Theta-star算法代码实现
A*和Theta*算法
A*搜索过程中仅考虑网格路径(路径只能是栅格的边或对角线);Theta*搜索和平滑操作交错执行(路径可以是任意直线,只要**视线检
查**通过),相当于在线平滑。
路径搜索
评估函数f(n)=g(n)+h(n),表示经过节点N完成路径的代价,其中:
g(n)为起点S到当前节点 n 的实际代价;
h(n)为从当前节点 n 到终点E的估算代价(启发式函数)。
算法的目标是始终扩展 f(n) 最小的节点。
代码演示
变量说明
open_set = []
heapq.heappush(open_set, (self._heuristic(start_idx, end_idx) / self.v_g_est, start_idx))
came_from = {}
g_score = defaultdict(lambda: float('inf'))
g_score[start_idx] = 0
S = (227, 612, 2);E = (27, 37, 2)。
open_set=[f(n),id]; heapq库实现的优先队列;根据节点的优先级f(n)进行排序;每次迭代,算法总是从 open_set 中取出 f_score 最小的那个节点。
came_from:字典,存储了每个节点的前一个节点(父节点)。键是子节点,值是其父节点。
一个节点可能是多个节点的父节点、但是每个节点至多只有一个父节点。(字典的每个键(子节点)都只对应一个值(父节点),因此
当前最优会被更优覆盖。)
根据父节点的更新规则,假设B的父节点是A,更新为B的父节点是C:'B': 'A'--->'B': 'C',
parent_idx = C ; neighbor_idx = B
说明:
从起点S到B的最短时间:g_score[neighbor_idx] 大于 从起点 S到C的时间(g_score[parent_idx=B]) + C到B的时间 (distance_BC / ground_speed);
而 g_score[neighbor_idx] 是之前使用A作为父节点计算的,= 从起点 S到A的时间(g_score[parent_idx=A]) + A到B的时间 (distance_AC / ground_speed);
需要注意:A的父节点为B仅仅表示从起点到A的最优路径是S-B-A,但是S-B的路径还需要看B的父节点是谁。
# 如果可见,尝试直接连接,并计算新路径代价
distance = self._heuristic(parent_idx, neighbor_idx)
ground_speed = self._calculate_ground_speed(parent_idx, neighbor_idx)
tentative_g_score = g_score[parent_idx] + distance / ground_speed
if tentative_g_score < g_score[neighbor_idx]:
came_from[neighbor_idx] = parent_idx
例子:
came_from = {
'B': 'A', # 从A到B
'C': 'B', # 从B到C
'D': 'B', # 从B到D
'E': 'C' # 从C到E
}
算法实现
从起点S开始,f(S)=g(S)+h(S)=0+h(S), 即:起点S到终点E的估算代价,open_set = [f(S),S];

came_from为空。
第一次迭代
迭代open-set,取出目前f最小的点(即移除,这是heapq的特性),Start_id --> C_id。
依次计算8个邻居N的g_score,记录邻居N_{i}_S的父节点为S;open_set 添加 [f(N_i),i],f_score最小的排在首位;
计算时通过came_from查询S的父节点,为None,不用视线检查,退化为A*的邻居检查。
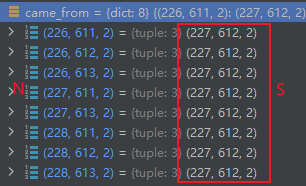
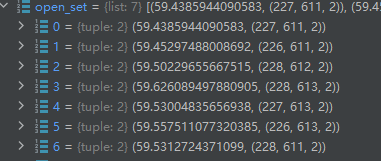
第二次迭代 : 迭代计算S的最优邻居N_{1}S的邻居N_N1。
取出目前f_score最小的点N_{1}_S --> C_id:

依次计算8个邻居N的g_score;计算时通过came_from查询C_id的父节点,发现是Start_id,需要进行视线检查(LoS);

核心思路为: 如果C_id的父节点Start_id 和 C_id的邻居节点 N_{i}_N1 之间无障碍物;则直接计算 **从父节点到邻居节点的
f_score**;将score更小的点并加入队列。如果视线检查不通过,则退化为A*.
例如,C_id的8个邻居节点中,有三个通过视线检查,直接成为了{C_id的父节点Start_id}的子节点,和C_id同等地位。

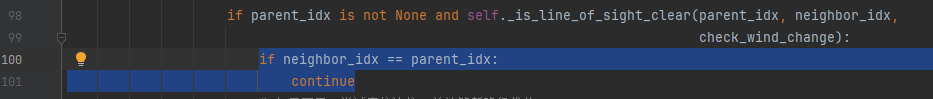
if parent_idx is not None and self._is_line_of_sight_clear(parent_idx, neighbor_idx,
check_wind_change):
# 如果可见,尝试直接连接,并计算新路径代价
distance = self._heuristic(parent_idx, neighbor_idx)
ground_speed = self._calculate_ground_speed(parent_idx, neighbor_idx)
tentative_g_score = g_score[parent_idx] + distance / ground_speed
if tentative_g_score < g_score[neighbor_idx]:
came_from[neighbor_idx] = parent_idx
g_score[neighbor_idx] = tentative_g_score
heapq.heappush(open_set,
(g_score[neighbor_idx] +
self._heuristic(neighbor_idx, end_idx) / self.v_g_est, neighbor_idx))
中间迭代 :
不断遍历openset中f_score最小的点作为current_idx,并计算C_id的8个邻居节点和C_id的父节点是否通过视线检查,将通过视线检查的点加
入came_from 和openset。
随着迭代的进行,搜索范围不断扩大,open_set 中的节点会越来越接近终点 E。
路径收敛:由于启发式函数 h(n) 的存在,算法会倾向于向终点方向扩展。通过 Theta* 的视线检查,路径会尽量拉直,避免不必要的拐点。
找到终点:当某个被取出的 current_idx 正好等于 end_idx 时,if current_idx == end_idx 条件成立,path_found 被设为 True,搜索循环结束。
迭代结束 路线重建
从end_idx开始,从came-from字典中逆向重建路径。
只要当前节点 current 是 came_from 字典中的一个键(即它有一个父节点),循环就继续执行。
- 将当前节点的坐标添加到 path 列表中。
- 将 current 的值更新为它的父节点。
- 。。。。。。。
最后 添加起点坐标,反转路径。
# 重建路径 (复用 A* 逻辑)
path = []
current = end_idx
while current in came_from:
path.append(voxel_idx_to_utm(current))
current = came_from[current]
path.append(voxel_idx_to_utm(start_idx))
path.reverse()
补充2025.9.23
实验发现一致情况:current_idx的邻居neighbor_idx和current_idx的父节点parent_idx如果是同一个点,应该跳过。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号