深度学习的始祖框架,grandfather级别的框架 —— Theano —— 示例代码学习(1)
示例代码1:
import theano
from theano import tensor
x = tensor.vector("x")
y = tensor.vector("y")
w = tensor.vector("w")
z = tensor.vector("z")
z = x+y+w
f = theano.function([x, theano.In(y, value=[1,1,1]), theano.In(w,value=[2,2,2], name='weights')], z)
# 不使用默认值
print( f([1,2,3], [2,3,4], [3,4,5]) )
# 使用默认值
print( f([1,2,3], [2,3,4]) )
print( f([1,2,3], weights=[2,3,4]) )
print( type(f([1,2,3], weights=[2,3,4])) )
运行结果:

示例代码2:(与示例代码1不同的地方在于设置变量数据类型为int而不是默认的double,即vector和ivector的区别)
import theano
from theano import tensor
x = tensor.ivector("x")
y = tensor.ivector("y")
w = tensor.ivector("w")
z = tensor.ivector("z")
z = x+y+w
f = theano.function([x, theano.In(y, value=[1,1,1]), theano.In(w,value=[2,2,2], name='weights')], z)
# 不使用默认值
print( f([1,2,3], [2,3,4], [3,4,5]) )
# 使用默认值
print( f([1,2,3], [2,3,4]) )
print( f([1,2,3], weights=[2,3,4]) )
print( type(f([1,2,3], weights=[2,3,4])) )
运行结果:
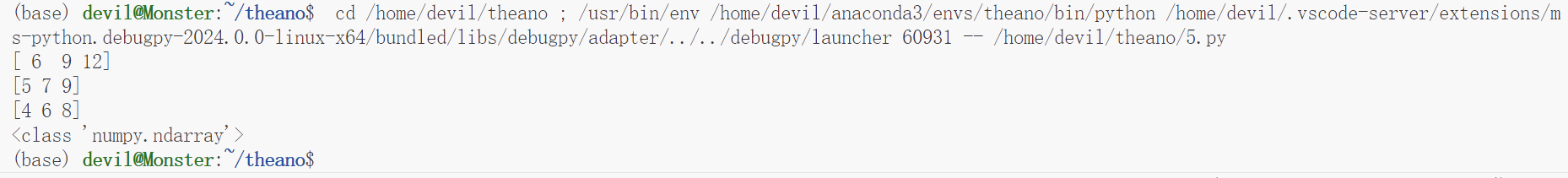
代码3:(加1操作,并复制给变量实现update的目的)
import theano
from theano import tensor
state = theano.shared(0)
inc = tensor.iscalar('inc')
# accumulator = theano.function([inc], [], updates=[(state, state+inc), ])
accumulator = theano.function([inc], state, updates=[(state, state+inc), ])
print(state.get_value())
print(accumulator(1))
print(state.get_value())
运行结果:

代码4:(求导操作)
import theano
import theano.tensor as tensor
x = tensor.dscalar('x')
y = x ** 2 # 定义函数y=x^2
gy = tensor.grad(y, x) # 导函数的表达式
f = theano.function([x], gy) # 将导函数编译成Theano函数
print( theano.pp(gy) ) # 打印优化之前的导函数表达式
print( f(4) ) # 带入数据计算x=4时的导数值
print( theano.pp(f.maker.fgraph.outputs[0]) ) # 打印编译优化后的导函数表达式
运行结果:

代码5:(神经网络实现2层MLP预测训练)
import theano
import theano.tensor as tensor
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #引入了matplotlib这个工具包, 用来实现绘图及数据可视化。
"""
定义层结构
接下来我们声明我们的Layer类
对于神经网络的每个Layer, 它需要具备输入来源input, 输入神经元维度in_size, 输出神经元纬度out_size,
和我们之前设计的神经元的激活函数activation_function, 默认为None。
"""
class Layer(object):
def __init__(self, inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None):
self.W = theano.shared(np.random.normal(0, 1, (in_size, out_size)))
self.b = theano.shared(np.zeros((out_size, )) + 0.1)
self.Wx_plus_b = tensor.dot(inputs, self.W) + self.b
self.activation_function = activation_function
if activation_function is None:
self.outputs = self.Wx_plus_b
else:
self.outputs = self.activation_function(self.Wx_plus_b)
"""
伪造数据
接下来,我们首先人工生成一个简单的带有白噪声的一维数据 y = x^2 - 0.5 + noise。
"""
# Make up some fake data
x_data = np.linspace(-1, 1, 300)[:, np.newaxis]
noise = np.random.normal(0, 0.05, x_data.shape)
y_data = np.square(x_data) - 0.5 + noise # y = x^2 - 0.5 + wihtenoise
# show the fake data
plt.scatter(x_data, y_data)
plt.show()
# determine the inputs dtype
x = tensor.dmatrix("x")
y = tensor.dmatrix("y")
# determine the inputs dtype
# add layers
l1 = Layer(x, 1, 10, tensor.nnet.relu)
l2 = Layer(l1.outputs, 10, 1, None)
# compute the cost
cost = tensor.mean(tensor.square(l2.outputs - y))
# compute the gradients
gW1, gb1, gW2, gb2 = tensor.grad(cost, [l1.W, l1.b, l2.W, l2.b])
# apply gradient descent
learning_rate = 0.05
train = theano.function(inputs=[x, y], outputs=cost, \
updates=[(l1.W, l1.W - learning_rate * gW1), \
(l1.b, l1.b - learning_rate * gb1), \
(l2.W, l2.W - learning_rate * gW2), \
(l2.b, l2.b - learning_rate * gb2)])
# prediction
predict = theano.function(inputs=[x], outputs=l2.outputs)
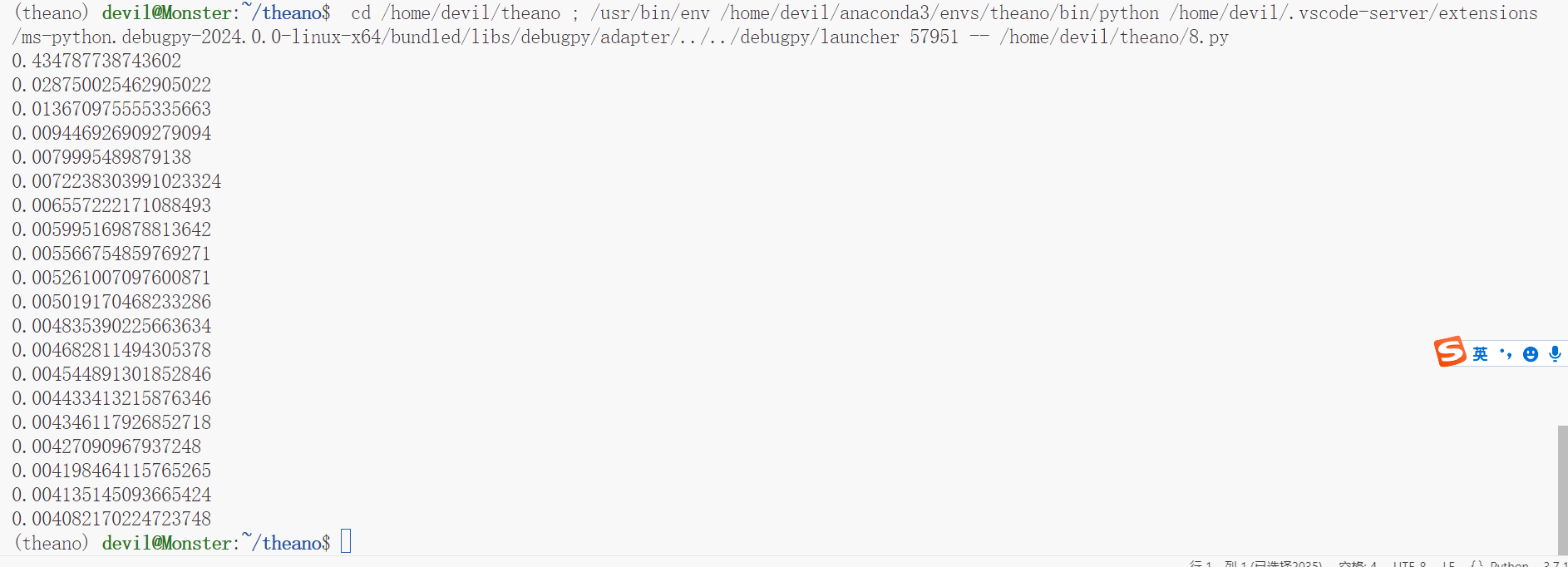
for i in range(1000):
# training
err = train(x_data, y_data)
if i % 50 == 0:
print(err)
运行结果:
参考:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/1f55c446ce3a
本博客是博主个人学习时的一些记录,不保证是为原创,个别文章加入了转载的源地址,还有个别文章是汇总网上多份资料所成,在这之中也必有疏漏未加标注处,如有侵权请与博主联系。
如果未特殊标注则为原创,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议。
posted on 2024-02-12 09:37 Angry_Panda 阅读(43) 评论(0) 收藏 举报




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号