深入理解JAVA I/O系列四:RandomAccessFile
一、简述

这个是JDK上的截图,我们可以看到它的父类是Object,没有继承字节流、字符流家族中任何一个类。并且它实现了DataInput、DataOutput这两个接口,也就意味着这个类既可以读也可以写。
二、存在的意义
1、是JAVA I/O流体系中功能最丰富的文件内容访问类,它提供了众多方法来访问文件内容。
2、由于可以自由访问文件的任意位置,所以如果需要访问文件的部分内容,RandomAccessFile将是更好的选择。
3、可以用来访问保存数据记录的文件,文件的记录的大小不必相同,但是其大小和位置必须是可知的。
这个类在很多资料上翻译成中文都是:随机访问文件,在中文里,随机是具有不确定的含义,指一会访问这里,一会访问那里的意思。如果以这种语义来解释的话,就会感到很困惑。其实,Random在英文中不仅仅有随机,还有任意的意思。如果中文名为任意访问文件是不是就会更好的理解。任意表示我们可以指定文件中任何一个位置去操作一个文件。
三、DEMO演示
(1)、写入文件
1 public class RandomAccessFileTest
2 {
3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
4 {
5 RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile("d:/data.txt","rw");
6 Person p = new Person(1001,"xiaoming",1.80d);
7 p.write(raf);
8 }
9 }
10 class Person
11 {
12 int id;
13 String name;
14 double height;
15 public Person()
16 {
17 }
18 public Person(int id, String name, double height)
19 {
20 this.id = id;
21 this.name = name;
22 this.height = height;
23 }
24
25 public void write(RandomAccessFile raf) throws IOException
26 {
27 raf.write(id);
28 raf.writeUTF(name);
29 raf.writeDouble(height);
30 }
31 }
执行结果:
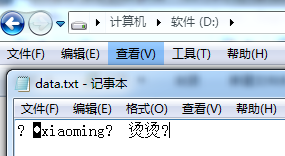
1、执行结果乱码是由于写入的是二进制文件,这个待会我们再使用程序读取。(这个跟前面介绍的DataInputStream、DataOutputStream类似)
2、第五行中,RandomAccessFile的构造函数除了指定了要写入了文件,还有另外一个参数:mod,主要用来指定打开文件的访问模式。

3、读取的方式就是读取基本数据类型,其中第28行使用的方法是:writeUTF(String str)
使用 modified UTF-8 编码以与机器无关的方式将一个字符串写入该文件,这个方法就是将字符串写入文件,而且不用担心会出现乱码,因为使用的编码方式是UTF-8
(2)、文件读取
由于刚才写入的是二进制文件,现在使用程序去读取文件:
1 public class RandomAccessFileTest
2 {
3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
4 {
5 RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile("d:/data.txt", "rw");
6 Person p = new Person(1001, "xiaoming", 1.80d);
7 p.write(raf);// 写入文件后,任意访问文件的指针在文件的结尾
8
9 raf.seek(0);// 读取时,将指针重置到文件的开始位置。
10 Person p2 = new Person();
11 p2.read(raf);
12 System.out.println("id=" + p2.getId() + ";name=" + p2.getName()
13 + ";height=" + p2.getHeight());
14
15 }
16 }
17 class Person
18 {
19 int id;
20 String name;
21 double height;
22 public Person()
23 {
24 }
25 public Person(int id, String name, double height)
26 {
27 this.id = id;
28 this.name = name;
29 this.height = height;
30 }
31
32 public void write(RandomAccessFile raf) throws IOException
33 {
34 raf.writeInt(id);
35 raf.writeUTF(name);
36 raf.writeDouble(height);
37 }
38
39 public void read(RandomAccessFile raf) throws IOException
40 {
41 this.id = raf.readInt();
42 this.name = raf.readUTF();
43 this.height = raf.readDouble();
44 }
45 public int getId()
46 {
47 return id;
48 }
49 public void setId(int id)
50 {
51 this.id = id;
52 }
53 public String getName()
54 {
55 return name;
56 }
57 public void setName(String name)
58 {
59 this.name = name;
60 }
61 public double getHeight()
62 {
63 return height;
64 }
65 public void setHeight(double height)
66 {
67 this.height = height;
68 }
69
70 }
执行结果:
id=1001;name=xiaoming;height=1.8
1、在39-43行代码中,由于是按基本数据类型写入和读取,所以在读取的时候一定严格按照写入的顺序。
2、第9行的位置上,由于在写入的时候,导致访问的指针的位置在文件的结尾处,现在读取的时候,需要将访问指针的位置重置到文件开头处。
(3)、追加内容
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
2 {
3 RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile("D:/out.txt","rw");
4 raf.seek(raf.length());
5 raf.write("\r\n中国移动阅读基地".getBytes());
6 }
执行结果:
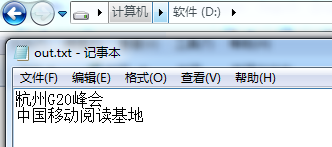
1、这段程序演示了在文件原有内容的基础上去追加内容。其中seek方法就是将访问指针移动到文件内容的末尾。
2、RandomAccessFile依然只能追加,不能像文件的指定位置插入内容。如果强制将文件记录指针移动到中间位置后开始输出内容,则新的内容会覆盖文件中原有的内容。
3、如果需要向文件指定的位置插入内容,程序需要先把插入点后面的内容读入缓冲区,等插入完成后,再讲缓冲区的内容追加到文件的后面。
(4)、指定位置插入
1 public static void main(String[] args)
2 {
3 try
4 {
5 insert("d:/out.txt",5,"插入的内容");
6 }
7 catch (IOException e)
8 {
9 e.printStackTrace();
10 }
11 }
12
13 private static void insert(String fileName,long pos,String content) throws IOException
14 {
15 //创建临时空文件
16 File tempFile = File.createTempFile("temp",null);
17 //在虚拟机终止时,请求删除此抽象路径名表示的文件或目录
18 tempFile.deleteOnExit();
19 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(tempFile);
20
21 RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(fileName,"rw");
22 raf.seek(pos);
23 byte[] buffer = new byte[4];
24 int num = 0;
25 while(-1 != (num = raf.read(buffer)))
26 {
27 fos.write(buffer,0,num);
28 }
29 raf.seek(pos);
30 raf.write(content.getBytes());
31 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(tempFile);
32 while(-1 != (num = fis.read(buffer)))
33 {
34 raf.write(buffer,0,num);
35 }
36 }
执行结果:

1、这里插入内容的原理就是:先把插入点后面的内容读入缓冲区,等插入完成后,再讲缓冲区的内容追加到文件的后面。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号