最远点采样(Farthest Point Sampling FPS)
点云处理中采样非常重要,通常有随机采样,体素采样,统一采样和最远点采样。这里先介绍下几种采样方式,后面再具体介绍下FPS采样。
一、采样方式
1.1 随机采样
随机从点云中均匀选择指定数量的点,是最简单的采样方法。
import open3d as o3d
import numpy as np
def random_sampling(pcd, num_points):
if len(pcd.points) <= num_points:
return pcd
indices = np.random.choice(len(pcd.points), num_points, replace=False)
sampled_pcd = pcd.select_by_index(indices)
return sampled_pcd
1.2 体素采样
将空间划分为体素网格,每个体素内保留一个点(通常是中心点或随机点)。
def voxel_sampling(pcd, voxel_size):
downpcd = pcd.voxel_down_sample(voxel_size)
return downpcd
# 使用示例
pcd = o3d.io.read_point_cloud("pointcloud.ply")
voxel_size = 0.05 # 体素大小
sampled_pcd = voxel_sampling(pcd, voxel_size)
1.3 统一采样
基于点云法线或曲率进行均匀采样,在特征丰富区域保留更多点。
def uniform_sampling(pcd, num_points):
pcd.estimate_normals(search_param=o3d.geometry.KDTreeSearchParamHybrid(
radius=0.1, max_nn=30))
points = np.asarray(pcd.points)
normals = np.asarray(pcd.normals)
curvatures = np.zeros(len(points))
for i in range(len(points)):
neighbor_indices = pcd_tree.search_radius_vector_3d(points[i], 0.1)[1]
if len(neighbor_indices) > 1:
neighbor_normals = normals[neighbor_indices]
curvature = np.std(neighbor_normals, axis=0).mean()
curvatures[i] = curvature
probabilities = curvatures / curvatures.sum()
indices = np.random.choice(len(points), num_points,
p=probabilities, replace=False)
sampled_pcd = pcd.select_by_index(indices)
return sampled_pcd
1.4 最远点采样
迭代选择距离已选点集最远的点,能更好地保持点云的几何特征。
import open3d as o3d
import open3d.core as o3c
import glob
import numpy as np
import os
def fps_sample(pts_file_path, save_dirs, number=20000):
data = np.load(pts_file_path)
map_to_tensors = {}
map_to_tensors["positions"] = o3c.Tensor(data[:, :3], o3c.float32)
map_to_tensors["normals"] = o3c.Tensor(data[:, 3:], o3c.float32)
pcd = o3d.t.geometry.PointCloud(map_to_tensors).to_legacy()
# ---- down sample -----
downpcd_farthest = pcd.farthest_point_down_sample(number)
dists = pcd.compute_point_cloud_distance(downpcd_farthest)
indexes = []
for i, d in enumerate(dists):
if d > 0:
continue
indexes.append(i)
down_pcd = pcd.select_by_index(indexes)
pts = np.asarray(down_pcd.points)
normals = np.asarray(down_pcd.normals)
down_data = np.column_stack((pts, normals))
file_name = os.path.basename(pts_file_path)
np.save(os.path.join(save_dirs, file_name), down_data)
return indexes
二、采样方式对比
| 采样方法 | 优点 | 缺点 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 随机采样 | 实现简单,速度快 | 可能丢失重要特征 | 快速预览,对特征要求不高 |
| 体素采样 | 保持空间分布,速度快 | 可能过度平滑细节 | 大规模点云预处理 |
| 统一采样 | 在特征区域保留更多点 | 需要法线/曲率计算 | 特征提取,表面重建 |
| 最远点采样 | 保持几何特征最好 | 计算复杂度高,速度慢 | 需要保持形状特征的应用 |
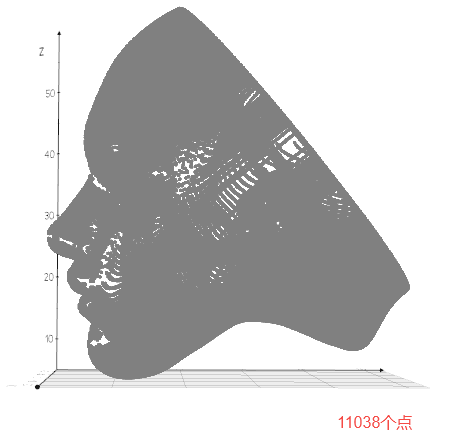
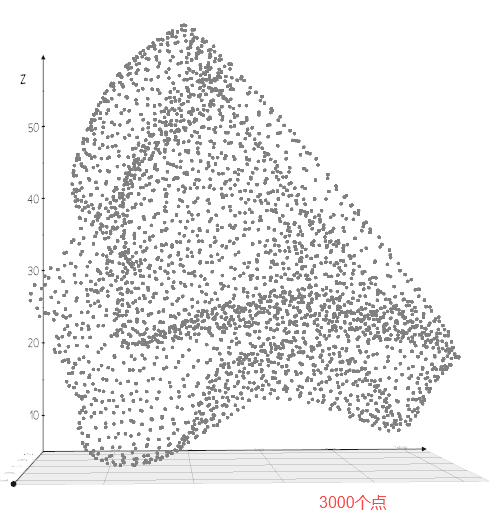
在点云相关的深度学习方法中,通常采用最远点采样,因为其可以最大程度保持形状特征,如下图所示
三、最远点采样算法及采样过程
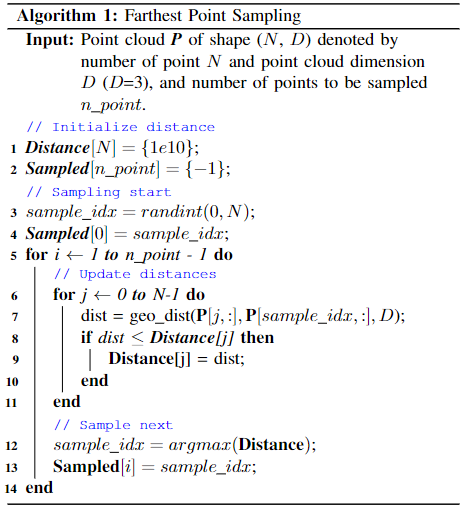
先随机选择一个点,然后从剩余点中挑选距离最远点的点,依次迭代,每次挑选出剩余点中离已采样点集最远的点
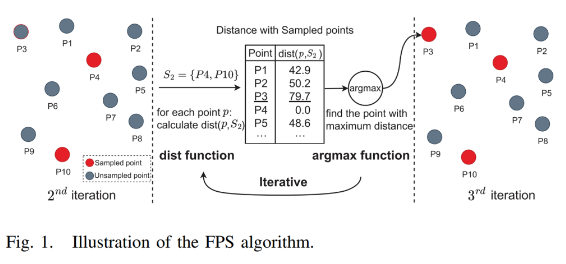
在上图示例中,S2 = {P4, P10}是采样的情况。(P4是第一个随机点,P10是距离P4最远的点)之后,计算每个点p到采样点的距离,最终选择了P3。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号