换根 & 树形
其实就是在树上 DP,由于树固有的递归性质,树形 DP 一般都是递归进行的。
一般而言,有如下模板可以套用。
void dfs(int from,int fa) {
for(遍历与from相连的边) {
if(to==fa) {
continue;
}
dfs(to,from);
使用 dp[to] 更新 dp[from];
}
}讲解一道模板题,了解树形 DP 使用方法。
在本题中,定义 如下:
- :以 为根的子树, 不参加的最大快乐指数。
- :以 为根的子树, 参加的最大快乐指数。
接下来探究状态转移方程:
- 对于 不参加, 的儿子参加与否均可。
- 对于 参加, 的儿子只能不参加。
定义集合 包含 的儿子,方程表示为:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=6e3+10;
struct edge{
int to,next;
}ee[N<<1];//两倍
int head[N],ne;
void ae(int from,int to) {//链式前向星
ee[++ne]={to,head[from]};
head[from]=ne;
}
int n,w[N],dp[N][2];
void dfs(int from,int fa) {
dp[from][1]=w[from];//设置初始状态
for(int i=head[from];i;i=ee[i].next) {
int to=ee[i].to;
if(to==fa) continue;//防止重复访问
dfs(to,from);//递归求解 dp[to]
//更新
dp[from][0]+=max(dp[to][0],dp[to][1]);
dp[from][1]+=dp[to][0];
}
}
int main() {
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>w[i];
for(int i=1,x,y;i<n;i++) {
cin>>x>>y;
ae(y,x),ae(x,y);
}
dfs(1,0);
//最后要在两个合法状态中取最大
cout<<max(dp[1][0],dp[1][1]);
return 0;
}有一个小提醒:用链式前向星存图要两倍!
有些情况,对于不同的根,有不同的答案。对每个点树形 dp,太慢。
此时就可以通过已知的根在较快(一般为 )求出一个新根的答案。
和树形 dp 不一样的地方在于:
- 树形 dp 通过儿子得出当前点。
- 换根 dp 通过父节点得出儿子。
模板为:
void dfs(int from,int fa) {
for(遍历与from相连的边) {
if(to==fa) {
continue;
}
dfs(to,from);
使用 dp[to] 更新 dp[from];
}
}
void ddfs(int from,int fa) {
for(遍历与from相连的边) {
if(to==fa) {
continue;
}
使用 dp[from] 更新 dp[to];
dfs(to,from);
}
}
/*
还有另外一种写法,本质上都是通过已知的更新未知。
void ddfs(int from,int fa) {
if(from不是根) {
使用 dp[fa] 更新 dp[from];
}
for(遍历与from相连的边) {
if(to==fa) {
continue;
}
dfs(to,from);
}
}
*/同样讲解一道模板题。
根据题意得出,根为 时,深度和为 。 其中 为以 为 为树的根节点, 的子树节点个数。我们可以定义 为以 为根的树深度和。根据定义得 。接下来思考如何转移。
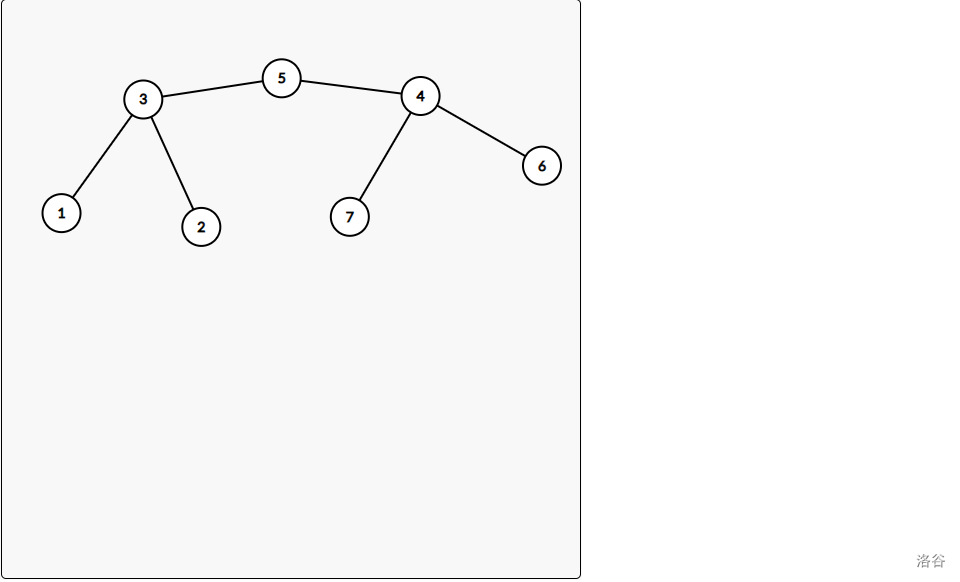 此时树的根在 ,假设 已经被求出来了。
此时树的根在 ,假设 已经被求出来了。
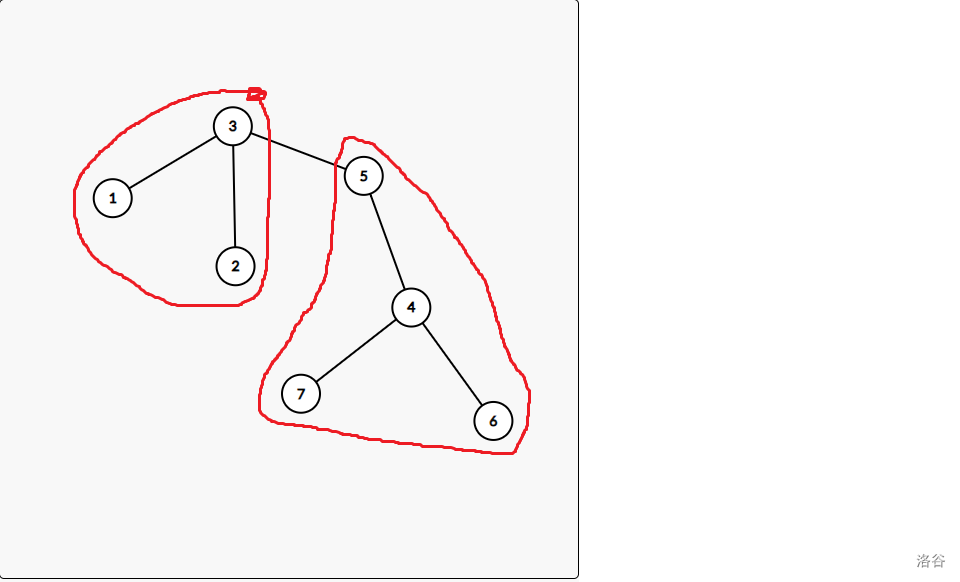 此时可以通过 来更新 。将树分为两个部分。
此时可以通过 来更新 。将树分为两个部分。
- 对于 的子树,里面的每个点,深度都被减少了 ,即
- 对于不属于 的节点,这些节点共有 个,他们的深度都增加了 。
所以可以得出状态转移方程为:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6+10;
struct edge{
int to,next;
}ee[N*2];
int up[N],head[N],ne,s[N],f[N];
int n;
void ae(int from,int to) {
ee[++ne]={to,head[from]};
head[from]=ne;
}
void dfs(int from) {
s[from]=1;
for(int i=head[from];i;i=ee[i].next) {
int to=ee[i].to;if(s[to]) continue;
dfs(to);
s[from]+=s[to];
}
}
void dfss(int from,int fa) {
for(int i=head[from];i;i=ee[i].next) {
int to=ee[i].to;
if(to==fa) continue;
f[to]=f[from]-s[to]*2+n;
dfss(to,from);
}
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
cin>>n;
for(int i=1,x,y;i<n;i++) {
cin>>x>>y;
ae(x,y),ae(y,x);
}
dfs(1);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) f[1]+=s[i];
dfss(1,0);
int ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
if(f[i]>f[ans]) ans=i;
}
cout<<ans;
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号