AOV网络拓扑排序
这个算法,主要是为输出一个无环图的拓扑序列
算法思想:
主要依赖一个栈,用来存放没有入度的节点,每次读取栈顶元素,并将栈顶元素的后继节点入度减一,如果再次出现入度为零的节点,就加入到栈中。参考《大话数据结构》,写下下面完整代码,并发现,其中程序的进行,出现错误。v6执行完,应该执行v9,因为此时v9是站顶元素,并不是v0.
算法流程:
int topGraph(graph g){ EdgeNode *e; int i,k,gettop; int top = 0 ; int count = 0; int *stack; stack = (int *)malloc(g->numVertexes * sizeof(int)); for(i=0;i<g->numVertexes;i++){ if(g->headlist[i].in == 0) //把入度为0的,即没有入度的点入栈 stack[++top] = i; } while(top){ gettop = stack[top--]; printf("%d ",gettop); count++; for(e = g->headlist[gettop].fnode; e ; e=e->next){ //一次遍历链表,减少各个子节点的入度 k = e->data; if(!(--g->headlist[k].in)) stack[++top] = k; } } if(count < g->numVertexes) return ERROR; else return OK; }
全部代码:
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define MAX 14 #define ERROR 1 #define OK 0 typedef struct edgeNode{ int data; struct edgeNode *next; }EdgeNode; typedef struct headNode{ int in; int data; EdgeNode *fnode; }HeadNode,HeadList[MAX]; typedef struct{ HeadList headlist; int numEdges,numVertexes; }Graph,*graph; void initGraph(graph g); int inputInfo(graph g,int tar,int in,int data,int first); void printGraph(graph g); int topGraph(graph g); int main(){ Graph *g = (Graph *)malloc(sizeof(Graph)); initGraph(g); printGraph(g); if(topGraph(g) == ERROR) printf("有环路!\n"); else printf("没有环路!\n"); free(g); getchar(); return 0; } int topGraph(graph g){ EdgeNode *e; int i,k,gettop; int top = 0 ; int count = 0; int *stack; stack = (int *)malloc(g->numVertexes * sizeof(int)); for(i=0;i<g->numVertexes;i++){ if(g->headlist[i].in == 0) //把入度为0的,即没有入度的点入栈 stack[++top] = i; } while(top){ gettop = stack[top--]; printf("%d ",gettop); count++; for(e = g->headlist[gettop].fnode; e ; e=e->next){ //一次遍历链表,减少各个子节点的入度 k = e->data; if(!(--g->headlist[k].in)) stack[++top] = k; } } if(count < g->numVertexes) return ERROR; else return OK; } void printGraph(graph g){ int i; printf("vertex:%d,edges:%d\n",g->numVertexes,g->numEdges); EdgeNode *e = (EdgeNode *)malloc(sizeof(EdgeNode)); for(i=0;i<MAX;i++){ printf("[in:%d]%d",g->headlist[i].in,g->headlist[i].data); e = g->headlist[i].fnode; while(e != NULL){ printf("->%d",e->data); e = e->next; } printf("\n"); } free(e); } void initGraph(graph g){ g->numVertexes = MAX; g->numEdges = 0; int i; for(i=0;i<MAX;i++){ g->headlist[i].fnode = NULL; } inputInfo(g,0,0,0,4); inputInfo(g,0,0,0,5); inputInfo(g,0,0,0,11); inputInfo(g,1,0,1,2); inputInfo(g,1,0,1,4); inputInfo(g,1,0,1,8); inputInfo(g,2,2,2,5); inputInfo(g,2,2,2,6); inputInfo(g,2,2,2,9); inputInfo(g,3,0,3,2); inputInfo(g,3,0,3,13); inputInfo(g,4,2,4,7); inputInfo(g,5,3,5,8); inputInfo(g,5,3,5,12); inputInfo(g,6,1,6,5); inputInfo(g,7,2,7,-1); inputInfo(g,8,2,8,7); inputInfo(g,9,1,9,10); inputInfo(g,9,1,9,11); inputInfo(g,10,1,10,13); inputInfo(g,11,2,11,-1); inputInfo(g,12,1,12,9); inputInfo(g,13,2,13,-1); } int inputInfo(graph g,int tar,int in,int data,int first){ g->numEdges++; if(first == -1){ //没有后继的边节点 g->headlist[tar].in = in; g->headlist[tar].data = data; return 1; } if(!g->headlist[tar].fnode){ //观察是否已经初始化 g->headlist[tar].in = in; g->headlist[tar].data = data; } EdgeNode *e = (EdgeNode *)malloc(sizeof(EdgeNode)); e->data = first; e->next = g->headlist[tar].fnode; g->headlist[tar].fnode = e; return 0; }
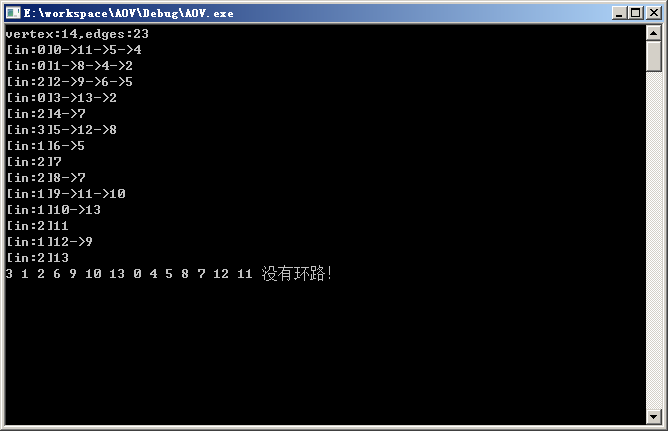
执行示例:


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号