浅谈网络流
并不会从零开始讲网络流 , 并且其中很多是个人理解.
\(①\) \(:\) 最大流 \(\cdot\) \(DK\)
每次去找 一条 (注意是一条) 路增广 , 再去更新.
\(vis\) 保证每次每个点只找到一次 , 也防止双向边成环卡死.
一定不能用 \(flow\) 单个变量去记录最小流 , 要用数组 \(flow\) 去更新 , 因为在一条路的路程中会产生最小流 , 但这条路不一定走得通.
关于反向边的建立 , 我认为就是让能流的残余流量流完
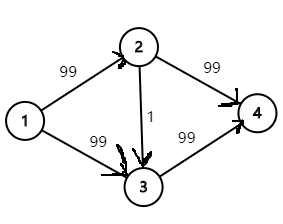
很显然答案是 : 198.
但若我们走的不是 "显然" 的路 , 走 \(1 \rightarrow 2 \rightarrow 3 \rightarrow 4\) , 则会变成 :
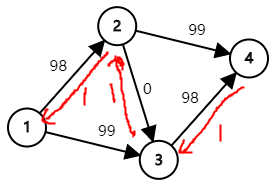
这一次我们只能走 \(1 \rightarrow 3 \rightarrow 2 \rightarrow 4\) , 则会变成 :
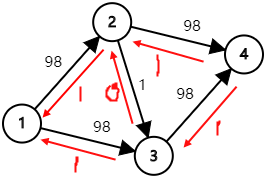
三个图总体来看发现 : \(2 - 3\) 反向边的建立让我们两条显然的路都经过了流量 \(1\) .
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 201;
const int M = 5001;
const int inf = 2147483647;
long long ans;
int n,m,s,t,cnt = 1;
int head[N],vis[N],pre[N],flow[N];
struct bian{
int to,v,next;
}len[M<<1];
void add(int from,int to,int v){
len[++cnt].v = v;
len[cnt].to = to;
len[cnt].next = head[from];
head[from] = cnt;
}
bool bfs(){
queue<int> Q;
flow[s] = inf;
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
Q.push(s) , vis[s] = 1;
while(Q.size()){
int now = Q.front();Q.pop();
for(int k=head[now];k;k=len[k].next){
int to = len[k].to , v = len[k].v;
if(!vis[to]&&v){
//flow = min(flow,v);
flow[to] = min(v,flow[now]);
pre[to] = k;
Q.push(to),vis[to] = 1;
if(to == t) return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
void updata(){
int x = t;
while(x != s){
int id = pre[x];
len[id].v -= flow[t];
len[id^1].v += flow[t];
x = len[id^1].to;
}
ans += flow[t];
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&n,&m,&s,&t);
for(int i=1;i<=m;++i){
int x,y,v;scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&v);
add(x,y,v),add(y,x,0);
}
while(bfs()) updata();
printf("%lld",ans);
return 0;
}
\(②\) \(:\) 最大流 \(\cdot\) \(Dinic\)
分层数组 \(dep\) : 保证能多路增广 , 且防止双向边成环卡死.
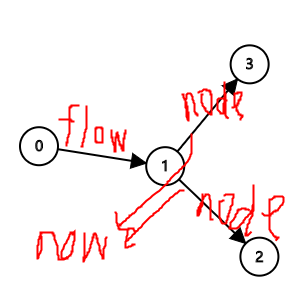
如图 : \(1 \rightarrow 2 \rightarrow 4\) , \(1 \rightarrow 3 \rightarrow 4\) , 两条路能在一次 \(dfs\) 中完成增广 , 而不是像 \(DK\) 那次被 \(vis\) 数组限定每次只能选一条.

当前弧优化 \(now\) 数组 : 当一条路进行了增广后 , 我们没必要在同一次 \(dfs\) 中对其再增广 , 不好解释看图吧.
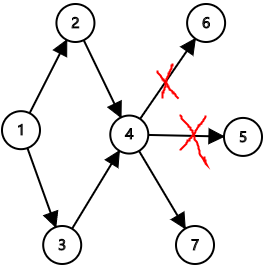
当我们走了 \(1 \rightarrow 2 \rightarrow 4 \rightarrow 6\) , \(1 \rightarrow 2 \rightarrow 4 \rightarrow 5\) 时 ,
下一次就只需走 \(1 \rightarrow 3 \rightarrow 4 \rightarrow 7\) 即可 , 从 \(6\) , \(5\) 走一定会遇到 边权为 \(0\) 边.
注意我们用 &k = now[x] 进行对 \(now\) 数组的实时更新.
小技巧优化 : nowflow < flow , nowflow += nodeflow.
结合图与递归就能理解了 :
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 201;
const int M = 5001;
const int inf = 2147482647;
long long ans;
int n,m,s,t,cnt = 1;
int head[N],now[N],dep[N];
struct bian{
int to,next,v;
}len[M<<1];
void add(int from,int to,int v){
len[++cnt].v = v;
len[cnt].to = to;
len[cnt].next = head[from];
head[from] = cnt;
}
bool bfs(){
queue<int> Q;
memset(dep,0,sizeof(dep));
Q.push(s) , dep[s] = 1;
while(Q.size()){
int pos = Q.front();Q.pop();
for(int k=head[pos];k;k=len[k].next){
int to = len[k].to , v = len[k].v;
if(!dep[to]&&v){
dep[to] = dep[pos] + 1;
Q.push(to);
if(to == t) return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
int dfs(int x,int flow){
if(x == t) return flow;
int nowflow = 0;
for(int &k=now[x];k&&nowflow<flow;k=len[k].next){
int to = len[k].to , v = len[k].v;
if(dep[to]==dep[x]+1&&v){
int nodeflow = dfs(to,min(v,flow-nowflow));
if(nodeflow > 0){
len[k].v -= nodeflow;
len[k^1].v += nodeflow;
nowflow += nodeflow;
}
}
}
return nowflow;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&n,&m,&s,&t);
for(int i=1;i<=m;++i){
int x,y,v;scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&v);
add(x,y,v),add(y,x,0);
}
while(bfs()){
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
now[i] = head[i];
while(int f = dfs(s,inf))
ans += f;
}
printf("%lld",ans);
return 0;
}
\(③\) \(:\) 最小费用最大流 \(\cdot\) \(DK\)
在每次我们找残余网络的基础上 (v != 0) , 加入对最短路的判断 .
同时注意我们这里的 \(vis\) 数组在数据弹出时要 \(vis = 0\) , 这在最大流 \(\cdot\) \(DK\) 里面是没有的 , 这里利用的是 \(spfa\) 更新最短路的原理 , 当前有效状态更新并非最优 . 利用 dis[to] > dis[x] + cost 不会陷入双向边成环卡死的现象.
同时注意要用 \(flow\) , \(dis\) 数组去维护最大值.
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 5e3+1;
const int M = 5e4+1;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int n,m,s,t,maxflow,sum,cnt = 1;
int head[N],dis[N],vis[N],flow[N],pre[N];
struct bian{
int to,next,v,cost;
}len[M<<1];
void add(int from,int to,int v,int cost){
len[++cnt].v = v;
len[cnt].to = to;
len[cnt].cost = cost;
len[cnt].next = head[from];
head[from] = cnt;
}
bool bfs(){
queue<int> Q;
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
memset(dis,0x3f,sizeof(dis));
Q.push(s);
vis[s] = 1 , dis[s] = 0 , flow[s] = inf;
while(Q.size()){
int now = Q.front();Q.pop();
vis[now] = 0;
for(int k=head[now];k;k=len[k].next){
int to = len[k].to , v = len[k].v , cost = len[k].cost;
if(v&&dis[to] > dis[now] + cost){
dis[to] = dis[now] + cost;
pre[to] = k;
flow[to] = min(flow[now],v);
if(!vis[to]) Q.push(to),vis[to] = 1;
}
}
}
return dis[t] != inf;
}
void updata(){
int x = t;
while(x != s){
int id = pre[x];
len[id].v -= flow[t];
len[id^1].v += flow[t];
x = len[id^1].to;
}
maxflow += flow[t];
sum += flow[t]*dis[t];
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&n,&m,&s,&t);
for(int i=1;i<=m;++i){
int x,y,v,cost;
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&x,&y,&v,&cost);
add(x,y,v,cost) , add(y,x,0,-cost);
}
while(bfs()) updata();
printf("%d %d",maxflow,sum);
return 0;
}
\(④\) \(:\) 最小费用最大流 \(\cdot\) \(Dinic\)
将分层顺序改为最短路顺序即可.
注意 \(dfs\) 中 \(vis\) 数组 , 因为条件变为 dis[to] == dis[pos] + cost , 并不能防止双向边成环卡死现象 , \(vis\) 为了防止这种情况.
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 5e3+1;
const int M = 5e4+1;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int n,m,s,t,maxflow,sum,cnt = 1;
int head[N],now[N],vis[N],dis[N];
struct bian{
int to,v,next,cost;
}len[M<<1];
void add(int from,int to,int v,int cost){
len[++cnt].v = v;
len[cnt].to = to;
len[cnt].cost = cost;
len[cnt].next = head[from];
head[from] = cnt;
}
bool bfs(){
queue<int> Q;
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
memset(dis,0x3f,sizeof(dis));
Q.push(s);
dis[s] = 0 , vis[s] = 1;
while(Q.size()){
int pos = Q.front();Q.pop();
vis[pos] = 0;
for(int k=head[pos];k;k=len[k].next){
int to = len[k].to , v = len[k].v , cost = len[k].cost;
if(v&&dis[to] > dis[pos]+cost){
dis[to] = dis[pos]+cost;
if(!vis[to]) Q.push(to),vis[to] = 1;
}
}
}
return dis[t] != inf;
}
int dfs(int x,int flow){
if(x == t) return flow;
vis[x] = 1;
int nowflow = 0;
for(int &k=now[x];k&&nowflow<flow;k=len[k].next){
int to = len[k].to , v = len[k].v , cost = len[k].cost;
if(v&&!vis[to]&&dis[to]==dis[x]+cost){
int nodeflow = dfs(to,min(v,flow-nowflow));
if(nodeflow){
len[k].v -= nodeflow;
len[k^1].v += nodeflow;
sum += nodeflow*cost;
nowflow += nodeflow;
}
}
}
vis[x] = 0;
return nowflow;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&n,&m,&s,&t);
for(int i=1;i<=m;++i){
int x,y,v,cost;
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&x,&y,&v,&cost);
add(x,y,v,cost) , add(y,x,0,-cost);
}
while(bfs()){
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
now[i] = head[i];
while(int f = dfs(s,inf))
maxflow += f;
}
printf("%d %d",maxflow,sum);
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号