JAVA中不同类型内存读写性能差异
数据载体
java中有三种数据载体,当我们进行序列化操作时,必然选择其中之一
- byte[],
- HeapByteBuffer,
- DirectByteBuffer
那么这三种之间数据的读写性能如何呢?
今天我测评了一下,方便今后做性能优化时进行参考
先上结论
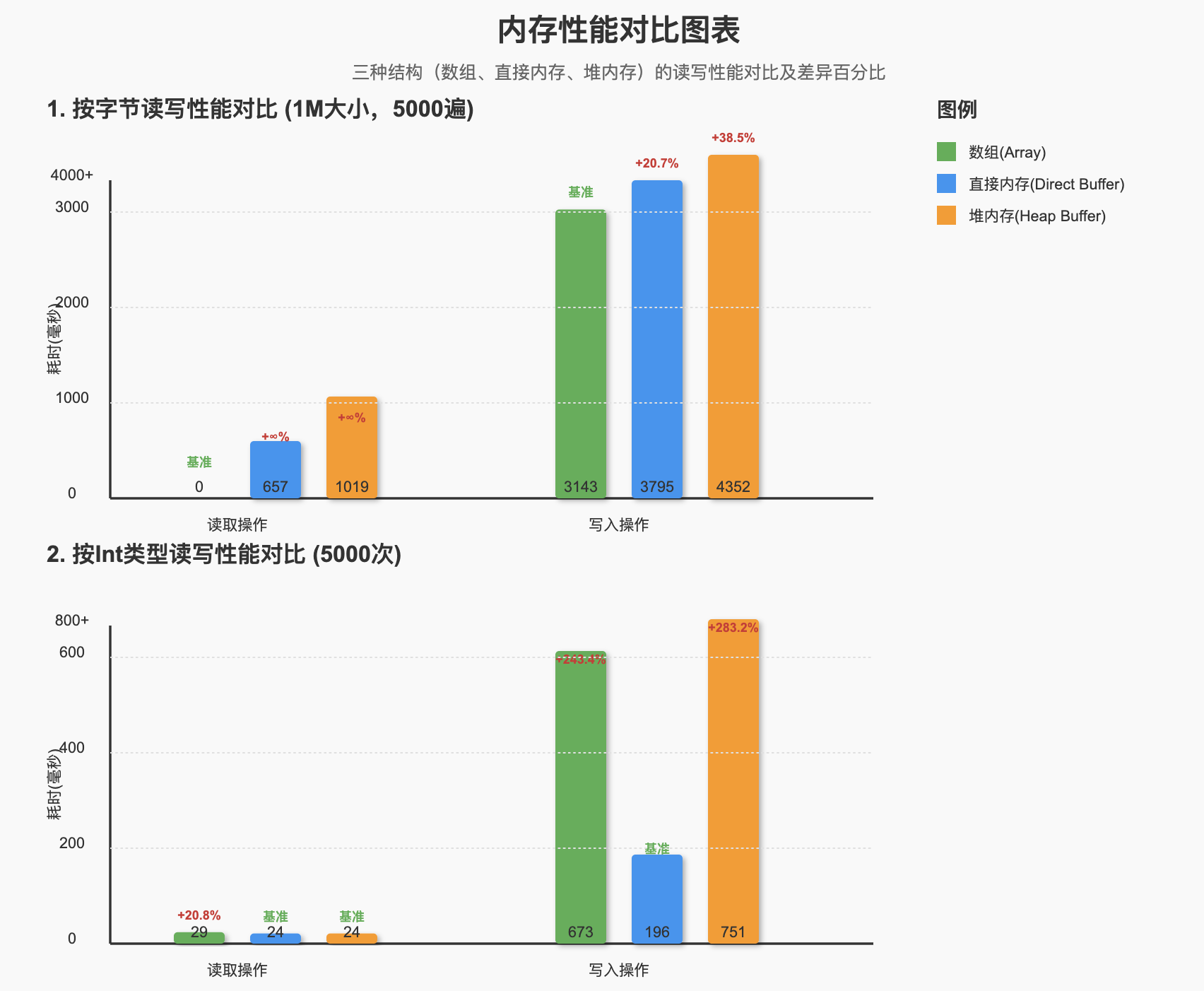
三种结构分别为1M大小,按字节读写5000遍的耗时,单位是毫秒
| 数组(Array) | 直接内存(Direct Buffer) | 堆内存(Heap Buffer) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 读取 | 0 | 657 | 1019 |
| 写入 | 3143 | 3795 | 4352 |
- 在读取方面,byte数组远超Buffer类型
- 直接内存比堆内存相对来说也要快不少
按Int类型的读写5000次耗时
| 数组(Array) | 直接内存(Direct Buffer) | 堆内存(Heap Buffer) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 读取 | 29 | 24 | 24 |
| 写入 | 673 | 196 | 751 |
- 三种结构读取方面,数组略差一些,但总体相差不大
- 写入方面直接内存显著快于其他两种
- 按int类型读写各方面都显著快于按字节读写
性能差异图
测试过程
主流程
private static final int BUFFER_SIZE = 1024 * 1024; // 1MB缓冲区
private static final int INT_COUNT = BUFFER_SIZE / 4; // 可容纳的int数量(每个int占4字节)
private static final int ITERATIONS = 5000; // 操作迭代次数
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteBuffer heapBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(BUFFER_SIZE);
ByteBuffer directBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(BUFFER_SIZE);
byte[] data = new byte[BUFFER_SIZE];
ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextBytes(data);
heapBuffer.put(data);
directBuffer.put(data);
System.out.println("预热开始");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
testIntByIntRead(directBuffer);
testIntByIntRead(heapBuffer);
testIntByIntWrite(heapBuffer);
testIntByIntWrite(directBuffer);
testIntByIntRead(data);
testIntByIntWrite(data);
}
System.out.println("预热结束");
long time;
time = testIntByIntRead(directBuffer);
System.out.println("Direct Buffer read" + ":" + TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMillis(time));
time = testIntByIntRead(heapBuffer);
System.out.println("Heap Buffer read" + ":" + TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMillis(time));
time = testIntByIntRead(data);
System.out.println("Array read" + ":" + TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMillis(time));
time = testIntByIntWrite(heapBuffer);
System.out.println("Heap Buffer write" + ":" + TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMillis(time));
time = testIntByIntWrite(directBuffer);
System.out.println("Direct Buffer write" + ":" + TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMillis(time));
time = testIntByIntWrite(data);
System.out.println("Array write" + ":" + TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMillis(time));
}
按字节读写
// 按byte写
private static long testByteByByteWrite(ByteBuffer buffer) {
long start = System.nanoTime();
for (int i = 0; i < ITERATIONS; i++) {
buffer.clear();
for (int j = 0; j < BUFFER_SIZE; j++) {
buffer.put((byte) (j % 127)); // 逐字节写入
}
}
return System.nanoTime() - start;
}
// 按byte读
private static long testByteByByteRead(ByteBuffer buffer) {
long start = System.nanoTime();
for (int i = 0; i < ITERATIONS; i++) {
buffer.flip();
for (int j = 0; j < BUFFER_SIZE; j++) {
buffer.get(); // 逐字节读取
}
}
return System.nanoTime() - start;
}
// 按byte读(byte数组)
private static long testByteByByteRead(byte[] buffer) {
long start = System.nanoTime();
for (int i = 0; i < ITERATIONS; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < BUFFER_SIZE; j++) {
byte b = buffer[j]; // 逐字节读取
}
}
return System.nanoTime() - start;
}
// 按byte写(byte数组)
private static long testByteByByteWrite(byte[] buffer) {
long start = System.nanoTime();
for (int i = 0; i < ITERATIONS; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < BUFFER_SIZE; j++) {
buffer[j] = (byte) (j % 127); // 逐字节写入
}
}
return System.nanoTime() - start;
}
按int读写
// 按int写
private static long testIntByIntWrite(ByteBuffer buffer) {
long start = System.nanoTime();
for (int i = 0; i < ITERATIONS; i++) {
buffer.clear();
for (int j = 0; j < INT_COUNT; j++) {
buffer.putInt(j); // 逐int写入
}
}
return System.nanoTime() - start;
}
// 按int读
private static long testIntByIntRead(ByteBuffer buffer) {
long start = System.nanoTime();
for (int i = 0; i < ITERATIONS; i++) {
buffer.flip();
for (int j = 0; j < INT_COUNT; j++) {
buffer.getInt(); // 逐int读取
}
}
return System.nanoTime() - start;
}
// 按int写(byte数组)
private static long testIntByIntWrite(byte[] buffer) {
long start = System.nanoTime();
for (int i = 0; i < ITERATIONS; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < INT_COUNT; j++) {
intToBytesLittleEndian(j,buffer,j*4); // 逐int写入
}
}
return System.nanoTime() - start;
}
// 按int读(byte数组)
private static long testIntByIntRead(byte[] buffer) {
long start = System.nanoTime();
for (int i = 0; i < ITERATIONS; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < INT_COUNT; j++) {
bytesToIntLittleEndian(buffer,j*4); // 逐int读取
}
}
return System.nanoTime() - start;
}
测试过程如有问题,欢迎指出

【广告】微信小程序 - “两步动态验证”
- 兼容谷歌验证码 :无缝支持Google Authenticator等标准TOTP验证器,通用各类平台账号
- 云端加密备份 :密钥数据端到端加密上传云端,换机不丢失,安全又便捷
- API快速集成 :提供开放API,轻松对接各类应用系统,实现自动化验证码获取
- 多端共享:基于微信小程度,可同时在手机,PC端共同使用,一键复制
- 扫描二维码试用,或微信小程序搜索“两步动态验证”





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号