题目集4~6的总结
前三次作业总结
前言:
题目集4:
7-1:考察对正则表达式的使用以及对输入字符串数据进行合法性校验及计算。使用Pattern和Matches方法简单获取键盘输入的字符串,逐个校对判断是否符合实现设计的字符串格式。难度高。
7-2:将多个类连接起来,创建DateUtil、Year、Month、Day类,完善各个类中的功能,再根据类图将每个类正确地连接起来。
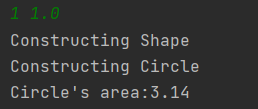
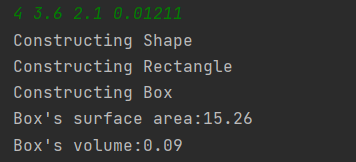
7-3:实现图形类的继承,并定义相应类对象并进行测试。创建父类定义属性和方法,根据类图创建对应的子类,使用 extends、super 等关键字来实现继承。
题目集5:
7-1:找出最长的单词,通过split方法用空格将输入的字符串分成单个的单词,用length得到每个单词的长度后,找出最长的单词并输出。
7-2:合并两个有序数组为新的有序数组,先分别接收两个数组,再将它们连接起来,使用一种排序方式重新改变数组的顺序最后输出。
7-3:编写三种排序方法,插入排序:在要排序的一组数中,假定前n-1个数已经排好序,现在将第n个数插到前面的有序数列中,使得这n个数也是排好顺序的。如此反复循环,直到全部排好顺序。 选择排序:在长度为N的无序数组中,第一次遍历n-1个数,找到最小的数值与第一个元素交换,第二次遍历n-2个数,找到最小的数值与第二个元素交换,第n-1次遍历,找到最小的数值与第n-1个元素交换,排序完成。冒泡排序:比较相邻的两个数据,如果第二个数小,就交换位置。从后向前两两比较,一直到比较最前两个数据。最终最小数被交换到起始的位置,这样第一个最小数的位置就排好了。继续重复上述过程,依次将第2.3...n-1个最小数排好位置。
7-4:统计Java程序中关键词的出现次数 ,使用使用Pattern和Matches方法简单获取键盘输入的字符串,将其分成单个的单词,统计每个java关键字出现的次数。难度高。
7-5:将多个类连接起来,创建DateUtil、Year、Month、Day类,完善各个类中的功能,再根据类图将每个类正确地连接起来。
题目集6:
7-1:在java中使用正则表达式,用Pattern和Matches简单匹配数字。
7-2:接受字符串使用toCharArray()将每个字符分出,再使用Arrays.sort()根据ASCII码排序。
7-3:在java中使用正则表达式,用Pattern和Matches检测输入的字符串是否是四位数字或者字母(包含大小写)组成的字符串。
7-4:在java中使用正则表达式,用Pattern和Matches简单匹配数字,同时把数字分为多个部分检验。
7-5:图形继承与多态 ,根据题目要求完善功能,将每个类用继承的方法连接。
设计与分析:
①题目集4(7-2)、题目集5(7-4)两种日期类聚合设计的优劣比较:
7-2
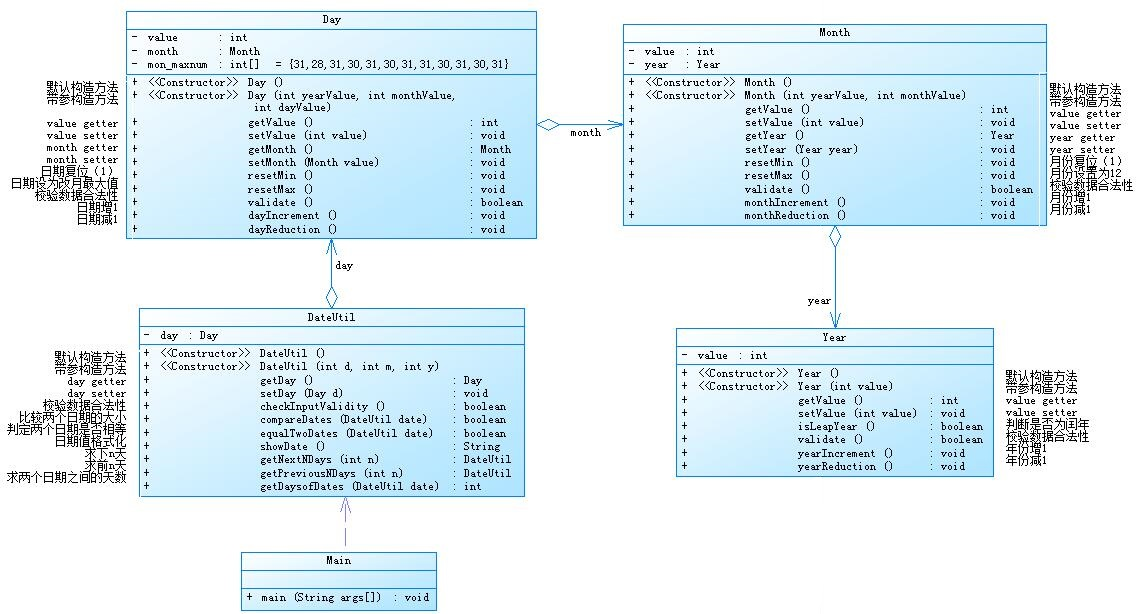
7-4
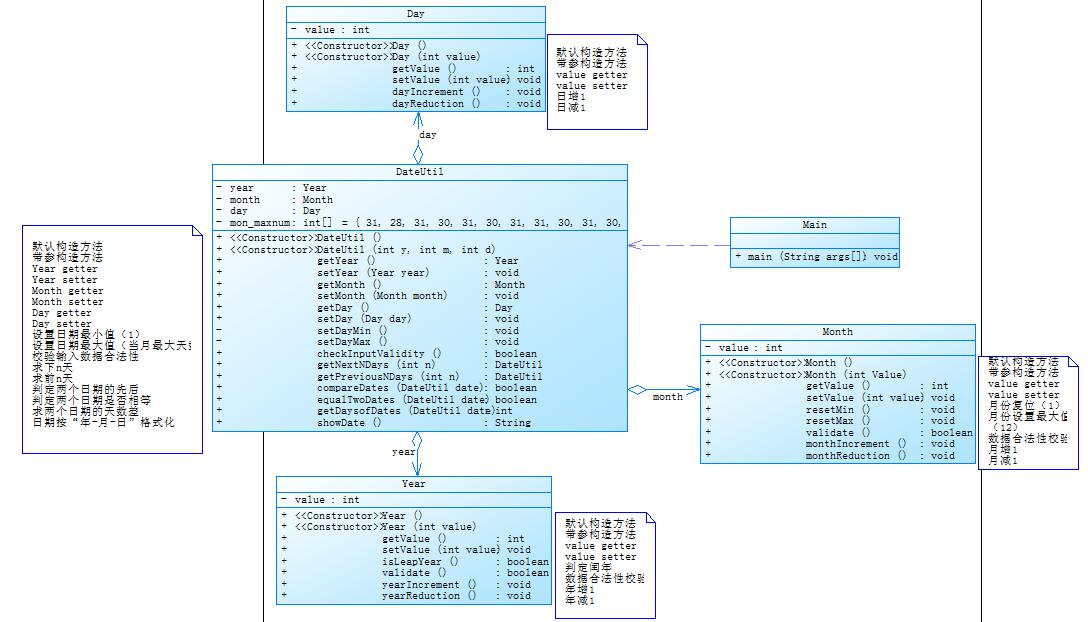
7-2类结构代码:
class Year{
int year;
public Year(){
}
public Year(int year){
this.year=year;
}
// getter setter
public int getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(int year) {
this.year = year;
}
//判断闰年平年
//判断年份是否合法
public boolean vaildate(int year)
{
// boolean vaildate=false;
if(this.year>=1900&&this.year<=2050)
// vaildate=true;
// return vaildate;
return true;
else
return false;
}
public boolean isLeapYear()//里面用了this 外面不用static
{
boolean isLeapYear=false;
if((this.year%4==0&&this.year%100!=0)||this.year%400==0)
isLeapYear=true;
return isLeapYear;
}
//年份加一
public int yearIncrement()
{
return this.year+1;
}
//年份减一
public int yearReduction()
{
return this.year-1;
}
}
class Month{
int month;
Year year;
public Month(int month){
this.month=month;
}
//判断月份是否合法
public boolean vaildate(int month)
{
// boolean vaildate=false;
if(this.month>=1&&this.month<=12)
// vaildate=true;
// return vaildate;
return true;
else
return false;
}
//
//月份加一
public int monthIncrement()
{
return this.month+1;
}
//月份减一
public int monthReduction()
{
return this.month-1;
}
}
class Day {
Year year;
int month;
int day;
int[] months={0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
// System.out.println(months[2]);
public Day(int day,int month){
this.day=day;
this.month=month;
}
public Day(int day) {
}
//2月天数
public void February()
{
if(year.isLeapYear()==true)
months[2]=29;
}
//判断日期是否合法
public boolean vaildate(int day)
{
// boolean vaildate=false;
if(this.day>=1&&this.day<=months[month])
// vaildate=true;
// return vaildate;
return true;
else
return false;
}
//日期加一
public int dayIncrement()
{
return this.day+1;
}
//日期减一
public int dayReduction()
{
return this.day-1;
}
}
class DataUtil extends Year{
}
②题目集4(7-3)、题目集6(7-5、7-6)三种渐进式图形继承设计的思路与技术运用(封装、继承、多态、接口等)
7-3:
class Shape {
public Shape()//构造无参函数 不能有void
{
System.out.println("Constructing Shape");
}
public double getArea()
{
return 0.0;
}
}
class Circle extends Shape{
private double radius;
public double getRadius()
{
return radius;
}
public void setRadius(double radius)
{
this.radius=radius;
}
public Circle()
{
System.out.println("Constructing Circle");
}
public void getCircle()
{
System.out.printf("Circle's area:%.2f",Math.PI*radius*radius);
}
}
class Rectangle extends Shape{
private double width;
private double length;
public Rectangle()
{
System.out.println("Constructing Rectangle");
}
public double getWidth()
{
return width;
}
public void setWidth(double width)
{
this.width=width;
}
public double getLength()
{
return length;
}
public void setLength(double length)
{
this.length=length;
}
public double getRectengle()
{
return width*length;
// System.out.printf("Circle's area:%.2f",width*length);
}
}
class Ball extends Circle{
// double radius=super.getRadius();//super//不要用
public Ball()
{
System.out.println("Constructing Ball");
}
public void getCirclearea()
{
System.out.printf("Ball's surface area:%.2f",4*Math.PI*super.getRadius()*super.getRadius());
}
public void getVolume()
{
System.out.printf("Ball's volume:%.2f",Math.PI*super.getRadius()*super.getRadius()*super.getRadius()*4/3);
}
}
class Box extends Rectangle{
private double height;
// double width=super.getWidth();//不要用 直接在公式里面用
// double length=super.getLength();
public Box()
{
System.out.println("Constructing Box");
}
public double getHeight()
{
return height;
}
public void setHeight(double height)
{
this.height=height;
}
public void getRectanglearea()
{
System.out.printf("Box's surface area:%.2f",super.getWidth()*super.getLength()*2+super.getWidth()*height*2+super.getLength()*height*2);
}
public void getVolume()
{
System.out.printf("Box's volume:%.2f",super.getWidth()*super.getLength()*height);
}
}
7-5:
class Shape{
public Shape(){
}
}
class Circle extends Shape{
double radius;
public Circle(){
}
public Circle(double radius){
this.radius=radius;
}
public double getRadius() {
return radius;
}
public void setRadius(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
public boolean isCircle(){
if(radius>0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
public double getArea(){
return Math.PI*radius*radius;
}
}
class Rectangle extends Shape{
double width;
double length;
public Rectangle(){
}
public Rectangle(double width,double length){
this.width=width;
this.length=length;
}
public double getWidth() {
return width;
}
public void setWidth(double width) {
this.width = width;
}
public double getLength() {
return length;
}
public void setLength(double length) {
this.length = length;
}
public boolean isRectangle(){
if(width>0&&length>0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
public double getArea(){
return width*length;
}
}
class Triangle extends Shape{
double len1;
double len2;
double len3;
public Triangle(){
}
public Triangle(double len1,double len2,double len3){
this.len1=len1;
this.len2=len2;
this.len3=len3;
}
public double getLen1() {
return len1;
}
public void setLen1(double len1) {
this.len1 = len1;
}
public double getLen2() {
return len2;
}
public void setLen2(double len2) {
this.len2 = len2;
}
public double getLen3() {
return len3;
}
public void setLen3(double len3) {
this.len3 = len3;
}
public boolean isTriangle(){
if((len1>0&&len2>0&&len3>0)&&(len1+len2>len3&&len1+len3>len2&&len2+len3>len1))
return true;
else
return false;
}
public double getArea(){
return Math.sqrt((len1+len2+len3)*(len1+len2-len3)*(len1+len3-len2)*(len2+len3-len1))/4;
}
}
7-6:
class Shape {
public Shape()//构造无参函数 不能有void
{
// System.out.println("Constructing Shape");
}
public double getArea()
{
return 0.0;
}
}
class Circle extends Shape{
private double radius;
public double getRadius()
{
return radius;
}
public void setRadius(double radius)
{
this.radius=radius;
}
public Circle()
{
// System.out.println("Constructing Circle");
}
public double getCircle()
{
return Math.PI*radius*radius;
}
}
class Rectangle extends Shape{
private double width;
private double length;
public Rectangle()
{
// System.out.println("Constructing Rectangle");
}
public double getWidth()
{
return width;
}
public void setWidth(double width)
{
this.width=width;
}
public double getLength()
{
return length;
}
public void setLength(double length)
{
this.length=length;
}
public double getRectengle()
{
return width*length;
// System.out.printf("Circle's area:%.2f",width*length);
}
}
class Ball extends Circle{
// double radius=super.getRadius();//super//不要用
public Ball()
{
// System.out.println("Constructing Ball");
}
public void getCirclearea()
{
System.out.printf("%.2f",4*Math.PI*super.getRadius()*super.getRadius());
}
public void getVolume()
{
System.out.printf("%.2f",Math.PI*super.getRadius()*super.getRadius()*super.getRadius()*4/3);
}
}
class Box extends Rectangle{
private double height;
// double width=super.getWidth();//不要用 直接在公式里面用
// double length=super.getLength();
public Box()
{
// System.out.println("Constructing Box");
}
public double getHeight()
{
return height;
}
public void setHeight(double height)
{
this.height=height;
}
public void getRectanglearea()
{
System.out.printf("%.2f",super.getWidth()*super.getLength()*2+super.getWidth()*height*2+super.getLength()*height*2);
}
public void getVolume()
{
System.out.printf("%.2f",super.getWidth()*super.getLength()*height);
}
}
③对三次题目集中用到的正则表达式技术的分析总结:
使用正则表达式来查找字符串,从一个长的文本中查找符合指定特征的字符串,Pattern complie()和Pattern.matcher()获取对比输入的字符。
踩坑心得:
题目集4的7-2:
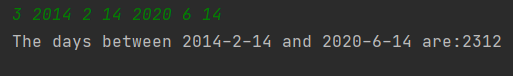
3 2014 2 14 2020 6 14
2312
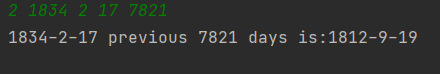
2 1935 2 17 125340
1591-12-17
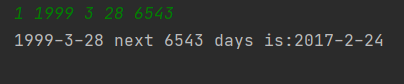
1 1999 3 28 6543
2017-2-24
0 2000 5 12 30
Wrong Format
题目集4的7-3:

题目集5的7-5:
题目集6的7-6:
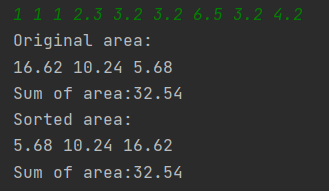
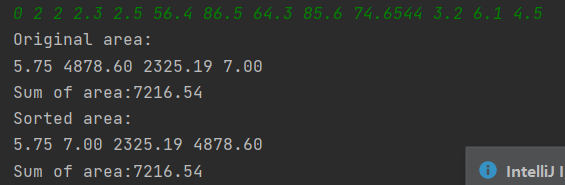
改进建议:
写题过程中,感到最吃力的题仍然关于正则表达式的题目,目前还不能熟练的使用正则表达式匹配字符串,使用正则表达式时,不能用简短的式子表达出所想查找的字符串,使得表达式过于繁琐,容易出错;还有就是定义多个类,将他们用一定的方法连接起来时,每个类中的属性和方法的传递使用不熟练,不知道哪些可以传递,需要用什么方法传递。之后应多看例题,多实践,从而总结出方法。
总结:
这次的题目集主要考察的是正则表达式和类之间的连接,如继承,封装,接口,多态等知识点。
继承就是子类继承父类的特征和行为,使得子类对象具有父类的实例域和方法,或子类从父类继承方法,使得子类具有父类相同的行为。在 Java 中通过 extends 关键字申明一个类来教程另外一个类。
封装就是将抽象性函式接口的实现细节部分包装、隐藏起来的方法,使我们能修改自己的实现代码,而不用修改那些调用我们代码的程序片段,让程式码更容易理解与维护,也加强了程式码的安全性。
接口是抽象方法的集合,接口通常以interface来声明,让一个类通过继承接口的方式,从而来继承接口的抽象方法,接口类型也可用来声明一个变量。
多态是同一个行为具有多个不同表现形式或形态的能力,用同一个接口,使用不同的实例而执行不同操作。具有消除类型之间的耦合关系、可替换性、可扩充性、接口性、灵活性、简化性等特点。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号