文件按文件类型显示
文件按文件类型显示
1. 实现方法简介
根据先前实现的程序,我已经完成了通过命令行设置指定文件夹路径,并且显示该路径下所有文件和子文件夹的信息。在本次实现的项目中,我需要完成的是,对指定的类型文件,进行筛选检出。
针对以上要求,我的设计如下:
-
在文件路径中,设置一个txt文件,用于存储文件的类型。
-
在命令行格式中,增加一个命令行参数,file_type_path用于表示存储文件的类型。
-
在程序运行时,读取存储文件类型的文件,并把文件类型导入,存储为特定后缀的形式。
-
通过递归搜索子文件和子文件夹时,通过
(filename.substr(filename.find_last_of('.') + 1)对文件名的后缀进行提取,并与文件中存储的fileType进行比较,如果比对成功,则通过语句
files.push_back(p.assign(root_path).append("\\").append(fileinfo.name)将文件信息存入vector中,传出函数。
-
在显示函数中,首先通过参数数量的变量argc,判断该程序的执行模式,若argc=2,是对文件路径全文件和子文件夹的信息显示;若argc=3,则证明有文件类型存储路径,对文件类型文件路径判断其存在与否,而后执行提取文件类型并检索文件的程序。
-
通过传回的files vector,对检索文件的绝对路径进行显示。
调试时遇到的问题
- 路径中不能出现空格,否则在命令行参数中会被识别为两个参数从而报错。所以路径可以用下划线_作为分隔
- 路径中的文件夹,在python中可以出现中文路径,而C++中则不支持,会报错。
- 读取文件时,由于存储是一行一个文件类型,所以要注意\n的问题,可以在python中,通过.strip()解决,而C++中则采用getline()所以不会将\n写入。
- Python中实现命令行的click包中的@click.command()等语句应跟随在主函数中执行的函数前,而不是像宏定义一样放在脚本的最开始部分。
2. 核心代码
C++实现
void Find_AllFiles(std::string root_path, std::vector<std::string>& files, std::string fileType) {
intptr_t hFile = 0;//文件句柄
struct _finddata_t fileinfo;//文件信息
std::string p;
if ((hFile = _findfirst(p.assign(root_path).append("\\*").c_str(), &fileinfo)) != -1) {
do {
if ((fileinfo.attrib & _A_SUBDIR)) { //比较文件类型是否是文件夹
if (strcmp(fileinfo.name, ".") != 0 && strcmp(fileinfo.name, "..") != 0) {
Find_AllFiles(p.assign(root_path).append("\\").append(fileinfo.name), files, fileType);
}
}
else {
std::string path = p.assign(root_path).append("\\").append(fileinfo.name);
std::string::size_type iPos = path.find_last_of('\\') + 1;
std::string filename = path.substr(iPos, path.length() - iPos);
if (filename.substr(filename.find_last_of('.') + 1) == fileType) {
files.push_back(p.assign(root_path).append("\\").append(fileinfo.name));
}
}
} while (_findnext(hFile, &fileinfo) == 0); //寻找下一个,成功返回0,否则-1
_findclose(hFile);
}
}
void Reveal_File_Info(int argc, char* argv[]) {
// argc == 1
// argv[0] == root_path
intptr_t hFile = 0;//文件句柄
std::vector<std::string> files_list;
SetConsoleOutputCP(936);
if (argc == 3) {
std::ifstream in(argv[2]);
std::string file_type;
std::string p;
if (in) { // 有该文件
while (std::getline(in, file_type)) { // line中不包括每行的换行符
struct _finddata_t fileinfo;//文件信息
Find_AllFiles(argv[1], files_list, file_type);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < files_list.size(); i++) {
hFile = _findfirst(p.assign(files_list[i]).c_str(), &fileinfo);
std::cout << "绝对路径:" << files_list[i] << std::endl;
}
}
}
else { // 没有该文件
std::cout << "no such file" << std::endl;
}
}
}
Python实现
def search_file(root_path, file_type):
path = pathlib.Path(root_path)
for file_path in path.rglob('*' + file_type):
print(str(file_path))
click.echo(str(file_path))
@click.command()
@click.option('--path', 'root_path', prompt='Directory Path', nargs=1, default=current_path, help='The Path of Directory you wanna reveal.', type=str)
@click.option('--type', 'file_type_path', prompt='File Type Path', nargs=1, default='./file_type_path.txt', help='The Path of Type List.', type=str)
def load_find_file_type(root_path, file_type_path):
print(root_path, file_type_path)
f = open(file_type_path, "r")
lines = f.readlines()
file_type_list = []
for line in lines:
file_type_list.append("." + line.strip('\n'))
for file_type in code_file:
print(root_path, file_type)
search_file(root_path, file_type)
结果
C++运行结果
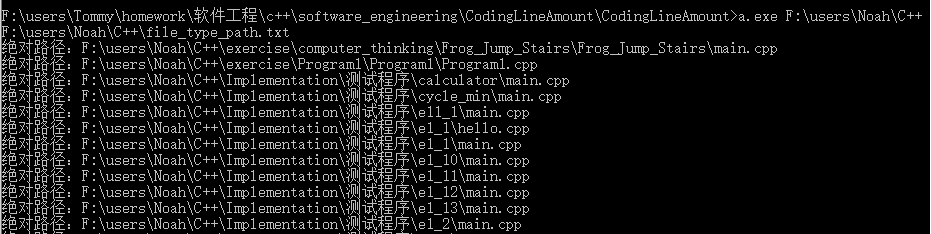
其中a.exe为g++编译后的源程序,第二个命令行参数规定了检索文件目录,第三个命令行参数指定文件类型存储txt文件所在的路径。
python运行结果
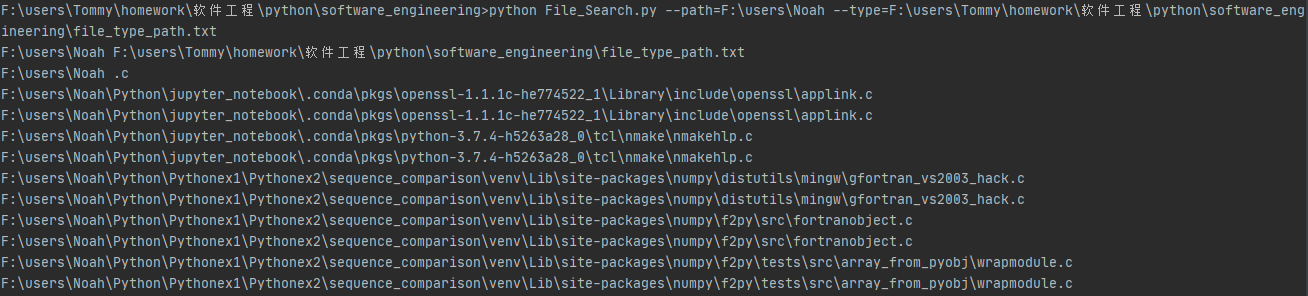
其中File_Search.py为源程序,第二个命令行参数通过--path规定了检索文件目录,并且该option限定只有1个参数,第三个命令行参数--type指定文件类型存储txt文件所在的路径,同样也限定只有一个参数。
3. PSP表格
| PSP各阶段 | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | ||
| · Estimate | · 明确需求和其他因素,估计以下各个任务需要多少时间 | 5 | 5 |
| Development | 开发 | ||
| · Analysis | · 需求分析 (包括学习新技术、新工具的时间) | 20 | 60 |
| · Design Spec | · 生成设计文档(整体框架的设计,各模块的接口) | 5 | 2 |
| · Design Review | · 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) | 5 | 0 |
| · Coding Standard | · 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定或选择合适的规范) | 5 | 1 |
| · Design | · 具体设计(用流程图、伪代码等方法来设计具体模块) | 5 | 1 |
| · Coding | · 具体编码 | 30 | 60 |
| · Code Review | · 代码复审 | 10 | 10 |
| · Test | · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 40 | 85 |
| Reporting | 报告 | ||
| · Test Report | · 测试报告(发现了多少bug,修复了多少) | 10 | 8 |
| · Size Measurement | · 计算工作量(多少行代码,多少次签入,多少测试用例,其他工作量) | 5 | 2 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | · 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划(包括写文档、博客的时间) | 30 | 40 |
| 合计 | 170 | 274 |



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号