自我测试
本篇文章的测试用例及调试方法见前言
说明
栈是一种遵循后进先出(LIFO)原则的有序集合.新添加元素或待删除的元素都保存在同一端,称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底,新的元素靠近栈顶,旧元素接近栈底.
作用
栈也被用在编程语言的编译器和内存中保存变量,方法调用等,也被用于浏览器历史记录(浏览器的返回按钮).栈的实际应用非常广泛.在回溯问题中,它可以存储访问过的任务或路径,撤销操作.Java和C#用栈来存储变量和方法的调用,特别是处理递归算法的时,有可能抛出一个栈溢出异常
简单图解
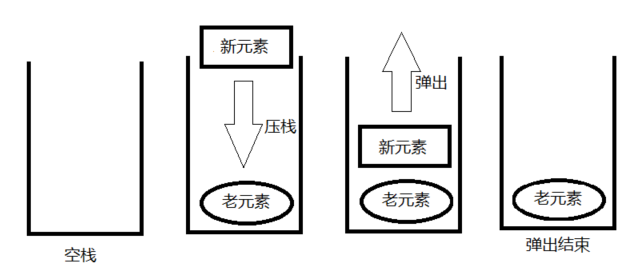
可以看到栈的数据结构只有一个口,进出数据都走这个口,这也导致了它有后进先出(LIFO)的原则,有点像是一种思想或者是一种约定吧!!!
一个栈基本方法
- push(element(s)) : 添加一个(或几个)新元素到栈顶
- pop() : 弹出栈顶元素,并返回
- peek() : 获取栈顶元素
- isEmpty() : 判断栈中是否有元素
- clear() : 移除栈中的所有元素
- size() : 返回栈的元素个数
使用数组编写一个栈
export class StackArray{
// 栈的元素多少 这里可以去掉,直接那数组的length属性
private stackSize:number = 0;
// 栈内部元素
private stackList:Array<any> = [];
//构造函数
constructor() {
}
// 添加一个或者多个元素
push(...elements : any){
this.stackList = this.stackList.concat(elements);
this.stackSize += elements.length;
return;
}
// 弹出栈顶元素,并返回
pop(){
if(this.stackSize > 0){
this.stackSize--;
// return this.stackList.splice(this.size, 1);
return this.stackList.pop();
}
}
// 获取栈顶元素
peek(){
return this.stackList[this.stackSize - 1];
}
// 判断栈中是否有元素
isEmpty(){
return this.stackSize <= 0;
}
// 移除栈中的所有元素
clear(){
this.stackList.splice(0, this.stackSize);
this.stackSize = 0;
}
// 获取元素个数
size(){
return this.stackSize;
}
}
使用对象编写一个栈
export class StackObject{
// 栈的元素多少
private stackSize:number = 0;
// 栈内部元素
private stackObject:any = {};
//构造函数
constructor() {
}
// 添加一个或者多个元素
push(...elements : any){
elements.forEach((element:any) => {
this.stackObject[++this.stackSize] = element;
})
}
// 弹出栈顶元素,并返回
pop(){
if(this.stackSize > 0){
let result = this.stackObject[this.stackSize];
delete this.StackObject[this.stackSize];
this.stackSize--;
return result;
}
}
// 获取栈顶元素
peek(){
return this.stackObject[this.stackSize];
}
// 判断栈中是否有元素
isEmpty(){
return this.stackSize <= 0;
}
// 移除栈中的所有元素
clear(){
this.stackObject = {};
this.stackSize = 0;
}
// 获取元素个数
size(){
return this.stackSize;
}
}
书中代码
数组版
export default class StackArray<T> {
private items: T[];
constructor() {
this.items = [];
}
push(element: T) {
this.items.push(element);
}
pop() {
return this.items.pop();
}
peek() {
return this.items[this.items.length - 1];
}
isEmpty() {
return this.items.length === 0;
}
size() {
return this.items.length;
}
clear() {
this.items = [];
}
toArray() {
return this.items;
}
toString() {
return this.items.toString();
}
}
对象版
export default class Stack<T> {
private count: number;
private items: any;
constructor() {
this.count = 0;
this.items = {};
}
push(element: T) {
this.items[this.count] = element;
this.count++;
}
pop() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return undefined;
}
this.count--;
const result = this.items[this.count];
delete this.items[this.count];
return result;
}
peek() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return undefined;
}
return this.items[this.count - 1];
}
isEmpty() {
return this.count === 0;
}
size() {
return this.count;
}
clear() {
/* while (!this.isEmpty()) {
this.pop();
} */
this.items = {};
this.count = 0;
}
toString() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return '';
}
let objString = `${this.items[0]}`;
for (let i = 1; i < this.count; i++) {
objString = `${objString},${this.items[i]}`;
}
return objString;
}
}
leetcode对应训练
如果对你有帮助,下次再见,嘻嘻



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号