SpringBoot系统列 2 - 配置文件,多环境配置(dev,qa,online)
实现项目的多环境配置的方法有很多,比如通过在Pom.xml中配置profiles(最常见) 然后在Install项目打War包的时候,根据需求打不同环境的包,如图:
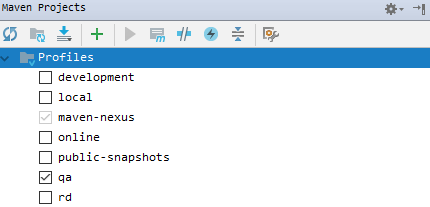
这种配置多环境的方法在SSM框架中使用的最多,但在SpringBoot中使用最多的是在启动SpringBoot项目的时候指定运行环境,下面也是主要描述这种配置的方法:
1.添加配置文件
在SpringBoot的Resources目录下建4个配置文件 application.yml、application-dev.yml、application-qa.yml、application-online.yml
dev:开发环境
qa:测试环境
online:生产环境
然后在application.yml配置文件中配置默认的运行环境:
spring:
profiles:
active: dev
然后在dev、qa、online中分别配置不同的配置内容,例如变更端口:
dev
server: port: 8085 servlet: context-path: /api tomcat: max-threads: 100 connection-timeout: 5000 spring: profiles: dev
qa
server: port: 8086 servlet: context-path: /api tomcat: max-threads: 100 connection-timeout: 5000 spring: profiles: qa
online
server: port: 8087 servlet: context-path: /api tomcat: max-threads: 100 connection-timeout: 5000 spring: profiles: online
然后在 SpringBoot系统列 1 - HelloWorld! 的基础上继续添加代码,新建WebConfig用于存放SpringBoot的一些配置信息(SpringBoot的配置即可以在配置文件中配置,也可以在类中配置):
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.boot.SpringBootConfiguration; /** * 配置类 * @author XIHONGLEI * @date 2018-10-31 */ @SpringBootConfiguration public class WebConfig { @Value("${server.port}") public String port; }
然后改造一下HelloContrlller,为了区分环境,我们在请求/api/hello的时候将端口号展示出:
import com.hello.WebConfig; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController public class HelloController { @Autowired private WebConfig webConfig; @RequestMapping("hello") public String hello() { return "Hello World! port:".concat(webConfig.port); } }
然后在pom.xml配置Jar包的打包配置:
<packaging>jar</packaging> <build> <finalName>spring-boot-hello</finalName> <resources> <resource> <directory>src/main/java</directory> <includes> <include>**/*.yml</include> <include>**/*.properties</include> <include>**/*.xml</include> </includes> <filtering>false</filtering> </resource> <resource> <directory>src/main/resources</directory> <includes> <include>**/*.yml</include> <include>**/*.properties</include> <include>**/*.xml</include> </includes> <filtering>false</filtering> </resource> </resources> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> <configuration> <fork>true</fork> <mainClass>com.hello.Application</mainClass> </configuration> <executions> <execution> <goals> <goal>repackage</goal> </goals> </execution> </executions> </plugin> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-resources-plugin</artifactId> <version>2.5</version> <configuration> <encoding>UTF-8</encoding> <useDefaultDelimiters>true</useDefaultDelimiters> </configuration> </plugin> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId> <version>2.18.1</version> <configuration> <skipTests>true</skipTests> </configuration> </plugin> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <version>2.3.2</version> <configuration> <source>1.8</source> <target>1.8</target> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build>
然后Install,找打Jar包 spring-boot-hello.jar;
在Window控制台或者Linux中可以使用java -jar spring-boot-hello.jar来启动SpringBoot项目,然后通过在后方添加--spring.profiles.active来指定启动SpringBoot项目时使用的环境:
# Dev环境 $ java -jar spring-boot-hello.jar --spring.profiles.active=dev # qa环境 $ java -jar spring-boot-hello.jar --spring.profiles.active=qa # online环境 $ java -jar spring-boot-hello.jar --spring.profiles.active=online
例启动Online环境:
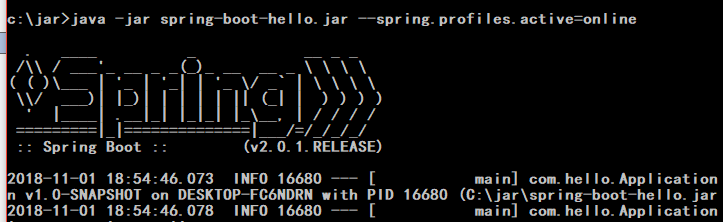
然后通过 http://localhost:8087/api/hello 来访问,因为Online中配置的端口是8087

完成!
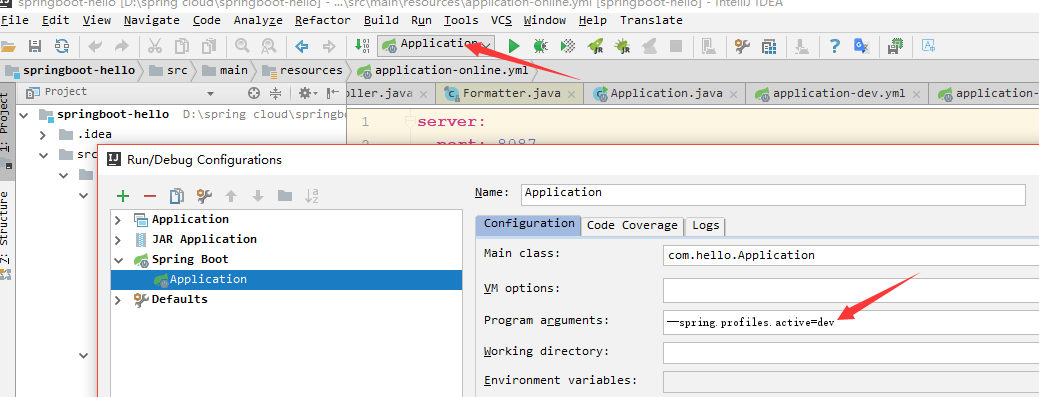
在IDEA中怎么在运行的时候选定执行环境,可以通过配置Application的program arguments中配置运行环境:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号