游戏开发中的数学和物理算法10-18
2010-04-23 08:51 宝宝合凤凰 阅读(710) 评论(0) 收藏 举报游戏开发中的数学和物理算法(10):矢量 vs 标量
1.标量
标量只有大小没有方向。
2.矢量
矢量既有大小又有方向。
3.常用举例:
物理上常用的矢量与标量的对应概念有:速度和速率;距离和位移等。如图:
距离:
假设A到B的距离为a,B到C的距离为b,C到D的距离为c;
那么A到D的距离就为a+b+c。
位移:
假设A到B的位移为a,B到C的位移为b,C到D的位移为c;
那么A到D的位移大小为|a+b+c|(数学上也叫a+b+c的模),方向是从A指向D。
4.计算机中矢量的表示:
//2D Vector
struct Vector2D
{
float x, y;
}
//3D Vector
struct Vector3D
{
float x, y, z;
}
游戏开发中的数学和物理算法(11):极坐标 vs 笛卡尔坐标
在1D的系统中利用正负去表示矢量是足够的,但是在2D和3D的系统中利用正负去表示矢量就不是很足够了。但是如果用极坐标系统去表示的话,就会比较直观。
极坐标表示矢量:
矢量 Ā=||A||@ θ (||A||代表大小, θ代表方向)
笛卡尔坐标表示矢量: (i代表x的方向,j代表y的方向)
极坐标和笛卡尔坐标相互转换:
b1=||B||*cosθ b2=||B||*sinθ
θ=tan-1(b2/b1)
2D和3D矢量的矩阵表示形式:
2D:A=2i+3j的矩阵表示为[2,3]或者
3D:A=2i+3j+4k矩阵表示为[2,3,4]或者
一个矢量,它的几何图形的表示为一个带箭头的线段,线段大小为矢量的大小(矢量的模),箭头的方向为矢量的方向。如图:
矢量的可以用平行四边形法则来进行计算。如下图,虚线表示的B和实线表示的B是等价的,即我们认为是相等的。
矢量的加法计算如图
设A=a1i+a2j , B=b1i+b2j那么A+B=(a1+b1)i+(a2+b2)j
一些性质:
矢量A和B,A+B=B+A
|A+B|不等于|A|+|B|。
矢量的减法,我们可以把A-B看成A+(-B)。如图。
设A=a1i+a2j , B=b1i+b2j那么A-B=(a1-b1)i+(a2-b2)j
计算举例:
正则化矢量:
=========================================================================
游戏开发中的数学和物理算法(13):点积和叉积
代数中的乘法应称为数乘,比如2×3=6,2·3=6。但是在几何中2·3为点积,2×3为叉积。
1.点积
A·B=|A| |B| cosq
2D:定义矢量A[a1,a2],矢量B[b1,b2] ;那么点积A·B=a1b1+a2b2。
3D:定义矢量A[a1,a2,a3],矢量B[b1,b2,b3] ;那么点积A·B=a1b1+a2b2+a3b3。
性质:
如果A·B = 0, 那么A┴B。
A·B = B· A。
如果 A·B < 0 (负), 那么q > 90°
如果 A·B > 0 (正), 那么q < 90°
举例:
C · D=5(6) + 3(–2) = 30 – 6 = 24
2.叉积
矢量A = [a1 a2 a3] 和矢量 B = [b1 b2 b3]。
A x B = [(a2b3 – a3b2) (a3b1 – a1b3) (a1b2 – a2b1)]
性质:
叉积是矢量(有大小和方向)。
A x B 不等于 B x A。
A × B=0说明A和B平行。
|A×B|=|A||B|sinq
--------------------------------------------------------
游戏开发中的数学和物理算法(14):矩阵的相等和转置
矩阵通常在游戏处理表示有行和列的数据。
只有一行的矩阵,我们可以将其看成一个矢量。
数学表示:如图
在计算机中的表示:
矩阵的在计算机中通常有一个二维数组来表示。下面是一个三行三列的矩阵。
struct Matrix3X3
{
float x[3][3];
}
矩阵相等:
矩阵的行数和列数相等,并且对应行列的数值也要相等。
计算机判定实现两矩阵是否相等。
bool areMatricesEqual(Matrix3X3 a, Matrix3X3 b)
{
int errorFlag = 0;
for(int i = 0;i<3;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<3;j++)
{
if((a.index[i][j]) != (b.index[i][j]))
errorFlag = 1;
}
}
//test for an error in equality.
if(errorFlag == 1)
return false;
else
return true;
}
矩阵的转置数学表示
矩阵的转置的计算机中的实现
Matrix4X4 transpose4X4Matrix(Matrix4X4 a)
{
Matrix4X4 temp;
for(int i = 0;i<4;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<4;j++)
{
temp.index[i][j] = a.index[j][i];
}
}
return temp;
}
===================================================
游戏开发中的数学和物理算法(15):矩阵的加减法
矩阵加法数学表示
矩阵减法数学表示:
计算机中矩阵加法的实现:
Matrix3X3 addMatrices(Matrix3X3 a, Matrix3X3 b)
{
Matrix3X3 temp;
for(int i = 0;i<3;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<3;j++)
{
temp.index[i][j] = (a.index[i][j] + b.index[i][j]);
}
}
return temp;
}
计算机中矩阵减法的实现:
Matrix4X4 subtractMatrices(Matrix4X4 a, Matrix4X4 b)
{
Matrix4X4 temp;
for(int i = 0;i<4;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<4;j++)
{
temp.index[i][j] = (a.index[i][j] - b.index[i][j]);
}
}
return temp;
}
=============================================
游戏开发中的数学和物理算法(16):矩阵的乘法
矩阵数乘数学形式:
计算机中矩阵数乘的实现:
Matrix3X3 scalarMultiply(Matrix3X3 a, float scale)
{
Matrix3X3 temp;
for(int i = 0;i<3;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<3;j++)
{
temp.index[i][j] = (a.index[i][j] * scale);
}
}
return temp;
}
矩阵的乘法:
计算机中矩阵乘法的实现:
Matrix3X1 multiplyMatrixNxM(Matrix3X3 a, Matrix3X1 b)
{
Matrix3X1 temp;
temp.index[0] = 0.0f;
temp.index[1] = 0.0f;
temp.index[2] = 0.0f;
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<3;j++)
{
temp.index[i] += (a.index[i][j] * b.index[j]);
}
}
return temp;
}
==============================
游戏开发中的数学和物理算法(17):平移
点的平移,可以通过矩阵相加和相乘来模拟。
2D加法平移:
例如:
点A(20,30),向右移50个像素,向下移100个像素,得到A'。
那么A'(70,-70)。
3D加法平移:
例如:
计算机中实现:
Matrix3X1 translate3DByAddition(Matrix3X1 start, Matrix3X1 trans)
{
Matrix3X1 temp;
temp = addMatrices(start,trans);
return temp;
}
2D乘法平移:
例如:
计算机中的实现:
Matrix3X1 translate2DByMultiplication(Matrix3X1 start,float dx, float dy)
{
Matrix3X3 temp;
Matrix3X1 result;
//Zero out the matrix.
temp = createFixed3X3Matrix(0);
//setup the 3x3 for multiplication;
temp.index[0][0] = 1;
temp.index[1][1] = 1;
temp.index[2][2] = 1;
//put in the translation amount
temp.index[0][2] = dx;
temp.index[1][2] = dy;
result = multiplyMatrixNxM(temp,start);
return result;
}
3D乘法平移:
例如:
计算机中的实现:
Matrix4X1 translate3DByMultiply(Matrix4X1 start,float dx, float dy,float dz)
{
Matrix4X4 temp;
Matrix4X1 result;
//Zero out the matrix.
temp = createFixed4X4Matrix(0);
//setup the 4X4 for multiplication;
temp.index[0][0] = 1;
temp.index[1][1] = 1;
temp.index[2][2] = 1;
temp.index[3][3] = 1;
//put in the translation amount
temp.index[0][3] = dx;
temp.index[1][3] = dy;
temp.index[2][3] = dz;
result = multiplyMatrixNxM(temp,start);
return result;
}
=======================================
游戏开发中的数学和物理算法(18):缩放
2D缩放的数学形式:
Sx代表x方向的缩放量,Sy代表y方向的缩放量。当Sx=Sy代表等比例缩放。
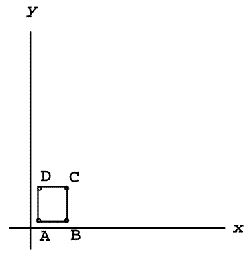
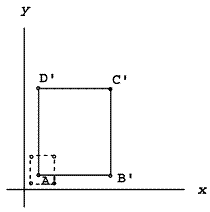
例如:将下图的矩形ABCD放大3倍。
设A(10,10),那么缩放后的A',将通过下列计算获得A'(30,30)。
同理可以计算出缩放后的B'(150,30), C'(150,120),和 D'(30,120)。如图:
虚线框表示的为缩放前的图形,实线框表示为缩放后的图形。
2D缩放在计算机中的实现:
Matrix3X1 scale2DByMultiplication(Matrix3X1 start, float dx, float dy)
{
Matrix3X3 temp;
Matrix3X1 result;
//Zero out the matrix.
temp = createFixed3X3Matrix(0);
//setup the 3x3 for multiplication;
temp.index[0][0] = dx;
temp.index[1][1] = dy;
temp.index[2][2] = 1;
result = multiplyMatrixNxM(temp,start);
return result;
}
3D缩放的数学形式:
3D缩放在计算机中的实现:
Matrix4X1 scale3DByMultiply(Matrix4X1 start, float dx, float dy, float dz)
{
Matrix4X4 temp;
Matrix4X1 result;
//Zero out the matrix to make sure nothing is left uninitialized.
temp = createFixed4X4Matrix(0);
//setup the 3x3 for multiplication;
temp.index[0][0] = dx;
temp.index[1][1] = dy;
temp.index[2][2] = dz;
temp.index[3][3] = 1;
result = multiplyMatrixNxM(temp,start);
return result;
}
=======================================



























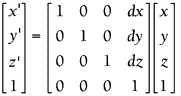
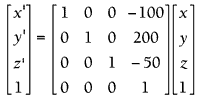
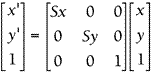
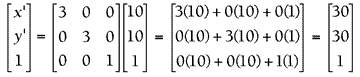
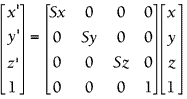

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号