自我测试
本篇文章的测试用例及调试方法见前言
说明
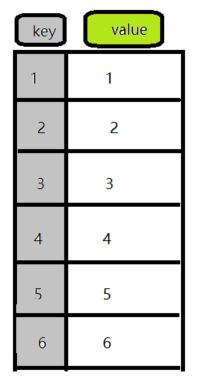
是由一组无序且唯一(即不能重复)的项组成的,以[值,值]的形式存储元素。这个数据结构使用了与有限集合相同的数学概念,但应用在计算机科学的数据结构中。
运算
集合有并集,交集,差集,子集这几种运算
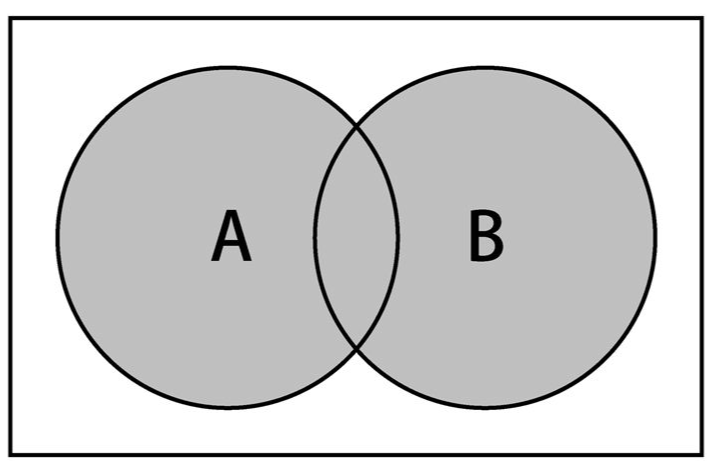
并集:对于给定的两个集合,返回一个包含两个集合中所有元素的新集合。
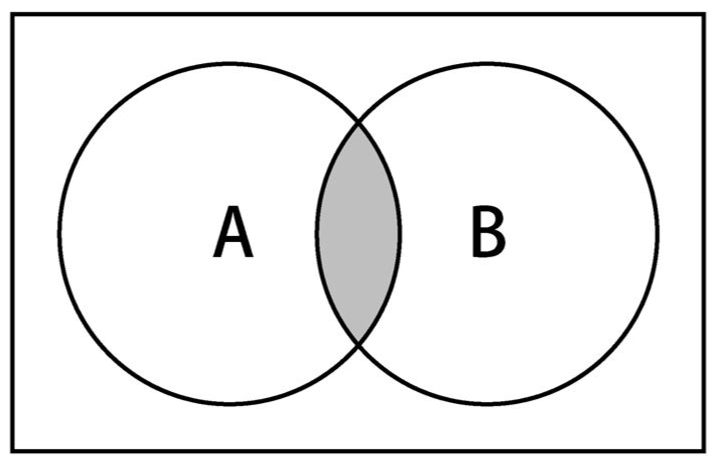
交集:对于给定的两个集合,返回一个包含两个集合中共有元素的新集合。
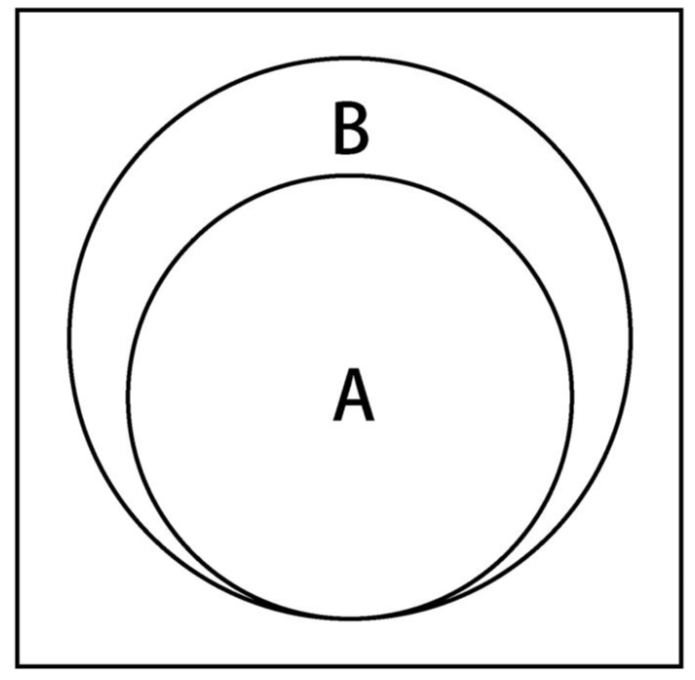
差集:对于给定的两个集合,返回一个包含所有存在于第一个集合且不存在于第二个集合的元素的新集合。

子集:验证一个给定集合是否是另一集合的子集。
简单图解
一个集合的基本方法
- add(value) : 添加一个(或几个)新元素到集合中
- delete(value) : 删除集合中元素,并返回
- has(value) : 判断集合中是否有该值
- values() : 返回一个包含集合中所有值的数组。
- isEmpty() : 判断集合中是否有元素
- clear() : 移除集合中的所有元素
- size() : 返回集合的元素个数
- union() : 并集
- intersection() : 交集
- difference() : 差集
- isSubsetOf() : 子集
集合实现
export default class Set<T> {
items: any;
count: number;
constructor() {
this.items = {};
this.count = 0;
}
/**
* 判断是否有这个元素
* @param element
*/
has(element: any) {
return Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(this.items, element)
}
/**
* 添加一个元素到对象中
* 如果有就返回false,无就添加并返回true
* @param element
*/
add(element: T) {
if (this.has(element)) {
return false;
}
//将元素添加到集合中
this.items[element] = element;
//记得维护个数
this.count++;
return true;
}
/**
* 删除集合中的一个元素
* 如果没有就返回false,有就删除并返回true
* @param element
*/
delete(element: T) {
if (this.has(element)) {
delete this.items[element];
//记得维护个数
this.count--;
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 以数组的形式返回集合中的所有元素
*/
values() {
let result = [];
let items = this.items;
for (const key in items) {
result.push(items[key])
}
return result;
}
/**
* 返回集合大小
*/
size() {
return this.count;
}
/**
* 是否有元素
*/
isEmpty() {
return this.count === 0;
}
/**
* 清空集合
*/
clear() {
this.items = {};
this.count = 0;
}
/**
* 并集
* 这里可以利用add不会重复的性质
* @param set
*/
union(set: Set<T>) {
let unionSet = new Set<T>();
this.values().forEach((value) => {
unionSet.add(value);
})
set.values().forEach((value) => {
unionSet.add(value);
})
return unionSet;
}
/**
* 交集
* @param set
*/
intersection(set: Set<T>) {
let intersectionSet = new Set<T>();
let lowSet = this.values();
lowSet.forEach((val) => {
if (set.has(val)) {
intersectionSet.add(val);
}
})
return intersectionSet;
}
/**
* 差集
* 当前集合中 包含 传入集合 不存在的元素
* @param set
*/
difference(set: Set<T>) {
let differenceSet = new Set<T>();
this.values().forEach((val) => {
if (!set.has(val)) {
differenceSet.add(val);
}
})
return differenceSet;
}
/**
* 子集
* 当前集合是否为传入的集合的子集
* @param set
*/
isSubsetOf(set: Set<T>) {
//当前集合小于传入集合
if(this.count > set.count){
return false;
}
//如果当前集合中的值都在传入的集合中,那么就说明是子集
for (let i = 0,values = this.values(), len = values.length; i < len; i++) {
if (!set.has(values[i])) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
toString() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return '';
}
const values = this.values();
let objString = `${values[0]}`;
for (let i = 1; i < values.length; i++) {
objString = `${objString},${values[i].toString()}`;
}
return objString;
}
}
书中代码
export default class Set<T> {
private items: any;
constructor() {
this.items = {};
}
add(element: T) {
if (!this.has(element)) {
this.items[element] = element;
return true;
}
return false;
}
delete(element: T) {
if (this.has(element)) {
delete this.items[element];
return true;
}
return false;
}
has(element: T) {
// return this.items.hasOwnProperty(element);
return Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(this.items, element);
}
values(): T[] {
return Object.values(this.items);
}
union(otherSet: Set<T>) {
const unionSet = new Set<T>();
this.values().forEach(value => unionSet.add(value));
otherSet.values().forEach(value => unionSet.add(value));
return unionSet;
}
intersection(otherSet: Set<T>) {
const intersectionSet = new Set<T>();
const values = this.values();
const otherValues = otherSet.values();
let biggerSet = values;
let smallerSet = otherValues;
if (otherValues.length - values.length > 0) {
biggerSet = otherValues;
smallerSet = values;
}
smallerSet.forEach(value => {
if (biggerSet.includes(value)) {
intersectionSet.add(value);
}
});
return intersectionSet;
}
difference(otherSet: Set<T>) {
const differenceSet = new Set<T>();
this.values().forEach(value => {
if (!otherSet.has(value)) {
differenceSet.add(value);
}
});
return differenceSet;
}
isSubsetOf(otherSet: Set<T>) {
if (this.size() > otherSet.size()) {
return false;
}
let isSubset = true;
this.values().every(value => {
if (!otherSet.has(value)) {
isSubset = false;
return false;
}
return true;
});
return isSubset;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.size() === 0;
}
size() {
return Object.keys(this.items).length;
}
clear() {
this.items = {};
}
toString() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return '';
}
const values = this.values();
let objString = `${values[0]}`;
for (let i = 1; i < values.length; i++) {
objString = `${objString},${values[i].toString()}`;
}
return objString;
}
}
leetcode对应训练
如果对你有帮助,下次再见,嘻嘻



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号