css层级选择器理论{#ek)
- E:first-child : 匹配的是E元素,E元素是父元素的第一个子元素
说明:利用 :first-child 这个伪类,只有当元素是另一个元素的第一个子元素时才能匹配。例如,p:first-child 会选择作为另外某个元素第一个子元素的所有 p 元素。一般可能认为这会选择作为段落第一个子元素的元素,但事实上并非如此,如果要选择段落的第一个子元素,应当写为 p > *:first-child。
- E:last-child : 匹配的是E元素,E元素是父元素的最后一个子元素
- E:nth-child(n): 匹配的是E元素,且E元素是父元素的正数第n个子元素
- E:nth-last-child(n): 匹配的是E元素,且E元素是父元素的倒数第n个子元素
- E:first-of-type: 匹配E元素,在所有的E元素中选择第一个子元素为E的元素
- E:last-of-type: 匹配E元素,在所有的E元素中选择倒数第一个子元素为E的元素
- E:nth-of-type(n): 匹配E元素,在所有的E元素中选择正数第n个子元素为E的元素
- E:nth-last-of-type(n): 匹配E元素,在所有的E元素中选择倒数第n个子元素为E的元素
nth中n的用法
- 数字
- odd: 奇数
- even: 偶数
- n+8: 8以后的
- -n+3: 前3个
代码展示
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>层级选择器</title>
<style>
ul{width: 100px;}
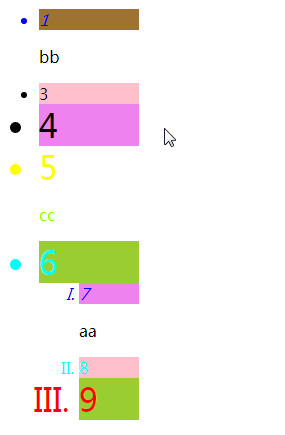
/* 1,7亮 */
li:first-child{color: blue;}
/* 9亮 6不亮是因为ul标签最后一个是ol,不是li*/
li:last-child{color: red;}
/* nth-child先数数再看是否匹配li */
li:nth-child(5){color: yellow;}
/* cc亮 */
p:nth-child(6){color: chartreuse;}
/* 8,6亮 ,在ul中6是倒数第二*/
li:nth-last-child(2){color: cyan;}
/* 没反应,因为ul和ol倒数第三都是p标签 */
li:nth-last-child(3){color: darkgoldenrod;}
/* 有过滤的功能 */
/* 1,7背景亮 */
li:first-of-type{background-color: rgb(158, 114, 49);}
/* 9,6亮,因为ul标签中过滤掉最后一个ol,选中li */
li:last-of-type{background-color: yellowgreen;}
/* 3,8亮 */
li:nth-of-type(2){background-color: pink;}
/* 4,7亮 */
li:nth-last-of-type(3){background-color: violet;}
/* li标签从第三个开始往后字体都相对于父元素都加倍大 */
li:nth-of-type(n+3){font-size: 2em;}
/* 1,7斜体 */
li:nth-child(-n+2){font-style: italic;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li>1</li>
<p>bb</p>
<li>3</li>
<li>4</li>
<li>5</li>
<p>cc</p>
<li>6</li>
<ol type="I">
<li>7</li>
<p>aa</p>
<li>8</li>
<li>9</li>
</ol>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
![]()


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号