使用C#调用Yolo26模型的ONNX
ONNX 和 ONNX Runtime
ONNX,即开放式神经网络交换,是由 Facebook 和 Microsoft 最初开发的社区项目。ONNX 的持续开发是一项协作努力,得到了 IBM、Amazon(通过 AWS)和 Google 等各种组织的支持。该项目旨在创建一种开放文件格式,用于以允许跨不同 AI 框架和硬件使用机器学习模型的方式来表示它们。将 Ultralytics YOLO26 模型导出为 ONNX 格式可简化部署,并确保在各种环境中实现最佳性能。由于讨厌CSDN的收费文章,作者自己研究了如何在C#中使用yolo导出的onnx模型实现图像检测功能,并支持最新的yolo26,免费分享给大家。
演示效果如:
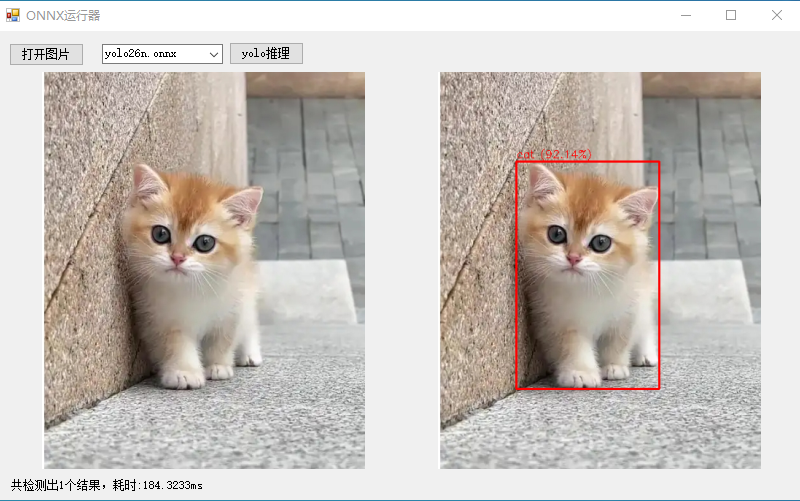
代码:
using OpenCvSharp; using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Drawing; using System.Windows.Forms; namespace onnxRuner { public partial class Form1 : Form { string image_path; string mode_path= "modes/";//模型文件路径 yolo26n.onnx yolov8n.onnx yolo11n.onnx public Form1() { InitializeComponent(); cmbModes.SelectedIndex = 0; } private void btnOpenFile_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { OpenFileDialog ofd=new OpenFileDialog(); ofd.Filter = "图片文件|*.jpg;*.jpeg;*.png;*.bmp;"; if (ofd.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK) { image_path = ofd.FileName; pictureBox1.Image = new Bitmap(image_path); } } private void btnRunYoloOnnx_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { if (image_path == "") { return; } pictureBox2.Image = null; lbmsg.Text = ""; Application.DoEvents(); //初始化YOLO实例 参数填你的onnx模型路径即可 using (var yolo = new YoloOnnxDetector(mode_path+cmbModes.Text)) { // 加载待检测图像 using (var image = new Mat(image_path)) { // 进行推理 DateTime dt1 = DateTime.Now; List<Prediction> predictions = yolo.Predict(image); // 在图像上绘制检测结果 foreach (var pred in predictions) { Cv2.Rectangle(image, pred.Box, Scalar.Red, 2); string label = $"{pred.Label} ({pred.Confidence:P2})"; Cv2.PutText(image, label, new OpenCvSharp.Point(pred.Box.X, pred.Box.Y - 5), HersheyFonts.HersheySimplex, 0.5, Scalar.Red, 1); } // 显示或保存结果图像 pictureBox2.Image = new Bitmap(image.ToMemoryStream()); lbmsg.Text =$"共检测出{predictions.Count}个结果,耗时:{(DateTime.Now-dt1).TotalMilliseconds}ms"; } } } } }
核心类:
using Microsoft.ML.OnnxRuntime; using Microsoft.ML.OnnxRuntime.Tensors; using OpenCvSharp; using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; namespace onnxRuner { /// <summary> /// YOLO ONNX 目标检测器类 /// 实现完整的图像预处理、模型推理、后处理流程 /// </summary> public class YoloOnnxDetector : IDisposable { private InferenceSession _session; // ONNX Runtime 推理会话实例 private readonly Size _modelSize = new Size(640, 640); // YOLOv8标准输入尺寸 bool _isYolo26 = false;//yolo26特殊格式 public Dictionary<int, string> _Names = new Dictionary<int, string>(0);//类别名称字典 /// <summary> /// 构造函数 - 初始化 YOLOv8 ONNX 检测器 /// 功能:创建ONNX推理会话,加载类别标签,准备模型运行环境 /// 注意:此构造函数会加载整个模型到内存,耗时操作应在程序初始化时执行 /// </summary> /// <param name="modelPath">ONNX模型文件路径(.onnx文件)</param> public YoloOnnxDetector(string modelPath) { // 初始化ONNX Runtime推理会话,加载模型文件 _session = new InferenceSession(modelPath); var metadata = _session.ModelMetadata.CustomMetadataMap; if (metadata.ContainsKey("description")) { _isYolo26 = metadata["description"].Contains("YOLO26"); } if (metadata.ContainsKey("names")) { _Names = ParseNames(metadata["names"]); } } private Dictionary<int, string> ParseNames(string names) { var nameList = names.TrimStart('{').TrimEnd('}').Split(','); var list = new Dictionary<int, string>(nameList.Length); foreach (var it in nameList) { int index = it.IndexOf(":"); if (int.TryParse(it.Substring(0, index), out int i)) list.Add(i, it.Substring(index + 2).Trim('\'')); } return list; } /// <summary> /// 主预测函数 - 执行完整的目标检测流程 /// 功能:协调预处理、模型推理、后处理三个核心步骤 /// 这是类的主要对外接口,接收原始图像返回检测结果 /// </summary> /// <param name="image">输入的OpenCV Mat图像对象</param> /// <returns>检测结果列表,包含边界框、置信度、类别标签</returns> public List<Prediction> Predict(Mat image) { // 步骤1:图像预处理 - 将原始图像转换为模型输入格式 var input = PreprocessImage(image); // 步骤2:准备模型输入 - 创建ONNX Runtime可识别的输入对象 var inputs = new List<NamedOnnxValue> { NamedOnnxValue.CreateFromTensor("images", input) // 输入名称必须与模型匹配 }; // 步骤3:模型推理 - 执行ONNX模型前向计算 using (IDisposableReadOnlyCollection<DisposableNamedOnnxValue> results = _session.Run(inputs)) { // 步骤4:后处理 - 解析模型输出,应用过滤和优化 return Postprocess(results, image); } } /// <summary> /// 图像预处理函数 /// 功能:将原始BGR图像转换为YOLOv8模型期望的输入格式 /// 处理流程: /// 1. 调整图像尺寸到640x640(保持长宽比可能会丢失,实际应用可改进) /// 2. 转换色彩空间BGR→RGB(模型训练通常使用RGB格式) /// 3. 像素值归一化到[0,1]范围(提高模型数值稳定性) /// 4. 转换为NCHW格式张量[1,3,640,640](模型标准输入格式) /// </summary> /// <param name="image">原始OpenCV图像(BGR格式,任意尺寸)</param> /// <returns>预处理后的4维张量,可直接输入ONNX模型</returns> private DenseTensor<float> PreprocessImage(Mat image) { // 步骤1:调整图像尺寸到模型输入大小(640x640) // 注意:此处直接缩放可能失真,生产环境建议保持宽高比 Mat resized = new Mat(); Cv2.Resize(image, resized, _modelSize); // 步骤2:转换色彩空间 BGR → RGB // OpenCV默认BGR格式,但大多数模型训练使用RGB格式 Mat rgb = new Mat(); Cv2.CvtColor(resized, rgb, ColorConversionCodes.BGR2RGB); // 步骤3:创建4维张量 [batch_size=1, channels=3, height=640, width=640] var tensor = new DenseTensor<float>(new[] { 1, 3, _modelSize.Height, _modelSize.Width }); // 步骤4:逐像素处理,填充张量数据 // 使用嵌套循环确保数据布局正确,避免内存拷贝错误 for (int y = 0; y < rgb.Height; y++) { for (int x = 0; x < rgb.Width; x++) { // 获取RGB像素值 Vec3b pixel = rgb.At<Vec3b>(y, x); // 归一化到[0,1]并按照NCHW格式填充 tensor[0, 0, y, x] = pixel[0] / 255.0f; // R通道 tensor[0, 1, y, x] = pixel[1] / 255.0f; // G通道 tensor[0, 2, y, x] = pixel[2] / 255.0f; // B通道 } } return tensor; } /// <summary> /// 后处理函数 - 解析模型原始输出并提取有意义信息 /// 功能:将模型输出的数值张量转换为实际检测结果 /// 处理流程: /// 1. 提取模型输出张量([1,84,8400]格式) /// 2. 解析每个检测框的坐标和类别置信度 /// 3. 应用置信度阈值过滤低质量检测 /// 4. 将归一化坐标转换回原始图像像素坐标 /// 5. 应用非极大值抑制去除重复检测 /// </summary> /// <param name="results">ONNX Runtime推理结果集合</param> /// <param name="originalImage">原始图像(用于坐标映射)</param> /// <returns>结构化检测结果列表</returns> private List<Prediction> Postprocess(IDisposableReadOnlyCollection<DisposableNamedOnnxValue> results, Mat originalImage) { var predictions = new List<Prediction>(); float confidenceThreshold = 0.5f; // 置信度阈值,过滤不可靠检测 // 步骤1:获取模型输出张量(假设第一个输出包含检测结果) if (_isYolo26) { if (results[0].Value is DenseTensor<float> tensor) { // 检查维度: [1, 300, 6],YOLO26模型输出格式 if (tensor.Dimensions.Length < 3 || tensor.Dimensions[2] != 6) return null; int detectionsCount = tensor.Dimensions[1]; // 检测框数量 int featureSize = 6; // 每个检测框的特征数量:x1,y1,x2,y2,confidence,class var tensorSpan = tensor.Buffer.Span; for (int i = 0; i < detectionsCount; i++) { int offset = i * featureSize; float score = tensorSpan[offset + 4]; // 置信度 if (score <= confidenceThreshold) continue; // 跳过置信度低的检测框 // 读取边界框坐标 float x1 = tensorSpan[offset + 0], y1 = tensorSpan[offset + 1], x2 = tensorSpan[offset + 2], y2 = tensorSpan[offset + 3]; x1 = x1 * originalImage.Width / _modelSize.Width; x2 = x2 * originalImage.Width / _modelSize.Width; y1 = y1 * originalImage.Height / _modelSize.Height; y2 = y2 * originalImage.Height / _modelSize.Height; // 步骤2.5:确保坐标在图像边界内(防止越界错误) x1 = Math.Max(0, Math.Min(x1, originalImage.Width)); y1 = Math.Max(0, Math.Min(y1, originalImage.Height)); x2 = Math.Max(0, Math.Min(x2, originalImage.Width)); y2 = Math.Max(0, Math.Min(y2, originalImage.Height)); // 计算边界框尺寸 predictions.Add(new Prediction { Box = new Rect((int)x1, (int)y1, (int)(x2 - x1), (int)(y2 - y1)), Confidence = score, Label = _Names[(int)tensorSpan[offset + 5]] }); } } } else { var output = results.First().AsTensor<float>(); // YOLOv5-v12输出维度解析:[batch_size, dimensions, num_proposals] // [1, 84, 8400] - 1:批大小, 84:4坐标+80类别, 8400:锚点数量 int dimensions = output.Dimensions[1]; // 84 = 4(box) + 80(coco classes) int numProposals = output.Dimensions[2]; // 8400个检测提议 // 步骤2:遍历所有检测提议(8400个) for (int i = 0; i < numProposals; i++) { // 步骤2.1:提取类别置信度,找到最大置信度类别 float maxConfidence = 0f; int classId = -1; // 遍历所有类别,找到置信度最高的类别 for (int j = 4; j < dimensions; j++) { float confidence = output[0, j, i]; if (confidence > maxConfidence) { maxConfidence = confidence; classId = j - 4; // 减去4个坐标维度得到类别索引 } } // 步骤2.2:应用置信度阈值过滤 if (maxConfidence > confidenceThreshold && classId >= 0) { // 步骤2.3:解析边界框坐标 [center_x, center_y, width, height] float cx = output[0, 0, i]; // 边界框中心x坐标(归一化) float cy = output[0, 1, i]; // 边界框中心y坐标(归一化) float w = output[0, 2, i]; // 边界框宽度(归一化) float h = output[0, 3, i]; // 边界框高度(归一化) // 步骤2.4:将归一化坐标转换为原始图像像素坐标 // 从中心点格式转换为左上角坐标格式 float x1 = (cx - w / 2) * originalImage.Width / _modelSize.Width; float y1 = (cy - h / 2) * originalImage.Height / _modelSize.Height; float x2 = (cx + w / 2) * originalImage.Width / _modelSize.Width; float y2 = (cy + h / 2) * originalImage.Height / _modelSize.Height; // 步骤2.5:确保坐标在图像边界内(防止越界错误) x1 = Math.Max(0, Math.Min(x1, originalImage.Width)); y1 = Math.Max(0, Math.Min(y1, originalImage.Height)); x2 = Math.Max(0, Math.Min(x2, originalImage.Width)); y2 = Math.Max(0, Math.Min(y2, originalImage.Height)); // 步骤2.6:创建检测结果对象并添加到列表 predictions.Add(new Prediction { Box = new Rect((int)x1, (int)y1, (int)(x2 - x1), (int)(y2 - y1)), Confidence = maxConfidence, Label = _Names[classId] }); } } } // 步骤3:应用非极大值抑制去除重叠检测框 return ApplyNMS(predictions); } /// <summary> /// 非极大值抑制函数 (NMS - Non-Maximum Suppression) /// 功能:消除重叠的检测框,保留每个物体最好的检测结果 /// 算法原理: /// 1. 按置信度降序排序所有检测框 /// 2. 选择置信度最高的框作为基准 /// 3. 计算其他框与基准框的IoU(交并比) /// 4. 移除IoU超过阈值的框(认为检测的是同一物体) /// 5. 重复2-4步骤直到处理完所有框 /// </summary> /// <param name="predictions">原始检测结果列表(可能包含重叠框)</param> /// <param name="iouThreshold">IoU阈值,默认0.5(超过此值认为重叠需要抑制)</param> /// <returns>过滤后的检测结果列表(无重叠框)</returns> private List<Prediction> ApplyNMS(List<Prediction> predictions, float iouThreshold = 0.5f) { // 步骤1:按置信度降序排序(置信度高的优先处理) var sorted = predictions.OrderByDescending(p => p.Confidence).ToList(); var selected = new List<Prediction>(); // 最终选择的检测框 // 步骤2:迭代处理,直到所有框都被检查 while (sorted.Count > 0) { // 取出当前置信度最高的框(总是列表第一个) var current = sorted[0]; selected.Add(current); // 添加到最终结果 sorted.RemoveAt(0); // 从待处理列表移除 // 步骤3:检查剩余框与当前框的重叠度 // 倒序遍历避免索引错位问题 for (int i = sorted.Count - 1; i >= 0; i--) { // 计算当前框与待检查框的IoU if (CalculateIoU(current.Box, sorted[i].Box) > iouThreshold) { // IoU超过阈值,认为检测的是同一物体,移除置信度较低的框 sorted.RemoveAt(i); } } } return selected; } /// <summary> /// 交并比计算函数 (IoU - Intersection over Union) /// 功能:计算两个矩形框的重叠程度,用于衡量检测框的相似性 /// 数学公式:IoU = 交集面积 / 并集面积 /// 取值范围:[0, 1],0表示无重叠,1表示完全重叠 /// </summary> /// <param name="a">第一个矩形框</param> /// <param name="b">第二个矩形框</param> /// <returns>IoU值,范围0-1,值越大表示重叠越多</returns> private float CalculateIoU(Rect a, Rect b) { // 步骤1:计算两个矩形的交集区域 var inter = a.Intersect(b); // 步骤2:检查是否有有效交集(宽度或高度为0表示无交集) if (inter.Width <= 0 || inter.Height <= 0) return 0; // 无重叠,IoU为0 // 步骤3:计算交集面积 float interArea = inter.Width * inter.Height; // 步骤4:计算并集面积 = 面积A + 面积B - 交集面积 float unionArea = a.Width * a.Height + b.Width * b.Height - interArea; // 步骤5:计算IoU比率 return interArea / unionArea; } /// <summary> /// 资源释放函数 - 实现IDisposable接口 /// 功能:正确释放ONNX Runtime占用的非托管资源 /// 重要性:防止内存泄漏,确保推理会话正确关闭 /// 使用模式:推荐使用using语句或确保在程序退出时调用 /// </summary> public void Dispose() { _session?.Dispose(); // 安全释放ONNX Runtime会话资源 } } /// <summary> /// 检测结果数据封装类 /// 功能:以结构化形式存储单个检测结果的所有信息 /// 设计目的:便于数据传递、序列化和可视化处理 /// </summary> public class Prediction { /// <summary> /// 检测框位置和尺寸 /// 使用OpenCvSharp的Rect结构,包含X,Y,Width,Height属性 /// 坐标单位为像素,相对于原始图像 /// </summary> public Rect Box { get; set; } /// <summary> /// 检测置信度 /// 取值范围:[0,1],表示模型对该检测结果的置信程度 /// 通常用于过滤低质量检测(如阈值0.5) /// </summary> public float Confidence { get; set; } /// <summary> /// 检测到的物体类别名称 /// 从标签文件加载,如"person", "car", "dog"等 /// 对应COCO数据集或其他自定义数据集的类别 /// </summary> public string Label { get; set; } } }
测试了yolov8n.onnx yolo11n.onnx yolo26n.onnx 都是没有问题的。
参考开源:
GitHub - Eviav/YoloSharp: 🤖 基于 ONNX Runtime 的 YOLO 目标检测库,支持多种 YOLO 模型,包括 YOLO26,提供了简洁易用的 C# API
以上两个开源功能更强大,更新也很快,大家也可直接使用。
还是喜欢博客园,这里的博主都是免费分享知识,分享的快乐CSDN们不懂。
-----------------------------------------------------------------
- 我做的各种程序们
- 小y的QQ:28657321 (欢迎交流)




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号