pointTransformerV1导出onnx并验证推理
前面介绍了pointTransformerV1训练自定义数据,在实际应用中往往还需要借助C++对其进行推理,这里记录一下导出和推理过程以及中途遇到的一些坑。
- 相关环境
python: 3.7.16
系统: Windows10和Ubuntu18.04
numpy 1.21.6
onnx 1.14.1
torch 1.9.0+cu111
onnxruntime 1.14.1
onnxruntime-extensions 0.8.0
onnxsim 0.4.36
一、转换成库导出
模型导出时比较麻烦的地方在于一些自定义算子导出成onnx模型可能不支持,这就会涉及到pytorch自定义算子导出,大体可以分为以下五个步骤,具体细节参考之前的文章pytorch自定义算子
转换流程
- step1 先C++ torch该写算子,导出库文件
- step2 torch加载库文件, 如:torch.ops.load_library("./fps.dll")
- step3 torch注册算子, 如:def my_fps(g, xyz, npoints): return g.op("my_ops::fps", xyz, npoints)
- step4 torch.onnx注册算子, 如: torch.onnx.register_custom_op_symbolic("my_ops::fps", my_fps, 9)
- step5 修改模型,如:farthest_point_sample(xyz, S)) 变为 torch.ops.my_ops.fps(xyz, S)
这里给出FurthestSampling的导出脚本示例。在根目录lib/pointops/functions/pointops.py中FurthestSampling定义如下:
class FurthestSampling(Function):
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, xyz, offset, new_offset):
"""
input: xyz: (n, 3), offset: (b), new_offset: (b)
output: idx: (m)
"""
assert xyz.is_contiguous()
n, b, n_max = xyz.shape[0], offset.shape[0], offset[0]
for i in range(1, b):
n_max = max(offset[i] - offset[i-1], n_max)
idx = torch.cuda.IntTensor(new_offset[b-1].item()).zero_()
n_int = n.item() if isinstance(n, torch.Tensor) else n # 确保 n 为标量
tmp = torch.full((n_int,), 1e10, dtype=torch.float32, device='cuda')
pointops_cuda.furthestsampling_cuda(b, n_max, xyz, offset, new_offset, tmp, idx)
del tmp
return idx
furthestsampling = FurthestSampling.apply
在模型部分,直接应用了该算子,但是如果直接导出onnx模型的话肯定是不支持的。
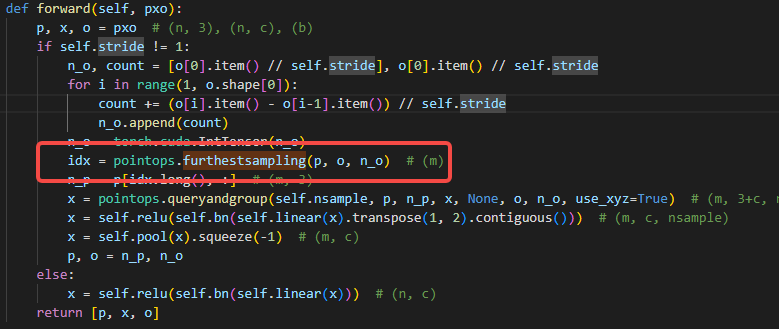
所以对其转换,只需自己实现furthestsampling_cpu_impl接口,即可将其导出成库文件:
#include <torch/script.h>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
torch::Tensor furthestsampling_cpu(
torch::Tensor xyz_tensor,
torch::Tensor offset_tensor,
torch::Tensor new_offset_tensor
) {
// 输入验证
TORCH_CHECK(xyz_tensor.is_contiguous(), "XYZ tensor must be contiguous");
TORCH_CHECK(offset_tensor.device().is_cpu(), "Offset tensor must be on CPU");
TORCH_CHECK(xyz_tensor.size(1) == 3, "XYZ tensor must have shape [N, 3]");
const int b = offset_tensor.size(0);
const int n = xyz_tensor.size(0);
auto tmp_tensor = torch::full({n}, 1e10,
torch::dtype(torch::kFloat32).device(torch::kCPU));
auto idx_tensor = torch::zeros({new_offset_tensor[-1].item<int>()},
torch::dtype(torch::kInt32).device(torch::kCPU));
const float* xyz = xyz_tensor.data_ptr<float>();
const int* offset = offset_tensor.data_ptr<int>();
const int* new_offset = new_offset_tensor.data_ptr<int>();
float* tmp = tmp_tensor.data_ptr<float>();
int* idx = idx_tensor.data_ptr<int>();
// 执行采样算法
furthestsampling_cpu_impl(b, xyz, offset, new_offset, tmp, idx);
return idx_tensor;
}
// 模块注册
TORCH_LIBRARY(my_ops, m) {
m.def("FurthestSampling", furthestsampling_cpu);
}
onnx自定义算子:https://onnxruntime.ai/docs/reference/operators/add-custom-op.html
二、借助占位符导出
前面提到的导出方式是按照导出成库然后再导出onnx模型,还可以借助torch.autograd.Function定义一个占位符导出,具体操作方式如下,在FurthestSampling类里面在实现一个静态函数symbolic,
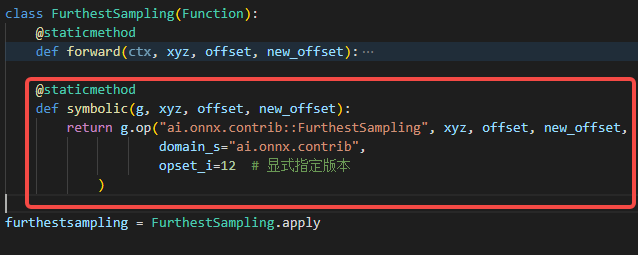
这样导出自定义算子时,也是可以的。
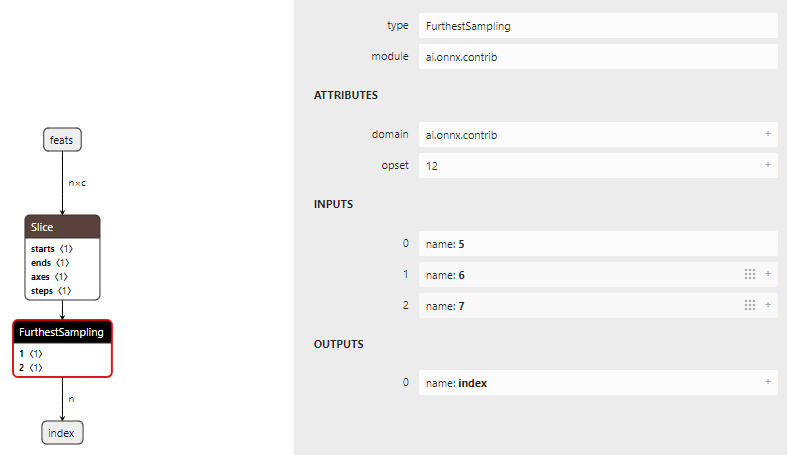
三、python onnxruntime验证
在模型导出后,我们可以借助onnxruntime对其进行验证,而对于带有自定义算子的onnx模型,直接加载会出现以下错误
加载模型时会报算子未定义:onnxruntime.capi.onnxruntime_pybind11_state.Fail: [ONNXRuntimeError] : 1 : FAIL : Load model from custom_inverse.onnx failed:Fatal error: ai.onnx.contrib:FurthestSampling is not a registered function/op
对于带有自定义算子的模型可以借助onnxruntime_extensions库对其进行装饰,进而可以在python上快速验证导出的模型是否推理正确。接下来分别对以上两种导出方式进行验证。参考:https://onnxruntime.ai/docs/extensions/add-op.html
onnxruntime_extensions提供了onnx_op装饰器,主要包含算子名称、作用域、输入输出类型。
3.1 按库导出
@onnx_op(
op_type="FurthestSampling", # 必须与 symbolic 中的 OpName 一致
domain="ai.onnx.contrib", # 必须与 symbolic 中的 domain 一致
inputs=[PyOp.dt_float, PyOp.dt_int32, PyOp.dt_int32], # 输入类型
outputs=[PyOp.dt_int32], # 输出类型
since_version=12
)
def FurthestSampling(xyz, offset, new_offset):
"""
input: xyz: (n, 3), offset: (b), new_offset: (b)
output: idx: (m)
"""
print("[DEBUG] PyOp called! Output shape:", xyz.shape)
xyz = torch.from_numpy(xyz)
offset = torch.from_numpy(offset)
new_offset = torch.from_numpy(new_offset)
torch.ops.load_library("/home/learn/point-transformer/tool/libFurthestSampling.so")
fps = torch.ops.my_ops.FurthestSampling
idx = fps(xyz, offset, new_offset)
return idx
3.2 占位符导出
验证时输入输出都是numpy,所以这里为了适配原有代码,进行了类型转换,注意借助onnxruntime_extensions验证,算子必须以ai.onnx.开头。对于复杂的模型,可以先单独对每一个自定义算子导出验证,验证成功后在整体导出,并借助onnx_op装饰后可以对其进行调试。
@onnx_op(
op_type="FurthestSampling", # 必须与 symbolic 中的 OpName 一致
domain="ai.onnx.contrib", # 必须与 symbolic 中的 domain 一致
inputs=[PyOp.dt_float, PyOp.dt_int32, PyOp.dt_int32], # 输入类型
outputs=[PyOp.dt_int32], # 输出类型
since_version=12
)
def FurthestSampling(xyz, offset, new_offset):
"""
input: xyz: (n, 3), offset: (b), new_offset: (b)
output: idx: (m)
"""
print("[DEBUG] PyOp called! Output shape:", xyz.shape)
xyz = torch.from_numpy(xyz).cuda()
offset = torch.from_numpy(offset).cuda()
new_offset = torch.from_numpy(new_offset).cuda()
assert xyz.is_contiguous()
n, b, n_max = xyz.shape[0], offset.shape[0], offset[0]
for i in range(1, b):
n_max = max(offset[i] - offset[i-1], n_max)
idx = torch.cuda.IntTensor(new_offset[b-1].item()).zero_()
n_int = n.item() if isinstance(n, torch.Tensor) else n # 确保 n 为标量
tmp = torch.full((n_int,), 1e10, dtype=torch.float32, device='cuda')
pointops_cuda.furthestsampling_cuda(b, n_max, xyz, offset, new_offset, tmp, idx)
del tmp
return idx
3.3 模型推理
session_options = ort.SessionOptions()
session_options.register_custom_ops_library(get_library_path())
session_options.log_severity_level = 2 # 日志级别
sess = ort.InferenceSession("./support.onnx", providers=["CPUExecutionProvider"], sess_options=session_options)
四、其他细节
4.1 模型简化
参考:https://github.com/daquexian/onnx-simplifier,新版本会自动跳过自定义算子
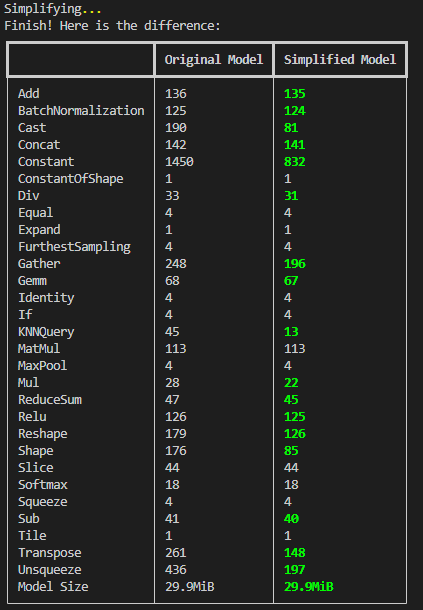
4.2 onnxruntime_extensions完整示例
ref: https://onnxruntime.ai/docs/extensions/add-op.html
def test_Inversion():
import torch
import torch.onnx
# 定义自定义算子(示例:矩阵逆运算 + 恒等连接)
class InverseFunction(torch.autograd.Function):
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, x):
inv_x = torch.inverse(x)
return inv_x + x # 自定义逻辑
@staticmethod
def symbolic(g, x):
# 映射到 ONNX 自定义算子(域名::算子名)
return g.op("ai.onnx.contrib::Inverse2", x) #
# 封装为模型
class CustomModel(torch.nn.Module):
def forward(self, x):
return InverseFunction.apply(x)
# 导出 ONNX 模型
model = CustomModel()
dummy_input = torch.randn(3, 3) # 确保矩阵可逆
torch.onnx.export(
model,
dummy_input,
"custom_inverse.onnx",
input_names=["input_matrix"],
output_names=["output"],
opset_version=12
)
import onnxruntime as ort
import numpy as np
@onnx_op(op_type="Inverse2", domain="ai.onnx.contrib")
def inverse2(x: np.ndarray):
return np.linalg.inv(x) + x
# 加载模型时传递 SessionOptions
# session = ort.InferenceSession("custom_inverse.onnx", providers=["CPUExecutionProvider"])
session = ort.InferenceSession("./custom_inverse.onnx", so, providers=['CPUExecutionProvider'])
# 准备输入(确保矩阵可逆)
input_matrix = np.array([
[1.0, 0.5, 0.0],
[0.2, 1.0, 0.3],
[0.0, 0.1, 1.0]
], dtype=np.float32)
# 运行推理
output = session.run(
output_names=["output"],
input_feed={"input_matrix": input_matrix}
)[0]
print("自定义算子输出:\n", output)
from onnxruntime_extensions import PyOrtFunction
model_func = PyOrtFunction.from_model("./custom_inverse.onnx")
out = model_func(input_matrix)
print("out: ", out)
参考链接
https://github.heygears.com/onnx/tutorials/tree/master/PyTorchCustomOperator
https://onnxruntime.ai/docs/reference/operators/add-custom-op.html
https://onnxruntime.ai/docs/extensions/add-op.html
https://onnxruntime.ai/docs/api/c/struct_ort_custom_op.html
https://github.com/daquexian/onnx-simplifier



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号