【Java】File-IO流
(一)Class File
1、构造方法
File(String pathname)Creates a new
File instance by converting the given pathname string into an abstract pathname.2、方法
(1)获取信息类
String getName()Returns the name of the file or directory denoted by this abstract pathname.(获取文件名,带后缀)
String getPath()Converts this abstract pathname into a pathname string.(获取文件定义时使用的路径)
String getAbsolutePath()Returns the absolute pathname string of this abstract pathname.(获取文件绝对路径)
boolean isDirectory()Tests whether the file denoted by this abstract pathname is a directory.(判断是否为文件夹)
boolean isFile()Tests whether the file denoted by this abstract pathname is a normal file.(判断是否未为文件)
long length() Returns the length of the file denoted by this abstract pathname.(获取文件长度)long lastModified()Returns the time that the file denoted by this abstract pathname was last modified.(获取文件最后修改时间)
(2)创建文件类
static File createTempFile(String prefix, String suffix)Creates an empty file in the default temporary-file directory, using the given prefix and suffix to generate its name.(创建一个空文件)
boolean mkdir()Creates the directory named by this abstract pathname.(创建一个一级文件夹)
boolean mkdirs()Creates the directory named by this abstract pathname, including any necessary but nonexistent parent directories.(创建多级文件夹)
boolean delete()Deletes the file or directory denoted by this abstract pathname.(删除文件夹或者文件,文件夹默认只能删除空文件夹,不走回收站)
(3)遍历类
String[] list()Returns an array of strings naming the files and directories in the directory denoted by this abstract pathname.(获取当前目录下所有一级文件名称)
File[] listFiles()Returns an array of abstract pathnames denoting the files in the directory denoted by this abstract pathname.(获取当前目录下所有一级文件对象)
注意:调用者不存在或者是一个文件时返回为null,当调用者是一个空文件夹时,返回一个长度为0的数组。
3、递归遍历目录
public static void eachFile(File rootFile){ if (rootFile != null || rootFile.isDirectory()) { File[] files = rootFile.listFiles(); if (files != null || files.length > 0) { for (File file : files) { if (file.isDirectory()) { eachFile(file); } System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath()); } } } }
(二)字符集
GBK中文默认编码暂用两个字节
UTF-8中文默认编码占用三个字节
编码解码使用方法
byte[] getBytes(Charset charset)Encodes this
String into a sequence of bytes using the given charset, storing the result into a new byte array.(不带参数使用当前编码)String(byte[] bytes, Charset charset)Constructs a new
String by decoding the specified array of bytes using the specified charset.((不带参数使用当前编码)注意:编码前和解码后的字符集必须一致否则会出现乱码。
(三)IO流
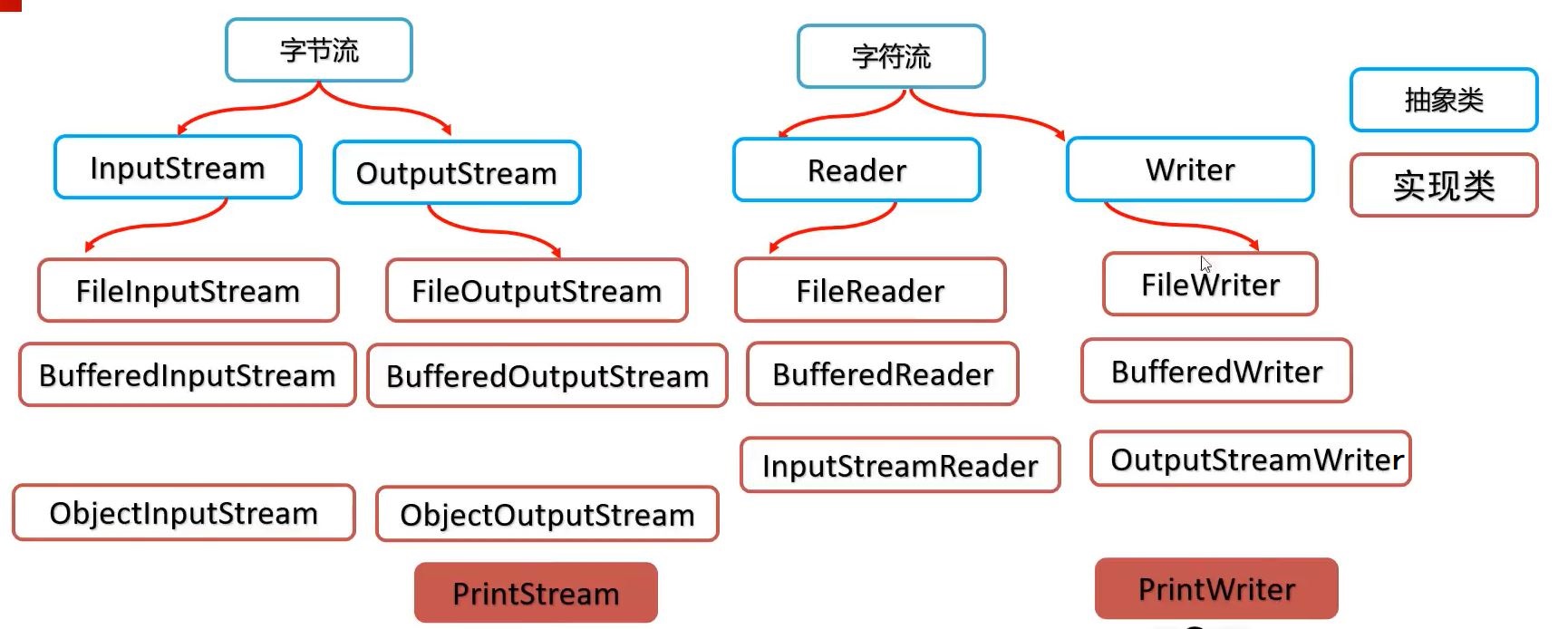
输出流使用文件追加的方式只需要使用构造函数参数append为true
1、字节流
-读写数据更加合适
(1)输入流使用实现类Class FileInputStream
abstract int read()Reads the next byte of data from the input stream.(每次读一个字节,读取失败返回-1)
int read(byte[] b)Reads some number of bytes from the input stream and stores them into the buffer array
b.(使用字节数组读取,返回读取长度,读取失败返回-1)byte[] readAllBytes()Reads all remaining bytes from the input stream.(读取所有字节)
void close()Closes this input stream and releases any system resources associated with the stream.
(2)输出流使用实现类Class FileOutputStream
void write(byte[] b)Writes
b.length bytes from the specified byte array to this file output stream.(写入字节数组)void write(int b)Writes the specified byte to this file output stream.(写入一个字节)
void flush()Flushes this output stream and forces any buffered output bytes to be written out.(将写入的数据刷新)
void close()Closes this output stream and releases any system resources associated with this stream.(关闭流管道,并且会数据刷新)
1、字符流
-读写文本更加合适
(1)输入流使用实现类Class FileReader
int read()Reads a single character.(读取一个字符)
int read(char[] cbuf)Reads characters into an array.(读取字符数组)
abstract void close()Closes the stream and releases any system resources associated with it.
(2)输出流使用实现类Class FileWriter
void write(char[] cbuf)Writes an array of characters.(写字符数组)
abstract void write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len)Writes a portion of an array of characters.(写字符数组,从off位置写len个)
void write(int c)(写一个字符)Writes a single character.
void write(String str)(写一个字符串)Writes a string.
void write(String str, int off, int len)(写一个字符串,从off位置写len个)Writes a portion of a string.
abstract void close()Closes the stream, flushing it first.
abstract void flush()Flushes the stream.
4、缓冲流
缓冲流自带缓冲区、可以提高原始字符流、字节流读写数据性能。
使用缓冲流拷贝文件示例:
try ( // 使用缓冲流包装原始流,缓冲流默认大小为8kb 8192b InputStream inputStream = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\Shura\\Desktop\\Spider\\紧张的影视配乐.mp3"), 1024 * 16); OutputStream outputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("C:\\Users\\Shura\\Desktop\\Spider\\copy紧张的影视配乐.mp3"), 1024 * 16); ){ byte[] bytes = new byte[1024 * 16]; int len = 0; while ((len = inputStream.read(bytes)) != -1){ outputStream.write(bytes, 0 ,len); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
5、字符转换流
将原始字节流包装为字符转换流。
Class InputStreamReader
InputStreamReader(InputStream in, String charsetName)Creates an InputStreamReader that uses the named charset.
Class OutputStreamWriter
OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, String charsetName)Creates an OutputStreamWriter that uses the named charset.
6、对象序列化和反序列化
序列化:将对象存储到文件中。
反序列化:从文件中获取到对象、
//对象序列化和反序列化 ObjectOutputStream outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("hello-app/test.txt")); outputStream.writeObject(new String("hello world")); ObjectInputStream inputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("hello-app/test.txt")); String ObjectString = (String) inputStream.readObject();
ObjectString等于上次存储到文件中的对象。
7、打印流
(1)PrintStream
(2)PrintStream
打印数据功能上是一模一样,使用方便,性能高效。
PrintStream继承自字节输出流OutputStream,支持写字节数据的方法。
PrintWriter继承自字符输出流Writer,支持写字符数据。
8、Properties属性文件
存储属性文件:
Properties properties = new Properties(); properties.setProperty("admin", "123456"); properties.setProperty("user", "123456"); properties.store(new FileOutputStream("hello-app/users.properties"), "this is users.properties!");
读取属性文件:
Properties properties = new Properties(); properties.load(new FileInputStream("hello-app/users.properties")); String rs= properties.getProperty("admin");
9、资源释放
(1)try-catch-finally
基本做法:
try{
可能出现异常的代码;
}catch(异常类名 变量名){
异常的处理代码;
}finally{
执行所有资源释放操作;
}
手动在finally释放资源。
(2)try-with-resource
资源都是实现了Closeable/AutoCloseable接口的类对象。(可以自定义资源对象)
JDK7和JDK9简化的资源释放操作
try(定义流对象){ //资源对象
可能出现异常的代码;
}catch(异常类名 变量名){
异常的处理代码;
}
资源用完自动释放



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号