前三次作业总结
前言:
题目集1:
前七道题的知识点都是基础知识点,Scanner定义变量,用nextInt()、nextDouble、nextLine()等函数获取键盘输入的数字或字符串;println换行输出显示结果;其他知识点和c语言的差不多。
题7-8:主要考察的知识点是条件语句,if-else语句,先判断输入的数据,再输出对应的结果,题目较简单。
题目集2:
前两道题分别是将二进制转换为十进制和合并数组并排序,题目较简单。
后三道题需要用到函数的定义和函数的调用,三道题类似,刚接触时会感觉比较吃力,写完一道题后再写其他两道题感觉轻松许多。
7-4:输入日期合法,先判断是否为闰年,根据闰年平年确定二月的天数,得出下一天
7-5:和上一天相似,不同的是找前n天或者后n天。
题目集3:
第一题Account类的构建,学完类的知识点就能写出题目,属于该题型的基础性难度。
题7-2:在第一题和题目集二的基础上,完成比较顺利,属于中等难度题目。
题7-3:是所有题目中难度最大的,有一些新的知识点和较难实现的需求,如:正则表达式、找到x从而得到指数和系数,再求导得出结果。
设计与分析:
题目集1:
7-8重点代码:
if(a>=1&&a<=200&&b>=1&&b<=200&&c>=1&&c<=200)
{
//是否为三角形
//为三角形
if(a+b>c&&a+c>b&&b+c>a)
{
//是否为等边三角形
//是等边三角形
if(a==b&&b==c)
{
System.out.println("Equilateral triangle");
}
//不是等边三角形
else
{
//是否等腰
//等腰直角和等腰
if((a==b)||(b==c)|(a==c))
{
//是否直角
//等腰直角
if((a*a+b*b-c*c<0.1)||(a*a+c*c-b*b<0.1)||(b*b+c*c-a*a<0.1))
{
System.out.println("Isosceles right-angled triangle");
}
//等腰非直角
else
System.out.println("Isosceles triangle");
}
//非等腰
else
{
//是否直角
//是直角
if((a*a+b*b-c*c<0.1)||(a*a+c*c-b*b<0.1)||(b*b+c*c-a*a<0.1))
{
System.out.println("Right-angled triangle");
}
//不是直角
else
System.out.println("General triangle");
}
}
}
//不是三角形
else
System.out.println("Not a triangle");
}
//非法
else
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
题目集2:
7-4、主要函数代码如下:
public static boolean isLeapYear(int year) //判断year是否为闰年,返回boolean类型
{
boolean isLeapYear=false;
if((year%4==0&&year%100!=0)||year%400==0)
isLeapYear=true;
else
isLeapYear=false;
return isLeapYear;
}
public static boolean checkInputValidity(int year,int month,int day)//判断输入日期是否合法,返回布尔值
{
boolean checkInputValidity=false;
int[] months={0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
if(isLeapYear(year)==true)
months[2]=29;
if(year<=2020&&year>=1820&&month<=12&&month>=1&&day>=1&&day<=months[month])
checkInputValidity=true;
else
checkInputValidity=false;
return checkInputValidity;
}
public static void nextDate(int year,int month,int day) //求输入日期的下一天
{
int[] months={0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
if(isLeapYear(year)==true)
months[2]=29;
int newyear=0;
int newmonth=0;
int newday=0;
if(checkInputValidity(year,month,day)==true)
{
//12月
if(month==12)
{
if(day==31)
{
newyear=year+1;
newmonth=1;
newday=1;
}
else
{
newyear=year;
newmonth=month;
newday=day+1;
}
}
else
{
if(day==months[month])
{
newyear=year;
newmonth=month+1;
newday=1;
}
else
{
newyear=year;
newmonth=month;
newday=day+1;
}
}
System.out.println("Next date is:"+newyear+"-"+newmonth+"-"+newday);
}
else
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
7-5主要函数代码如下:
public static boolean isLeapYear(int year) //判断year是否为闰年,返回boolean类型
{
boolean isLeapYear=false;
if((year%4==0&&year%100!=0)||year%400==0)
isLeapYear=true;
else
isLeapYear=false;
return isLeapYear;
}
public static void f(int year,int month ,int day ,int n)//求出year-month-day到0001-1-1的距离天数,返回整型数
{
int[] months={0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
if(isLeapYear(year)==true)
months[2]=29;
int newyear=0;
int newmonth=0;
int newday=0;
if(year<=2020&&year>=1820&&month<=12&&month>=1&&day>=1&&day<=months[month]&&n>=-10&&n<=10)
{
if(n==0)
{
newyear=year;
newmonth=month;
newday=day;
}
if(n<0)
{
n=-n;
if(month==12)
{
if(day+n>31)
{
newyear=year+1;
newmonth=1;
newday=day+n-31;
}
else
{
newyear=year;
newmonth=month;
newday=day+n;
}
}
else
{
if(day+n>months[month])
{
newyear=year;
newmonth=month+1;
newday=day+n-months[month];
}
else
{
newyear=year;
newmonth=month;
newday=day+n;
}
}
n=-n;
}
if(n>0)//往前
{
if(month==1)
{
if(day-n<1)//day=5 n=7 29
{
newyear=year-1;
newmonth=12;
newday=months[12]-(n-day);
}
else
{
newyear=year;
newmonth=month;
newday=day-n;
}
}
else
{
if(day-n<1)
{
newyear=year;
newmonth=month-1;
newday=months[month-1]-(n-day);
}
else
{
newyear=year;
newmonth=month;
newday=day-n;
}
}
}
System.out.println(n+" days"+" ago"+" is:"+newyear+"-"+newmonth+"-"+newday);
}
else
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
题目集3:
7-2类方法定义的主要函数结构:
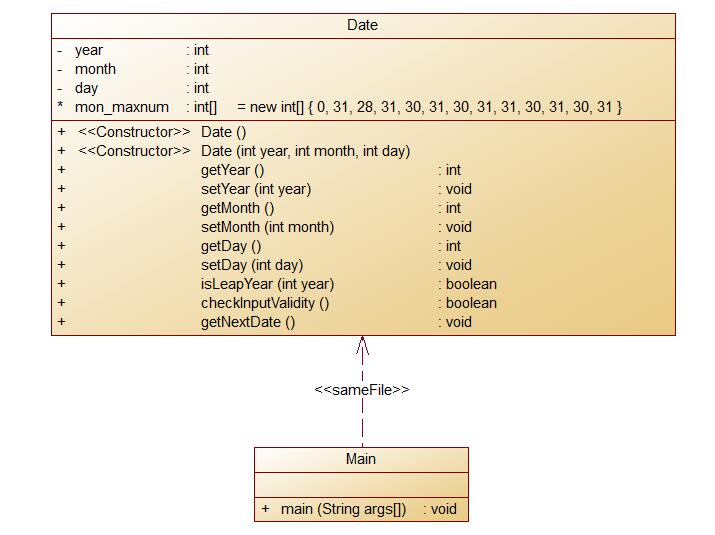
class Data {
int year;
int month;
int day;
int[] months = new int[]{0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};
Data() {
}
public int getYear(int year) {
return year;
}
public void setYear() {
this.year = year;
}
public int getMonth(int month) {
return month;
}
public void setMonth() {
this.month = month;
}
public int getDay(int day) {
return day;
}
public void setDay() {
this.day = day;
}
}
7-3正则表达式有关代码
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
Derivation d=new Derivation();
d.input=in.nextLine();
d.judge(d.input,d.totalRegex,d.sbuRegex,d.k);
}
static class Derivation{
String input;
String totalRegex ="[-+]?((([2-9]+[0-9]*)|([1-9]+[0-9]+))(\\*)?)?x?(\\^[+-]?(([2-9]+[0-9]*)|([1-9]+[0-9]+)))?";
String sbuRegex = "[-+]?([1-9]+[0-9]*(\\*)?)?x?(\\^[+-]?[0-9]+)?";
String k = "([2-9]+[0-9]*)|(1+[0-9]+)";
public String getInput(String input){
return input;
}
public void judge(String input,String totalRegex,String sbuRegex,String k){
boolean b1=Pattern.matches(totalRegex, input);
boolean b2=Pattern.matches(sbuRegex,input);
boolean b3=Pattern.matches(k,input);
if(b1==false||b2==false)
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
else if(b3==true)
System.out.println(0);
}
}
踩坑心得:
题目集1的7-8:
一步一步分析输入数据,判断是否构成三角形,是否构成等边三角形、等腰直角三角形、等腰非直角三角形、直角三角形、一般三角形。
样例:
1 2 3
Not a triangle
3 3 3
Equilateral triangle
2 2 3
Isosceles right-angled triangle
3 4 5
Right-angled triangle
题目集2的7-4:
先用isLeapYear判断输入年份是否为闰年,将结果转给checkInputValidity函数,判断输入年份是否合法并根据闰年平年确定二月的天数,最后用nextDate求下一天并输出,该功能主要是把时间分为该年的最后一天、该月的最后一天和其他时间。
样例:
1999 2 28
Next date is:1999-3-1
2000 2 28
Next date is:2000-2-29
2012 12 31
Next date is:2013-1-1
2015 6 12
Next date is:2015-6-13
题目集2的7-5:
前部分和上一题相似,先用isLeapYear判断输入年份是否为闰年,将结果转给checkInputValidity函数,判断输入年份是否合法并根据闰年平年确定二月的天数,通过判断输入n值的正负,确定是n天前还是n天后。如果是n天后,将时间分为:n天后是下一年的某天、n天后是下一个月的某天和n天后仍是本月的某天。如果是n天前,将时间分为:n天前是去年的某天、n天前是上一个月的某天和n天前仍是本月的某天。
样例:
2011 12 28 -5
-5 days ago is:2012-1-2
2011 5 27 -7
-7 days ago is:2011-6-3
2011 8 23 -2
-2 days ago is:2011-8-25
2011 1 5 9
9 days ago is:2010-12-27
2011 3 4 8
8 days ago is:2011-2-24
2011 6 22 5
5 days ago is:2011-6-17
题目集3的7-2:
按照图片所给的形参类型和返回值类型定义类和构造函数Date。获取year、month和day,通过isLeapYear函数判断闰年平年,再用checklnputValidity函数判断输入是否合法并确定二月的天数。最后用getNextDate函数输出下一天。
样例:
1912 12 25
Next day is:1912-12-26
2001 2 30
Date Format is Wrong
题目集3的7-4:
该题是这些题目里面最难的题目,先用正则表达式判断输入的字符串是否合法,再对式子求导:找到每个x前面的系数和后面的指数,指数减一,系数为原系数乘以指数。
改进建议:
写题过程中,感到最吃力的一道题就是题目集3的最后一题一元多项式求导,这道题包含了类方法的使用、正则表达式和字符的查找。使用正则表达式时,不能用简短的式子表达出所想查找的字符串,使得表达式过于繁琐,容易出错,之后应多看例题,多实践,从而总结出方法。
总结:
从第一次的这些题目中,学会了java的基本语法,从上一门编程语言过渡过来。如:
每个java程序必有的基本结构:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
}
}
使用import java.util.Scanner;从键盘获取数字或字符串用:
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
int a=in.nextInt();
double b=in.nextDouble();
String c=in.nextLine();
输出结果用:
System.out.println();
System.out.print();
System.out.printf(%d,a);
定义数组:
int[] a=new int[10];
获取字符串中每个字符:
k=in.nextLine();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++0)
{
k.charAt(i);
}
在public static void main 中构造函数时,函数的返回值可以时int、double、String等,
函数内部的最后一定有return 返回对应类型的值;也可以是void类型即无返回值。
返回值为boolen类型时,在函数内需要定义一个变量,
它的值只能时true或者false,根据条件返回对应的boolen类型值。
在public class Main 外定义一个类,类中的元素和方法可以设置权限,如果是私有,
则只能在类中使用如果是public的,则可以调用到main函数中使用,
此时还需要在main中定义一个新的该类类型变量,用"."访问类中的元素和方法。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号