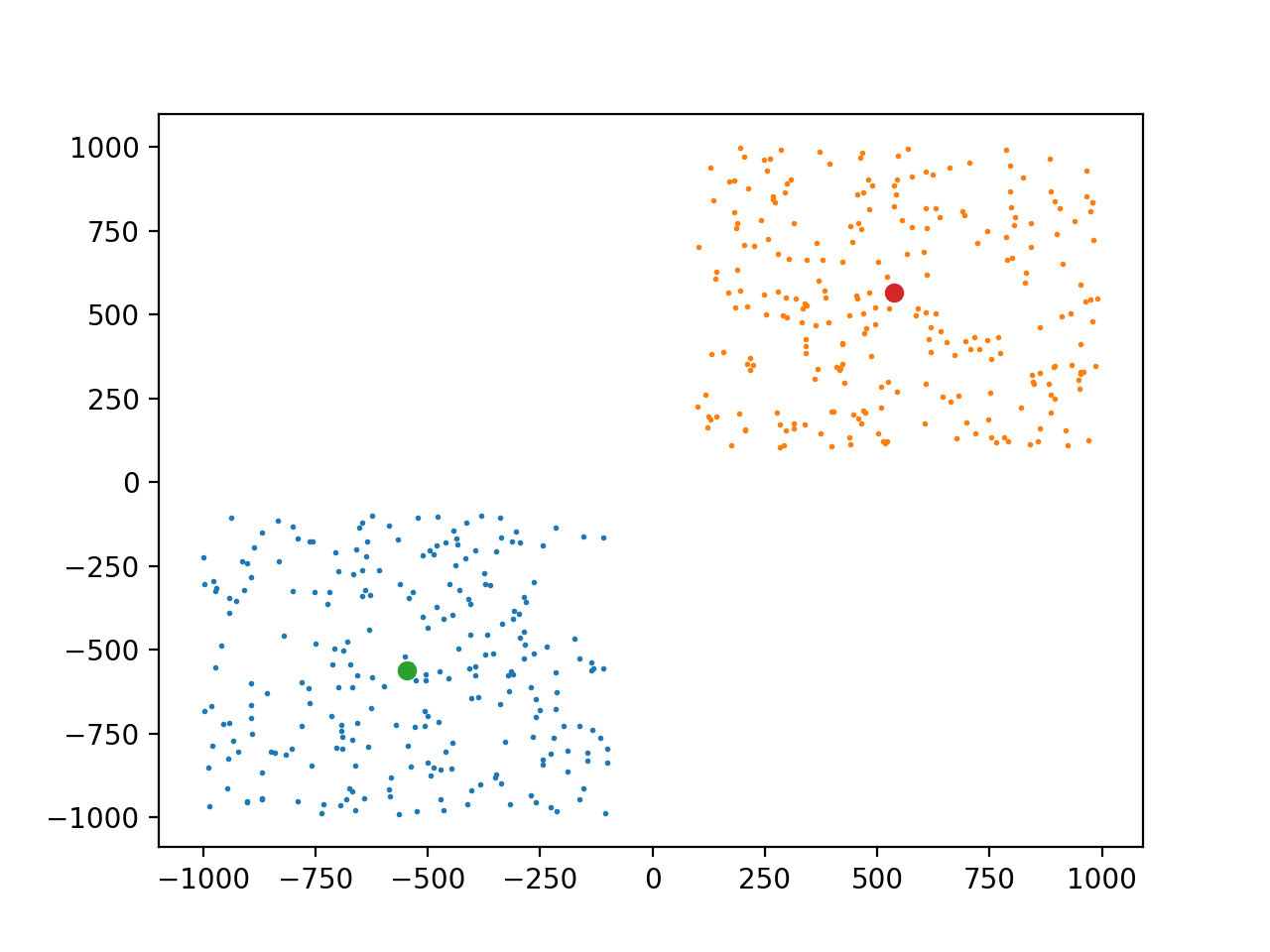
给定一些离散点,然后将这些离散点进行分类,这也叫做聚类。例如,将以下离散点分为两类,中心点也就是绿点和橙色的点也叫做簇心。
二、步骤
- 选取k个初始质心(作为初始cluster);
- repeat:对每个样本点,计算得到距其最近的质心,将其类别标为该质心所对应的cluster; 重新计算k个cluser对应的质心;
- 质心的计算方法,将同簇的点,计算它们的平均坐标值作为新的质心
- until 质心不再发生变化
由上可见,kmeans的缺点是聚类的好坏和质心起始位置的选取有关
三、CODE(SKLEARN)
1 from numpy import * 2 from sklearn.cluster import KMeans 3 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 6 # create data 7 n_data = array([[random.randint(100, 1000), random.randint(100, 1000)] for i in range(0, 1000)]) 8 label_n = array([0 for i in range(0, 1000)]) 9 p_data = array([[-1 * random.randint(100, 1000), -1 * random.randint(100, 1000)] for i in range(0, 1000)]) 10 label_p = array([1 for i in range(0, 1000)]) 11 data_all = concatenate((n_data, p_data), axis=0) 12 label_all = concatenate((label_n, label_p), axis=0) 13 14 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(data_all, label_all) 15 16 km = KMeans(n_clusters=2) # 初始化 17 km.fit(X_train, y_train) 18 predict = km.predict(X_test) 19 20 21 def accuracy(pred, real): 22 score = 0 23 for i in range(0, len(predict)): 24 if predict[i] == y_test[i]: 25 score += 1 26 return score * 1.0 / len(predict) * 1.0 27 28 29 center = km.cluster_centers_ 30 31 fig = plt.figure() 32 ax = fig.add_subplot(111) 33 34 35 ax.scatter(data_all[:, 0], data_all[:, 1], s=1) 36 ax.scatter(center[0, 0], center[0, 1]) 37 ax.scatter(center[1, 0], center[1, 1]) 38 plt.show()
四、时间复杂度
时间复杂度为 O(nkl)
- n为离散点个数
- k为簇心个数
- l为迭代次数
五、kmeans++
通过概率化的质心选择策略,使初始化质心尽可能分散。流程:
- 随机选择一个质心 C1.
- 计算每个点到当前点最短距离 D(xi)
- 计算下一个点选择质心的概率 P (xi) = D(xi)**2 / sum(D(xj)**2)
- 重复2、3选出k个质心
-
六、Capacitated K-Means++
- 初始化,选k个中心点
- 分配阶段,将每个点分配到最近的中心,如果簇已满,算法学昭下一个最近,且有容量的簇。(贪心,或者其他复杂效果更优的解法)
- 更新阶段,根据重新分配的点重新计算中心
- 收敛判断,中心点不再变化
谢谢!


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号